Abstract
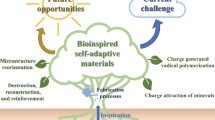
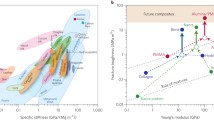
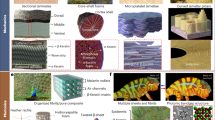
Biological structural materials not only exhibit remarkable mechanical properties but also often embody dynamic characteristics such as environmental responsiveness, autonomy, and self-healing, which are difficult to achieve in conventional engineering materials. By merging materials science, synthetic biology, and other disciplines, engineered living materials (ELMs) provide a promising solution to combine living organisms with abiotic components, thus facilitating the construction of functional “living” materials. Like natural materials, ELMs possess vitality and hold immense application potential in areas such as medicine, electronics, and construction, captivating increasing research attention recently. As an emerging branch of ELMs, structural ELMs aim to mimic living biological structural materials by achieving desired mechanical performance while maintaining important “living” characteristics. Here we summarize the recent progress and provide our perspectives for this emerging research area. We first summarize the superiority of structural ELMs by reviewing biological structural materials and biomimetic material design strategies. Subsequently, we provide a systematic discussion on the definition and classifications of structural ELMs, their mechanical performance, and physiological behaviors. Finally, we summarize some critical challenges faced by structural ELMs and highlight directions of future development. We hope this review article can provide a timely summary of the state of the art and relevant perspectives for future development of structural ELMs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kakani, S. L.; Kakani, A. Material Science. Delhi: New Age International Publishers, 2004.
Han, S. Y.; Chen, F. M.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Z. F.; Chen, L. T.; Wang, G. Bamboo-inspired renewable, lightweight, and vibration-damping laminated structural materials for the floor of a railroad car. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42645–42655.
Liu, Y. Q.; He, K.; Chen, G.; Leow, W. R.; Chen, X. D. Nature-inspired structural materials for flexible electronic devices. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12893–12941.
Williams, J. C.; Starke, E. A. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5775–5799.
He, S. M.; Chen, C. J.; Li, T.; Song, J. W.; Zhao, X. P.; Kuang, Y. D.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Hitz, E.; Kong, W. Q. et al. An energy-efficient, wood-derived structural material enabled by pore structure engineering towards building efficiency. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900747.
Wegst, U. G. K.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A. P.; Ritchie, R. O. Bioinspired structural materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36.
Mao, L. B.; Gao, H. L.; Yao, H. B.; Liu, L.; Cölfen, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, S. M.; Li, S. K.; Yan, Y. X.; Liu, Y. Y. et al. Synthetic nacre by predesigned matrix-directed mineralization. Science 2016, 354, 107–110.
Sun, J. Y.; Bhushan, B. Hierarchical structure and mechanical properties of nacre: A review. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7617–7632.
Liu, D. G.; Song, J. W.; Anderson, D. P.; Chang, P. R.; Hua, Y. Bamboo fiber and its reinforced composites: Structure and properties. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1449–1480.
Ritchie, R. O. The conflicts between strength and toughness. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 817–822.
Harrington, M. J.; Masic, A.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Waite, J. H.; Fratzl, P. Iron- clad fibers: A metal-based biological strategy for hard flexible coatings. Science 2010, 328, 216–220.
Li, J. T.; Li, S. T.; Huang, J. Y.; Khan, A. Q.; An, B. G.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. F.; Zhu, M. F. Spider silk-inspired artificial fibers. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2103965.
Matsuo, K.; Irie, N. Osteoclast-osteoblast communication. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 473, 201–209.
Kim, M. Y.; Lee, K.; Shin, H. I.; Lee, K. J.; Jeong, D. Metabolic activities affect femur and lumbar vertebrae remodeling, and anti-resorptive risedronate disturbs femoral cortical bone remodeling. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 103–114.
Graham, A. J.; Keitz, B. K. Living Synthetic Polymerizations. In Engineered Living Materials; Srubar, W. V., Ed.; Springer International: Cham, 2022, pp 27–49.
Rodrigo-Navarro, A.; Sankaran, S.; Dalby, M. J.; Del Campo, A.; Salmeron-Sanchez M. Engineered living biomaterials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1175–1190.
