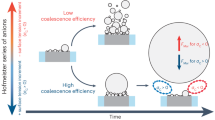
Abstract
Understanding bubbles evolution kinetics on electrodes with varied geometries is of fundamental importance for advanced electrodes design in gas evolution reaction. In this work, the evolution kinetics of electro-generated hydrogen bubbles are recorded in situ on three (i.e. smooth, nanoporous, and nanoarray) Pt electrodes to identify the geometry dependence. The bubble radius shows a time-dependent growth kinetic, which is tightly-connected to the electrode geometry. Among the three electrodes, the smooth one shows a typical time coefficient of 0.5, in consistence with reported values; the nanoporous one shows a time coefficient of 0.47, less than the classic one (0.5); while the nanoarray one exhibits fastest bubble growth kinetics with a time coefficient higher than 0.5 (0.54). Moreover, the nanoarray electrode has the smallest bubble detachment size and the largest growth coefficient (23.3) of all three electrodes. Based on the experimental results, a growth model combined direct bottom- injection with micro-convection is proposed to illustrate the surface geometry dependent coefficients, i.e., the relationship between geometry and bubble evolution kinetics. The direct injection of generated gas molecules from the bottom of bubbles at the three phase boundaries are believed the key to tailor the bubble wetting states and thus determine the bubble evolution kinetics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X. C.; Maeda, K.; Thomas, A.; Takanabe, K.; Xin, G.; Carlsson, J. M.; Domen, K.; Antonietti, M. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 76–80.
Li, L. J.; Liu, S. Y.; Manthiram, A. Co3O4 nanocrystals coupled with O- and N-doped carbon nanoweb as a synergistic catalyst for hybrid Li-air batteries. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 852–860.
Cheng, Y.; Xu, C. W.; Jia, L. C.; Gale, J. D.; Zhang, L. L.; Liu, C.; Shen, P. K.; Jiang, S. P. Pristine carbon nanotubes as non-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction of water splitting. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 163, 96–104.
Rees, N. V.; Compton, R. G. Carbon-free energy: A review of ammonia- and hydrazine-based electrochemical fuelcells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1255–1260.
Meng, Y. Y.; Zou, X. X.; Huang, X. X.; Goswami, A.; Liu, Z. W.; Asefa, T. Polypyrrole-derived nitrogen and oxygen Co-doped mesoporous carbons as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for hydrazine oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6510–6516.
Han, L. L.; Guo, L. M.; Dong, C. Q.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Niu, J. Z.; Peng, Z. Q.; Zhang, Z. H. Ternary mesoporous cobalt-iron-nickel oxide efficiently catalyzing oxygen/hydrogen evolution reactions and overall water splitting. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2281–2287.
Hernández, S.; Barbero, G.; Saracco, G.; Alexe-Ionescu, A. L. Considerations on oxygen bubble formation and evolution on BiVO4 porous anodes used in water splitting photoelectrochemical cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 9916–9925.
Hetsroni, G.; Zakin, J. L.; Lin, Z.; Mosyak, A.; Pancallo, E. A.; Rozenblit, R. The effect of surfactants on bubble growth, wall thermal patterns and heat transfer in pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 44, 485–497.
Ahn, S. H.; Choi, I.; Park, H. Y.; Hwang, S. J.; Yoo, S. J.; Cho, E. A.; Kim, H. J.; Henkensmeier, D.; Nam, S. W.; Kim, S. K.; et al. Effect of morphology of electrodeposited Ni catalysts on the behavior of bubbles generated during the oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water electrolysis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9323–9325.
Scriven, L. E. On the dynamics of phase growth. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1959, 10, 1–13.
Kiuchi, D.; Matsushima, H.; Fukunaka, Y.; Kuribayashi, K. Ohmic resistance measurement of bubble froth layer in water electrolysis under microgravity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, E138–E143.
Hanwright, J.; Zhou, J.; Evans, G. M.; Galvin, K. P. Influence of surfactant on gas bubble stability. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4912–4920.
Jones, S. F.; Evans, G. M.; Galvin, K. P. Bubble nucleation from gas cavities -a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 80, 27–50.
Huang, C.; Guo, Z. G. The wettability of gas bubbles: From macro behavior to nano structures to applications. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19659–19672.
Brandon N. P.; Kelsall, G. H. Growth kinetics of bubbles electrogenerated at microelectrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1985, 15, 475–484.
Burman, J. E. Bubble growth in supersaturated solution. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of London, London, 1974.
Strenge, P. H.; Orell, A.; Westwater, J. W. Microscopic study of bubble growth during nucleate boiling. AIChE J. 1961, 7, 578–583.
Yang, F. C.; Manjare, M.; Zhao, Y. P.; Qiao, R. On the peculiar bubble formation, growth, and collapse behaviors in catalytic micro-motor systems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 6.
Yang, X. G.; Karnbach, F.; Uhlemann, M.; Odenbach, S.; Eckert, K. Dynamics of single hydrogen bubbles at a platinum microelectrode. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8184–8193.
