Abstract
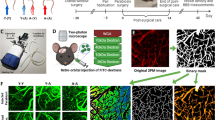
To repair the blood—brain barrier (BBB) after traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a multidisciplinary challenge. No first-line drugs are available. Here, we reported a novel and non-toxic functional negative-charged carbon dots (CDs) generated from green Semen pruni persicae and Carthamus tinctorius L. (TH-CDs) through a hydrothermal synthesis without any organic solvent. The surface of TH-CDs retained part functional groups of active pharmacophores from both drugs. TH-CDs could improve the neurological function, brain edema, neuronal damage, and the BBB permeability by tail vein injection of mice models without systemic toxicity. Furthermore, higher expression of tight junction proteins claudin 5 and ZO-1 was observed after TH-CDs administration, which may be due to the electrostatic interaction between TH-CDs and claudin 5. Our study highlights an inexpensive, green, non-toxic, and intravenous functional TH-CD, which represents a potential TBI treatment strategy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, J. Y.; Gao, G. Y.; Feng, J. F.; Mao, Q.; Chen, L. G.; Yang, X. F.; Liu, J. F.; Wang, Y. H.; Qiu, B. H.; Huang, X. J. Traumatic brain injury in china. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 286–295.
Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R. M. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596.
Martin, M.; Vermeiren, S.; Bostaille, N.; Eubelen, M.; Spitzer, D.; Vermeersch, M.; Profaci, C. P.; Pozuelo, E.; Toussay, X.; Raman-Nair, J. et al. Engineered Wnt ligands enable blood-brain barrier repair in neurological disorders. Science 2022, 375, eabm4459.
Shlosberg, D.; Benifla, M.; Kaufer, D.; Friedman, A. Blood-brain barrier breakdown as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 393–403.
Strbian, D.; Durukan, A.; Pitkonen, M.; Marinkovic, I.; Tatlisumak, E.; Pedrono, E.; Abo-Ramadan, U.; Tatlisumak, T. The blood-brain barrier is continuously open for several weeks following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 175–181.
Zhang, M. L.; Cheng, J. J.; Hu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Kong, H.; Qu, H. H.; Zhao, Y. Green Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex-based carbon dots for ameliorating imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 105.
Lindblad, C.; Pin, E.; Just, D.; Al Nimer, F.; Nilsson, P.; Bellander, B. M.; Svensson, M.; Piehl, F.; Thelin, E. P. Fluid proteomics of CSF and serum reveal important neuroinflammatory proteins in blood-brain barrier disruption and outcome prediction following severe traumatic brain injury: A prospective, observational study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 103.
Neuwelt, E.; Abbott, N. J.; Abrey, L.; Banks, W. A.; Blakley, B.; Davis, T.; Engelhardt, B.; Grammas, P.; Nedergaard, M.; Nutt, J. et al. Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 84–96.
Kingwell, K. New targets for drug delivery across the BBB. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 84–85.
Masserini, M. Nanoparticles for brain drug delivery. ISRN Biochem. 2013, 2013, 238428.
Wen, H. J.; Watry, D. D.; Marcondes, M. C. G.; Fox, H. S. Selective decrease in paracellular conductance of tight junctions: Role of the first extracellular domain of claudin-5. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8408–8417.
Matter, K.; Balda, M. S. Holey barrier: Claudins and the regulation of brain endothelial permeability. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 459–460.
Ohtsuki, S.; Sato, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kamoi, M.; Asashima, T.; Terasaki, T. Exogenous expression of claudin-5 induces barrier properties in cultured rat brain capillary endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 210, 81–86.
Citi, S. Cell biology: Tight junctions as biomolecular condensates. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R83–R86.
Lv, Y. N.; Fu, L. S. The potential mechanism for hydroxysafflor yellow an attenuating blood-brain barrier dysfunction via tight junction signaling pathways excavated by an integrated serial affinity chromatography and shotgun proteomics analysis approach. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 38–48.
Irudayanathan, F. J.; Nangia, S. Paracellular gatekeeping: What does it take for an ion to pass through a tight junction pore? Langmuir 2020, 36, 6757–6764.
Zheng, Q.; Peng, M. Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, S. Y.; Han, R. C.; Ouyang, H.; Fan, Y. B.; Pan, C. F.; Hu, W. G.; Zhai, J. Y. et al. Dynamic real-time imaging of living cell traction force by piezo-phototronic light nano-antenna array. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe7738.