An, B. L.; Wang, Y. Y.; Huang, Y. Y.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, Y. Z.; Xun, D. M.; Church, G. M.; Dai, Z. J.; Yi, X.; Tang, T. C. et al. Engineered living materials for sustainability. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 2349–2419.
Srubar, W. V. Engineered living materials: Taxonomies and emerging trends. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 574–583.
Meyers, M. A.; Chen, P. Y.; Lin, A. Y. M.; Seki, Y. Biological materials: Structure and mechanical properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 1–206.
Eder, M.; Amini, S.; Fratzl, P. Biological composites-complex structures for functional diversity. Science 2018, 362, 543–547.
Jia, Z. A.; Deng, Z. F.; Li, L. Biomineralized materials as model systems for structural composites: 3D architecture. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106259.
Fratzl, P.; Weinkamer, R. Nature’s hierarchical materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 1263–1334.
Reznikov, N.; Bilton, M.; Lari, L.; Stevens, M. M.; Kröger, R. Fractal-like hierarchical organization of bone begins at the nanoscale. Science 2018, 360, eaao2189.
Yang, T.; Chen, H. S.; Jia, Z. A.; Deng, Z. F.; Chen, L. N.; Peterman, E. M.; Weaver, J. C.; Li, L. A damage-tolerant, dual-scale, single-crystalline microlattice in the knobby starfish. Protoreaster nodosus. Science 2022, 375, 647–652.
Vukusic, P.; Sambles, J. R. Photonic structures in biology. Nature 2003, 424, 852–855.
Li, L.; Goodrich, C.; Yang, H. Z.; Phillips, K. R.; Jia, Z. A.; Chen, H. S.; Wang, L. F.; Zhong, J. J.; Liu, A. H.; Lu, J. F. et al. Microscopic origins of the crystallographically preferred growth in evaporation-induced colloidal crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107588118.
Parker, A. R.; Lawrence, C. R. Water capture by a desert beetle. Nature 2001, 414, 33–34.
Kim, B. H.; Li, K.; Kim, J. T.; Park, Y.; Jang, H.; Wang, X. J.; Xie, Z. Q.; Won, S. M.; Yoon, H. J.; Lee, G. et al. Three-dimensional electronic microfliers inspired by wind-dispersed seeds. Nature 2021, 597, 503–510.
Forterre, Y.; Skotheim, J. M.; Dumais, J.; Mahadevan, L. How the Venus flytrap snaps. Nature 2005, 433, 421–425.
Pierantoni, M.; Brumfeld, V.; Addadi, L.; Weiner, S. A 3D study of the relationship between leaf vein structure and mechanical function. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 111–119.
Habibi, M. K.; Samaei, A. T.; Gheshlaghi, B.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y. Asymmetric flexural behavior from bamboo’s functionally graded hierarchical structure: Underlying mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2015, 16, 178–186.
Norell, M. A.; Wiemann, J.; Fabbri, M.; Yu, C. Y.; Marsicano, C. A.; Moore-Nall, A.; Varricchio, D. J.; Pol, D.; Zelenitsky, D. K. The first dinosaur egg was soft. Nature 2020, 583, 406–410.
Hou, X. C.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Z. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094.
Weaver, J. C.; Milliron, G. W.; Allen, P.; Miserez, A.; Rawal, A.; Garay, J.; Thurner, P. J.; Seto, J.; Mayzel, B.; Friesen, L. J. et al. Unifying design strategies in demosponge and hexactinellid skeletal systems. J. Adhes. 2010, 86, 72–95.
Williams, N. Species highs. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R721–R722.
Florencio-Silva, R.; Da Silva Sasso, G. R.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Simões, M. J.; Cerri, P. S. Biology of bone tissue: Structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 421746.
Ghazlan, A.; Ngo, T.; Tan, P.; Xie, Y. M.; Tran, P.; Donough, M. Inspiration from Nature’s body armours-A review of biological and bioinspired composites. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 205, 108513.
Studart, A. R. Additive manufacturing of biologically-inspired materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 359–376.
Zhang, C. Q.; Mcadams II, D. A.; Grunlan, J. C. Nano/micoo-manufacturing of bioinspired materials: A review of methods to mimic natural structures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6292–6321.
Chen, Y. L.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Q. F.; Pan, F.; Cui, C. J.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Liu, B. Advances in mechanics of hierarchical composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 214, 108970.
