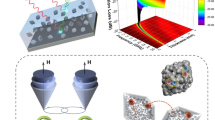
Abstract
Dedicating to the exploration of efficient electromagnetic (EM) absorption and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials is the main strategy to solve the EM radiation issues. The development of multifunction EM attenuation materials that are compatible together EM absorption and EMI shielding properties is deserved our exploration and study. Here, the graphene-wrapped multiloculated NiFe2O4 composites are reported as multifunction EM absorbing and EMI shielding materials. The conductive networks configurated by the overlapping flexible graphene promote the riched polarization genes, as well as electron transmission paths, and thus optimize the dielectric constant of the composites. Meanwhile, the introduction of magnetic NiFe2O4 further establishes the magnetic-dielectric synergy effect. The abundant non-homogeneous interfaces not only generate effective interfacial polarization, also the deliberate multiloculated structure of NiFe2O4 strengthens multi-scattering and multi-reflection sites to expand the transmission path of EM waves. As it turns out, the best impedance matching is matched at a lower filled concentration to achieve the strongest reflection loss value of −48.1 dB. Simultaneously, green EMI shielding based on a predominantly EM absorption and dissipation is achieved by an enlargement of the filled concentration, which is helpful to reduce the secondary EM wave reflection pollution to the environment. In addition, the electrocatalytic properties are further examined. The graphene-wrapped multiloculated NiFe2O4 shows the well electrocatalytic activity as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which is mainly attributed to the interconnected structures formed by graphene and NiFe2O4 connection. The structural advantages of multiloculated NiFe2O4 expose more active sites, which plays an important role in optimizing catalytic reactions. This work provides an excellent jumping-off point for the development of multifunction EM absorbing materials, eco-friendliness EMI shielding materials and electrocatalysts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Y. L.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, M. S. Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: Cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1426–1436.
Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, B. H.; Liao, Q. L.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on the broadband electromagnetic wave absorption properties and mechanism of Co3O4-nanosheets/reduced-graphene-oxide composite. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 980–990.
Liu, L. Y.; Deng, H.; Tang, X. P.; Lu, Y. X.; Zhou, J. Y.; Wang, X. F.; Zhao, Y. Y.; Huang, B.; Shi, Y. G. Specific electromagnetic radiation in the wireless signal range increases wakefulness in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105838118.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Variable-temperature electron transport and dipole polarization turning flexible multifunctional microsensor beyond electrical and optical energy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907156.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807398.
Shu, J. C.; Yang, X. Y.; Zhang, X. R.; Huang, X. Y.; Cao, M. S.; Li, L.; Yang, H. J.; Cao, W. Q. Tailoring MOF-based materials to tune electromagnetic property for great microwave absorbers and devices. Carbon 2020, 162, 157–171.
Wang, X. X.; Cao, W. Q.; Cao, M. S.; Yuan, J. Assembling Nanomicroarchitecture for electromagnetic absorbers and smart devices. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002112.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553.
Han, Y. X.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. Janus (BNNS/ANF)-(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4747–4755.
Song, P.; Liu, B.; Qiu, H.; Shi, X. T.; Cao, D. P.; Gu, J. W. MXenes for polymer matrix electromagnetic interference shielding composites: A review. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100653.
Liu, Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhan, Q. Q.; Dong, Y. H.; Xu, Q. M.; Wu, G. L. Magnetic manganese-based composites with multiple loss mechanisms towards broadband absorption. Nano Res., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4287-5.
Wang, C. X.; Jia, Z. R.; He, S. Q.; Zhou, J. X.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M. L.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, G. L. Metal-organic framework-derived CoSn/NC nanocubes as absorbers for electromagnetic wave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 108, 236–243.
Liu, T. T.; Cao, M. Q.; Fang, Y. S.; Zhu, Y. H.; Cao, M. S. Green building materials lit up by electromagnetic absorption function: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 112, 329–344.
He, N.; He, Z. D.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F. Q.; Wu, W. H.; Tong, G. X. Ni2+ guided phase/structure evolution and ultra-wide bandwidth microwave absorption of CoxNi1−x alloy hollow microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122743.
Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. W.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Guan, J. G.; Tong, G. X. Low-cost carbothermal reduction preparation of monodisperse Fe3O4/C core-shell nanosheets for improved microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16511–16520.
Qiao, M. T.; Lei, X. F.; Ma, Y.; Tian, L. D.; He, X. W.; Su, K. H.; Zhang, Q. Y. Application of yolk-shell Fe3O4@N-doped carbon nanochains as highly effective microwave-absorption material. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1500–1519.
Lusk, M. T.; Carr, L. D. Nanoengineering defect structures on graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 175503.
Ren, Y. L.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Y.; Chen, Y. J.; Gao, P.; Yang, P. P.; Ouyang, Q. Y. Three-dimensional SiO2@Fe3O4 core/shell nanorod array/graphene architecture: Synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12296–12303.
Zhang, M.; Cao, M. S.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Li, L.; Yuan, J. Electromagnetic absorber converting radiation for multifunction. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 145, 100627.
Song, Z. M.; Liu, X. F.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, X. Y.; Tang, W. K.; Yu, R. H.; Shui, J. L. Alginate-templated synthesis of CoFe/carbon fiber composite and the effect of hierarchically porous structure on electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2019, 151, 36–45.
Xu, L. L.; Tao, J. Q.; Zhang, X. F.; Yao, Z. J.; Zavabeti, A.; Zhou, J. T. Co@N-doped double-shell hollow carbon via self-templating-polymerization strategy for microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 188, 34–44.
Thomassin, J. M.; Huynen, I.; Jerome, R.; Detrembleur, C. Functionalized polypropylenes as efficient dispersing agents for carbon nanotubes in a polypropylene matrix; application to electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorber materials. Polymer 2010, 51, 115–121.
Gupta, T. K.; Singh, B. P.; Dhakate, S. R.; Singh, V. N.; Mathur, R. B. Improved nanoindentation and microwave shielding properties of modified MWCNT reinforced polyurethane composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9138–9149.
Hu, H. H.; Zheng, Y.; Ren, K.; Wang, J. Y.; Zhang, Y. H.; Zhang, X. F.; Che, R. C.; Qin, G. W.; Jiang, Y. Position selective dielectric polarization enhancement in CNT based heterostructures for highly efficient microwave absorption. Nanoscale 2012, 13, 2324–2332.
Novoselov, K. S.; Fal’ko, V. I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P. R.; Schwab, M. G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2022, 490, 192–200.
Mayorov, A. S.; Gorbachev, R. V.; Morozov, S. V.; Britnell, L.; Jalil, R.; Ponomarenko, L. A.; Blake, P.; Novoselov, K. S.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T. et al. Micrometer-scale ballistic transport in encapsulated graphene at room temperature. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2396–2399.
Compton, O. C.; Nguyen, S. T. Graphene oxide, highly reduced graphene oxide, and graphene: Versatile building blocks for carbon-based materials. Small 2010, 6, 711–723.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 2018, 14, 1800987.
El-Barbary, A. A.; Telling, R. H.; Ewels, C. P.; Heggie, M. I.; Briddon, P. R. Structure and energetics of the vacancy in graphite. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 144107.
Wen, B.; Cao, M. S.; Lu, M. M.; Cao, W. Q.; Shi, H. L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. X.; Jin, H. B.; Fang, X. Y.; Wang, W. Z. et al. Reduced graphene oxides: Light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3484–3489.
Wen, B.; Cao, M. S.; Hou, Z. L.; Song, W. L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M. M.; Jin, H. B.; Fang, X. Y.; Wang, W. Z.; Yuan, J. Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 2013, 65, 124–139.
Han, M. K.; Yin, X. W.; Kong, L.; Li, M.; Duan, W. Y.; Zhang, L. T.; Cheng, L. F. Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16403–16409.
Xu, X. F.; Shi, S. H.; Tang, Y. L.; Wang, G. Z.; Zhou, M. F.; Zhao, G. Q.; Zhou, X. C.; Lin, S. W.; Meng, F. B. Growth of NiAl-layered double hydroxide on graphene toward excellent anticorrosive microwave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002658.
