Abstract
Prenylated flavonoids are a special kind of flavonoid derivative possessing one or more prenyl groups in the parent nucleus of the flavonoid. The presence of the prenyl side chain enriched the structural diversity of flavonoids and increased their bioactivity and bioavailability. Prenylated flavonoids show a wide range of biological activities, such as anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, cardioprotective effects, and anti-osteoclastogenic activities. In recent years, many compounds with significant activity have been discovered with the continuous excavation of the medicinal value of prenylated flavonoids, and have attracted the extensive attention of pharmacologists. This review summarizes recent progress on research into natural active prenylated flavonoids to promote new discoveries of their medicinal value.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
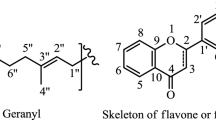
Prenylated flavonoids are a special type of flavonoid derivative that is characteristic of modified by prenylation of the skeleton. Prenylation refers to alkyl-substituent groups, such as prenyl, geranyl, lavandulyl, and farnesyl groups, which have more potential for further modification, such as oxidation, cyclization, and hydroxylation, and enrich the structural and biological diversity of prenylated flavonoids (Shi et al. 2021). According to reported studies over the past decade, more than 1000 prenylated flavonoids have been discovered from natural sources.
Prenylated flavonoids are the main active ingredient in many traditional Chinese medicines and functional food resources, such as Morus alba, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Humulus lupulus, Artocarpus heterophyllus, Glycine max, and Ficus carica fruits, and are promising lead compounds or nutraceuticals due to their diverse health benefits in oncotherapy (Wen et al. 2021), glycolipid metabolism balance (Jo et al. 2021), and the cardiovascular system (Song et al. 2011). Compared with nonprenylated flavonoids, prenylated flavonoids possess higher lipid solubility, an affinity for the cell membrane, and gastrointestinal absorption capacity due to the presence of prenyl groups (Hošek et al. 2011; Jakimiuk et al. 2021). Therefore, prenylated flavonoids show more potential to interact with diverse cellular targets. In recent years, the biological activity of prenylated flavonoids has attracted great attention from many research teams due to their promising pharmacological properties.
In the present review, a total of 1036 prenylated flavonoids obtained from 127 species belonging to 62 genera of 26 families (Tables 1, 2 and 3, Fig. 1) during the past decade were systematically summarized. The prenylated flavonoids were classified into 6 categories (Fig. 2), prenylated flavones (1-261), prenylated flavanones (262–567), prenylated chalcones (568–689), prenylated isoflavones (690–908), prenylated flavans (909–943) and isoflavans (944–1005), and prenylated flavonostilbenes and biflavonoids (1006–1036) according to their structural features (Fig. 3). Fabaceae, Moraceae, and Euphorbiaceae are the three leading families with abundant prenylflavonoids. The biosynthesis of prenylated flavonoids, preliminary active screening results, structure-activity relationships (SARs), and mechanism of active prenylated flavonoids were also summarized, aiming to provide an overview of natural, active prenylated flavonoids and their pharmacological properties.
Biosynthesis of prenylated flavonoids
In general, prenylated flavonoid biosynthesis in plant can conveniently be divided into three stages: (a) formation of the C6–C3–C6 skeleton (Fig. 4a). l-phenylalanine or l-tyrosine was used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA, which can be combined with three molecules of malonyl-CoA to yield the chalcone backbone. (b) biosynthesis of the different classes of flavonoids (Fig. 4b). Chalcones are proved to be the precursors to other subclasses of flavonoids and can be catalyzed by chalcone flavanone isomerase to obtain the basic skeleton of flavonoid which continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavones, flavans, isoflavones, and so on. (c) biosynthesis of the prenylated flavonoids (Figs. 5 and 6). Prenyltransferases are the key catalytic enzyme for prenylated modification of the flavonoids and have been attracting increasing attention due to greatly contributing to the structural diversity of flavonoids. The reaction catalyzed by prenyltransferases represents a Friedel–Crafts alkylation of the flavonoid skeleton in the biosynthesis of natural prenylflavonoids. Most of the prenyltransferases exhibit strict substrate specificity and low catalytic efficiency. Metal ion, especially Mg2+, is required for the catalytic activity. Up to now, only a few flavonoid prenyltransferases have been identified. The general characteristic of flavonoid prenyltransferases discovered from natural sources was summarized in Table 4..
Biosynthesis of the chalcone skeleton and the different classes of flavonoids. Enzyme names are abbreviated as follows: PAL phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; CPR cytochrome P450 reductase; TAL tyrosine ammonia lyase; 4CL 4-coumarate-CoA ligase; CHS chalcone synthase; CHR chalcone reductase; CHI chalcone isomerase; F3H flavanone 3-hydroxylase; FNS flavone synthas; IFS isoflavone synthase; HID 2-hydroxyisoflavanone dehydratase; FLS flavonol synthase; DFR dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; I2′H isoflavone hydroxylase; IFR isoflavone reductase; PTS pterocarpan synthase.