Zhao, Y. J.; Xie, Z. Y.; Gu, H. C.; Zhu, C.; Gu, Z. Z. Bio-inspired variable structural color materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3297–3317.
Wang, S. T.; Liu, K. S.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired surfaces with superwettability: New insight on theory, design, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293.
Liu, Z. Q.; Meyers, M. A.; Zhang, Z. F.; Ritchie, R. O. Functional gradients and heterogeneities in biological materials: Design principles, functions, and bioinspired applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 467–498.
Schaedler, T. A.; Carter, W. B. Architected cellular materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 187–210.
Jia, Z. A.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L. F. Learning from nature: Use material architecture to break the performance tradeoffs. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107650.
Pham, M. S.; Liu, C.; Todd, I.; Lertthanasarn, J. Damage-tolerant architected materials inspired by crystal microstructure. Nature 2019, 565, 305–311.
Jia, Z. A.; Chen, H. S.; Deng, Z. F.; Li, L. Architected microlattices for structural and functional applications: Lessons from nature. Matter 2023, 6, 1082–1095.
Jia, Z. A.; Liu, F.; Jiang, X. H.; Wang, L. F. Engineering lattice metamaterials for extreme property, programmability, and multifunctionality. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 150901.
Munch, E.; Launey, M. E.; Alsem, D. H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A. P.; Ritchie, R. O. Tough, bio-inspired hybrid materials. Science 2008, 322, 1516–1520.
Cao, P. H. The strongest size in gradient nanograined Metals. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1440–1446.
Wong, T. S.; Kang, S. H.; Tang, S. K. Y.; Smythe, E. J.; Hatton, B. D.; Grinthal, A.; Aizenberg, J. Bioinspired self-repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity. Nature 2011, 477, 443–447.
Jia, Z. A.; Fernandes, M. C.; Deng, Z. F.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q. T.; Lethbridge, A.; Yin, J.; Lee, J. H.; Han, L.; Weaver, J. C. et al. Microstructural design for mechanical-optical multifunctionality in the exoskeleton of the flower beetle Torynorrhina flammea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101017118.
Ke, Y. J.; Chen, J. W.; Lin, G. J.; Wang, S. C.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, J.; Lee, P. S.; Long, Y. Smart windows: Electro-, thermo-, mechano-, photochromics, and beyond. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902066.
White, S. R.; Sottos, N. R.; Geubelle, P. H.; Moore, J. S.; Kessler, M. R.; Sriram, S. R.; Brown, E. N.; Viswanathan, S. Autonomic healing of polymer composites. Nature 2001, 409, 794–797.
Kang, D.; Pikhitsa, P. V.; Choi, Y. W.; Lee, C.; Shin, S. S.; Piao, L.; Park, B.; Suh, K. Y.; Kim, T. I.; Choi, M. Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system. Nature 2014, 516, 222–226.
Mimee, M.; Nadeau, P.; Hayward, A.; Carim, S.; Flanagan, S.; Jerger, L.; Collins, J.; Mcdonnell, S.; Swartwout, R.; Citorik, R. J. et al. An ingestible bacterial-electronic system to monitor gastrointestinal health. Science 2018, 360, 915–9185.
Nguyen, P. Q.; Botyanszki, Z.; Tay, P. K. R.; Joshi, N. S. Programmable biofilm-based materials from engineered curli nanofibres. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4945.
Huang, J. F.; Liu, S. Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Y.; Pu, J. H.; Ba, F.; Xue, S.; Ye, H. F.; Zhao, T. X.; Li, K. et al. Programmable and printable Bacillus subtilis biofilms as engineered living materials. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 34–41.
Gao, M. H.; Li, J.; Bao, Z. X.; Hu, M. D.; Nian, R.; Feng, D. X.; An, D.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Zhang, H. B. A natural in situ fabrication method of functional bacterial cellulose using a microorganism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 437.
Charrier, M.; Li, D.; Mann, V. R.; Yun, L. S.; Jani, S.; Rad, B.; Cohen, B. E.; Ashby, P. D.; Ryan, K. R.; Ajo-Franklin, C. M. Engineering the S-layer of Caulobacter crescentus as a foundation for stable, high-density, 2D living materials. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 181–190.
