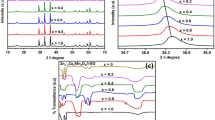
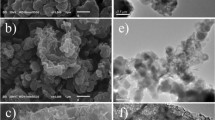
Abstract
The strategy of combining highly conductive frameworks with abundant active sites is desirable in the preparation of alternative catalysts to commercial Pt/C for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). In this study, N-doped graphene (NG) and carbon nanotubes (CNT) were grown in-situ on Co-containing carbon nanofibers (CNF) to form three-dimensional (3D) interconnected networks. The NG and CNT bound the interlaced CNF together, facilitating electron transfer and providing additional active sites. The 3D interconnected fiber networks exhibited excellent ORR catalytic behavior with an onset potential of 0.924 V (vs. reversible hydrogen electrode) and a higher current density than Pt/C beyond 0.720 V. In addition, the hybrid system exhibited superior stability and methanol tolerance to Pt/C in alkaline media. This method can be extended to the design of other 3D interconnected network architectures for energy storage and conversion applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, L.; Hu, L. P.; Li, J.; Wei, Z. D. Enhanced stability of Pt nanoparticle electrocatalysts for fuel cells. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 418–440.
Gong, K. P.; Du, F.; Xia, Z. H.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L. M. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Science 2009, 323, 760–764.
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303.
Wu, G.; More, K. L.; Johnston, C. M.; Zelenay, P. Highperformance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt. Science 2011, 332, 443–447.
Trogadas, P.; Fuller, T. F.; Strasser, P. Carbon as catalyst and support for electrochemical energy conversion. Carbon 2014, 75, 5–42.
Paraknowitsch, J. P.; Thomas, A. Doping carbons beyond nitrogen: An overview of advanced heteroatom doped carbons with boron, sulphur and phosphorus for energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2839–2855.
Lin, Z. Y.; Waller, G. H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. L.; Wong, C. P. Simple preparation of nanoporous few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene for use as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. Carbon 2013, 53, 130–136.
Yang, S. B.; Zhi, L. J.; Tang, K.; Feng, X. L.; Maier, J.; Mü llen, K. Efficient synthesis of heteroatom (N or S)-doped graphene based on ultrathin graphene oxide-porous silica sheets for oxygen reduction reactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3634–3640.
Wang, S. Y.; Zhang, L. P.; Xia, Z. H.; Roy, A.; Chang, D. W.; Baek, J. B.; Dai, L. M. BCN graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4209–4212.
Dou, S.; Shen, A. L.; Tao, L.; Wang, S. Y. Molecular doping of graphene as metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10672–10675.
Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, X. D.; Su, Y. Z.; Zhang, F.; Feng, X. L. Polyaniline nanosheet derived B/N co-doped carbon nanosheets as efficient metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7742–7746.
Yang, S. B.; Feng, X. L.; Wang, X. C.; Mü llen, K. Graphenebased carbon nitride nanosheets as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5339–5343.
Zhao, A. Q.; Masa, J.; Schuhmann, W.; Xia, W. Activation and stabilization of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as electrocatalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction at strongly alkaline conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24283–24291.
Wang, S. Y.; Iyyamperumal, E.; Roy, A.; Xue, Y. H.; Yu, D. S.; Dai, L. M. Vertically aligned BCN nanotubes as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: A synergetic effect by co-doping with boron and nitrogen. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11756–11760.
Liu, D.; Zhang, X. P.; Sun, Z. C.; You, T. Y. Free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber films as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9528–9531.
Kumar, P. S.; Sundaramurthy, J.; Subramanian, S.; Babu, V. J.; Singh, G.; Allakhverdiev, S. I.; Ramakrishna, S. Hierarchical electrospun nanofibers for energy harvesting, production and environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3192–3222.
Inagaki, M.; Yang, Y.; Kang, F. Y. Carbon nanofibers prepared via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2547–2566.
Guo, L. P.; Bai, J.; Liang, H. O.; Li, C. P.; Sun, W. Y.; Meng, Q. R. Preparation and application of carbon nanofiberssupported palladium nanoparticles catalysts based on electrospinning. J. Inorg. Mater. 2014, 29, 814–820.
