Abstract
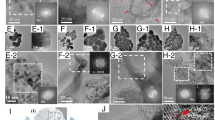
High-symmetry crystals exhibit isotropic properties. Inducing anisotropy, e.g., by facet selective etching, is considered implausible in face-centered cubic (FCC) metals, particularly gold, which, in addition to being an FCC, is noble. We report for the first time the facet selective etching of Au microcrystals obtained in the form of cuboctahedra and pentagonal rods from the thermolysis of a goldorganic precursor. The selective etching of {111} and {100} facets was achieved using a capping method in which tetraoctylammonium cations selectively cap the {111} facets while Br– ions protect the {100} facets. The exposed facets are oxidized by O2/Cl–, yielding a variety of interesting geometries. The facet selective etching of the Au microcrystallites is governed only by the nature of the facets; the geometry of the microcystallite does not appear to play a significant role. The etched surfaces appear rough, but a closer examination reveals well-defined corrugations that are indexable to high hkl values. Such surfaces exhibit enhanced Raman activity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seidel, H.; Csepregi, L.; Heuberger, A.; Baumgärtel, H. Anisotropic etching of crystalline silicon in alkaline solutions: I. Orientation dependence and behavior of passivation layers. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1990, 137 3612–3626.
Leancu, R.; Moldovan, N.; Csepregi, L.; Lang, W. Anisotropic etching of germanium. Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys, 1995, 46 35–37.
Ng, H. M.; Weimann, N. G.; Chowdhury, A. GaN nanotip pyramids formed by anisotropic etching. J. Appl. Phys., 2003, 94 650–653.
Kan, C. X.; Wang, C. S.; Li, H. C.; Qi, J. S.; Zhu, J. J.; Li, Z. S.; Shi, D. N. Gold microplates with well-defined shapes. Small, 2010, 6 1768–1775.
Magnussen, O. M. Ordered anion adlayers on metal electrode surfaces. Chem. Rev., 2002, 102 679–726.
Kilin, D. S.; Prezhdo, O. V.; Xia, Y. N. Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Ab initio study of preferential surface coordination with citric acid. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2008, 458 113–116.
Liu, M. C.; Zheng, Y. Q.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L. J.; Xia, Y. N. Transformation of Pd nanocubes into octahedra with controlled sizes by maneuvering the rates of etching and regrowth. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135 11752–11755.
Meena, S. K.; Sulpizi, M. Understanding the microscopic origin of gold nanoparticle anisotropic growth from molecular dynamics simulations. Langmuir, 2013, 29 14954–14961.
Long, R.; Zhou, S.; Wiley, B. J.; Xiong, Y. J. Oxidative etching for controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: Atomic addition and subtraction. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43 6288–6310.
Kou, X. S.; Ni, W. H.; Tsung, C.-K.; Chan, K.; Lin, H.-Q.; Stucky, G. D.; Wang, J. F. Growth of gold bipyramids with improved yield and their curvature-directed oxidation. Small, 2007, 3 2103–2113.
Rodríguez-Fernandez, J.; Perez-Juste, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzá n, L. M. Spatially-directed oxidation of gold nanoparticles by Au(III)-CTAB complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109 14257–14261.
Zou, R. X.; Guo, X.; Yang, J.; Li, D. D.; Peng, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. J.; Yu, H. Selective etching of gold nanorods by ferric chloride at room temperature. CrystEngComm, 2009, 11 2797–2803.
Chen, Z. P.; Liu, R. L.; Wang, S. S.; Qu, C. L.; Chen, L. X.; Wang, Z. Colorimetric sensing of copper(II) based on catalytic etching of gold nanorods. RSC Adv., 2013, 3 13318–13323.
Wen, T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X. P.; Chu, W. G.; Liu, W. Q.; Ji, Y. L.; Hu, Z. J.; Hou, S.; Hu, X. N.; Wu, X. C. Copper ion assisted reshaping and etching of gold nanorods: Mechanism studies and applications. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117 25769–25777.
Dai, D. G.; Xu, D.; Cheng, X. D.; He, Y. Direct imaging of single gold nanoparticle etching: Sensitive detection of lead ions. Anal. Methods, 2014, 6 4507–4511.
Mulvihill, M. J.; Ling, X. Y.; Henzie, J.; Yang, P. D. Anisotropic etching of silver nanoparticles for plasmonic structures capable of single-particle SERS. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 132 268–274.
Zhang, J. F.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y. D.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y. T.; Shen, B.; Zhong, C.; Hu, W. B. Shape-controlled synthesis of palladium single-crystalline nanoparticles: The effect of hcl oxidative etching and facet-dependent catalytic properties. Chem. Mater., 2014, 26 1213–1218.
Jana, N. R.; Gearheart, L.; Obare, S. O.; Murphy, C. J. Anisotropic chemical reactivity of gold spheroids and nanorods. Langmuir, 2002, 18 922–927.
Shao, J. R.; Josephs, E. A.; Lee, C.; Lopez, A.; Ye, T. Electrochemical etching of gold within nanoshaved selfassembled monolayers. ACS Nano, 2013, 7 5421–5429.