Jo, H.; Sim, S. Programmable living materials constructed with the dynamic covalent interface between synthetic polymers and engineered B. subtilis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20729–20738.
Saha, A.; Johnston, T. G.; Shafranek, R. T.; Goodman, C. J.; Zalatan, J. G.; Storti, D. W.; Ganter, M. A.; Nelson, A. Additive manufacturing of catalytically active living materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13373–13380.
Rivera-Tarazona, L. K.; Shukla, T.; Singh, K. A.; Gaharwar, A. K.; Campbell, Z. T.; Ware, T. H. 4D printing of engineered living materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2106843.
Zhang, P. C.; Shao, N.; Qin, L. D. Recent advances in microfluidic platforms for programming cell-based living materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005944.
Discher, D.; Dong, C.; Fredberg, J. J.; Guilak, F.; Ingber, D.; Janmey, P.; Kamm, R. D.; Schmid-Schönbein, G. W.; Weinbaum, S. Biomechanics: Cell research and applications for the next decade. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 37, 847–859.
Liu, S.; Xu, W. N. Engineered living materials-based sensing and actuation. Frontiers in Sensors 2020, 1, 586300.
Chen, C. J.; Kuang, Y. D.; Zhu, S. Z.; Burgert, I.; Keplinger, T.; Gong, A.; Li, T.; Berglund, L.; Eichhorn, S. J.; Hu, L. B. Structure-property-function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 642–666.
Geng, Y.; Jiao, K.; Liu, X.; Ying, P. J.; Odunmbaku, O.; Zhang, Y. X.; Tan, S. C.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, M. Applications of bio-derived/bio-inspired materials in the field of interfacial solar steam generation. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3122–3142.
Nurazzi, N. M.; Asyraf, M. R. M.; Athiyah, S. F.; Shazleen, S. S.; Rafiqah, S. A.; Harussani, M. M.; Kamarudin, S. H.; Razman, M. R.; Rahmah, M.; Zainudin, E. S. et al. A review on mechanical performance of hybrid natural fiber polymer composites for structural applications. Polymers (Basel) 2021, 13, 2170.
Song, J. W.; Chen, C. J.; Zhu, S. Z.; Zhu, M. W.; Dai, J. Q.; Ray, U.; Li, Y. J.; Kuang, Y. D.; Li, Y. F.; Quispe, N. et al. Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material. Nature 2018, 554, 224–228.
Li, S. W.; Li, J.; Geng, Y.; Liao, Y. N.; Chen, S. S.; Sun, K.; Li, M. Shape-stable phase change composites based on carbonized waste pomelo peel for low-grade thermal energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103556.
Geng, Y.; Sun, W.; Ying, P. J.; Zheng, Y. J.; Ding, J.; Sun, K.; Li, L.; Li, M. Bioinspired fractal design of waste biomass-derived solar-thermal materials for highly efficient solar evaporation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007648.
Camere, S.; Karana, E. Fabricating materials from living organisms: An emerging design practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 570–584.
Oren, A.; Garrity, G. M. Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005056.
Schulz, H. N.; Jørgensen, B. B. Big Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 105–137.
Van Mullem, T.; Gruyaert, E.; Caspeele, R.; De Belie, N. De Belie First large scale application with self-healing concrete in Belgium: Analysis of the laboratory control tests. Materials (Basel) 2020, 13, 997.
Qian, C. X.; Yu, X. N.; Zheng, T. W.; Chen, Y. Q. Review on bacteria fixing CO2 and bio-mineralization to enhance the performance of construction materials. J. CO2Utilizat. 2022, 55, 101849.
Qiu, J. S.; Artier, J.; Cook, S.; Srubar III, W. V.; Cameron, J. C.; Hubler, M. H. Engineering living building materials for enhanced bacterial viability and mechanical properties. iScience 2021, 24, 102083.
Duraj-Thatte, A. M.; Manjula-Basavanna, A.; Courchesne, N. M. D.; Cannici, G. I.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Frank, B. P.; Van’t Hag, L.; Cotts, S. K.; Fairbrother, D. H.; Mezzenga, R. et al. Water-processable, biodegradable and coatable aquaplastic from engineered biofilms. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 732–738.
Manjula-Basavanna, A.; Duraj-Thatte, A. M.; Joshi, N. S. Robust self-regeneratable stiff living materials fabricated from microbial cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010784.
