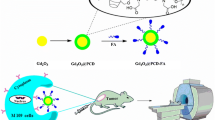
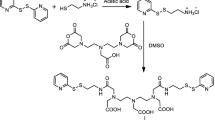
Abstract
The development of more sensitive diagnostic tools allowing an early-stage and highly efficient medical imaging of tumors remains a challenge. Magnetic nanoparticles seem to be the contrast agents with the highest potential, if properly constructed. Therefore, in this study, hybrid magnetic nanoarchitectures were developed using a new amphiphilic inulin-based graft copolymer (INU-LAPEG-FA) as coating material for 10-nm spinel iron oxide (magnetite, Fe3O4) superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPION). Folic acid (FA) covalently linked to the coating copolymer in order to be exposed onto the nanoparticle surface was chosen as the targeting agent because folate receptors are upregulated in many cancer types. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro biocompatibility study was then performed on the prepared magnetic nanoparticles. The improved targeting and imaging properties of the prepared FA-SPIONs were further evaluated in nude mice using 7-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). FA-SPIONs exhibited the ability to act as efficient contrast agents in conventional MRI, providing a potential nanoplatform not only for tumor diagnosis but also for cancer treatment, through the delivery of anticancer drug or locoregional magnetic hyperthermia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakhtiary, Z.; Saei, A. A.; Hajipour, M. J.; Raoufi, M.; Vermesh, O.; Mahmoudi, M. Targeted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for early detection of cancer: Possibilities and challenges. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 287–307.
Liu, X. L.; Ng, C. T.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Yang, H. T.; Zhao, L. Y.; Peng, E.; Lv, Y. B.; Xiao, W.; Fang, J.; Yi, J. B. et al. Synthesis of ferromagnetic Fe0.6Mn0.4O nanoflowers as a new class of magnetic theranostic platform for in vivo T 1–T 2 dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2092–2104.
Lee, N.; Yoo, D.; Ling, D. S.; Cho, M. H.; Hyeon, T.; Cheon, J. Iron oxide based nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and magnetoresponsive therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10637–10689.
Sharifi, S.; Seyednejad, H.; Laurent, S.; Atyabi, F.; Saei, A. A.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Contrast Media Mol. I. 2015, 10, 329–355.
Li, J. C.; He, Y.; Sun, W. J.; Luo, Y.; Cai, H. D.; Pan, Y. Q.; Shen, M. W.; Xia, J. D.; Shi, X. Y. Hyaluronic acid-modified hydrothermally synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted tumor MRimaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3666–3677.
Zhang, Z. X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. H.; Zhang, C. Z.; Wang, Z. L.; Shi, X. Y.; Zhang, G. X. Facile synthesis of folic acid-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted MRimaging in pulmonary tumor xenografts. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 569–578.
Scialabba, C.; Licciardi, M.; Mauro, N.; Rocco, F.; Ceruti, M.; Giammona, G. Inulin-based polymer coated SPIONs as potential drug delivery systems for targeted cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 695–705.
Berry, C. C.; Wells, S.; Charles, S.; Aitchison, G.; Curtis, A. S. G. Cell response to dextran-derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles post internalisation. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5405–5413.
Kohler, N.; Sun, C.; Fichtenholtz, A.; Gunn, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, M. Q. Methotrexate-immobilized poly(ethylene glycol) magnetic nanoparticles for MR imaging and drug delivery. Small 2006, 2, 785–792.
Licciardi, M.; Li Volsi, A.; Sardo, C.; Mauro, N.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Inulin-ethylenediamine coated SPIONs magnetoplexes: A promising tool for improving siRNA delivery. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 3674–3687.
Namgung, R.; Singha, K.; Yu, M. K.; Jon, S.; Kim, Y. S.; Ahn, Y.; Park, I. K.; Kim, W. J. Hybrid superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-branched polyethylenimine magnetoplexes for gene transfection of vascular endothelial cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4204–4213.
Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Fantechi, E.; Giammona, G. Cell uptake enhancement of folate targeted polymer coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 949–964.
Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Fiorica, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Cassata, G.; Giammona, G. Polymeric nanocarriers for magnetic targeted drug delivery: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2013, 10, 4397–4407.
Laurent, S.; Saei, A. A.; Behzadi, S.; Panahifar, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic agents: Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1449–1470.
Wang, Y.-X. J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2011, 1, 35–40.
Mauro, N.; Li Volsi, A.; Scialabba, C.; Licciardi, M.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Photothermal ablation of cancer cells using folate-coated gold/grapheme oxide composite. Curr. Drug Deliv., in press, DOI: 10.2174/ 1567201813666160520113804.
Licciardi, M.; Li Volsi, A.; Mauro, N.; Scialabba, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona G., Preparation and characterization of inulin coated gold nanoparticles for selective delivery of doxorubicin to breast cancer cells. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2078315.
Sardo, C.; Craparo, E. F.; Fiorica, C.; Giammona, G.; Cavallaro, G. Inulin derivatives obtained via enhanced microwave synthesis for nucleic acid based drug delivery. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1650–1659.
