Abstract
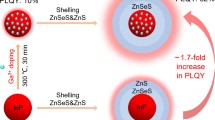
High-quality, Cd-free InP quantum dots (QDs) have been conventionally synthesized by exclusively selecting tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine (P(TMS)3) as a phosphorus (P) precursor, which is problematic from the standpoint of green and economic chemistry. Thus, other synthetic chemistries adopting alternative P sources to P(TMS)3 have been introduced, however, they could not guarantee the production of satisfactorily fluorescence-efficient, color-pure InP QDs. In this study, the unprecedented controlled synthesis of a series of band-gap-tuned InP QDs is demonstrated through a hot-injection of a far safer and cheaper tris(dimethylamino)phosphine in the presence of a key coordinating solvent of oleylamine that enables successful QD nucleation/growth. Effects of the co-existence of Zn additive, the core growth temperature, and the amount of P source injected on the growth behaviors of InP QD are investigated. After ZnS overcoating by a successive injection of 1-dodecanethiol only, high-fluorescence-quality, green-to-red color emission-tunable core/shell QDs of InP/ZnS are obtained. The fluorescent characteristics of different color-emitting QDs desirably exhibit little fluctuations in quantum yield and emission bandwidth, specifically ranging 51–53 % and 60–64 nm, respectively. Lastly, the utility of the introduction of a secondary shelling process in rendering the QDs are more bright, photostable is also proved.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battaglia D, Peng X (2002) Formation of high quality InP and InAs nanocrystals in a noncoordinating solvent. Nano Lett 2:1027–1030
Byun HJ, Song WS, Yang H (2011) Facile consecutive solvothermal growth of highly fluorescent InP/ZnS core/shell quantum dots using a safer phosphorus source. Nanotechnology 22:235605–235610
De Trizio L, Prato M, Genovese A, Casu A, Povia M, Simonutti R, Alcocer MJP, D’Andrea C, Tassone F, Manna L (2012) Strongly fluorescent quaternary Cu–In–Zn–S nanocrystals prepared from Cu1−xInS2 nanocrystals by partial cation exchange. Chem Mater 24:2400–2406
Guzelian AA, Katari JEB, Kadavanich AV, Banin U, Hamad K, Juban E, Alivisatos AP, Wolters RH, Arnold CC, Heath JR (1996) Synthesis of size-selected, surface-passivated InP nanocrystals. J Phys Chem 100:7212–7219
Hussain S, Won N, Nam J, Bang J, Chung H, Kim S (2009) One-pot fabrication of high-quality InP/ZnS (core/shell) quantum dots and their application to cellular imaging. Chemphyschem 10:1466–1470
Kim S, Kim T, Kang M, Kwak SK, Yoo TW, Park LS, Yang I, Hwang S, Lee JE, Kim SK, Kim SW (2012) Highly luminescent InP/GaP/ZnS nanocrystals and their application to white light-emitting diodes. J Am Chem Soc 134:3804–3809
Li L, Reiss P (2008) One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent InP/ZnS nanocrystals without precursor injection. J Am Chem Soc 130:11588–11589
Li C, Ando M, Enomoto H, Murase N (2008) Highly luminescent water-soluble InP/ZnS nanocrystals prepared via reactive phase transfer and photochemical processing. J Phys Chem C 112:20190–20199
Li L, Pandey A, Werder DJ, Khanal BP, Pietryga JM, Klimov VI (2011) Efficient synthesis of highly luminescent copper indium sulfide-based core/shell nanocrystals with surprisingly long-lived emission. J Am Chem Soc 133:1176–1179
Lim J, Bae WK, Lee D, Nam MK, Jung J, Lee C, Char K, Lee S (2011) InP@ZnSeS, core@composition gradient shell quantum dots with enhanced stability. Chem Mater 23:4459–4463
Lim K, Jang HS, Woo K (2012) Synthesis of blue emitting InP/ZnS quantum dots through control of competition between etching and growth. Nanotechnology 23:485609–485615
Liu Z, Kumbhar A, Xu D, Zhang J, Sun Z, Fang J (2008) Coreduction colloidal synthesis of III–V nanocrystals: the case of InP. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:3540–3542
Micic OI, Cheong HM, Fu H, Zunger A, Sprague JR, Mascarenhas A, Nozik AJ (1997) Size-dependent spectroscopy of InP quantum dots. J Phys Chem B 101:4904–4912
Mutlugun E, Hernandez-Martinez PL, Eroglu C, Coskun Y, Erdem T, Sharma VK, Unal E, Panda SK, Hickey SG, Gaponik N, Eychmuller A, Demir HV (2012) Large-area (over 50 cm × 50 cm) freestanding films of colloidal InP/ZnS quantum dots. Nano Lett 12:3986–3993
Protiere M, Reiss P (2007) Amine-induced growth of an In2O3 shell on colloidal InP nanocrystals. Chem Commun 23:2417–2419
Ryu E, Kim S, Jang E, Jun S, Jang H, Kim B, Kim SW (2009) Step-wise synthesis of InP/ZnS core-shell quantum dots and the role of zinc acetate. Chem Mater 21:573–575
Song WS, Yang H (2012) Efficient white-light-emitting diodes fabricated from highly fluorescent copper indium sulfide core/shell quantum dots. Chem Mater 24:1961–1967
Song WS, Kim JH, Lee JH, Lee HS, Do YR, Yang H (2012) Synthesis of color-tunable Cu–In–Ga–S solid solution quantum dots with high quantum yields for application to white light-emitting diodes. J Mater Chem 22:21901–21908
Xie R, Battaglia D, Peng X (2007) Colloidal InP nanocrystals as efficient emitters covering blue to near-infrared. J Am Chem Soc 129:15432–15433
Xie R, Li Z, Peng X (2009) Nucleation kinetics vs chemical kinetics in the initial formation of semiconductor nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 131:15457–15466
Xu S, Kumar S, Nann T (2006) Rapid synthesis of high-quality InP nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 128:1054–1055
Xu S, Ziegler J, Nann T (2008) Rapid synthesis of highly luminescent InP and InP/ZnS nanocrystals. J Mater Chem 18:2653–2656
Yang X, Divayana Y, Zhao D, Leck KS, Lu F, Tan ST, Abiyasa AP, Zhao Y, Demir HV, Sun XW (2012a) A bright cadmium-free, hybrid organic/quantum dot white light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett 101:233110–233113
Yang X, Zhao D, Leck KS, Tan ST, Tang YX, Zhao J, Demir HV, Sun XW (2012b) Full visible range covering InP/ZnS nanocrystals with high photometric performance and their application to white quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 24:4180–4185
Zan F, Ren J (2012) Gas–liquid phase synthesis of highly luminescent InP/ZnS core/shell quantum dots using zinc phosphide as a new phosphorus source. J Mater Chem 22:1794–1799
Zhang J, Xie R, Yang W (2011) A simple route for highly luminescent quaternary Cu–Zn–In–S nanocrystal emitters. Chem Mater 23:3357–3361
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2011-0013377 and 2012K001320). This work was also supported by LG Electronics Co., Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, WS., Lee, HS., Lee, J.C. et al. Amine-derived synthetic approach to color-tunable InP/ZnS quantum dots with high fluorescent qualities. J Nanopart Res 15, 1750 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1750-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1750-y