Natural prenylated flavonoids
Prenylated flavonoids with cytotoxicity
Prenylated flavonoids were found to possess more potential cytotoxicity against various cancer cells due to the introduction of the prenyl side chain on the flavonoid skeleton which enhances the binding affinity of flavonoids toward P-glycoprotein. 2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-8-(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-chroman-4-one (1) (Fig. 7) isolated from Artocarpus heterophyllus and displaying strong cytotoxic effect against MCF-7, A-549, SW480, and HL-60 cells, with IC50 values ranging from 1.03 to 5.28 µM (Liu et al. 2020). Licoflavone C (3), also called 4′,5,7-trihydroxy-8-prenylflavone (Ye et al. 2021), was identified in Ficus hirta, Retama raetam, and Morus alba. It exhibited cytotoxicity against HL-60, HepG2, A549, and NCI-H292 cells with IC50 values ranging from 7.0 to 13.85 µM (Qin et al. 2015a; Li et al. 2018). Three prenylated flavonols (5, 139, and 164) were isolated from leaves of Macaranga barteri and showed antiproliferative activity against four human cancer cell lines, MCF-7, A549, PC-3, and HeLa cells. Broussoflavonol F (164) displayed the highest cytotoxicity against these four human cancer cell lines with IC50 value of 3.83–4.13 µM. While 8-prenylkaempferol (5) lacks the C-3′ prenyl side chain on the B ring had a slight lower cytotoxicity (IC50 value of 6.22–6.88 µM) than 164. Isomacarangin (139) bearing a geranyl group in position C-8 also led to a slight reduction in antiproliferative activity (IC50 value of 8.43–8.72 µM) (Segun et al. 2019).
Nine prenylated flavonoids, isolated from the fruits of Sinopodophyllum hexandrum, were tested for their cytotoxicity against human breast-cancer T47D cells in vitro. Sinopodophylline B (10), 6-prenylquercetin 3-methyl ether (71), topazolin (72), and 5, 7, 4′-trihydroxy-3′-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-3-methoxy flavone (104) showed cytotoxicity against T47D cells with IC50 values of 1.5, 6.3, 11.9, and 2.0 µM, respectively, whereas sinopodophyllines C (197) and D (219) exhibited weak cytotoxicity against T47D cells with IC50 values of 46.0 and 36.8 µM. It suggested that 3′-hydroxyl group on the B ring and unmodified monoprenyl side chain promote the cytotoxicity, and the cyclization of the prenyl side chain would decrease the cytotoxicity (Wang et al. 2017c)0.5,7,3′,5′-Tetramethoxy-6-C-prenylflavone (61), 6-(3-methyl-(E)-1-butenyl) chrysin (79), bracteflavone B (80), and dinklagin C (81), from Artocarpus heterophyllus displayed strong cytotoxic effects against MCF-7, A-549, SMMC-7721, SW480, and HL-60 cells with IC50 values ranging from 1.46 to 16.26 µM (Liu et al. 2020).
72 and licoflavonol (73), isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, exhibited cytotoxicities against SW480 cells with IC50 values of 14.53 and 8.23 µM, respectively (Tang et al. 2016). Most prenylflavonoids isolated from the twigs of Artocarpus nigrifolius exhibited cytotoxicity against SiHa and SGC-7901 cells. 6-Prenyl-4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone (64) showed inhibitory activity against SiHa (IC50 value of 13.3) and SGC-7901(IC50 value of 9.6). Comparing the structures of 64 and artocarpesin (65), it suggested that the hydroxyl group of C-2′ on the B ring would dramatically decrease cytotoxicity. Eleocharin A (84) showed strong cytotoxicity against SiHa and SGC-7901 cells with IC50 values of 0.7 and 8.3 µM, respectively. The inhibitory activities of two structurally similar analogues, 5,4′-dihydroxy-3′-methoxy-(6:7)-2,2-dimethylpyrano-flavone (85) and carpachromenol (86), declined sharply against both two cell lines, which revealed the 3′-methoxyl group was unfavorable, but the 3′-hydroxyl maybe was crucial for the antiproliferative activity (Liu et al. 2018b).
Sinoflavonoid U (91) is from Sinopodophyllum hexandrum and exhibited cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2 cells with IC50 values of 6.25 and 3.83 µM, respectively. However, Sinoflavonoid T (90) possessing the same B and C rings from flavone skeleton as 91 displayed no cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2 cell lines, which suggested 2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)dihydrofurano group on ring A is structurally required for the cytotoxity against the MCF-7 and HepG2 cells lines (Sun et al. 2019). The cytotoxicity of prenylated flavonoids from the fruits of Sinopodophyllum emodi was evaluated against MCF-7 and HepG2 cells. Podoverine A (106) exhibited cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2 cells with IC50 values of 9.50 and 2.46 µM, respectively. However, oxidation or hydroxylation of prenyl group dramatically decrease cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2. Additionally, quercetin-3-methyl ether, a non-prenylation flavone, show more potent cytotoxicity than quercetin, suggesting methoxy at C-3 may contribute to its cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2 (Sun et al. 2015).
6,8-Diprenylkaempferol (154) displayed a strong cytotoxic effect against the H460 cell line with an IC50 value of 4.67 µM (Long et al. 2022). 6,8-Diprenyleriodictyol (155), isolated from Derris ferruginea, showed cytotoxicity against MRC-5 and KB cells with IC50 values of 8.0 and 8.5 µM, respectively (Morel et al. 2013).
