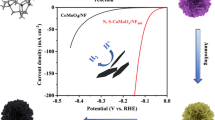
Abstract
Development of earth-abundant electrocatalysts, particularly for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) under benign conditions, is highly desired, but still remains a serious challenge. Herein, we report a high-performance amorphous CoMoS4 nanosheet array on carbon cloth (CoMoS4 NS/CC), prepared by hydrothermal treatment of a Co(OH)F nanosheet array on a carbon cloth (Co(OH)F NS/CC) in (NH4)2MoS4 solution. As a three-dimensional HER electrode, CoMoS4 NS/CC exhibits remarkable activity in 1.0 M phosphate buffer saline (pH 7), only requiring an overpotential of 183 mV to drive a geometrical current density of 10 mA·cm–2. This overpotential is 140 mV lower than that for Co(OH)F NS/CC. Notably, this electrode also shows outstanding electrochemical durability and nearly 100% Faradaic efficiency. Density functional theory calculations suggest that CoMoS4 has a more favorable hydrogen adsorption free energy than Co(OH)F.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, C.; Cheng, N. Y.; Pu, Z. H.; Xing, W.; Sun, X. P. NiSe nanowire film supported on nickel foam: An efficient and stable 3D bifunctional electrode for full water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9351–9355.
Lewis, N. S.; Nocera, D. G. Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15729–15735.
Walter, M. G.; Warren, E. L.; McKone, J. R.; Boettcher, S. W.; Mi, Q.; Santori, E. A.; Lewis, N. S. Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473.
Wang, J. H.; Cui, W.; Liu, Q.; Xing, Z. C.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Recent progress in cobalt-based heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 215–230.
Zou, X. X.; Zhang, Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5148–5180.
Le Goff, A.; Artero, V.; Jousselme, B.; Tran, P. D.; Guillet, N.; Métayé, R.; Fihri, A.; Palacin, S.; Fontecave, M. From hydrogenases to noble metal-free catalytic nanomaterials for H2 production and uptake. Science 2009, 326, 1384–1387.
Yang, N.; Tang, C.; Wang, K. Y.; Du, G.; Asiri, AM.; Sun, X. P. Iron-doped nickel disulfide nanoarray: A highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for water splitting. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3346–3354.
Pu, Z. H.; Luo, Y. L.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Efficient electrochemical water splitting catalyzed by electrodeposited nickel diselenide nanoparticles based film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4718–4723.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: An efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0−14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7587–7590.
Tang, C.; Gan, L. F.; Zhang, R.; Lu, W. B.; Jiang, X. E.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Ternary FexCo1−xP nanowire array as a robust hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst with Pt-like activity: Experimental and theoretical insight. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6617–6621.
Losse, S.; Vos, J. G.; Rau, S. Catalytic hydrogen production at cobalt centres. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 2492–2504.
Liu, T. T.; Ma, X.; Liu, D. N.; Hao, S.; Du, G.; Ma, Y. J.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P.; Chen, L. Mn doping of CoP nanosheets array: An efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction with enhanced activity at all pH values. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 98–102.
Li, K. D.; Zhang, J. F.; Wu, R.; Yu, Y. F.; Zhang, B. Anchoring CoO domains on CoSe2 nanobelts as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting in neutral media. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500426.
Sun, Y. J.; Liu, C.; Grauer, D. C.; Yano, J.; Long, J. R.; Yang, P. D.; Chang, C. J. Electrodeposited cobalt-sulfide catalyst for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17699–17702.
Merki, D.; Fierro, S.; Vrubel, H.; Hu, X. Amorphous molybdenum sulfide films as catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen production in water. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1262–1267.
Morales-Guio, C. G.; Hu, X. Amorphous molybdenum sulfides as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2671−2681.
Merki, D.; Vrubel, H.; Rovelli, L.; Fierro, S.; Hu, X. Fe, Co, and Ni ions promote the catalytic activity of amorphous molybdenum sulfide films for hydrogen evolution. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2515–2525.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, N. Y.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported Cu3P nanowire arrays as an integrated high-performance three-dimensional cathode for generating hydrogen from water. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9577–9581.
Jiang, P.; Liu, Q.; Liang, Y. H.; Tian, J. Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. A cost-Effective 3D hydrogen evolution cathode with high catalytic activity: FeP nanowire array as the active phase. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12855–12859.
Xie, L. S.; Zhang, R.; Cui, L.; Liu, D. N.; Hao, S.; Ma, Y. J.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. High-performance electrolytic oxygen evolution in neutral media catalyzed by a cobalt phosphate nanoarray. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1064–1068.
Ren, X.; Ge, R. X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D. N.; Wu, D.; Sun, X.; Du B.; Wei, Q. Cobalt–borate nanowire array as a highperformance catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in nearneutral media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7291–7294.
