Abstract
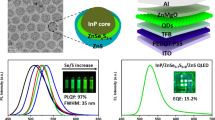
Environment-friendly indium phosphide (InP)-based quantum dots (QDs) with efficient red-emitting properties are sufficiently needed to satisfy the requirement of burgeoning display and lighting technology. Currently, the syntheses of InP QDs using tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine as the precursor are highly toxic and expensive. Herein, we successfully introduced gallium (Ga) ions into tris(dimethylamino)phosphine-based red InP cores through thermally-promoted cation exchange, and the obtained Ga-doped InP cores exhibited significantly increased photoluminescence quantum yields (PLQY) of up to 26%. The existence of Ga was directly confirmed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and the functions of Ga were systematically studied. After subsequent coating of Ga-doped InP cores with ZnSeS and ZnS shells, the resulting Ga-InP/ZnSeS/ZnS QDs achieved a high PLQY of 62% with an emission maximum at 640 nm. In contrast, without Ga-doping, the PLQY only attained 36% using the same synthetic approach. This indicated an approximate 1.7-fold increase in PLQY. The enhancement of photoluminescence was related to the Ga3+, as it not only passivated surface defects of InP cores but also reduced core-shell interface stress. The Ga-InP/ZnSeS/ZnS QDs exhibited good stability towards heat treatment and ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Moreover, the red light-emitting diode (LED) based on Ga-InP/ZnSeS/ZnS QDs performed well in a wide injected current range of 2 to 200 mA, with a maximum power efficiency of 0.68 lm/W. This work showcases Ga-doping through cation exchange as a promising strategy for enhancing the efficiency of InP-based red emitters.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Arquer, F. P. G.; Talapin, D. V.; Klimov, V. I.; Arakawa, Y.; Bayer, M.; Sargent, E. H. Semiconductor quantum dots: Technological progress and future challenges. Science 2021, 373, eaaz8541.
Jang, E.; Jang, H. Review: Quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 4663–4692.
Mohkam, M.; Sadraeian, M.; Lauto, A.; Gholami, A.; Nabavizadeh, S. H.; Esmaeilzadeh, H.; Alyasin, S. Exploring the potential and safety of quantum dots in allergy diagnostics. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 145.
Cui, Z. J.; Yang, D.; Qin, S. T.; Wen, Z. Q.; He, H. Y.; Mei, S. L.; Zhang, W. L.; Xing, G. C.; Liang, C.; Guo, R. Q. Advances, challenges, and perspectives for heavy-metal-free blue-emitting indium phosphide quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2202036.
Peng, Z. A.; Peng, X. G. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 183–184.
Hanifi, D. A.; Bronstein, N. D.; Koscher, B. A.; Nett, Z.; Swabeck, J. K.; Takano, K.; Schwartzberg, A. M.; Maserati, L.; Vandewal, K.; Van De Burgt, Y. et al. Redefining near-unity luminescence in quantum dots with photothermal threshold quantum yield. Science 2019, 363, 1199–1202.
Fakharuddin, A.; Gangishetty, M. K.; Abdi-Jalebi, M.; Chin, S. H.; Bin Mohd Yusoff, A. R.; Congreve, D. N.; Tress, W.; Deschler, F.; Vasilopoulou, M.; Bolink, H. J. Perovskite light-emitting diodes. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 203–216.
Ren, X.; Hu, H. L.; Chen, Z. Y.; Gao, L. X.; Hao, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. L. Highly stable perovskite nanocrystals with pure red emission for displays. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 6092–6102.
Hardman, R. A toxicologic review of quantum dots: Toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 165–172.
Cui, Z. J.; Qin, S. T.; He, H. Y.; Wen, Z. Q.; Yang, D.; Piao, Z.; Mei, S. L.; Zhang, W. L.; Guo, R. Q. Sequential growth of InP quantum dots and coordination between interfacial heterovalency and shell confinement: Implication for light-emitting devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 1181–1190.
Qin, S. T.; Cui, Z. J.; Wen, Z. Q.; Yang, D.; He, H. Y.; Zhao, J. C.; Zhang, M. L.; Mei, S. L.; Zhang, W. L.; Guo, R. Q. Unveiling the novel interfacial anchoring effect of neodymium(III) for realization of blue-emitting InP/ZnS quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 630, 157483.
Kim, K.; Yoo, D.; Choi, H.; Tamang, S.; Ko, J. H.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y. H.; Jeong, S. Halide-amine co-passivated indium phosphide colloidal quantum dots in tetrahedral shape. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3714–3718.
Chen, B.; Li, D. Y.; Wang, F. InP quantum dots: Synthesis and lighting applications. Small 2020, 16, 2002454.
Almeida, G.; Ubbink, R. F.; Stam, M.; Du Fossé, I.; Houtepen, A. J. InP colloidal quantum dots for visible and near-infrared photonics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 742–758.