Zhou, J. J.; Chizhik, A. I.; Chu, S.; Jin, D. Y. Single-particle spectroscopy for functional nanomaterials. Nature 2020, 579, 41–50.
Chizhik, A. M.; Stein, S.; Dekaliuk, M. O.; Battle, C.; Li, W. X.; Huss, A.; Platen, M.; Schaap, I. A. T.; Gregor, I.; Demchenko, A. P. et al. Super-resolution optical fluctuation bio-imaging with dual-color carbon nanodots. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 237–242.
Weiss, M.; Fan, J. H.; Claudel, M.; Sonntag, T.; Didier, P.; Ronzani, C.; Lebeau, L.; Pons, F. Density of surface charge is a more predictive factor of the toxicity of cationic carbon nanoparticles than zeta potential. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 5.
Lu, S. S.; Guo, S. S.; Xu, P. X.; Li, X. R.; Zhao, Y. M.; Gu, W.; Xue, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with realtime live-cell imaging and blood-brain barrier penetration capabilities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6325–6336.
Zhang, W.; Sigdel, G.; Mintz, K. J.; Seven, E. S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Leblanc, R. M. Carbon dots: A future blood-brain barrier penetrating nanomedicine and drug nanocarrier. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5003–5016.
Lou, Y.; Hao, X. Y.; Liao, L.; Zhang, K. Y.; Chen, S. P.; Li, Z. Y.; Ou, J.; Qin, A. M.; Li, Z. Recent advances of biomass carbon dots on syntheses, characterization, luminescence mechanism, and sensing applications. Nano Select. 2021, 2, 1117–1145.
Tong, T.; Hu, H. W.; Zhou, J. W.; Deng, S. F.; Zhang, X. T.; Tang, W. T.; Fang, L. R.; Xiao, S. B.; Liang, J. G. Glycyrrhizic-acid-based carbon dots with high antiviral activity by multisite inhibition mechanisms. Small 2020, 16, 1906206.
Luo, W. K.; Zhang, L. L.; Yang, Z. Y.; Guo, X. H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, J. K.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Herbal medicine derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in therapeutics, bioimaging and sensing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 320.
McCrea, M. A.; Giacino, J. T.; Barber, J.; Temkin, N. R.; Nelson, L. D.; Levin, H. S.; Dikmen, S.; Stein, M.; Bodien, Y. G.; Boase, K. et al. Functional outcomes over the first year after moderate to severe traumatic brain injury in the prospective, longitudinal TRACK-TBI study. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 982–992.
Fu, C. Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z. M.; Xia, Z. A.; Liu, Z. Y.; Lu, H. M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, G. Development of a sensitive and rapid UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of nine compounds in rat plasma and application in a comparative pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction and nimodipine. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4872.
Zhong, Y. Y.; Luo, J. K.; Tang, T.; Li, P. F.; Liu, T.; Cui, H. J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. B. Exploring pharmacological mechanisms of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in the treatment of traumatic brain injury via a network pharmacology approach. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8916938.
Zhao, S. Y.; Chen, X. R.; Zhang, C. X.; Zhao, P. T.; Ragauskas, A. J.; Song, X. P. Fluorescence enhancement of lignin-based carbon quantum dots by concentration-dependent and electron-donating substituent synergy and their cell imaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 61565–61577.
Wang, Z. L.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, M. X.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y. Q.; Xu, X.; Yong, Q.; Wang, S. F. An easily available camphor-derived ratiometric fluorescent probe with AIE feature for sequential Ga3+ and ATP sensing in a near-perfect aqueous media and its bio-imaging in living cells and mice. Sens. Actuators B:Chem. 2020, 320, 128249.
Wang, Y.; Fan, X. G.; Tang, T.; Fan, R.; Zhang, C. H.; Huang, Z. B.; Peng, W. J.; Gan, P. P.; Xiong, X. G.; Huang, W. et al. Rhein and rhubarb similarly protect the blood-brain barrier after experimental traumatic brain injury via gp91phox subunit of nadph oxidase/ROS/ERK/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37098.
Li, T.; Hu, E.; Li, P. F.; Yang, Z. Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, R. Q.; Zhu, X. F.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Metabolomics deciphers potential targets of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction against traumatic brain injury in rat. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 559618.