Portela, R.; Leal, C. R.; Almeida, P. L.; Sobral, R. G. Bacterial cellulose: A versatile biopolymer for wound dressing applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 586–610.
Suryanto, H.; Muhajir, M.; Sutrisno, T. A.; Mudjiono; Zakia, N.; Yanuhar, U. The mechanical strength and morphology of bacterial cellulose films: The effect of NaOH concentration. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 515, 012053.
Chawla, P. R.; Bajaj, I. B.; Survase, S. A.; Singhal, R. S. Microbial cellulose: Fermentative production and applications. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 107–124.
Huang, Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Yang, J. Z.; Nie, Y.; Chen, C. T.; Sun, D. P. Recent advances in bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1–30.
Schaffner, M.; Rühs, P. A.; Coulter, F.; Kilcher, S.; Studart, A. R. 3D printing of bacteria into functional complex materials. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao6804.
Caro-Astorga, J.; Walker, K. T.; Herrera, N.; Lee, K. Y.; Ellis, T. Bacterial cellulose spheroids as building blocks for 3D and patterned living materials and for regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5027.
Binelli, M. R.; Rühs, P. A.; Pisaturo, G.; Leu, S.; Trachsel, E.; Studart, A. R. Living materials made by 3D printing cellulose-producing bacteria in granular gels. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 141, 213095.
Ednie-Brown, P. bioMASON and the speculative engagements of biotechnical architecture. Architect. Des. 2013, 83, 84–91.
Heveran, C. M.; Williams, S. L.; Qiu, J. S.; Artier, J.; Hubler, M. H.; Cook, S. M.; Cameron, J. C.; Srubar, W. V. Biomineralization and successive regeneration of engineered living building materials. Matter 2020, 2, 481–494.
Hawksworth, D. L. The magnitude of fungal diversity: The 1.5 million species estimate revisited. Mycol. Res. 0011, 105, 1422–1432.
Gow, N. A. R.; Latge, J. P.; Munro, C. A. The fungal cell wall: Structure, biosynthesis, and function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, FUNK-0035-2016.
Appels, F. V. W.; Camere, S.; Montalti, M.; Karana, E.; Jansen, K. M. B.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Krijgsheld, P.; Wösten, H. A. B. Fabrication factors influencing mechanical, moisture- and water-related properties of mycelium-based composites. Mater Des 2019, 161, 64–71.
Nawawi, W. M. F. W.; Jones, M. P.; Kontturi, E.; Mautner, A.; Bismarck, A. Plastic to elastic: Fungi-derived composite nanopapers with tunable tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 198, 108327.
Liu, R.; Long, L.; Sheng, Y.; Xu, J. F.; Qiu, H. Y.; Li, X. Y.; Wang, Y. X.; Wu, H. G. Preparation of a kind of novel sustainable mycelium/cotton stalk composites and effects of pressing temperature on the properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 1117322.
Sun, W. J.; Tajvidi, M.; Hunt, C. G.; McIntyre, G.; Gardner, D. J. Fully bio-based hybrid composites made of wood, fungal mycelium and cellulose nanofibrils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3766.
Jones, M. P.; Lawrie, A. C.; Huynh, T. T.; Morrison, P. D.; Mautner, A.; Bismarck, A.; John, S. Agricultural by-product suitability for the production of chitinous composites and nanofibers utilising Trametes versicolor and Polyporus brumalis mycelial growth. Process Biochem. 2019, 80, 95–102.
Lee, T.; Choi, J. Mycelium- composite panels for atmospheric particulate matter adsorption. Results Mater. 2021, 11, 100208.
Pelletier, M. G.; Holt, G. A.; Wanjura, J. D.; Bayer, E.; McIntyre, G. An evaluation study of mycelium based acoustic absorbers grown on agricultural by-product substrates. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 51, 480–485.
Dias, P. P.; Jayasinghe, L. B.; Waldmann, D. Investigation of Mycelium-Miscanthus composites as building insulation material. Results in Materials 2021, 10, 100189.
Schritt, H.; Vidi, S.; Pleissner, D. Spent mushroom substrate and sawdust to produce mycelium-based thermal insulation composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127910.
