Abstract
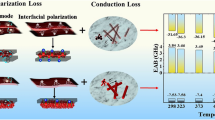
Due to the temperature and frequency response of electromagnetic (EM) loss, how to realize the effective design of microwave absorption materials (MWAMs) at elevated temperature is highly desirable for practical applications. Herein, transition metal-doped titanium nitride (M-TiN, M = Fe or Co) fibers were fabricated, the distortion of TiN lattice could cause the adjustable charge enrichment, which played a profound influence on the dielectric response and EM microwave absorption (EMWA) performances. Benefiting from the negative correlation between dielectric loss and temperature, more loss mechanism could be introduced, which would effectively enhance dielectric loss and EMWA performances at elevated temperature. The optimal EMWA performances of Fe-TiN fibers/polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) composites were realized with a wide temperature range (298–423 K): the reflection loss (RL) could reach 99% (RL < −20 dB) at 12.2 GHz with 1.8 mm, when the filler content was only 15.0 wt.%. Compared with the undoped-TiN fibers/PDMS and Co-TiN fibers/PDMS composites, the excellent EMWA of Fe-TiN fibers/PDMS composite could be attributed to the reasonably synergistic polarization loss and conduction loss. Based on systematic analysis of the variable-temperature EM parameters and EMWA performances, the optimization of EMWA performances in wide temperature domain could be realized by introducing appropriate polarization loss and its compensating. Hopefully, this work provides a new strategy for regulating the dielectric response and designing effective MWAMs at elevated temperature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, Z. L.; Xiang, X. L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Gu, J. W. Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200705.
Zhang, C.; Li, X. A.; Shi, Y. N.; Wu, H. J.; Shen, Y. F.; Wang, C. S.; Guo, W. C.; Tian, K. S.; Wang, H. Y. Structure engineering of graphene nanocages toward high-performance microwave absorption applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2101904.
Li, C.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y. L.; Xie, R.; Zhong, W. Magnetic-dielectric synergy and interfacial engineering to design yolk-shell structured CoNi@void@C and CoNi@void@C@MoS2 nanocomposites with tunable and strong wideband microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6761–6771.
Gao, N.; Li, W. P.; Wang, W. S.; Liu, D. P.; Cui, Y. M.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. S. Balancing dielectric loss and magnetic loss in Fe-NiS2/NiS/PVDF composites toward strong microwave reflection loss. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14416–14424.
Song, Z. M.; Liu, X. F.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, X. Y.; Tang, W. K.; Yu, R. H.; Shui, J. L. Alginate-templated synthesis of CoFe/carbon fiber composite and the effect of hierarchically porous structure on electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2019, 151, 36–45.
Lan, X. L.; Wang, Z. J. Efficient high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption enabled by structuring binary porous SiC with multiple interfaces. Carbon 2020, 170, 517–526.
Cao, W. Q.; Wang, X. X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, W. Z.; Cao, M. S. Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10017–10022.
Zhou, Q.; Yin, X. W.; Ye, F.; Tang, Z. M.; Mo, R.; Cheng, L. F. High temperature electromagnetic wave absorption properties of SiCf/Si3N4 composite induced by different SiC fibers. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 6514–6522.
Shi, Y. P.; Li, D.; Wei, Y.; Gong, C. H.; Zhang, J. W. Magnetic TiN composites for efficient microwave absorption: Nanoribbons vs. nanoparticles. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100919.
Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gong, C. H.; Liu, S. C.; Zhang, M. M.; Shi, Y. P.; Zhang, J. W. Fabrication of TiN/carbon nanofibers by electrospinning and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1488–1493.
Wei, Y.; Shi, Y. P.; Zhang, X. F.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Zhang, Y. H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. W.; Gong, C. H. Electrospinning of lightweight TiN fibers with superior microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 14519–14527.
Jiang, Z. Y.; Si, H. X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, H. H.; Gong, C. H.; Zhang, J. W. Reduced graphene oxide@carbon sphere based metacomposites for temperature-insensitive and efficient microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8546–8554.
Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H. R.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels containing pod-like N-doped carbon nanotubes and FeNi nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2020, 159, 357–365.
Li, T.; Zhi, D. D.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z. W.; Meng, F. B. Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 477–484.
Hu, F. Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. H.; Li, Y. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. X.; Fan, B. B. Ultrabroad band microwave absorption from hierarchical MoO3/TiO2/Mo2TiC2Tx hybrids via annealing treatment. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 1466–1478.
Gao, Z. G.; Ma, Z. H.; Lan, D.; Zhao, Z. H.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J.; Hou, Y. L. Synergistic polarization loss of MoS2-based multiphase solid solution for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112294.
Wen, B.; Cao, M. S.; Lu, M. M.; Cao, W. Q.; Shi, H. L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. X.; Jin, H. B.; Fang, X. Y.; Wang, W. Z. et al. Reduced graphene oxides: Light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3484–3489.