Mauro, N.; Campora, S.; Scialabba, C.; Adamo, G.; Licciardi, M.; Ghersi, G.; Gaetano, G. Self-organized environmentsensitive inulin–doxorubicin conjugate with a selective cytotoxic effect towards cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32421–32430.
Mandracchia, D.; Tripodo, G.; Trapani, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Annese, T.; Chlapanidas, T.; Trapani, G.; Ribatti, D. Inulin based micelles loaded with curcumin or celecoxib with effective anti-angiogenic activity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 141–146.
Li, Y. P.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, W.; Deng, W. B.; Lam, K. S. Stimuli-responsive cross-linked micelles for on-demand drug delivery against cancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 58–73.
Wu, L. L.; Zou, Y.; Deng, C.; Cheng, R.; Meng, F. H.; Zhong, Z. Y. Intracellular release of doxorubicin from corecrosslinked polypeptide micelles triggered by both pH and reduction conditions. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5262–5272.
Riemer, J.; Hoepken, H. H.; Czerwinska, H.; Robinson, S. R.; Dringen, R. Colorimetric ferrozine-based assay for the quantitation of iron in cultured cells. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 331, 370–375.
Asadov, Y. G.; Alyev, Y. I.; Jafarov, K. M. X-ray diffraction study of compounds in the Ag2S-Cu2S system. Inorg. Mater. 2008, 44, 460–466.
Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Sardo, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Amphiphilic inulin graft co-polymers as self-assembling micelles for doxorubicin delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4262–4271.
Li Volsi, A.; Jimenez De Aberasturi, D.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Giammona, G.; Licciardi, M.; Liz-Marzán, L. M. Inulin coated plasmonic gold nanoparticles as a tumor-selective tool for cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1150–1155.
Suk, J. S.; Xu, Q. G.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L. M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51.
Cavallaro, G.; Licciardi, M.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G. Folate-mediated targeting of polymers as components of colloidal drug delivery systems. In Handbook of Drug Targeting and Monitoring; Andreev, B., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: NY,2010.
Zwicke, G. L.; Mansoori, G. A.; Jeffery, C. J. Utilizing the folate receptor for active targeting of cancer nanotherapeutics. Nano Rev. 2012, 3, 18496–18507.
Hilgenbrink, A. R.; Low, P. S. Folate receptor-mediated drug targeting: From therapeutics to diagnostics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2135–2146.
Lamberti, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Sardo, C.; Scialabba, C.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G. Smart inulin-based polycationic nanodevices for siRNA delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 224–230.
Palumbo, F. S.; Fiorica, C.; Di Stefano, M.; Pitarresi, G.; Gulino, A.; Agnello, S.; Gaetano, G. In situ forming hydrogels of hyaluronic acid and inulin derivatives for cartilage regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 408–416.
Mandracchia, D.; Tripodo, G.; Latrofa, A.; Dorati, R. Amphiphilic inulin-D-a-tocopherol succinate (INVITE) bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 46–54.
Mandracchia, D.; Denora, N.; Franco, M.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G.; Trapani, G. New biodegradable hydrogels based on inulin and α,β-polyaspartylhydrazide designed for colonic drug delivery: In vitro release of glutathione and oxytocin. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2011, 22, 313–328.
Yoon, H. Y.; Saravanakumar, G.; Heo, R.; Choi, S. H.; Song, I. C.; Han, M. H.; Kim, K.; Park, J. H.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I. C. et al. Hydrotropic magnetic micelles for combined magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 692–698.
Muscas, G.; Concas, G.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Orrù, F.; Fiorani, D.; Laureti, S.; Rinaldi, D.; Piccaluga, G. et al. Magnetic properties of small magnetite nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 23378–23384.
Belviso, C.; Agostinelli, E.; Belviso, S.; Cavalcante, F.; Pascucci, S.; Peddis, D.; Varvaro, G.; Fiore, S. Synthesis of magnetic zeolite at low temperature using a waste material mixture: Fly ash and red mud. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 202, 208–216.
Peddis, D.; Cannas, C.; Piccaluga, G.; Agostinelli, E.; Fiorani, D. Spin-glass-like freezing and enhanced magnetization in ultra-small CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 125705.
Gittleman, J. I.; Abeles, B.; Bozowski, S. Superparamagnetism and relaxation effects in granular Ni-SiO2 and Ni-Al2O3 films. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 3891–3897.
Peddis, D.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Orrù, F.; Fiorani, D.; Laureti, S.; Rinaldi, D.; Muscas, G.; Concas, G. et al. Beyond the effect of particle size: Influence of CoFe2O4 nanoparticle arrangements on magnetic properties. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2005–2013.
Peddis, D.; Rinaldi, D.; Ennas, G.; Scano, A.; Agostinelli, E.; Fiorani, D. Superparamagnetic blocking and superspin-glass freezing in ultra small δ-(Fe0.67Mn0.33)OOH particles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 3162–3169
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale della Sicilia “A. Mirri”, Palermo, Italy for the use of MRI scanner. The authors also thank the MIUR and the University of Palermo for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scialabba, C., Puleio, R., Peddis, D. et al. Folate targeted coated SPIONs as efficient tool for MRI. Nano Res. 10, 3212–3227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1540-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1540-4