McBee, R. M.; Lucht, M.; Mukhitov, N.; Richardson, M.; Srinivasan, T.; Meng, D. C.; Chen, H. R.; Kaufman, A.; Reitman, M.; Munck, C. et al. Engineering living and regenerative fungal-bacterial biocomposite structures. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 471–478.
Jones, M.; Gandia, A.; John, S.; Bismarck, A. Leather-like material biofabrication using fungi. Nat Sustain 2021, 4, 9–16.
Elsacker, E.; Zhang, M.; Dade-Robertson, M. Fungal engineered living materials: The viability of pure mycelium materials with self-healing functionalities. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301875.
Van Wylick, A.; Monclaro, A. V.; Elsacker, E.; Vandelook, S.; Rahier, H.; De Laet, L.; Cannella, D.; Peeters, E. A review on the potential of filamentous fungi for microbial self-healing of concrete. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 16.
Shakya, M.; Sharma, P.; Meryem, S. S.; Mahmood, Q.; Kumar, A. Heavy metal removal from industrial wastewater using fungi: Uptake mechanism and biochemical aspects. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, C6015001.
Gantenbein, S.; Colucci, E.; Käch, J.; Trachsel, E.; Coulter, F. B.; Rühs, P. A.; Masania, K.; Studart, A. R. Three-dimensional printing of mycelium hydrogels into living complex materials. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 128–134.
Shen, S. C.; Lee, N. A.; Lockett, W. J.; Acuil, A. D.; Gazdus, H. B.; Spitzer, B. N.; Buehler, M. J. Robust myco-composites as a platform for versatile hybrid-living structural materials. arXiv: 2305, 12151, 2023.
Jones, M.; Mautner, A.; Luenco, S.; Bismarck, A.; John, S. Engineered mycelium composite construction materials from fungal biorefineries: A critical review. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108397.
Sağlam, S. S.; Özgünler, S. A. An experimental study on production opportunities of biocomposite by using fungal mycelium. J. Des. Resil. Architect. Plann. 2022, 3, 237–260.
Haneef, M.; Ceseracciu, L.; Canale, C.; Bayer, I. S.; Heredia-Guerrero, J. A.; Athanassiou, A. Advanced materials from fungal mycelium: Fabrication and tuning of physical properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41292.
Chang, J. H.; Chan, P. L.; Xie, Y. C.; Ma, K. L.; Cheung, M. K.; Kwan, H. S. Modified recipe to inhibit fruiting body formation for living fungal biomaterial manufacture. PLoS One, 2019, 14, e0209812.
Vallas, T.; Courard, L. Using nature in architecture: Building a living house with mycelium and trees. Front. Architect. Res. 2017, 6, 318–328.
Ghavami, K. 2-Introduction to nonconventional materials and an historic retrospective of the field. In Nonconventional and Vernacular Construction Materials, Harries, K. A.; Sharma, B.; Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxfor, 2016; pp 37–61.
Ludwig, F.; Schwertfreger, H.; Storz, O. Living systems: Designing growth in baubotanik. Architect. Des. 2012, 82, 82–87.
Middleton, W.; Shu, Q. G.; Ludwig, F. Representing living architecture through skeleton reconstruction from point clouds. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1549.
Roumeli, E.; Bonanomi, L.; Hendrickx, R.; Rinaldi, K.; Daraio, C. Plant cells-based biological matrix composites. arrivv 1909, 01926, 2019.
Schmidt, D.; Asmis, L. M.; Odermatt, B.; Kelm, J.; Breymann, C.; Gössi, M.; Genoni, M.; Zund, G.; Hoerstrup, S. P. Engineered living blood vessels: Functional endothelia generated from human umbilical cord-derived progenitors. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 1465–1471.
Murphy, S. V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785.
Discher, D. E.; Janmey, P.; Wang, Y. L. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science 2005, 310, 1139–1143.
Kang, S.; Park, J. B.; Lee, T. J.; Ryu, S.; Bhang, S. H.; La, W. G.; Noh, M. K.; Hong, B. H.; Kim, B. S. Covalent conjugation of mechanically stiff graphene oxide flakes to three-dimensional collagen scaffolds for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbon 2015, 83, 162–172.
Jiang, Y. R.; Zhou, D. Z.; Yang, B. 3D bioprinted GelMA/GO composite induces osteoblastic differentiation. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 37, 527–537.