Byun, H. J.; Song, W. S.; Yang, H. Facile consecutive solvothermal growth of highly fluorescent InP/ZnS core/shell quantum dots using a safer phosphorus source. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 235605.
Matsumoto, T.; Maenosono, S.; Yamaguchi, Y. Organometallic synthesis of InP quantum dots using tris(dimethylamino)phosphine as a phosphorus source. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1492–1493.
Xu, S.; Ziegler, J.; Nann, T. Rapid synthesis of highly luminescent InP and InP/ZnS nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2653–2656.
Xie, R. G.; Battaglia, D.; Peng, X. G. Colloidal InP nanocrystals as efficient emitters covering blue to near-infrared. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15432–15433.
Li, L.; Reiss, P. One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent InP/ZnS nanocrystals without precursor injection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11588–11589.
Song, W. S.; Lee, H. S.; Lee, J. C.; Jang, D. S.; Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Yang, H. Amine-derived synthetic approach to color-tunable InP/ZnS quantum dots with high fluorescent qualities. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1750.
Tessier, M. D.; Dupont, D.; De Nolf, K.; De Roo, J.; Hens, Z. Economic and size-tunable synthesis of InP/ZnE (E = S, Se) colloidal quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4893–4898.
Hahm, D.; Chang, J. H.; Jeong, B. G.; Park, P.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, W. D.; Rhee, S.; Lim, J. et al. Design principle for bright, robust, and color-pure InP/ZnSexS1−x/ZnS heterostructures. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3476–3484.
Jo, J. H.; Kim, J. H.; Lee, K. H.; Han, C. Y.; Jang, E. P.; Do, Y. R.; Yang, H. High-efficiency red electroluminescent device based on multishelled InP quantum dots. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 3984–3987.
Jalali, H. B.; Sadeghi, S.; Yuksel, I. B. D.; Onal, A.; Nizamoglu, S. Past, present and future of indium phosphide quantum dots. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4468–4489.
Tessier, M. D.; De Nolf, K.; Dupont, D.; Sinnaeve, D.; De Roo, J.; Hens, Z. Aminophosphines: A double role in the synthesis of colloidal indium phosphide quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5923–5929.
Kim, M. R.; Chung, J. H.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.; Jang, D. J. Fabrication, spectroscopy, and dynamics of highly luminescent core–shell InP@ZnSe quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 350, 5–9.
Shin, S.; Gwak, N.; Yoo, H.; Jang, H.; Lee, M.; Kang, K.; Kim, S.; Yeon, S.; Ann Kim, T.; Kim, S. et al. Fluoride-free synthesis strategy for luminescent InP cores and effective shelling processes via combinational precursor chemistry. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143223.
Li, H. Y.; Bian, Y. Y.; Zhang, W. J.; Wu, Z. H.; Ahn, T. K.; Shen, H. B.; Du, Z. L. High performance InP-based quantum dot light-emitting diodes via the suppression of field-enhanced electron delocalization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204529.
Wu, Z. H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W. D.; Wang, K.; Sun, X. W. Development of InP quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 1095–1106.
Li, H. Y.; Zhang, W. J.; Bian, Y. Y.; Ahn, T. K.; Shen, H. B.; Ji, B. T. ZnF2-assisted synthesis of highly luminescent InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots for efficient and stable electroluminescence. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 4067–4073.
Thuy, U. T. D.; Reiss, P.; Liem, N. Q. Luminescence properties of In(Zn)P alloy core/ZnS shell quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 193104.
Lim, J.; Bae, W. K.; Lee, D.; Nam, M. K.; Jung, J.; Lee, C.; Char, K.; Lee, S. InP@ZnSeS, core@composition gradient shell quantum dots with enhanced stability. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4459–4463.
Chen, P. X.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y. Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. W.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, J. J.; He, T. C. Inner shell influence on the optical properties of InP/ZnSeS/ZnS quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 2464–2470.
Kim, S.; Kim, T.; Kang, M.; Kwak, S. K.; Yoo, T. W.; Park, L. S.; Yang, I.; Hwang, S.; Lee, J. E.; Kim, S. K. et al. Highly luminescent InP/GaP/ZnS nanocrystals and their application to white light-emitting diodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3804–3809.
Park, J. P.; Lee, J. J.; Kim, S. W. Highly luminescent InP/GaP/ZnS QDs emitting in the entire color range via a heating up process. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30094.
Friedfeld, M. R.; Stein, J. L.; Johnson, D. A.; Park, N.; Henry, N. A.; Enright, M. J.; Mocatta, D.; Cossairt, B. M. Effects of Zn2+ and Ga3+ doping on the quantum yield of cluster-derived InP quantum dots. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 194702.
Jo, J. H.; Jo, D. Y.; Choi, S. W.; Lee, S. H.; Kim, H. M.; Yoon, S. Y.; Kim, Y.; Han, J. N.; Yang, H. Highly bright, narrow emissivity of InP quantum dots synthesized by aminophosphine: Effects of double shelling scheme and Ga treatment. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100427.