Donose, B. C.; Harnisch, F.; Taran, E. Electrochemically produced hydrogen bubble probes for gas evolution kinetics and force spectroscopy. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 24, 21–24.
Wang, M. Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. C. Water electrolysis enhanced by super gravity field for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 3198–3205.
Koza, J. A.; Mühlenhoff, S.; Żabiński, P.; Nikrityuk, P. A.; Eckert, K.; Uhlemann, M.; Gebert, A.; Weier, T.; Schultz, L.; Odenbach, S. Hydrogen evolution under the influence of a magnetic field. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2665–2675.
Rivas, D. F.; Prosperetti, A.; Zijlstra, A. G.; Lohse, D.; Gardeniers, H. J. G. E. Efficient sonochemistry through microbubbles generated with micromachined surfaces. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9699–9701.
Xu, W. W.; Lu, Z. Y.; Wan, P. B.; Kuang, Y.; Sun, X. M. Highperformance water electrolysis system with double nanostructured superaerophobic electrodes. Small 2016, 12, 2492–2498.
Lu, Z. Y.; Sun, M.; Xu, T. H.; Li, Y. J.; Xu, W. W.; Chang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X. M.; Jiang, L. Superaerophobic electrodes for direct hydrazine fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2361–2366.
Zhang, J.; Sheng, X.; Jin, J.; Feng, X. J.; Jiang, L. High performance metal oxide based sensing device using an electrode with a solid/liquid/air triphase interface. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2998–3004.
Xu, W. W.; Lu, Z. Y.; Sun, X. M.; Jiang, L.; Duan, X. Superwetting electrodes for gas-involving electrocatalysis. Accounts Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1590–1598.
Li, Y. J.; Zhang, H. C.; Xu, T. H.; Lu, Z. Y.; Wu, X. C.; Wan, P. B.; Sun, X. M.; Jiang, L. Under-water superaerophobic pine-shaped Pt nanoarray electrode for ultrahigh-performance hydrogen evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1737–1744.
Yu, X. X.; Yu, Z. Y.; Zhang, X. L.; Zheng, Y. R.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wu, R.; Sun, B.; Gao, M. R.; Wang, G. X. et al. “Superaerophobic” nickel phosphide nanoarray catalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution at ultrahigh current densities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7537–7543.
Liu, M. J.; Wang, S. T.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036.
Yan, Y. Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking natural superhydrophobic surfaces and grasping the wetting process: A review on recent progress in preparing superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 80–105.
Chandra Sekhar, S.; Nagaraju, G.; Ramulu, B.; Hussain, S. K.; Narsimulu, D.; Yu, J. S. Multifunctional core-shell-like nanoarchitectures for hybrid supercapacitors with high capacity and long-term cycling durability. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2597–2608.
Wang, Y. C.; Hu, X. W.; Cao, Z. S.; Guo, L. J. Investigations on bubble growth mechanism during photoelectrochemical and electrochemical conversions. Colloid Surf. A:Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 505, 86–92.
Sakuma, G.; Fukunaka, Y.; Matsushima, H. Nucleation and growth of electrolytic gas bubbles under microgravity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 7638–7645.
Li, Z. G.; Kong, Q.; Ma, X. Y.; Zang, D. Y.; Guan, X. H.; Ren, X. H. Dynamic effects and adhesion of water droplet impact on hydrophobic surfaces: Bouncing or sticking. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8249–8255.
Zhang, X. J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. H.; Ahmed, S. I. U. Controllable and switchable capillary adhesion mechanism for bio-adhesive pads: Effect of micro patterns. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 1648–1654.
Brussieux, C.; Viers, P.; Roustan, H.; Rakib, M. Controlled electrochemical gas bubble release from electrodes entirely and partially covered with hydrophobic materials. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7194–7201.
Hu, X. W.; Cao, Z. S.; Wang, Y. H.; Shen, S. H.; Guo, L. J.; Chen, J. W. Single photogenerated bubble at gas-evolving TiO2 nanorodarray electrode. Electrochim. Acta. 2016, 202, 175–185.
Haider, S. I.; Webb, R. L. A transient micro-convection model of nucleate pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 40, 3675–3688.
Lee, R. C.; Nydahl, J. E. Numerical calculation of bubble growth in nucleate boiling from inception through departure. J. Heat Transf. 1989, 111, 474–479.
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Weng-Feng Lin from Loughborough University and Hongjie Dai from Stanford University for the valuable discussion. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), the National Key Research and Development Project (Nos. 2018YFB1502401 and 2018YFA0702002), the Royal Society and the Newton Fund through the Newton Advanced Fellowship award (NAF R1191294), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovation Research Team in the University (No. IRT1205), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the long-term subsidy mechanism from the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Education of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., Xie, T., Zhou, D. et al. Kinetic study of electrochemically produced hydrogen bubbles on Pt electrodes with tailored geometries. Nano Res. 14, 2154–2159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3132-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3132-y