Liang, J. J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y. F.; Liu, Z. F.; Cai, J. M.; Zhang, C. D.; Gao, H. J.; Chen, Y. S. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922–925.
Zhang, H. B.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W. G.; He, Z. X.; Yu, Z. Z. Tough graphene-polymer microcellular foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 918–924.
Jiang, W. C.; Wu, F.; Jiang, Y. J.; Sun, M. X.; Zhang, K.; Xia, Y. L.; Wang, D. R.; Xie, A. M. Synthesis of hollow Cu1.8S Nano-cubes for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10961–10965.
Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Gao, S. P.; Jing, L.; Li, K. R.; Yang, H. T.; Fu, F. F.; Lee, J. Y.; Guo, Y. X.; Ho, J. S. et al. Reversible crumpling of 2D titanium carbide (MXene) nanocoatings for stretchable electromagnetic shielding and wearable wireless communication. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907451.
Wang, X. X.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J. Cao, M. S. Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 1068–1077.
Cao, M. S.; Song, W. L.; Hou, Z. L.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 2010, 48, 788–796.
Wang, X. X.; Ma, T.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, M. S. Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 321–330.
He, P.; Cao, M. S.; Cai, Y. Z.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Yuan, J. Self-assembling flexible 2D carbide MXene film with tunable integrated electron migration and group relaxation toward energy storage and green EMI shielding. Carbon 2020, 157, 80–89.
Liu, R. T.; Miao, M.; Li, Y. H.; Zhang, J. F.; Cao, S. M.; Feng, X. Ultrathin biomimetic polymeric Ti3C2Tx MXene composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44787–44795.
Wang, Y. C.; Liu, X. Y.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, M. S. Metal-organic frameworks based photocatalysts: Architecture strategies for efficient solar energy conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129459.
Xia, X. H.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Chao, D. L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Y. J.; Li, L.; Ge, X.; Bacho, I. M.; Tu, J. P.; Fan, H. J. Solution synthesis of metal oxides for electrochemical energy storage applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5008–5048.
Chen, Y. J.; Qu, B. H.; Hu, L. L.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. H.; Wang, T. H. High-performance supercapacitor and lithium-ion battery based on 3D hierarchical NH4F-induced nickel cobaltate nanosheet-nanowire cluster arrays as self-supported electrodes. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9812–9820.
Rana, S.; Srivastava, R. S.; Sorensson, M. M.; Misra, R. D. K. Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles with magnetic core and photocatalytic shell: Anatase TiO2-NiFe2O4 system. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 119, 144–151.
Wang, X. F.; Sun, K. M.; Li, S. J.; Song, X. Z.; Cheng, L.; Ma, W. Porous javelin-like NiFe2O4 nanorods as n-propanol sensor with ultrahigh-performance. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12871–12877.
Joshi, S.; Kumar, M.; Chhoker, S.; Srivastava, G.; Jewariya, M.; Singh, V. N. Structural, magnetic, dielectric and optical properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1076, 55–62.
Lv, H. L.; Zhang, H. Q.; Zhao, J.; Ji, G. B.; Du, Y. W. Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1813–1822.
Cao, M. S.; Shu, J. C.; Wang, X. X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Electronic structure and electromagnetic properties for 2D electromagnetic functional materials in gigahertz frequency. Ann. Phys. 2019, 531, 1800390.
Liu, X. Y.; Chen, Z.; Cao, M. S. NiFe layered double hydroxide on nitrogen doped TiO2 nanotube arrays toward efficient oxygen evolution. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 5960–5967.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 52177014, 51977009, 11774027, 51372282 and 51132002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4428_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Graphene-wrapped multiloculated nickel ferrite: A highly efficient electromagnetic attenuation material for microwave absorbing and green shielding
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yao, L., Zheng, Q. et al. Graphene-wrapped multiloculated nickel ferrite: A highly efficient electromagnetic attenuation material for microwave absorbing and green shielding. Nano Res. 15, 6751–6760 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4428-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4428-x