Ji, X. Q.; Cui, L.; Liu, D. N.; Hao, S.; Liu, J. Q.; Qu, F. L.; Ma, Y. J.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. A nickel-borate nanoarray: A highly active 3D oxygen-evolving catalyst electrode operating in near-neutral water. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3070–3073.
Ma, M.; Qu, F. L.; Ji, X. Q.; Liu, D. N.; Hao, S.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Yao, Y. D.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. P. Bimetallic nickel-substituted cobalt-borate nanowire array: An earthabundant water oxidation electrocatalyst with superior activity and durability at near neutral pH. Small 2017, 13, 1700394.
Ge, R. X.; Ren, X.; Qu, F. L.; Liu, D. N.; Ma, M.; Hao, S.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. P. Three-dimensional nickel-borate nanosheets array for efficient oxygen evolution at near-neutral pH. Chem.—Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6959–6963.
Zhu, G. L.; Ge, R. X.; Qu, F. L.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Yao, Y. D.; Sun, X. P. In situ surface derivation of an Fe–Co–Bi layer on an Fe-doped Co3O4 nanoarray for eficient water oxidation electrocatalysis under near-neutral conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6388–6392.
Zhang, R.; Tang, C.; Kong, R. M.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. P. Al-doped CoP nanoarray: A durable water-splitting electrocatalyst with superhigh activity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4793–4800.
Sun, X.; Guo, Y. Q.; Wu, C. Z.; Xie, Y. The hydric effect in inorganic nanomaterials for nanoelectronics and energy applications. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3850–3867.
Bi, W. T.; Hu, Z. P.; Li, X. G.; Wu, C. Z.; Wu, J. C.; Wu, Y. B.; Xie, Y. Metallic mesocrystal nanosheets of vanadium nitride for high-performance all-solid-state pseudocapacitors. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 193–200.
Xu, R.; Wu, R.; Shi, Y. M.; Zhang, J. F.; Zhang, B. Ni3Se2 nanoforest/Ni foam as a hydrophilic, metallic, and selfsupported bifunctional electrocatalyst for both H2 and O2 generations. Nano Energy 2016, 24, 103–110.
Shi, Y. M.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1529–1541.
Wu, R.; Zhang, J. F.; Shi, Y. M.; Liu, D. L.; Zhang, B. Metallic WO2−carbon mesoporous nanowires as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6983−6986.
Xia, X. H.; Zhu, C. R.; Luo, J. S.; Zeng, Z. Y.; Guan, C.; Ng, C. F.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H. J. Synthesis of free-standing metal sulfide nanoarrays via anion exchange reaction and their electrochemical energy storage application. Small 2014, 10, 766–773.
Wang, H.; Zhuo, S. F.; Liang, Y.; Han, X. L.; Zhang, B. General self-template synthesis of transition-metal oxide and chalcogenide mesoporous nanotubes with enhanced electrochemical performances. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9055–9059.
Zhu, L. P.; Wen, Z.; Mei, W. M.; Li, Y. G.; Ye, Z. Z. Porous CoO nanostructure arrays converted from rhombic Co(OH)F and needle-like Co(CO3)0.5(OH)·0.11H2O and their electrochemical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 20465−20473.
Jiang, J.; Liu, J. P.; Huang, X. T.; Li, Y. Y.; Ding, R.M.; Ji, X. X.; Hu, Y. Y.; Chi, Q. B.; Zhu, Z. H. General synthesis of large-scale arrays of one-dimensional nanostructured Co3O4 directly on heterogeneous substrates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 70−75.
Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a planewave basis set. Comp. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50.
Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186.
Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal–amorphous-semiconductor transition in germaniu. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 14251–14269.
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996)]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1396.
Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775.
Blochl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979.
Monkhorst, H. J.; Pack, J. D. Special points for Brillouinzone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192.
Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799.
Nøskov, J. K.; Bligaard, T.; Logadottir, A.; Kitchin, J. R.; Chen, J. G.; Pandelov, S.; Stimming, U. Trends in the exchange current for hydrogen evolutio. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, J23–J26.
Sivanantham, A.; Ganesan, P.; Shanmugam, S. Hierarchical NiCo2S4 nanowire arrays supported on Ni foam: An efficient and durable bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4661−4672.
Gu, D.; Jia, C.-J.; Weidenthaler, C.; Bongard, H.-J.; Spliethoff, B.; Schmidt, W.; Schüth, F. Highly ordered mesoporous cobalt-containing oxides: Structure, catalytic properties, and active sites in oxidation of carbon monoxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11407−11418.
Martin-Aranda, R. M.; Portela, M. F.; Madeira, L. M.; Freire, F.; Oliveira, M. Effect of alkali metal promoters on nickel molybdate catalysts and its relevance to the selective oxidation of butane. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1995, 127, 201–217.
