Abstract
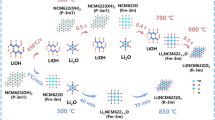
Spinel LiNi0.5−xMn1.5+xO4 (LNMO) has attracted intensive interest for lithium-ion battery due to its high voltage and high energy density. However, severe capacity fade attributed to unstable surface structure has hampered its commercialization. Oxygen vacancies (OVs) tend to occur in the surface of the material and lead to surface structure reconstruction, which deteriorates the battery performance during electrochemical cycling. Here, we utilize high-temperature-shock (HTS) method to synthesize LNMO materials with fewer surface OVs. Rapid calcination drives lower surface OVs concentration, reducing the content of Mn3+ and surface reconstruction layers, which is beneficial to obtain a stable crystal structure. The LNMO material synthesized by HTS method delivers an initial capacity of 127 mAh·g−1 at 0.1 C and capacity retention of 81.6% after 300 cycles at 1 C, and exhibits excellent performance at low temperature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, N. J.; Deng, W. J.; Xu, Z. X.; Wang, X. L. Upcycling of spent LiCoO2 cathodes via nickel- and manganese-doping. Carbon Energy 2023, 5, e231.
Wang, H.; Ben, L. B.; Yu, H. L.; Chen, Y. Y.; Yang, X. N.; Huang, X. J. Understanding the effects of surface reconstruction on the electrochemical cycling performance of the spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 822–834.
Manthiram, A. A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1550.
Xiao, B. W.; Liu, H. S.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B. Q.; Kaliyappan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Banis, M. N.; Liu, Y. L.; Li, R. Y. et al. Nanoscale manipulation of spinel lithium nickel manganese oxide surface by multisite ti occupation as high-performance cathode. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703764.
Huang, Y. H. The discovery of cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries from the view of interdisciplinarity. Interdiscip. Mater. 2022, 1, 323–329.
Cui, B. H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B. Q.; Kaliyappan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Banis, M. N.; Liu, Y. L.; Li, R. Y. et al. Heterogeneous lamellar-edged Fe-Ni(OH)2/Ni3S2 nanoarray for efficient and stable seawater oxidation. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1149–1155.
He, S. Y.; Zeng, J. B.; Habte, B. T.; Jiang, F. M. Numerical reconstruction of microstructure of graphite anode of lithium-ion battery. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 656–664.
Liu, Y. G.; Zhang, C. P.; Liu, C. F.; Song, H. Q.; Nan, X. H.; Cao, G. Z. The effect of nitrogen annealing on lithium ion intercalation in nickel-doped lithium trivanadate. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 587–593.
Zhang, L. X.; Liu, Y. M.; You, Y.; Vinu, A.; Mai, L. NASICONs-type solid-state electrolytes: The history, physicochemical properties, and challenges. Interdiscip. Mater. 2023, 2, 91–110.
Liu, Y. C.; Chen, Y. F.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Ding, Z. Y.; Li, L. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. D.; Wu, J. W.; Chen, Y. N. Hierarchical yolk–shell structured Li-rich cathode boosting cycling and voltage stabled LIBs. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3178–3186.
Liang, G. M.; Peterson, V. K.; See, K. W.; Guo, Z. P.; Pang, W. K. Developing high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes for high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries: Current achievements and future prospects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15373–15398.
Liang, G. M.; Peterson, V. K.; Wu, Z. B.; Zhang, S. L.; Hao, J. N.; Lu, C. Z.; Chuang, C. H.; Lee, J. F.; Liu, J.; Leniec, G. et al. Crystallographic-site-specific structural engineering enables extraordinary electrochemical performance of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2101413.
Liang, G. M.; Wu, Z. B.; Didier, C.; Zhang, W. C.; Cuan, J.; Li, B. H.; Ko, K. Y.; Hung, P. Y.; Lu, C. Z.; Chen, Y. Z. et al. A long cycle-life high-voltage spinel lithium-ion battery electrode achieved by site-selective doping. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10594–10602.
Li, W. D.; Song, B. H.; Manthiram, A. High-voltage positive electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3006–3059.
Piao, J. Y.; Gu, L.; Wei, Z. X.; Ma, J. M.; Wu, J. P.; Yang, W. L.; Gong, Y.; Sun, Y. G.; Duan, S. Y.; Tao, X. S. et al. Phase control on surface for the stabilization of high energy cathode materials of lithium ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4900–4907.
Yi, T. F.; Mei, J.; Zhu, Y. R. Key strategies for enhancing the cycling stability and rate capacity of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as high-voltage cathode materials for high power lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 316, 85–105.
Han, Y.; Jiang, Y. S.; Yu, F. D.; Deng, L.; Ke, W.; Zhang, S. J.; Que, L. F.; Wu, B.; Ding, F.; Zhao, L. et al. Addressing Mn dissolution in high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes via interface phase modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207285.