Seven prenylated flavonoids (6, 15, 92, 99, 162, 191, and 192) from the leaves of Epimedium Koreanum were evaluated for cytotoxic activities against lung cancer A549 and NCI-H292 cells. Baohuoside I (15), epimedokoreanin D (99), epimedokoreanin B (162), epicornuin F (191), and epicornuin B (192) of which inhibited the proliferation of A549 and NCI-292 cells with IC50 values of 5.7–23.5 µM. Compound 162 showed cytotoxicity against A549 and NCI-H292 cells with IC50 values of 7.90 and 5.69 µM, respectively and 191 exhibited cytotoxicity against NCI-H292 cells with an IC50 value of 6.44 µM. Compounds 191 and 192 were structurally similar to 162, only one hydroxyl substitution in one prenyl decreased the cytotoxicity. Compared to the structures of these compounds, it suggested that glycosylation of the flavonoid and hydroxylation of the prenyl group decreased the cytotoxicity of the compounds (Zhang et al. 2020).
A diprenylated flavonol (164) exhibited significant cytotoxicity against MCF-7, A549, PC-3, and HeLa cells with IC50 values ranging from 5.40 to 5.82 µM (Segun et al. 2019). Daphnegiravone D (165), a 3-methoxy derivative of 164, showed cytotoxic activity against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2 and Hep3B cells) with IC50 values of 9.89 and 1.63 µM, respectively (Wang et al. 2017a).
Several prenylated flavonoids with pyran ring at A or B ring show potential cytotoxicity against different cancer cells. Kuwanon C (166) and morusinol (207) are from Morus alba root bark and showed cytotoxicity against THP-1 human monocytic leukemic cells with IC50 values of 1.7 and 4.3 µM, respectively (Zelová et al. 2014). Three flavonols, macarindicin E (199), macadenathin B (200), and macarindicin F (227), each bearing a pyran ring showed stronger cytotoxic activity than macarindicin D (63) and glyasperin A (168) as well as the non-prenylated flavonoids, kaempferol, quercetin, and quercitrin (Huonga et al. 2019). Artonin E (202) is from the bark of Artocarpus elasticus and possessed cytotoxicities against MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells with IC50 values of 2.6 and 13.5 µg/mL, respectively (Ramli et al. 2016). The diprenylated flavones (204, 207, and 229) exhibited cytotoxicity against A549, NCI-H292, HepG2, and Hep3B cells with IC50 values ranging from 8.91 to 29.2 µM. Morusin (204) possessing an intact prenyl side chain exhibit more potent cytotoxicity than 207 bearing a hydroxylated prenyl side chain at C-3, suggesting hydroxylation of the prenyl side chain at C-3 decreased the cytotoxicity (Li et al. 2018; Wang et al. 2017a).
Paulownia tomentosa fruits are rich in geranylated flavonoids (368–371, 373, 382, 385, 412, and 420) (Fig. 8) which exhibited potent antiproliferative activities against THP-1 (IC50 < 10 µM). However, the non-geranylated flavonoids, 3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyflavanone, eriodictyol, and naringenin, were inactive in comparison to flavonoids with geranyl side chains. The cytotoxic effect of geranylated flavonoids is possibly related to their lipophilicity and to their greater ability to penetrate the membranes of cells. The presence of a β-carbon (proximal) OH group on a geranyl chain (385, IC50 = 6.5 µM) did not affect the cytotoxicity, but an OH group on the distal end of the side-chain (399, IC50 > 20 µM) caused a loss of cytotoxic effect. The substituents on ring B of the flavonoid structure seemed to have minor effects on the cytotoxic potential of the geranylated flavonoids (Hanáková et al. 2015). Another phytochemical study of the fruit of Paulownia tomentosa led to the isolation of twelve natural geranylated flavonoids. Two flavonoids, diplacone (374) and 3′-O-methyl-5′-hydroxydiplacone (375) each bearing an unmodified geranyl side chain, possessed the strongest antiproliferative activities against THP-1 with IC50 values of 9.31 and 12.61 µM, respectively. The geranylated flavanones exhibited significantly greater cytotoxicity than the corresponding non-geranylated flavanones, taxifolin, naringenin, and hesperetin, which suggested that the presence of a geranyl side chain is a crucial structural requirement for the cytotoxic effect of flavanones. The addition of a methoxy group on ring B decreased the activity of tomentone B (409) as compared to tomentone II (410), and of 3ʹ-O-methyl-5ʹ-hydroxyisodiplacone (424) as compared to 374 (Molčanová et al. 2021). Kuwanon E (434), isolated from the roots of Morus alba, also inhibited the proliferation of THP-1 human monocytic leukemic cells with an IC50 value of 4.0 µM (Zelová et al. 2014). In addition, 6-Farnesyl-3′,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavanone (449), isolated from Macaranga triloba, strongly inhibited the growth of HeLa and HL-60 cells with IC50 values of 1.3 and 3.3 µg/mL, respectively (Zakaria et al. 2012). Calycinigin A (543), a C-3′ lavandulylated flavonone, exhibited an antiproliferative effect against HeLa cells with an IC50 value of 9.7 µM (Win et al. 2012).