Tsoi, R.; Wu, F. L.; Zhang, C.; Bewick, S.; Karig, D.; You, L. C. Metabolic division of labor in microbial systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2526–2531.
Gilbert, C.; Tang, T. C.; Ott, W.; Dorr, B. A.; Shaw, W. M.; Sun, G. L.; Lu, T. K.; Ellis, T. Living materials with programmable functionalities grown from engineered microbial co-cultures. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 691–700.
Raman, J.; Kim, D. S.; Kim, H. S.; Oh, D. S.; Shin, H. J. Mycofabrication of mycelium-based leather from brown-rot fungi. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 317.
Estroff, L. A. Introduction: Biomineralization. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4329–4331.
Xin, A.; Su, Y. P.; Feng, S. W.; Yan, M. L.; Yu, K. H.; Feng, Z. Z. R.; Lee, K.H.; Sun, L. Z.; Wang, Q. M. Growing living composites with ordered microstructures and exceptional mechanical properties. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006946.
Wiktor, V.; Jonkers, H. M. Bacteria- based concrete: From concept to market. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 084006.
Wang, Y. Y.; An, B. L.; Xue, B.; Pu, J. H.; Zhang, X. L.; Huang, Y. Y.; Yu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, C. Living materials fabricated via gradient mineralization of light-inducible biofilms. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 351–359.
Wallace, A. K.; Chanut, N.; Voigt, C. A. Silica nanostructures modifications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000849.
Konak, B. M. K.; Bakar, M. E.; Ahan, R. E.; Özyürek, E. U.; Dökmeci, S.; Şeker, U. Ö. Ş. A living material platform for the biomineralization of biosilica. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 17, 100461.
Park, H.; Schwartzman, A. F.; Tang, T. C.; Wang, L.; Lu, T. K. Ultra-lightweight living structural material for enhanced stiffness and environmental sensing. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 18, 100504.
Araújo, G. R. D. S.; Viana, N. B.; Gómez, F.; Pontes, B.; Frases, S. The mechanical properties of microbial surfaces and biofilms. Cell Surf. 2019, 5, 100028.
Charlton, S. G. V.; White, M. A.; Jana, S.; Eland, L. E.; Jayathilake, P. G.; Burgess, J. G.; Chen, J. J.; Wipat, A.; Curtis, T. P. Regulating, measuring, and modeling the viscoelasticity of bacterial biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00101–19.
Wilking, J. N.; Angelini, T. E.; Seminara, A.; Brenner, M. P.; Weitz, D. A. Biofilms as complex fluids. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 385–391.
Wan Nawawi, W. M. F.; Lee, K. Y.; Kontturi, E.; Murphy, R. J.; Bismarck, A. Chitin nanopaper from mushroom extract: Natural composite of nanofibers and glucan from a single biobased source. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6492–6496.
Menon, R. R.; Luo, J.; Chen, X. B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zhou, G. W.; Zhang, N.; Jin, C. R. Screening of fungi for potential application of self-healing concrete. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2075.
Zhang, J. H.; Shi, X. Z.; Chen, X.; Huo, X. F.; Yu, Z. Microbial-induced carbonate precipitation: A review on influencing factors and applications. Adv. Civil Eng. 2021, 2021, 9974027.
Sandak, A.; Sandak, J.; Brzezicki, M.; Kutnar, A. Biomaterials for Building Skins. In: Bio-based Building Skin. Environmental Footprints and Eco-design of Products and Processes. Springer, Singapore. 2019.
Hy-Fi. urbanNext [Online]. https://urbannext.net/hy-fi/ (Accessed Jun 17, 2023).
Diana Scherer Interwoven [Online]. https://dianascherer.nl/ (Accessed Jun 21, 2023).
Jones, M.; Bhat, T.; Wang, C. H.; Moinuddin, K; John, S. Thermal degradation and fire reaction properties of mycelium composites. In Proceedings of the 21stinternational conference on composite materials, Xi’an, China, 2017, pp. 20–25.
Acknowledgements
Ling Li gratefully acknowledges the funding support from the National Science Foundation (No. DMR-1942865), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Nos. FA9550-19-1-0033 and FA9550-20-1-0161), and Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, Y., Jia, Z. & Li, L. Structural engineered living materials. Nano Res. 17, 715–733 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6313-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6313-7