Ma, J.; Hu, P.; Cui, G. L.; Chen, L. Q. Surface and interface issues in spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4: Insights into a potential cathode material for high energy density lithium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3578–3606.
Yin, C. J.; Zhou, H. M.; Yang, Z. H.; Li, J. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for Li-ion batteries by the metal-organic framework method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13625–13634.
Lin, M. X.; Ben, L. B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z. Z.; Gu, L.; Yu, X. Q.; Yang, X. Q.; Zhao, H. F.; Yu, R. C. et al. Insight into the atomic structure of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material in the first cycle. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 292–303.
Liu, T. C.; Dai, A.; Lu, J.; Yuan, Y. F.; Xiao, Y. G.; Yu, L.; Li, M.; Gim, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, J. J. et al. Correlation between manganese dissolution and dynamic phase stability in spinel-based lithium-ion battery. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4721.
Deng, S. X.; Wang, B. Q.; Yuan, Y. F.; Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Doyle-Davis, K.; Banis, M. N.; Liang, J. N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. J. et al. Manipulation of an ionic and electronic conductive interface for highly-stable high-voltage cathodes. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 103988.
Kuppan, S.; Xu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. J.; Chen, G. Y. Phase transformation mechanism in lithium manganese nickel oxide revealed by single-crystal hard X-ray microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14309.
Wei, L. Y.; Tao, J. M.; Yang, Y. M.; Fan, X. Y.; Ran, X. X.; Li, J. X.; Lin, Y. B.; Huang, Z. G. Surface sulfidization of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for enhanced electrochemical performance in lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123268.
Fang, X.; Lin, F.; Nordlund, D.; Mecklenburg, M.; Ge, M. Y.; Rong, J. P.; Zhang, A. Y.; Shen, C. F.; Liu, Y. H.; Cao, Y. et al. Atomic insights into the enhanced surface stability in high voltage cathode materials by ultrathin coating. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1602873.
Luo, J. W.; Zhang, J. C.; Guo, Z. X.; Liu, Z. D.; Dou, S. M.; Liu, W. D.; Chen, Y. N.; Hu, W. B. Recycle spent graphite to defect-engineered, high-power graphite anode. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 4240–4245.
Lee, Y.; Mun, J.; Kim, D. W.; Lee, J. K.; Choi, W. Surface modification of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes with ZnAl2O4 by a sol-gel method for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 326–331.
Liu, H. D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. F.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Qiu, B.; Fang, J. H.; Kloepsch, R.; Schumacher, G.; Liu, Z. P. et al. Morphological evolution of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: The critical effects of surface orientations and particle size. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4661–4675.
Wang, K. X.; Li, X. H.; Chen, J. S. Surface and interface engineering of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 527–545.
Wang, D. D.; Gao, C.; Zhou, X. F.; Peng, S.; Tang, M. X.; Wang, Y. G.; Huang, L. J.; Yang, W. G.; Gao, X. Enhancing reversibility of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by regulating surface oxygen deficiency. Carbon Energy, in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/cey2.338.
Lee, S.; Jin, W.; Kim, S. H.; Joo, S. H.; Nam, G.; Oh, P.; Kim, Y. K.; Kwak, S. K.; Cho, J. Oxygen vacancy diffusion and condensation in lithium-ion battery cathode materials. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10478–10485.
Yan, P. F.; Zheng, J. M.; Tang, Z. K.; Devaraj, A.; Chen, G. Y.; Amine, K.; Zhang, J. G.; Liu, L. M.; Wang, C. M. Injection of oxygen vacancies in the bulk lattice of layered cathodes. Nat Nanotechnol 2019, 14, 602–608.
Gao, X.; Ikuhara, Y. H.; Fisher, C. A. J.; Huang, R.; Kuwabara, A.; Moriwake, H.; Kohama, K.; Ikuhara, Y. Oxygen loss and surface degradation during electrochemical cycling of lithium-ion battery cathode material LiMn2O4. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8845–8854.
Zhang, Y. H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, L. R.; Ma, J.; Yi, Q.; Wang, Z. X.; Wang, X. F.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, N. F. et al. Stabilization of lattice oxygen in li-rich Mn-based oxides via swing-like non-isothermal sintering. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202341.
Luo, X. L.; Chen, H. X.; Liu, Z. Z.; Luo, H.; Zhou, H. M. Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by a dual modification of Ti doping and in situ coating using metal-organic frameworks as precursors. Ionics 2022, 28, 2099–2115.
Zhu, W.; Zhang, J. C.; Luo, J. W.; Zeng, C. H.; Su, H.; Zhang, J. F.; Liu, R.; Hu, E. Y.; Liu, Y. S.; Liu, W. D. et al. Ultrafast non-equilibrium synthesis of cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2208974.