Several diprenylated flavonones show potential antiproliferative activities against different cancer cells. 6,8-Diprenyl-4′-methyl-naringenin (452), isolated from the fruits of Macaranga balansae, showed cytotoxic activity against PanC1, A549, KB, and Lu-1 cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 7.89 to 22.81 µM (Mai et al. 2020). Lonchocarpol A (457) and dorsmanine I (504) from the stems of Derris ferruginea inhibited the growth of MRC-5 and KB cells with an IC50 value range of 6.2–23.8 µM (Morel et al. 2013). Maackiaflavanone (463) and 5-hydroxysophoranone (482) exhibited cytotoxicity against HeLa and SK-MEL-5 cells. The IC50 values of 463 were 8.2 and 6.5 µM, whereas the IC50 values of 482 were 12 and 7.7 µM, respectively. However, the structurally similar analogues, isomaackiaflavanone A (465), isomaackiaflavanone B (473), and abyssinone V (479), exhibit weak cytotoxicity against HeLa and SK-MEL-5 cells with IC50 value range of 16–36 µM suggesting that 8-prenyl side chain promotes the cytotoxicity, and methoxy at C-2′ on the B ring decreased the cytotoxicity (Veselova et al. 2017). Sanggenol Q (480), isolated from the root bark of Morus alba, showed cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells with an EC50 value of 6.94 µM (Jung et al. 2015). Three diprenylated flavonoids, addisoniaflavanones I (487) and II (488) and 5,7-dihydroxy-5′-prenyl-[2′′,2′′-(3′′-hydroxy)-dimethylpyrano]-(5′′,6′′:3′,4′)flavanone (516) isolated from Erythrina addisoniae, showed higher toxicity to H4IIE hepatoma cells than the monoprenyl-substituted flavonoids, with EC50 values of 5.25, 8.5, and 14.7 µM, respectively. Both 487 and 488 induced apoptosis via caspase-3 and -7 activation (Passreiter et al. 2015).
Xanthohumol (579) (Fig. 9), a prenylated chalcone isolated from H. lupulus, exhibited diverse bioactivities. It exhibited cytotoxic activity against WI-38, J774, HepG2, MG-63, HT-29, and SW620 cell lines with IC50 values of 19.5, 9.6, 7.1, 29.4, 12.0, and 25.0 µM, respectively (Bocquet et al. 2019; Harish et al. 2021; Hudcová et al. 2014). Two structurally similar chalcones sanjuanolide (582) and sanjoseolide (583), isolated from D. frutescens, show different cytotoxic activities against PC-3 and DU 145 prostate cancer cells. It was noted that 582 was 3.2- and 3.6-fold more potent than 583 against PC-3 and DU 145 cells, respectively. These compounds differ only by the replacement of a 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methyl-3-butenyl group in 583 by a 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-3-butanyl group in 582, which suggested the hydroxylation of prenyl side chain decrease the cytotoxicity (Shaffer et al. 2016). 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxylonchocarpin (601) is a prenylated chalcone from the seeds of Millettia pachycarpa and exhibited cytotoxicity against K562 cells with an IC50 value of 2.4 µg/mL (Su et al. 2012). Gemichalcone B (602) is from the twigs of Artocarpus nigrifolius and showed strong cytotoxicity against SiHa cells with an IC50 value of 8.7 µM (Liu et al. 2018b).
Chalcones (607, 608, 613–615, and 666–670) (Figs. 9 and 10) from Desmodium renifolium and D. podocarpum exhibited cytotoxicity against NB4, A549, SHSY5Y, PC3, and MCF-7 cells (Li et al. 2014a, b; Qin et al. 2015b). Artonin ZA-1 (607) and artonin ZA-2 (608) exhibited cytotoxicity against these human tumor cells with IC50 values ranging from 5.8 to 10 µM. Renifolin C (613) showed cytotoxicity against NB4 and PC3 cells with IC50 values of 6.4 and 8.5 µM, respectively. 2′,4-Hydroxy-3,4′-dimethoxychalcone (614) inhibited SHSY5Y, PC3, and NB4 cells with IC50 values of 3.8, 3.6, and 4.2 µM, respectively, whereas 2′,3-hydroxy-4,4′-dimethoxychalcone (615) exerted cytotoxicity against A549, PC3, and MCF-7 cells with IC50 values of 3.5, 6.8, and 6.2 µM, respectively. Renifolins D–H (666–670) each bearing a five-membered carbocycle showed cytotoxicity against these cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 2.2 to 9.7 µM.
Kanzonol C (644) and hedysarumine F (645) showed cytotoxicity against A549 cells with IC50 values of 9.67 and 7.79 µM, respectively, whereas 644 exhibited cytotoxic activity against HCT116 cells with an IC50 value of 8.85 µM (Liu et al. 2018c). Flemiphilippinone C (689) bearing two prenyl moieties at C-3′ was isolated from the roots of Flemingia philippinensis. It exhibited antiproliferative activity against PC-3, Bel-7402, and CaEs-17 with GI50 values of 14.12, 1.91, and 2.58 µM, respectively. Mechanistically, 689 increased S/G2 arrest and induced apoptosis in Bel-7402 cells through a mitochondria-related pathway (Kang et al. 2016).
