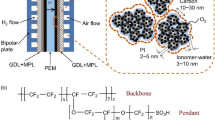
Abstract
The microstructures of the ionomer–catalyst interfaces in the catalyst layers are important for the fuel cell performance because they determine the distribution of the active triple-phase boundaries. Here, we investigate the ionomer–catalyst interactions in hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells (HEMFCs) using poly(aryl piperidinium) and compare them with proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). It is found that different catalyst layer microstructures are between the two types of fuel cell. The ionomer/carbon (I/C) ratio does not have a remarkable impact on the HEMFC performance, while it has a strong impact on the PEMFC performance, indicating the weaker interaction between the HEMFC ionomer and catalyst. Molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that the HEMFC ionomer tends to distribute on the carbon support, unlike the PEMFC ionomer, which heavily covers the Pt nanoparticles. These results suggest that the poisoning effect of the ionomer on the catalyst is much weaker in HEMFCs, and the improved ionomer/catalyst interaction is beneficial for the HEMFC performances.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, S.; Sun, T.; Li, J. R.; Li, Q. Z.; Hou, C. C.; Sun, Q. The cathode catalysts of hydrogen fuel cell: From laboratory toward practical application. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 4365–4380.
Kang, Y. Q.; Wang, J. Q.; Wei, Y. P.; Wu, Y. L.; Xia, D. S.; Gan, L. Engineering nanoporous and solid core–shell architectures of low-platinum alloy catalysts for high power density PEM fuel cells. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6148–6155.
Zhao, F. L.; Zheng, L. R.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Q. H.; Sheng, T.; Yang, X. T.; Gu, L.; Wang, X. PtCu subnanoclusters epitaxial on octahedral PtCu/Pt skin matrix as ultrahigh stable cathode electrocatalysts for room-temperature hydrogen fuel cells. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2252–2258.
Chao, T. T.; Luo, X.; Zhu, M. Z.; Hu, Y. M.; Zhang, Y. D.; Qu, Y. T.; Peng, H. T.; Shen, X. S.; Zheng, X. S.; Zhang, L. et al. The promoting effect of interstitial hydrogen on the oxygen reduction performance of PtPd alloy nanotubes for fuel cells. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2366–2372.
Ma, S.; Lin, M.; Lin, T. E.; Lan, T.; Liao, X.; Maréchal, F.; Van Herle, J.; Yang, Y. P.; Dong, C. Q.; Wang, L. G. Fuel cell-battery hybrid systems for mobility and off-grid applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110119.
Wu, D.; Peng, C.; Yin, C.; Tang, H. Review of system integration and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2020, 3, 466–505.
Gottesfeld, S.; Dekel, D. R.; Page, M.; Bae, C.; Yan, Y. S.; Zelenay, P.; Kim, Y. S. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells: Current status and remaining challenges. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 170–184.
Gu, S.; Cai, R.; Luo, T.; Chen, Z. W.; Sun, M. W.; Liu, Y.; He, G. H.; Yan, Y. S. A soluble and highly conductive ionomer for high-performance hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6499–6502.
Peng, X.; Kulkarni, D.; Huang, Y.; Omasta, T. J.; Ng, B.; Zheng, Y. W.; Wang, L. Q.; LaManna, J. M.; Hussey, D. S.; Varcoe, J. R. et al. Using operando techniques to understand and design high performance and stable alkaline membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3561.
Xue, Y. R.; Shi, L.; Liu, X. R.; Fang, J. J.; Wang, X. D.; Setzler, B. P.; Zhu, W.; Yan, Y. S.; Zhuang, Z. B. A highly-active, stable and low-cost platinum-free anode catalyst based on RuNi for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5651.
Ohyama, J.; Sato, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Arai, S.; Satsuma, A. Size specifically high activity of Ru nanoparticles for hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 153, 8016–8021.
Setzler, B. P.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Wittkopf, J. A.; Yan, Y. S. Activity targets for nanostructured platinum-group-metal-free catalysts in hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 1020–1025.
Chen, R. Z.; Chen, S. H.; Wang, L. Q.; Wang, D. S. Nanoscale metal particle modified single-atom catalyst: Synthesis, characterization, and application. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2304713.
Li, R. Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B. Z.; Wang, D. S. Atomic distance engineering in metal catalysts to regulate catalytic performance. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308653.
Gan, T.; Wang, D. S. Atomically dispersed materials: Ideal catalysts in atomic era. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 18–38.