Zhang, C. L.; Yu, S. H. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423–4448.
Wang, Y. D.; Han, C.; Zheng, D. C.; Lei, Y. P. Large-scale, flexible and high-temperature resistant ZrO2/SiC ultrafine fibers with a radial gradient composition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9607–9612.
Wang, H. G.; Yuan, S.; Ma, D. L.; Zhang, X. B.; Yan, J. M. Electrospun materials for lithium and sodium rechargeable batteries: From structure evolution to electrochemical performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1660–1681.
Li, X. H.; Antonietti, M. Polycondensation of boron- and nitrogen-codoped holey graphene monoliths from molecules: Carbocatalysts for selective oxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4572–4576.
Wang, X. R.; Li, X. L.; Zhang, L.; Yoon, Y.; Networker, P. K.; Wang, H. L.; Guo, J.; Dai, H. J. N-doping of graphene through electrothermal reactions with ammonia. Science 2009, 324, 768–771.
Dallmeyer, I.; Lin, L. T.; Li, Y. J.; Ko, F.; Kadla, J. F. Preparation and characterization of interconnected, kraft lignin-based carbon fibrous materials by electrospinning. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 540–551.
Cheng, Y. L.; Huang, L.; Xiao, X.; Yao, B.; Yuan, L. Y.; Li, T. Q.; Hu, Z. M.; Wang, B.; Wan, J.; Zhou, J. Flexible and cross-linked N-doped carbon nanofiber network for high performance freestanding supercapacitor electrode. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 66–74.
Ye, T. N.; Lv, L. B.; Li, X. H.; Xu, M.; Chen, J. S. Strongly veined carbon nanoleaves as a highly efficient metal-free electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6905–6909.
Park, M.; Jung, Y. J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H. I.; Cho, J. Synergistic effect of carbon nanofiber/nanotube composite catalyst on carbon felt electrode for high-performance all-vanadium redox flow battery. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4833–4839.
Liang, Y. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Diao, P.; Chang, W.; Hong, G. S.; Li, Y. G.; Gong, M.; Xie, L. M.; Zhou, J. G.; Wang, J. et al. Oxygen reduction electrocatalyst based on strongly coupled cobalt oxide nanocrystals and carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15849–15857.
Zhang, B.; Huang, J. Q.; Kim, J. K. Ultrafine amorphous SnOx embedded in carbon nanofiber/carbon nanotube composites for Li-ion and Na-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5222–5228.
Lü, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. T.; Li, H. L.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Xie, Z. X.; Kuang, Q.; Zheng, L. S. MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13604–13611.
Wang, B.; Wang, Y. D.; Lei, Y. P.; Wu, N.; Gou, Y. Z.; Han, C.; Fang, D. Hierarchically porous SiC ultrathin fibers mat with enhanced mass transport, amphipathic property and high-temperature erosion resistance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20873–20881.
Liang, Y. Y.; Li, Y. G.; Wang, H. L.; Zhou, J. G.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. J. Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 780–786.
Liu, Z. W.; Peng, F.; Wang, H. J.; Yu, H.; Zheng, W. X.; Yang, J. Phosphorus-doped graphite layers with high electrocatalytic activity for the O2 reduction in an alkaline medium. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3257–3261.
Liang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Sulfur and nitrogen dual-doped mesoporous graphene electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction with synergistically enhanced performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11496–11500.
Han, C.; Wang, Y. D.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, B.; Wu, N.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q. In situ synthesis of graphitic-C3N4 nanosheet hybridized N-doped TiO2 nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic H2 production and degradation. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1199–1209.
Zou, X. X.; Huang, X. X.; Goswami, A.; Silva, R.; Sathe, B. R.; Mikmeková, E.; Asefa, T. Cobalt-embedded nitrogen-rich carbon nanotubes efficiently catalyze hydrogen evolution reaction at all pH values. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4372–4376.
Huang, D. K.; Luo, Y. P.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, B. Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, M. K. Active catalysts based on cobalt oxide@cobalt/ N–C nanocomposites for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline solutions. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1054–1064.