Zhang, J. C.; Wen, J.; Liu, W. D.; Cui, X. Y.; Chen, Y. N. Cryo-EM for nanomaterials: Progress and perspective. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2613–2626.
Zhang, J. C.; Luo, J. W.; Guo, Z. X.; Liu, Z. D.; Duan, C. P.; Dou, S. M.; Yuan, Q. Y.; Liu, P.; Ji, K. M.; Zeng, C. H. et al. Ultrafast manufacturing of ultrafine structure to achieve an energy density of over 120 Wh·kg−1 in supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203061.
Liu, Z. D.; Duan, C. P.; Dou, S. M.; Yuan, Q. Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, W. D.; Chen, Y. N. Ultrafast porous carbon activation promises high-energy density supercapacitors. Small 2022, 18, 2200954.
Chen, Y. N.; Egan, G. C.; Wan, J. Y.; Zhu, S. Z.; Jacob, R. J.; Zhou, W. B.; Dai, J. Q.; Wang, Y. B.; Danner, V. A.; Yao, Y. G. et al. Ultra-fast self-assembly and stabilization of reactive nanoparticles in reduced graphene oxide films. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12332.
Zeng, C. H.; Duan, C. P.; Guo, Z. X.; Liu, Z. D.; Dou, S. M.; Yuan, Q. Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. C.; Luo, J. W.; Liu, W. D. et al. Ultrafastly activated needle coke as electrode material for supercapacitors. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2022, 32, 786–792.
Cui, B. H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. F.; Lu, J. J.; Liu, S. L.; Chen, F. S.; Zhou, W.; Qian, G. Y.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Y. D. et al. Waste to wealth: Defect-rich Ni-incorporated spent LiFePO4 for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 2710–2718.
Okamoto, Y. Ambivalent effect of oxygen vacancies on Li2MnO3: A first-principles study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A152–A157.
Liu, W. J.; Shi, Q.; Qu, Q. T.; Gao, T.; Zhu, G. B.; Shao, J.; Zheng, H. H. Improved Li-ion diffusion and stability of a LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode through in situ co-doping with dual-metal cations and incorporation of a superionic conductor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 145–154.
Xia, Y. Y.; Sakai, T.; Fujieda, T.; Yang, X. Q.; Sun, X.; Ma, Z. F.; Mcbreen, J.; Yoshio, M. Correlating capacity fading and structural changes in Li1+yMn2−yO4−δ spinel cathode materials: A systematic study on the effects of Li/Mn ratio and oxygen deficiency. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A723–A729.
Lan, L. F.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, S. J.; Pan, C. Y.; Zhao, F. H. Enhancement of the electrochemical performance of the spinel structure LiNi0.5−xGaxMn1.5O4 cathode material by Ga doping. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 251.
Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Jiang, X. F.; Pinto, J.; Yang, G. Microwave rapid preparation of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and the improved high rate performance for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 100, 125–132.
Nisar, U.; Al-Hail, S. A. J. A.; Kumar, P. R.; Abraham, J. J.; Mesallam, S. M. A.; Shakoor, R. A.; Amin, R.; Essehli, R.; Al-Qaradawi, S. Fast and scalable synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode by sol-gel-assisted microwave sintering. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100085.
Huang, R.; Ikuhara, Y. H.; Mizoguchi, T.; Findlay, S. D.; Kuwabara, A.; Fisher, C. A. J.; Moriwake, H.; Oki, H.; Hirayama, T.; Ikuhara, Y. Oxygen-vacancy ordering at surfaces of lithium manganese(III, IV) oxide spinel nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3053–3057.
Hwang, S.; Chang, W.; Kim, S. M.; Su, D.; Kim, D. H.; Lee, J. Y.; Chung, K. Y.; Stach, E. A. Investigation of changes in the surface structure of LixNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 cathode materials induced by the initial charge. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1084–1092.
Zuo, W. H.; Luo, M. Z.; Liu, X. S.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. D.; Li, J.; Winter, M.; Fu, R. Q.; Yang, W. L.; Yang, Y. Li-rich cathodes for rechargeable Li-based batteries: Reaction mechanisms and advanced characterization techniques. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4450–4497.
Hu, E. Y.; Yu, X. Q.; Lin, R. Q.; Bi, X. X.; Lu, J.; Bak, S.; Nam, K. W.; Xin, H. L.; Jaye, C.; Fischer, D. A. et al. Evolution of redox couples in Li-and Mn-rich cathode materials and mitigation of voltage fade by reducing oxygen release. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 690–698.
Wang, S. N.; Hua, W. B.; Zhou, S.; He, X. F.; Liu, L. J. In situ synchrotron radiation diffraction study of the Li+ de/intercalation behavior in spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4−δ. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125998.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52171219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Zeng, C., Zhu, W. et al. Boosting cycling stability by regulating surface oxygen vacancies of LNMO by rapid calcination. Nano Res. 17, 2671–2677 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6076-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6076-1