Zhuang, Z. C.; Xia, L. X.; Huang, J. Z.; Zhu, P.; Li, Y.; Ye, C. L.; Xia, M. G.; Yu, R. H.; Lang, Z. Q.; Zhu, J. X. et al. Continuous modulation of electrocatalytic oxygen reduction activities of single-atom catalysts through p-n junction rectification. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202212335.
Han, A. L.; Sun, W. M.; Wan, X.; Cai, D. D.; Wang, X. J.; Li, F.; Shui, J. L.; Wang, D. S. Construction of Co4 atomic clusters to enable Fe-N4 motifs with highly active and durable oxygen reduction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303185.
Sui, R.; Chai, J.; Liu, X. R.; Pei, J. J.; Zhang, X. J.; Wang, X. D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J. C.; Zhu, W.; Chen, W. X. et al. Introducing highly polarizable cation in M-N-C type catalysts to boost their oxygen reduction reaction performance. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2024, 341, 123251.
Sui, R.; Zhang, X. J.; Wang, X. D.; Wang, X. Y.; Pei, J. J.; Zhang, Y. F.; Liu, X. R.; Chen, W. X.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, Z. B. Silver based single atom catalyst with heteroatom coordination environment as high performance oxygen reduction reaction catalyst. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7968–7975.
Shang, H. S.; Sun, W. M.; Sui, R.; Pei, J. J.; Zheng, L. R.; Dong, J. C.; Jiang, Z. L.; Zhou, D. N.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Chen, W. X. et al. Engineering isolated Mn-N2C2 atomic interface sites for efficient bifunctional oxygen reduction and evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 5443–5450.
Xue, Y. R.; Wang, X. D.; Zhang, X. Q.; Fang, J. J.; Xu, Z. Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Liu, X. R.; Liu, M. Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, Z. B. Cost-effective hydrogen oxidation reaction catalysts for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2021, 37, 2009103.
Wang, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, J. H.; Zhao, Y.; Setzler, B. P.; Rojas-Carbonell, S.; Yan, Y. S. High- performance hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells through optimization of relative humidity, backpressure and catalyst selection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F3305–F3310.
Li, Q. H.; Peng, H. Q.; Wang, Y. M.; Xiao, L.; Lu, J. T.; Zhuang, L. The Comparability of Pt to Pt-Ru in catalyzing the hydrogen oxidation reaction for alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells operated at 80 °C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1442–1446.
Peng, H. Q.; Li, Q. H.; Hu, M. X.; Xiao, L.; Lu, J. T.; Zhuang, L. Alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells stably working at 80 °C. J. Power Sources 2018, 390, 165–167.
Alia, S. M.; Pivovar, B. S.; Yan, Y. S. Platinum- coated copper nanowires with high activity for hydrogen oxidation reaction in base. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13473–13478.
Xu, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. L. Triple-phase boundaries (TPBs) in fuel cells and electrolyzers. Encycl. Energy Storage 2022, 2, 299–328.
O’Hayre, R.; Barnett, D. M.; Prinz, F. B. The triple phase boundary: A mathematical model and experimental investigations for fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc 2005, 152, A439–A444.
Zhang, X. Y.; Liu, Q. T.; Shui, J. L. Effect of catalyst layer hydrophobicity on Fe-N-C proton exchange membrane fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1775–1780.
Kodama, K.; Motobayashi, K.; Shinohara, A.; Hasegawa, N.; Kudo, K.; Jinnouchi, R.; Osawa, M.; Morimoto, Y. Effect of the side-chain structure of perfluoro-sulfonic acid ionomers on the oxygen reduction reaction on the surface of Pt. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 694–700.
Ahn, C. Y.; Cheon, J. Y.; Joo, S. H.; Kim, J. Effects of ionomer content on Pt catalyst/ordered mesoporous carbon support in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 477–482.
Chen, G. Y.; Wang, C.; Lei, Y. J.; Zhang, J. B.; Mao, Z. M.; Mao, Z. Q.; Guo, J. W.; Li, J. Q.; Ouyang, M. G. Gradient design of Pt/C ratio and Nafion content in cathode catalyst layer of PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29960–29965.
Chen, F. D.; Chen, S. G.; Wang, A. X.; Wang, M.; Guo, L.; Wei, Z. D. Blocking the sulfonate group in Nafion to unlock platinum’s activity in membrane electrode assemblies. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 392–401.
Zhou, Y. W.; Yu, H. M.; Xie, F.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X. Y.; Yao, D. W.; Jiang, G.; Geng, J. T.; Shao, Z. G. Improving cell performance for anion exchange membrane fuel cells with FeNC cathode by optimizing ionomer content. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 5266–5275.
Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19.