Ye, S.; Ishibashi, C.; Uosaki, K. Anisotropic dissolution of an Au(111) electrode in perchloric acid solution containing chloride anion investigated by in situ STM-The important role of adsorbed chloride anion. Langmuir, 1999, 15 807–812.
Sreeprasad, T. S.; Samal, A. K.; Pradeep, T. Body-or tipcontrolled reactivity of gold nanorods and their conversion to particles through other anisotropic structures. Langmuir, 2007, 23 9463–9471.
Saa, L.; Coronado-Puchau, M.; Pavlov, V.; Liz-Marzan, L. M. Enzymatic etching of gold nanorods by horseradish peroxidase and application to blood glucose detection. Nanoscale, 2014, 6 7405–7409.
Tsung, C. K.; Kou, X. S.; Shi, Q. H.; Zhang, J. P.; Yeung, M. H.; Wang, J. F.; Stucky, G. D. Selective shortening of singlecrystalline gold nanorods by mild oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128 5352–5353.
Fan, N. N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W. F.; Zhang, L. J.; Chen, W.; Zou, C.; Huang, S. M. Selective etching induces selective growth and controlled formation of various platinum nanostructures by modifying seed surface free energy. ACS Nano, 2012, 6 4072–4082.
Radha, B.; Arif, M.; Datta, R.; Kundu, T. K.; Kulkarni, G. U. Movable Au microplates as fluorescence enhancing substrates for live cells. Nano Res., 2010, 3 738–747.
Radha, B.; Kulkarni, G. U. A real time microscopy study of the growth of giant au microplates. Cryst. Growth Des., 2011, 11 320–327.
Zhang, Z.-C.; Nosheen, F.; Zhang, J.-C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.-P.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. Growth of concave polyhedral Pd nanocrystals with 32 facets through in situ facet-selective etching. ChemSusChem, 2013, 6 1893–1897.
Levinstein, H. J.; Robinson, W. H. Etch pits at dislocations in silver single crystals. J. Appl. Phys., 1962, 33 3149–3152.
Radha, B.; Kiruthika, S.; Kulkarni, G. U. Metal anion–alkyl ammonium complexes as direct write precursors to produce nanopatterns of metals, nitrides, oxides, sulfides, and alloys. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133 12706–12713.
Gilroy, K. D.; Farzinpour, P.; Sundar, A.; Tan, T.; Hughes, R. A.; Neretina, S. Substrate-based galvanic replacement reactions carried out on heteroepitaxially formed silver templates. Nano Res., 2013, 6 418–428.
Pileni, M. P. Supra-and nanocrystallinities: A new scientific adventure. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2011, 23 503102.
Personick, M. L.; Langille, M. R.; Zhang, J.; Harris, N.; Schatz, G. C.; Mirkin, C. A. Synthesis and isolation of {110}-faceted gold bipyramids and rhombic dodecahedra. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133 6170–6173.
Zhang, J. A.; Langille, M. R.; Personick, M. L.; Zhang, K.; Li, S. Y.; Mirkin, C. A. Concave cubic gold nanocrystals with high-index facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132 14012–14014.
Tsao, Y. H.; Yang, S. X.; Evans, D. F.; Wennerstroem, H. Interactions between hydrophobic surfaces. Dependence on temperature and alkyl chain length. Langmuir, 1991, 7 3154–3159.
Mettela, G.; Boya, R.; Singh, D.; Kumar, G. V. P.; Kulkarni, G. U. Highly tapered pentagonal bipyramidal Au microcrystals with high index faceted corrugation: Synthesis and optical properties. Sci. Rep., 2013, 3 1793.
Mettela, G.; Bhogra, M.; Waghmare, U. V.; Kulkarni, G. U. Ambient stable tetragonal and orthorhombic phases in pentatwinned bipyramidal Au microcrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137 3024–3030.
Personick, M. L.; Langille, M. R.; Zhang, J.; Mirkin, C. A. Shape control of gold nanoparticles by silver underpotential deposition. Nano Lett., 2011, 11 3394–3398.
Mettela, G.; Siddhanta, S.; Narayana, C.; Kulkarni, G. U. Nanocrystalline Ag microflowers as a versatile SERS platform. Nanoscale, 2014, 6 7480–7488.
Zhang, Z. Y.; Chen, Z. P.; Pan, D. W.; Chen, L. X. Fentonlike reaction-mediated etching of gold nanorods for visual detection of Co2+. Langmuir, 2015, 31 643–650.
Luthra, S. S.; Yang, X. J.; dos Santos, L. M. F.; White, L. S.; Livingston, A. G. Phase-transfer catalyst separation and re-use by solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1468–1469.
Lindquist, N. C.; Nagpal, P.; Lesuffleur, A.; Norris, D. J.; Oh, S.-H. Three-dimensional plasmonic nanofocusing. Nano Lett., 2010, 10 1369–1373.
Brolo, A. G.; Irish, D. E.; Szymanski, G.; Lipkowski, J. Relationship between SERS intensity and both surface coverage and morphology for pyrazine adsorbed on a polycrystalline gold electrode. Langmuir, 1998, 14 517–527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mettela, G., Kulkarni, G.U. Facet selective etching of Au microcrystallites. Nano Res. 8, 2925–2934 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0797-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0797-8