Gancaonin G (729) (Fig. 11) is from Glycyrrhiza uralensis and exhibited cytotoxicity against SW480 cells with an IC50 value of 9.84 µM (Tang et al. 2016). 4′-Hydroxy-5,7-dimethoxy-6-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-isoflavone (730), gancaonin N (731), isopiscerythrone (732), viridiflorin (733), and ficucaricone D (741) exhibited cytotoxicity against five human cancer cell lines HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW480, with IC50 values ranging from 0.42 to 8.48 µM (Liu et al. 2019c). Eleven prenylated isoflavones (690, 736, 749, 757, 778, 795, 796, 813, 847, 848, and 870) and two coumaronochromones (887 and 888) from the fruits of Ficus altissima were evaluated for their anti-proliferative activities against three human tumor cell lines (HepG2, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231) through MTT assay. Ficusaltin B (848), isolupalbigenin (847), and lupinalbin D (888) exhibited more effective cytotoxic activities to tested cell lines, which speculated that the prenyl substituent at C-3′ of the B ring was the active group in these isolated compounds. The structurally similar analogue isowigtheone (778) bearing only one prenyl substituent at C-3′ was inactivated. It suggested that the simultaneous presence of a prenyl group at C-6 or C-8 in the A ring and a prenyl group at C-3′ in B ring might be essential for those prenylated isoflavones to exert obvious anti-proliferative effects. For prenylated coumaronochromones, once the position of prenyl group changed to C-6 as lupinalbin B (887), the anti-proliferative activity against tumor cell lines would significantly reduce (Yao et al. 2021). Auriculasin (818) from the roots of Flemingia philippinensis exhibited an antiproliferative effect against PC-3 cells with a GI50 value of 8.33 µM. However, eriosematin, a chromone derivative, showed no activity (GI50 > 100 µM) which suggested B ring with 3′,4′-dihydroxy group in 818 would play an important role in inhibiting the growth of PC-3 cells (Kang et al. 2016). Flemiphilippinin G (822) and 5,7,3′-trihydroxy-2′-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-4′,5′-(3,3-dimethylpyrano) isoflavone (867) showed cytotoxicity against MCF-7, A549, and HepG2 cells with IC50 values ranging from 4.8 to 24.8 µM (Fu et al. 2012). Tephrosin (893), cis-(6aβ,12aβ)-hydroxyrotenone (894), and rotenone (895), isolated from Indigofera spicata, exhibited cytotoxicity against HT-29, 697 human acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Raji human Burkitt’s lymphoma cells with IC50 values ranging from 0.1 to 9.0 µM. Additionally, 894 (IC50 0.1 µM against HT-29 cells) and 895 (IC50 0.1 µM against HT-29 cells) did not show obvious toxic effects on normal CCD-112CoN cells, with IC50 values over 100 µM (Bueno Perez et al. 2013).
The prenylated flavans (909, 916–927, 932, and 935–942) (Fig. 12), isolated from the stem and root bark of Daphne giraldii, were evaluated their cytotoxicity against Hep3B cells. Among them, 919–921, 926, 927, and 935–937 exhibited cytotoxicity against Hep3B cells with an IC50 value range of 5.15–9.66 µM (Sun et al. 2016a; Li et al. 2016). By comparing two similar flavans daphnegiravans A (917) and B (918), the presence of a methoxyl connected to the pyran ring reduced the cytotoxicity against all tested cancer cell lines (MCF-7, Bcap37, HepG2, Hep3B, and A549). The activity of the compound possessing a 2,2-dimethylpyran was greater than that of 2, 2-dimethyldihydropyran and furan substituents according to the IC50 values of daphnegiravans K (920), J (926), and I (927). A comparison of the activity data between daphnegiravan H (925) and 926 indicated that the cyclization between the prenyl and hydroxyl moieties in ring B produced a significant improvement in the reduction of cancer cell growth. This also supported that 917 and 924 with a pyran or dihydropyran ring produced more potent inhibition than (2 S)-7,4′-dihydroxy-3′-prenylflavan (916) and (2 S)-kazinol I (932), respectively (Sun et al. 2016a).
Glyurallin A (966) (Fig. 13) is from Glycyrrhiza uralensis and exhibited cytotoxicity against SW480 cells with an IC50 value of 10.86 µM (Tang et al. 2016). Thonningine A (996), asthonningine B (997), indicanine A (998), ficucaricones A (999) and B (1000), 3′′,4′′-dihydrothonningine C (1001), and indicanine B (1004) showed promising cytotoxic effects towards five human cancer cell lines HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW480, with IC50 values ranging from 0.18 to 18.76 µM (Liu et al. 2019c). Alopecurone J (1011) (Fig. 14) exhibited cytotoxic activities against HeLa, HCT116, A2780, and A549 cells with IC50 values ranging from 9.97 to 30.91 µM. (Soltani et al. 2020). Sanggenon E (1025) is from Morus nigra and showed cytotoxicity against THP-1 human monocytic leukemic cells with an IC50 value of 4.0 µM. (Zelová et al. 2014).