Luo, H.; Tan, Y. Q.; Li, Y.; Xiao, P.; Deng, L. W.; Zeng, S. F.; Zhang, G. J.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhou, X. S.; Peng, S. M. Modeling for high-temperature dielectric behavior of multilayer Cf/Si3N4 composites in X-band. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1961–1968.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Variable-temperature electron transport and dipole polarization turning flexible multifunctional microsensor beyond electrical and optical energy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907156.
Shi, Y. P.; Li, D.; Si, H. X.; Duan, Y. P.; Gong, C. H.; Zhang, J. W. TiN/Fe2Ni2N/SiO2 composites for magnetic-dielectric balance to facilitate temperature-stable broadband microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165603.
Shi, Y. P.; Li, D.; Si, H. X.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Li, M. Y.; Gong, C. H. TiN/BN composite with excellent thermal stability for efficiency microwave absorption in wide temperature spectrum. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 249–255.
Liu, Y.; Zhou, X. F.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, H. J.; Wu, G. L. Oxygen vacancy-induced dielectric polarization prevails in the electromagnetic wave-absorbing mechanism for Mn-based MOFs-derived composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204499.
Liu, J. L.; Zhang, L. M.; Zang, D. Y.; Wu, H. J. A competitive reaction strategy toward binary metal sulfides for tailoring electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105018.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Zhao, X. R.; Wu, H. J. Defect induced polarization loss in multi-shelled spinel hollow spheres for electromagnetic wave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004640.
Kuang, B. Y.; Dou, Y. K.; Wang, Z. H.; Ning, M. Q.; Jin, H. B.; Guo, D. Y.; Cao, M. S.; Fang, X. Y.; Zhao, Y. J.; Li, J. B. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Co-doped SiC at elevated temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 383–390.
Zhang, X. F.; Guo, J. J.; Guan, P. F.; Qin, G. W.; Pennycook, S. J. Gigahertz dielectric polarization of substitutional single niobium atoms in defective graphitic layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 147601.
Zhang, X. C.; Shi, Y. N.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, Q. Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. L.; Chen, Y. J. Identification of the intrinsic dielectric properties of metal single atoms for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 27.
Song, L. L.; Duan, Y. P.; Liu, J.; Pang, H. F. Transformation between nanosheets and nanowires structure in MnO2 upon providing Co2+ ions and applications for microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 95–104.
He, G. H.; Duan, Y. P.; Song, L. L.; Zhang, X. F. Doping strategy to boost electromagnetic property and gigahertz tunable electromagnetic attenuation of hetero-structured manganese dioxide. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2407–2421.
Song, L. L.; Duan, Y. P.; He, G. H.; Zhang, X. F. Enhanced thermal stability and dielectric performance of δ-MnO2 by Ni2+ doping. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 15362–15370.
Quan, L.; Qin, F. X.; Lu, H. T.; Estevez, D.; Wang, Y. F.; Li, Y. H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, H. X. Sequencing dual dopants for an electromagnetic tunable graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127421.
Dou, Y. K. The study of temperature dependence of electrical performance for typical semiconductor materials. Ph. D. Dissertation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 2015.
Gao, Z. G.; Lan, D.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Simultaneous manipulation of interfacial and defects polarization toward Zn/Co phase and ion hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106677.
Fu, X. K.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Q.; Li, Z. B.; Yan, H. L.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Ti2O3 and vacancy enhancement effective bandwidth. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 76, 166–173.
Yan, J. Q.; Saparov, B.; Sefat, A. S.; Yang, H.; Cao, H. B.; Zhou, H. D.; Sales, B. C.; Mandrus, D. G. Absence of structural transition in M0.5IrTe2 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni). Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 134502.
Hu, L.; Luo, W.; Qin, F. X.; Xv, W. T.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. F. Flexible and tunable microwave absorption structures using carbonyl iron@polydimethylsiloxane pillar arrays. J. Phys. D:Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 145001.
Gong, C. H.; Zhang, J. W.; Yan, C.; Cheng, X. Q.; Zhang, J. W.; Yu, L. G.; Jin, Z. S.; Zhang, Z. J. Synthesis and microwave electromagnetic properties of nanosized titanium nitride. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3370–3376.
Gong, C. H.; Meng, H. J.; Zhao, X. W.; Zhang, X. F.; Yu, L. G.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhang, Z. J. Unique static magnetic and dynamic electromagnetic behaviors in titanium nitride/carbon composites driven by defect engineering. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18927.
Yan, C.; Cheng, X. Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, D. Z.; Gong, C. H.; Yu, L. G.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhang, Z. J. Ferromagnetism and microwave electromagnetism of iron-doped titanium nitride nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 26006–26012.
Guo, Y. F.; Li, J. Y.; Meng, F. B.; Wei, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. G.; Peng, F. X.; Zhou, Z. W. Hybridization-induced polarization of graphene sheets by intercalation-polymerized polyaniline toward high performance of microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17100–17107.
Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, F. X.; Huang, F.; Tian, W.; Lou, S.; Jian, X.; Li, J. Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Defect-enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption property of hierarchical graphite capsules@helical carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 28710–28720.
Jian, X.; Wu, B.; Wei, Y. F.; Dou, S. X.; Wang, X. L.; He, W. D.; Mahmood, N. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/GCs composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6101–6109.
Xiang, J.; Li, J. L.; Zhang, X. H.; Ye, Q.; Xu, J. H.; Shen, X. Q. Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16905–16914.
Liu, P. J.; Yao, Z. J.; Zhou, J. T.; Yang, Z. H., Kong, L. B. Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9738–9749.
Liu, W.; Tan, S. J.; Yang, Z. H.; Ji, G. B. Enhanced low-frequency electromagnetic properties of MOF-derived cobalt through interface design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31610–31622.
Tian, H. Y.; Qiao, J.; Yang, Y. F.; Xu, D. M.; Meng, X. W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, B. D.; Wu, L. L.; Zeng, Z. H. et al. ZIF-67-derived Co/C embedded boron carbonitride nanotubes for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138011.
Xia, L.; Feng, Y. M.; Zhao, B. Intrinsic mechanism and multiphysics analysis of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials: New horizons and breakthrough. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 136–156.
Zhao, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. G. 3D flower-like hollow CuS@PANI microspheres with superb X-band electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 141–151.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G. Z.; Huang, Y.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Hollow engineering to Co@N-Doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102812.
Xu, H. X.; Zhang, G. Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. R.; Wang, H. L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. B. Heteroatoms-doped carbon nanocages with enhanced dipolar and defective polarization toward light-weight microwave absorbers. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8705–8713.
Li, C.; Li, Z. H.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y. L.; Peng, Q.; Deng, C. Y.; Jing, T.; Zhong, W. A generalizable strategy for constructing ultralight three-dimensional hierarchical network heterostructure as high-efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 13–22.
Cao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. B.; Xu, J. Z.; Che, R. C. Dual-surfactant templated hydrothermal synthesis of CoSe2 hierarchical microclews for dielectric microwave absorption. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 504–514.
Lu, M. M.; Cao, M. S.; Chen, Y. H.; Cao, W. Q.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. L.; Zhang, D. Q.; Wang, W. Z.; Yuan, J. Multiscale assembly of grapelike ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: A smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19408–19415.
Wang, X.; Shu, J. C.; He, X. M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. X.; Gao, C.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M. S. Green approach to conductive PEDOT: PSS decorating magnetic-graphene to recover conductivity for highly efficient absorption. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14017–14025.
Liang, L. L.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. P.; Xie, L. J.; Jia, H.; Kong, Q. Q.; Sun, G. H.; Chen, C. M. Constructing Ni12P5/Ni2P heterostructures to boost interfacial polarization for enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 52208–52220.
Yuan, H. R.; Yan, F.; Li, C. Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. Nickel nanoparticle encapsulated in few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene supported by nitrogen-doped graphite sheets as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1399–1407.
Liu, P. B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R. X.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, X. F.; Che, R. C. Hierarchical engineering of double-shelled nanotubes toward hetero-interfaces induced polarization and microscale magnetic interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202588.
Han, Y. X.; He, M. K.; Hu, J. W.; Liu, P. B.; Liu, Z. W.; Ma, Z. L.; Ju, W. B.; Gu, J. W. Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res., in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5111-y.
Song, L. M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Q.; Guan, L.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, H. L.; Putra, B. R.; Zhang, R.; Fan, B. B. Multifunctional SiC@SiO2 nanofiber aerogel with ultrabroadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 152.
Dai, X. Y.; Du, Y. Z.; Yang, J. Y.; Wang, D.; Gu, J. W.; Li, Y. F.; Wang, S.; Xu, B. B.; Kong, J. Recoverable and self-healing electromagnetic wave absorbing nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 27–32.
Qin, G. Y.; Huang, X. X.; Yan, X.; He, Y. F.; Liu, Y. H.; Xia, L.; Zhong, B. Carbonized wood with ordered channels decorated by NiCo2O4 for lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 105–119.
Zhang, Y. L.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. W. New generation electromagnetic materials: Harvesting instead of dissipation solo. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1413–1415.
Xu, H. X.; Zhang, G. Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, M. Q.; Ouyang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. B. Size-dependent oxidation-induced phase engineering for MOFs derivatives via spatial confinement strategy toward enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 102.
Acknowledgments
Thanks for the financial support of the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. U1704253), the Key Scientific Research Project Plan in Universities of Henan Province (No. 23A430037), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Henan Province (No. 212102210474).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Li, D., Zhang, L. et al. Boosted microwave absorption performance of transition metal doped TiN fibers at elevated temperature. Nano Res. 16, 3570–3579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5398-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5398-3