Jagadeesh, R. V.; Junge, H.; Pohl, M. M.; Radnik, J.; Brü ckner, A.; Beller, M. Selective oxidation of alcohols to esters using heterogeneous Co3O4–N@C catalysts under mild conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10776–10782.
Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, G. X.; Lu, Z. Y.; Jin, X. Y.; Chang, Z.; Sun, X. M. One-step scalable preparation of N-doped nanoporous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 293–301.
Yan, M.; Song, W.; Chen, Z. H. In situ growth of a carbon interphase between carbon fibres and a polycarbosilanederived silicon carbide matrix. Carbon 2011, 49, 2869–2872.
Wu, N.; Wang, Y. D.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, B.; Han, C. Flexible N-doped TiO2/C ultrafine fiber mat and its photocatalytic activity under simulated sunlight. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 319, 136–142.
Xie, S.; Wang, Y. D.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, B.; Wu, N.; Guo, Y. Z.; Fang, D. A simply prepared flexible SiBOC ultrafine fiber mat with enhanced high-temperature stability and chemical resistance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 64911–64917.
Choi, C. H.; Park, S. H.; Woo, S. I. Binary and ternary doping of nitrogen, boron, and phosphorus into carbon for enhancing electrochemical oxygen reduction activity. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7084–7091.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Ge, L.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Two-step boron and nitrogen doping in graphene for enhanced synergistic catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3110–3116.
Kang, Y.; Chu, Z. Y.; Zhang, D. J.; Li, G. Y.; Jiang, Z. H.; Cheng, H. F.; Li, X. D. Incorporate boron and nitrogen into graphene to make BCN hybrid nanosheets with enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Carbon 2013, 61, 200–208.
Wood, K. N.; O' Hayre, R.; Pylypenko, S. Recent progress on nitrogen/carbon structures designed for use in energy and sustainability applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1212–1249.
Artyushkova, K.; Kiefer, B.; Halevi, B.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Schlogl, R.; Atanassov, P. Density functional theory calculations of XPS binding energy shift for nitrogencontaining graphene-like structures. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2539–2541.
Lee, J. S.; Park, G. S.; Kim, S. T.; Liu, M. L.; Cho, J. A highly efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction: N-doped ketjenblack incorporated into Fe/Fe3Cfunctionalized melamine foam. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1026–1030.
Saadi, F. H.; Carim, A. I.; Verlage, E.; Hemminger, J. C.; Lewis, N. S.; Soriaga, M. P. CoP as an acid-stable active electrocatalyst for the hydrogen-evolution reaction: Electrochemical synthesis, interfacial characterization and performance evaluation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29294–29300.
Liang, J.; Du, X.; Gibson, C.; Du, X. W.; Qiao, S. Z. N-doped graphene natively grown on hierarchical ordered porous carbon for enhanced oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6226–6231.
Liang, J.; Zhou, R. F.; Chen, X. M.; Tang, Y. H.; Qiao, S. Z. Fe–N decorated hybrids of CNTs grown on hierarchically porous carbon for high-performance oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6074–6079.
Kim, M.; Nam, D. H.; Park, H. Y.; Kwon, C.; Eom, K.; Yoo, S. J.; Jang, J. H.; Kim, H. J.; Cho, E.; Kwon, H. Cobalt–carbon nanofibers as an efficient support-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction with a systematic study of active site formation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14284–14290.
Wu, J. F.; Yuan, X. Z.; Martin, J. J.; Wang, H. J.; Zhang, J. J.; Shen, J.; Wu, S. H.; Merida, W. A review of PEM fuel cell durability: Degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Power. Sources 2008, 184, 104–119.
Liang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Facile oxygen reduction on a three-dimensionally ordered macroporous graphitic C3N4/ carbon composite electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3892–3896.
Qu, L. T.; Liu, Y.; Baek, J. B.; Dai, L. M. Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1321–1326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Q., Wang, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Three-dimensional (3D) interconnected networks fabricated via in-situ growth of N-doped graphene/carbon nanotubes on Co-containing carbon nanofibers for enhanced oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 9, 317–328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0911-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0911-y