According to the cytotoxic activities of aforementioned compounds, the general SARs of prenylated flavonoids was summarized in Figs. 15 and 16.
Prenylated flavonoids with anti-inflammatory activity
Inflammation is a primary pathological process involved in the progression of various diseases. Many prenylated flavonoids exhibited promising anti-inflammatory activities and regulated the expression of various inflammatory cytokines and related proteins, such as nitric oxide (NO), TNF-α, interleukins (ILs), induced NO synthase (iNOS), and NF-κB, etc. Anti-inflammatory effect of Epimedium grandiflorum was attributed to the presence of prenylflavonoid glycosides. The prenylated flavones desmethylicaritin (5), icariside II (15), epimedigrandioside A (21), and korepimeosides A (22) and B (23) from Epimedium grandiflorum possessed inhibitory activities against NF-κB and iNOS with IC50 values ranging from 16.6 to 26.5 µM and 14.0 to 17.5 µM, respectively. Epimedoside (19), epimedokreanoside II (20), and epimedins I (40), K (41), and L (42) also exhibited inhibitory activities of iNOS with IC50 values of 14–30 µM, respectively, however, they did not show any effect on NF-κB or transcription factor Sp-1 (Zulfiqar et al. 2017).
Morus alba has long been used in traditional Chinese medicine and the root bark of M. alba, named Sang-bai-pi, is listed as an important herb medicine in Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The prenylated flavones, albanin D (146), (7′′R)-(−)-6-(7′′-hydroxy-3′′,8′′-dimethyl-2′′,8′′-octadien-1′′-yl)apigenin (147), 10-oxomornigrol F (190), 204, 2-(2,4-dihydrophenyl)-5-hydroxy-8-(hydroxymethyl)-8-methyl-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-(9CI) (205), and mulberranol (225), and one chalcone, morachalcone A (575), isolated from the twigs of Morus alba, showed inhibitory activities against NO production with IC50 values of 2.2 to 5.3 µg/mL in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells. Compounds 146, 147, 190, 225, and 575 reduced LPS-induced iNOS expression in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, compounds 146, 190, and 225 significantly suppressed LPS-induced expression of COX-2 protein (Tran et al. 2017). Treatments of kuwanon T (176), 204, 434, sanggenol A (435), sanggenon A (545), sanggenon M (546), and kuwanon G (1027) at a dose of 100 µg/mL strongly inhibited the production of IL-6 with the inhibition values ranging from 90.9 to 99.1% in TNF-α stimulated MG 63 cells (Chang et al. 2019). Sanggenol L (431), isolated from the root bark of Morus alba, showed inhibitory effect against NO production with an IC50 value of 12.5 µM in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages (Qin et al. 2015a).
Six cyclized geranylflavonoids (237–242) were isolated from the rhizomes of Helminthostachys zeylanica. (10R,11 S)-ugonin S (237), ugonin V (238), ugonin W (239), and ugonin Y (240) exhibited NO inhibition with IC50 values of 19.7, 18.0, 7.0, and 6.7 µM, respectively (Huang et al. 2017). Nymphaeol A (386), 3′-geranyl-naringenin (437), isonymphaeol-B (438), and nymphaeols B (445) and C (446), isolated from Okinawa propolis, repressed NO production with IC50 values ranging from 2.4 to 7.0 µM and inhibited COX-2 activity with IC50 values ranging from 11.74 to 24.03 µM in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells (Shahinozzaman et al. 2018).
The geranylated flavonoids from Paulownia tomentosa were evaluated for their ability to inhibit cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2). Mimulone (369), 3′,4′-O-dimethyl-5′-hydroxydiplacone (370), 374, 375, and tomentodiplacone O (411) showed significant effects on COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition with IC50 values range of 1.8–26.3 µM, comparable with the positive control ibuprofen with IC50 values of 6.3 µM for COX-1, and 4.2 µM for COX-2, respectively. Compound 411 showed greater selectivity against COX-2 than ibuprofen, which is a relatively nonselective COX inhibitor. According to the SARs of the geranylated flavonoids, the unmodified prenylated side chain and substitution of ring B appeared to be crucial for the COX inhibitory activity of flavanones. What’s more, these geranylated flavonoids were also evaluated for their inhibitory activities against 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX). 374, 375, 3′-O-methyl-5′-methoxydiplacone (371), tomentone (408), and paulownione C (415) show inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 0.05–2.46 µM. Compounds 374 and 375 both bearing two hydroxy groups on the ring B and an unmodified geranyl side chain showed inhibitory activities against 5-LOX almost 10 times greater than the positive control zileuton (IC50 value: 0.35 µM) (Hanáková et al. 2017). Additionally, 369 also named bonannione A was isolated from Macaranga denticulata (Zhang et al. 2016). Another study assayed the geranylated flavonoids (373, 379–382, 394–398, and 400–406) from the fruits of Paulownia tomentosa were tested for inhibitory effect on human neutrophil elastase (HNE) in vitro which stimulates the release of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, and other cytokines, exacerbating the inflammatory process. 3′-O-methyldiplacone (373), 6-geranyl-5,7,3′,5′-tetrahydroxy-4′-methoxyflavanone (379), prokinawan (395), tomentin J (396), isopaucatalinone B (398), and tomentin A (400) displayed potent inhibition with IC50 values of 7.8, 3.3, 6.7, 6.3, 2.4, and 8.4 µM, respectively, showing more potent than the non-prenylated flavones quercetin (IC50: 14.3 µM), luteolin (IC50: 12.7 µM), and apigenin (IC50: 46.1 µM). The activities of the geranylated flavonoids indicated a positional requirement for the geranyl derivatives. However, hydroxylation at C-3 and methoxylation at C-5′ might tend to reduce the HNE inhibitory potencies (Ryu et al. 2017).