Ozkar, S.; Ozin, G. A.; Prokopowicz, R. A. Photooxidation of hexacarbonylmolybdenum(0) in sodium zeolite Y to yield redox-interconvertible molybdenum(VI) oxide and molybdenum(IV) oxide monomers. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 1380–1388.
Voiry, D.; Salehi, M.; Silva, R.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M. W.; Asefa, T.; Shenoy, V. B.; Eda, G.; Chhowalla, M. Conducting MoS2 nanosheets as catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 6222–6227.
Xing, Z. C.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Closely interconnected network of molybdenum phosphide nanoparticles: A highly efficient electrocatalyst for generating hydrogen from water. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5702–5707.
Zou, X. X.; Huang, X. X.; Goswami, A.; Silva, R.; Sathe, B. R.; Mikmeková, E.; Asefa, T. Cobalt-embedded nitrogen-rich carbon nanotubes efficiently catalyze hydrogen evolution reaction at all pH values. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4372–4376.
Gu, H. H.; Huang, Y. P.; Zuo, L. Z.; Fan, W.; Liu, T. X. Electrospun carbon nanofiber@CoS2 core/sheath hybrid as an efficient all-pH hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 1280–1288.
Tran, P. D.; Chiam, S. Y.; Boix, P. P.; Ren, Y.; Pramana, S. S.; Fize, J.; Artero V.; Barber, J. Novel cobalt/nickel-tungstensulfide catalysts for electrocatalytic hydrogen generation from water. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2452–2459.
Shin, S.; Jin, Z. Y.; Kwon, D. H.; Bose, R.; Min, Y.-S. High turnover frequency of hydrogen evolution reaction on amorphous MoS2 thin film directly grown by atomic layer deposition. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1196–1201.
Xu, Y. F.; Gao, M. R.; Zheng, Y. R.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S. H. Nickel/nickel(II) oxide nanoparticles anchored onto cobalt(IV) diselenide nanobelts for the electrochemical production of hydrogen. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8546–8550.
Lu, X. Y.; Zhao, C. Electrodeposition of hierarchically structured three-dimensional nickel–iron electrodes for efficient oxygen evolution at high current densities. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6616.
Wang, J. M.; Ma, X.; Qu, F. L.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Fe-doped Ni2P nanosheet array for high-efficiency electrochemical water oxidation. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1041–1044.
Jiang, J.; Gao, M. R.; Sheng, W. C.; Yan, Y. S. Hollow chevrel-phase NiMo3S4 for hydrogen evolution in alkaline electrolytes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15240–15245.
Yan, X. D.; Tian, L. H.; He, M.; Chen, X. B. Threedimensional crystalline/amorphous Co/Co3O4 core/shell nanosheets as efficient electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6015–6021.
Chen, W.; Wang, H. T.; Li, Y. Z.; Liu, Y. Y.; Sun, J.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, J.-S.; Cui, Y. In situ electrochemical oxidation tuning of transition metal disulfides to oxides for enhanced water oxidation. ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 244–251.
Karunadasa, H. I.; Chang, C. J.; Long, J. R. A molecular molybdenum-oxo catalyst for generating hydrogen from water. Nature 2010, 464, 1329–1333.
Ren, X.; Wang, W. Y.; Ge, R. X.; Hao, S.; Qu, F. L.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Wei, Q.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. P. An amorphous FeMoS4 nanorod array toward efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis under neutral conditions. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9000–9003.
Li, H. M.; Qian, X.; Zhu, C. L.; Jiang, X. C.; Shao, L.; Hou, L. X. Template synthesis of CoSe2/Co3Se4 nanotubes: Tuning of their crystal structures for photovoltaics and hydrogen evolution in alkaline medium. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4513–4526.
Wang, W. Y.; Yang, L.; Qu, F. L.; Liu, Z. A.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M.; Yao, Y. D.; Chen L.; Sun X. P. A self-supported NiMoS4 nanoarray as an efficient 3D cathode for the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16585–16589.
Shao, L.; Qian, X.; Wang, X. Y.; Li, H. M.; Yan, R. C.; Hou, L. X. Low-cost and highly efficient CoMoS4/NiMoS4-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reactions over a wide pH range. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 236–243.
Yu, L.; Xia, B. Y.; Wang, X.; Lou, X. W. General formation of M–MoS3 (M = Co, Ni) hollow structures with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 92–97.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of China (No. 21627809), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21375047, 21377046, 21405059, 21575137, 21575050, and 21601064), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. ZR2016JL013 and ZR2016BQ10), Graduate Innovation Foundation of University of Jinan (No. YCXB15004), and the Special Foundation for Taishan Scholar Professorship of Shandong Province (No. ts20130937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Wu, D., Ge, R. et al. Self-supported CoMoS4 nanosheet array as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction at neutral pH. Nano Res. 11, 2024–2033 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1818-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1818-6