Li, W.; Wang, S. C.; Li, Y.; Ma, C. H.; Huang, Z. H.; Wang, C. S.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. J.; Liu, S. X. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescent nanocrystalline cellulose/carbon dot hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 7–17.
Ding, X. G.; Peng, F.; Zhou, J.; Gong, W. B.; Slaven, G.; Loh, K. P.; Lim, C. T.; Leong, D. T. Defect engineered bioactive transition metals dichalcogenides quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 41.
Wang, Y. H.; Xie, Z. M.; Wang, X. H.; Peng, X.; Zheng, J. P. Fluorescent carbon-dots enhance light harvesting and photosynthesis by overexpressing PsbP and PsiK genes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 260.
Jiang, Q. J.; Liu, L.; Li, Q. Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, D.; Du, Q. S.; Yang, X. B.; Huang, D. P.; Pei, R. J.; Chen, X. et al. NIR-laser-triggered gadolinium-doped carbon dots for magnetic resonance imaging, drug delivery and combined photothermal chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 64.
Liu, Y. S.; Zhao, Y. N.; Zhang, Y. Y. One-step green synthesized fluorescent carbon nanodots from bamboo leaves for copper(II) ion detection. Sens. Actuators B:Chem. 2014, 196, 647–652.
He, M. Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Kong, Y. R.; Xiao, Y. M.; Xu, W. Material and optical properties of fluorescent carbon quantum dots fabricated from lemon juice via hydrothermal reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 175.
Tang, W.; Fan, W. P.; Lau, J.; Deng, L. M.; Shen, Z. Y.; Chen, X. Y. Emerging blood-brain-barrier-crossing nanotechnology for brain cancer theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2967–3014.
Lin, C. J.; Chang, L.; Chu, H. W.; Lin, H. J.; Chang, P. C.; Wang, R. Y. L.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Mao, J. Y.; Chen, S. Y.; Huang, C. C. High amplification of the antiviral activity of curcumin through transformation into carbon quantum dots. Small 2019, 15, 1902641.
Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. N.; Lu, F.; Zhang, M. L.; Kong, H.; Cheng, J. J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, H. H. The neuroprotective effect of pretreatment with carbon dots from Crinis carbonisatus (carbonized human hair) against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 257.
Đorđević, L.; Haines, P.; Cacioppo, M.; Arcudi, F.; Scharl, T.; Cadranel, A.; Guldi, D. M.; Prato, M. Synthesis and excited state processes of arrays containing amine-rich carbon dots and unsymmetrical rylene diimides. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 3640–3648.
Kong, B.; Yang, T.; Cheng, F.; Qian, Y.; Li, C. M.; Zhan, L.; Li, Y. F.; Zou, H. Y.; Huang, C. Z. Carbon dots as nanocatalytic medicine for anti-inflammation therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 545–553.
Zhang, X. Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Y.; Liu, X. Y.; Jiang, F. L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots with bright fluorescence for intracellular detection of iron ion and thiol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 255–264.
Gao, L. F.; Wang, L. D.; Kuklin, A. V.; Gao, J.; Yin, S. C.; Ågren, H.; Zhang, H. A facile approach for elemental-doped carbon quantum dots and their application for efficient photodetectors. Small 2021, 17, 2105683.
Liu, J. J.; Geng, Y. J.; Li, D. W.; Yao, H.; Huo, Z. P.; Li, Y. F.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, S. J.; Wei, H. T.; Xu, W. Q. et al. Deep red emissive carbonized polymer dots with unprecedented narrow full width at half maximum. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906641.
Qiu, T. Y.; Yang, L.; Xiang, Y. E.; Ye, Y.; Zou, G. Q.; Hou, H. S.; Ji, X. B. Heterogeneous interface design for enhanced sodium storage: Sb quantum dots confined by functional carbon. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100188.
Li, S. H.; Su, W.; Wu, H.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, C.; Liu, J.; Deng, G.; Gao, X. C.; Chen, Z. M.; Bao, Y. M. et al. Targeted tumour theranostics in mice via carbon quantum dots structurally mimicking large amino acids. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 704–716.
Dong, C.; Xu, M. S.; Wang, S. N.; Ma, M. H.; Akakuru, O. U.; Ding, H. Z.; Wu, A. G.; Zha, Z. B.; Wang, X. M.; Bi, H. Fluorescent carbon dots with excellent moisture retention capability for moisturizing lipstick. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 299.