A series of prenylated flavonoids (154, 501–503, 665, 681, 687, 805–807, 818, 819, 855, 857, and 874) from the roots of Flemingia philippinensis were evaluated for their HNE inhibitory activity. The results indicate that HNE inhibitory activity was significantly affected by subtle changes in the respective structures of the prenylated flavonoids. The 4′-hydroxy group in flavanones strongly affected the inhibition by comparing lupinifolin (501) (IC50 = 13.3 µM) and flemichin D (502) (IC50 = 5.3 µM) with khonklonginol H (503) (IC50 = 110.2 µM). 8-γ,γ-Dimethylallylwighteone (805) (IC50 = 6.0 µM) with two prenyl groups on the A-ring was 9 times more effective than the non-prenylated compound genistein (IC50 = 51.4 µM), which suggested the prenylation at the A-ring plays a pivotal role in HNE inhibition. Similar prenylation effects were also observed for flemingsin (806) (IC50 = 12.0 µM) and osajin (819) (IC50 = 26.0 µM). A comparison of 6,8-diprenylorobol (807) (IC50 = 1.3 µM) with 819 (IC50 = 26.0 µM) showed that the catechol motif of the B-ring significantly influences HNE inhibition. However, prenylation on the B-ring diminished the inhibitory activity by comparing genistein (IC50 = 51.4 µM) with 5,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy-2′,5′-di(3-methylbut-2-enyl)isoflavone (855) (IC50 = 213.1 µM) (Kim et al. 2018).
The prenylated chalcones (646, 648, 653–655, and 647) were isolated from the roots of Hedysarum gmelinii and showed NO inhibition activities with IC50 values ranging from 3.25 to 18.18 µM in LPS-treated BV-2 cells. Among them, hedysarumine B (648), paratocarpin F (654), and hedysarumine G (655) exhibited higher activities than the positive control dexamethasone (IC50: 9.47 µM), with IC50 values of 5.12, 8.48, and 3.25 µM, respectively (Liu et al. 2018c).
Fruits of Ficus carica have been consumed as a very popular health-promoting fruit worldwide since ancient times. A series of prenylated isoflavone derivatives were separated from the fruits of F. carica. Among these isolated compounds, 730, 741, and 997–1000 showed stronger inhibitory effects against NO production with IC50 values below that of positive control hydrocortisone, while the other compounds (732–734, 996, 1001, and 1004) exhibited weaker inhibitory effects against NO production by comparison with that of hydrocortisone. The compounds with the hydrogen atom at C-3′, the 2-propan-2-ol group at C-2″, and the furan ring were more likely to hold significant inhibitory effects against NO production by comprehensive analysis of the structures and the inhibitory activities of 997, 996, 1001 − 1000, and 1004. The compounds with a para-disubstituted benzene ring were more likely to possess potent inhibitory effects against NO production by comparing the structures of 730–734 (Liu et al. 2019c).
Two diprenylated isoflavones, 819 and pomiferin (820), isolated from the fruit of Maclura pomifera, exhibited inhibitory activities against NF-κB with IC50 values of 12.0 and 13.0 µg/mL in SW1353 cells and against iNOS with values of 7.2 and 6.4 µg/mL in LPS-treated macrophages, respectively. Compounds 819 and 820 also enhanced the activity of NAG-1 by 1.8- and 1.5-fold increases at 6.0 µM, respectively, whereas 820 inhibited intracellular oxidative stress with an IC50 of 3.3 µg/mL (Abourashed et al. 2015). A prenylated flavonostilbene cajanusflavanol A (1028) featuring a unique highly functionalized cyclopenta[1,2,3-de]isobenzopyran-1-one tricyclic core possessed inhibitory effect against NO production with an IC50 value of 13.62 µM (He et al. 2018).