Zhang, H.; Ma, X. Y.; Lin, Q. L.; Zeng, Z. P.; Wang, H. Z.; Li, L. S.; Shen, H. B.; Jia, Y.; Du, Z. L. High-brightness blue InP quantum dot-based electroluminescent devices: The role of shell thickness. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 960–967.
Srivastava, V.; Kamysbayev, V.; Hong, L.; Dunietz, E.; Klie, R. F.; Talapin, D. V. Colloidal chemistry in molten salts: Synthesis of luminescent In1−xGaxP and In1−xGaxAs quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12144–12151.
Kim, K. H.; Jo, J. H.; Jo, D. Y.; Han, C. Y.; Yoon, S. Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y. H.; Ko, Y. H.; Kim, S. W.; Lee, C. et al. Cation-exchange-derived InGaP alloy quantum dots toward blue emissivity. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3537–3544.
Hudson, M. H.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, V.; Janke, E. M.; Talapin, D. V. Synthesis of In1−xGaxP quantum dots in Lewis basic molten salts: The effects of surface chemistry, reaction conditions, and molten salt composition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 1564–1580.
Wegner, K. D.; Pouget, S.; Ling, W. L.; Carrière, M.; Reiss, P. Gallium-a versatile element for tuning the photoluminescence properties of InP quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1663–1666.
Parvizian, M.; Bechter, J.; Huber, J.; Chettata, N.; De Roo, J. An experimental introduction to colloidal nanocrystals through InP and InP/ZnS quantum dots. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1613–1620.
Kim, Y.; Ham, S.; Jang, H.; Min, J. H.; Chung, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, E. Bright and uniform green light emitting InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots for wide color gamut displays. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1496–1504.
Cho, E.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Jang, E. Modeling on the size dependent properties of InP quantum dots: A hybrid functional study. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 215201.
Suh, Y. H.; Lee, S.; Jung, S. M.; Bang, S. Y.; Yang, J. J.; Fan, X. B.; Zhan, S. J.; Samarakoon, C.; Jo, J. W.; Kim, Y. et al. Engineering core size of InP quantum dot with incipient ZnS for blue emission. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102372.
Gao, Y.; Peng, X. G. Photogenerated excitons in plain core CdSe nanocrystals with unity radiative decay in single channel: The effects of surface and ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4230–4235.
Choi, Y.; Hahm, D.; Bae, W. K.; Lim, J. Heteroepitaxial chemistry of zinc chalcogenides on InP nanocrystals for defect-free interfaces with atomic uniformity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 43.
Wu, Q. Q.; Cao, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. M.; Sun, Z. J.; Feng, J. W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, Q.; Li, Y. G. et al. Quasi-shell-growth strategy achieves stable and efficient green InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2200959.
Tamang, S.; Lincheneau, C.; Hermans, Y.; Jeong, S.; Reiss, P. Chemistry of InP nanocrystal syntheses. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2491–2506.
Owen, J. The coordination chemistry of nanocrystal surfaces. Science 2015, 347, 615–616.
Cho, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.; Kwon, H.; Bang, J. Effects of Zn impurity on the photoluminescence properties of InP quantum Dots. J. Lumin. 2022, 245, 118647.
Won, Y. H.; Cho, O.; Kim, T.; Chung, D. Y.; Kim, T.; Chung, H.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, E. Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature 2019, 575, 634–638.
Shen, C.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Li, Z. X.; Li, J. L.; Tao, H.; Zou, J. H.; Xu, X. Q.; Xu, G. Highly luminescent InP-In(Zn)P/ZnSe/ZnS core/shell/shell colloidal quantum dots with tunable emissions synthesized based on growth-doping. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 9599–9609.
Chen, Y. R.; Wang, R. X.; Kuang, Y. M.; Bian, Y. Y.; Chen, F.; Shen, H. B.; Chi, Z.; Ran, X.; Guo, L. J. Suppressed Auger recombination and enhanced emission of InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots through inner shell manipulation. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 18920–18927.
Lim, J.; Park, M.; Bae, W. K.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Char, K. Highly efficient cadmium-free quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by the direct formation of excitons within InP@ZnSeS quantum dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9019–9026.
Hao, H.; Hu, H. L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. L. Trioctylphosphine- and octanethiol-induced photoluminescence recovery of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots after dilution-quenching: Implications for quantum dot films. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 3085–3094.
Hu, H. L.; Hao, H.; Ren, X.; Chen, Z. Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. L. Bright InP quantum dots by mid-synthetic modification with zinc halides. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 2877–2886.
Roy, P.; Virmani, M.; Pillai, P. P. Blue-emitting InP quantum dots participate in an efficient resonance energy transfer process in water. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 5167–5176.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFA1504703), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21973071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, KZ., He, XH., Chen, ZY. et al. Bright InP quantum dots by Ga-doping for red emitters. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6603-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6603-8