Plimpton, S.; Pollock, R.; Stevens, M. Particle-mesh Ewald and rRESPA for parallel molecular dynamics simulations. In Proceedings of the 8th SIAM Conference on Parallel Processing or Scientific Computing, Minneapolis, USA, 1997.
Portella, G.; Pohl, P.; de Groot, B. L. Invariance of single-file water mobility in gramicidin-like peptidic pores as function of pore length. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3930–3937.
Dubbeldam, D.; Calero, S.; Ellis, D. E.; Snurr, R. Q. RASPA: Molecular simulation software for adsorption and diffusion in flexible nanoporous materials. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 81–101
Frenkel, D.; Smit, B. Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2023.
Purdue, M. J.; Qiao, Z. W. Molecular simulation study of wet flue gas adsorption on zeolite 13X. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 181–197.
Joos, L.; Swisher, J. A.; Smit, B. Molecular simulation study of the competitive adsorption of H2O and CO2 in zeolite 13X. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15936–15942.
Dehghani, M.; Asghari, M.; Mohammadi, A. H.; Mokhtari, M. Molecular simulation and Monte Carlo study of structural-transport-properties of PEBA-MFI zeolite mixed matrix membranes for CO2, CH4 and N2 separation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 103, 12–22.
Zhou, W. N.; Wang, H. B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. X.; Liu, X. L. Molecular simulation of CO2/CH4/H2O competitive adsorption and diffusion in brown coal. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 3004–3011.
Hou, T. J.; Zhu, L. L.; Xu, X. J. Adsorption and diffusion of benzene in ITQ-1 type zeolite: Grand canonical Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 9356–9364.
Mashio, T.; Ohma, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Shinohara, K. Analysis of reactant gas transport in a catalyst layer. ECS Trans. 2007, 11, 529–542.
Bird, R. B.; Stewart, W. E.; Lightfoot, E. N.; Meredith, R. E. Transport phenomena. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1961, 108, 78C.
Wang, J. H.; Zhao, Y.; Setzler, B. P.; Rojas-Carbonell, S.; Ben Yehuda, C.; Amel, A.; Page, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, K. D.; Shi, L. et al. Poly(aryl piperidinium) membranes and ionomers for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 392–398.
Thompson, S. T.; Peterson, D.; Ho, D.; Papageorgopoulos, D. Perspective—The next decade of AEMFCs: Near-term targets to accelerate applied R&D. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 084514.
Jeon, S.; Lee, J.; Rios, G. M.; Kim, H. J.; Lee, S. Y.; Cho, E.; Lim, T. H.; Hyun Jang, J. Effect of ionomer content and relative humidity on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) performance of membrane-electrode assemblies (MEAs) prepared by decal transfer method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9678–9686.
Soboleva, T.; Zhao, X. S.; Malek, K.; Xie, Z.; Navessin, T.; Holdcroft, S. On the micro-, meso-, and macroporous structures of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell catalyst layers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 375–384.
Soboleva, T.; Malek, K.; Xie, Z.; Navessin, T.; Holdcroft, S. PEMFC catalyst layers: The Role of micropores and mesopores on water sorption and fuel cell activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1827–1837.
Yarlagadda, V.; Carpenter, M. K.; Moylan, T. E.; Kukreja, R. S.; Koestner, R.; Gu, W. B.; Thompson, L.; Kongkanand, A. Boosting fuel cell performance with accessible carbon mesopores. ACS Energy Lett. 2011, 3, 618–621.
Pivac, I.; Šimić, B.; Barbir, F. Experimental diagnostics and modeling of inductive phenomena at low frequencies in impedance spectra of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 240–248.
Shao, M. H.; Peles, A.; Shoemaker, K. Electrocatalysis on platinum nanoparticles: Particle size effect on oxygen reduction reaction activity. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3714–3719.
Sharma, H. N.; Sharma, V.; Mhadeshwar, A. B.; Ramprasad, R. Why Pt survives but Pd suffers from SOx poisoning. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1140–1148.
Olsson, J. S.; Pham, T. H.; Jannasch, P. Poly(arylene piperidinium) hydroxide ion exchange membranes: Synthesis, alkaline stability, and conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 28, 1702758.
Li, H. Y.; Cheng, X. J.; Yan, X. H.; Shen, S. Y.; Zhang, J. L. A perspective on influences of cathode material degradation on oxygen transport resistance in low Pt PEMFC. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 377–390.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. Z210016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2024_6584_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
The difference of the ionomer–catalyst interfaces for poly(aryl piperidinium) hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells and proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, X., Zhang, C. et al. The difference of the ionomer–catalyst interfaces for poly(aryl piperidinium) hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells and proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6584-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6584-7