Vallan, L.; Urriolabeitia, E. P.; Ruipérez, F.; Matxain, J. M.; Canton-Vitoria, R.; Tagmatarchis, N.; Benito, A. M.; Maser, W. K. Supramolecular-enhanced charge transfer within entangled polyamide chains as the origin of the universal blue fluorescence of polymer carbon dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12862–12869.
Liu, H. J.; Lv, X. T.; Qian, J. C.; Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, X. Y.; Meng, X. F.; Lin, W. C.; Wang, H. Graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots embedded in carbon nanosheets for near-infrared imaging-guided combined photo-chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13304–13315.
Zhao, W. B.; Wang, R. T.; Liu, K. K.; Du, M. R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Q.; Zhou, R.; Liang, Y. C.; Ma, R. N.; Sui, L. Z. et al. Near-infrared carbon nanodots for effective identification and inactivation of Gram-positive bacteria. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1699–1708.
Liu, J. J.; Li, D. W.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M. X.; Sun, H. C.; Yang, B. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small 2018, 11, 1703919.
Wu, H. J.; Zheng, J. W.; Xu, S. B.; Fang, Y. J.; Wu, Y. X.; Zeng, J. X.; Shao, A. W.; Shi, L. G.; Lu, J. N.; Mei, S. H. et al. Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 2.
Sawant-Pokam, P. A.; Vail, T. J.; Metcalf, C. S.; Maguire, J. L.; McKean, T. O.; McKean, N. O.; Brennan, K. C. Preventing neuronal edema increases network excitability after traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 6005–6020.
Zou, Z. M.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, K.; Liu, C. Y.; Cai, D. Z.; Maegele, M.; Gu, Z. T.; Huang, Q. B. The role of S100B/RAGE-enhanced ADAM17 activation in endothelial glycocalyx shedding after traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 46.
Liu, Z. H.; Chen, N. Y.; Tu, P. H.; Wu, C. T.; Chiu, S. C.; Huang, Y. C.; Lim, S. N.; Yip, P. K. DHA attenuates cerebral edema following traumatic brain injury via the reduction in blood-brain barrier permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6291.
Li, T.; Lu, X. M.; Zhang, M. R.; Hu, K.; Li, Z. Peptide-based nanomaterials: Self-assembly, properties and applications. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 11, 268–282.
Umeda, K.; Ikenouchi, J.; Katahira-Tayama, S.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Nakayama, M.; Matsui, T.; Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 2006, 126, 741–754.
Nitta, T.; Hata, M.; Gotoh, S.; Seo, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 653–660.
Hawkins, B. T.; Davis, T. P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185.
Willis, E. F.; MacDonald, K. P. A.; Nguyen, Q. H.; Garrido, A. L.; Gillespie, E. R.; Harley, S. B. R.; Bartlett, P. F.; Schroder, W. A.; Yates, A. G.; Anthony, D. C. et al. Repopulating microglia promote brain repair in an IL-6-dependent manner. Cell 2020, 180, 833–846.E16.
Liu, L.; Duan, J. A.; Tang, Y. P.; Guo, J. M.; Yang, N. Y.; Ma, H. Y.; Shi, X. Q. Taoren-Honghua herb pair and its main components promoting blood circulation through influencing on hemorheology, plasma coagulation and platelet aggregation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 381–387.
Logsdon, A. F.; Lucke-Wold, B. P.; Turner, R. C.; Huber, J. D.; Rosen, C. L.; Simpkins, J. W. Role of microvascular disruption in brain damage from traumatic brain injury. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1147–1160.
Liu, C.; Li, X.; Yang, H. G.; Mao, X. H.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Y. Effect of natural β-glucosidase inhibitors in reducing toxicity of amygdalin in persicae semen. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 771–777.
Hansen, S. F.; Lennquist, A. Carbon nanotubes added to the SIN list as a nanomaterial of very high concern. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 3–4.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973665), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2021RC3030), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (No. 2021zzts1028), and the Innovation-Driven Project of Central South University (No. 2020CX047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4616_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Green functional carbon dots derived from herbal medicine ameliorate blood—brain barrier permeability following traumatic brain injury
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, W., Zhang, L., Li, X. et al. Green functional carbon dots derived from herbal medicine ameliorate blood—brain barrier permeability following traumatic brain injury. Nano Res. 15, 9274–9285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4616-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4616-8