Prenylated flavonoids with antihyperglycemic activity
Postprandial hyperglycaemia is an important risk factor in the onset and development of type 2 diabetes. Inhibition of α-glucosidase would delay the digestion as well as absorption of carbohydrates, which consequently, suppress the postprandial hyperglycaemia. Prenylation of flavonoids increased the potency of α-glucosidase inhibition. 6-Prenylquercetin (70) and 71 from Glycyrrhiza uralensis leaves showed α-glucosidase inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 3.7 and 21.3 µg/mL, respectively (Fan et al. 2019). Hirtacoumaroflavonoside (77) act as a noncompetitive α-glucosidase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 22 µM (Sheliya et al. 2015). Hirtaflavonoside B (157) showed α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 71 µM and acted in a mixed noncompetitive inhibitory pattern (Sheliya et al. 2015). 207 and dioxycudraflavone A (229) also exhibited α-glucosidase inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 23.2 and 25.27 µM, respectively (Li et al. 2018). 6-Prenyleriodictyol (266), 6-prenylnaringenin (267), and 5′-prenyleriodictyol (312) showed α-glucosidase inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 27.5, 15.4 and 53.4 µg/mL, respectively (Fan et al. 2019). Three 8-prenylflavonones euchrenone a7 (279), 8-prenylnaringenin (280), and isoxanthohumol (281) from Morus alba and H. lupulus showed inhibition activities against α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 6.28, 50, and 40 µM, respectively (Wang et al. 2022; Yang et al. 2012). 4′,1′′-Dihydroxy-3′-methoxy-6,7-furanflavanone (349) is from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia and exhibited inhibitory activity on α-glucosidase with an IC50 value of 53.1 µM, lower than the positive control acarbose (IC50 = 214.5 µM) (Fei et al. 2020). Four geranylated flavonones nymphaeol A (367), 437, 438, and 445, isolated from Okinawa propolis, strongly suppressed in vitro α-glucosidase enzyme activity with IC50 values of 3.77–5.66 µM (Shahinozzaman et al. 2018). Kushenols E (460), L (461), and A (526) inhibited α-glucosidase activity with IC50 values of 24.6, 32.6, and 50.6 µM, respectively. 460 showed an uncompetitive inhibitory pattern, whereas 461 and 526 had a noncompetitive binding mechanism (Kim et al. 2017). Kushenol B (554) inhibited α-glucosidase activity in an uncompetitive inhibitory pattern with an IC50 value of 11.0 µM (Kim et al. 2017). 579 showed α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 47 µM below that of positive control acarbose (IC50 = 58 µM) (Wang et al. 2022). 5,3′,4′-trihydroxy-1′′-methoxy-6,7-furanbavachalcone (609) is from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia and exhibited inhibitory activity on α-glucosidase with an IC50 value of 90.3 µM. The IC50 value of the positive control acarbose was 214.5 µM (Fei et al. 2020). A phytochemical investigation of Masclura tricuspidata leaves resulted in the isolation of 47 prenylated isoflavonoids. They were evaluated for their α-glucosidase inhibitory and anti-glycation activities. Most isoflavonoids showed good inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase, with IC50 values of < 30.0 µM. Among the isolates, gancaonin M (698), millewanin G (808), erysenegalensein E (810), and cudracusisoflavone L (812) showed strong α-glucosidase inhibition with IC50 values of 8.2, 3.2, 4.2, and 8.9 µM, respectively. The prenylated isoflavonoids were further divided into one linear prenyl moiety, two linear prenyl moieties, one cyclized prenyl moiety, and two prenyl moieties with one linear and one cyclized type. Comparing the type of prenyl group, the inhibitory activity was stronger in isoflavonoids with linear prenyl group than cyclized ones. The addition of the hydroxyl group to the prenyl group increased the inhibitory effects, while the addition of the OCH3 group caused a decrease in the inhibitory effect. The molecular docking analysis also supported the aforementioned speculation (Jo et al. 2021).
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that function as ligand-inducible transcription factors modulating the expression of target genes involved in controlling glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism and inflammation. 22 prenylated flavonoids, isolated from Psoralea corylifolia, were screened on the PPAR-γ agonist activity. Bavachin (273), bavachinin (277), 4′-O-methylbavachalcone (573), broussochalcone B (574), and corylifol A (869) exhibited potent PPAR-γ agonist activation from 6.16-fold to 13.12-fold at a test concentration of 25 µM. Substituting methoxyl at C-7 of A-ring to hydroxyl, such as 273 and 574, reduced PPAR-γ agonist activation compared to 277 and 573, indicating that the methoxyl in the C-7 position of A-ring is crucial for PPAR-γ agonist activity. Isobavachin (289) and isobavachalcone (575) show less PPAR-γ agonist activity than 273 and 574, suggesting that the prenyl in the C-6 position of A-ring may contribute to their agonist activities. 573 and 574 showed less PPAR-γ agonist activity than 273 and 274, which indicated that the C-ring structure is an important determinant for PPAR-γ agonist activity, opening the C-ring results in remarkably lower activity. In addition, the cyclization of the prenyl group on the A-ring and B-ring also markedly reduced PPAR-γ agonist activity (Fig. 17) (Ma et al. 2016).
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a negative regulator in the insulin signaling pathway, was evidenced as a promising drug target for type 2 diabetes. The prenylated flavonoids, macarangin (143), bonannione A (337), bonanniol A (378), (2E)-1-(5,7-dihydroxy-2,2,6-trimethyl-2 H-benzopyran-8-yl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one (588), (2E)-1-(5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2 H-benzopyran-8-yl)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-one (589), and laxichalcone (656), from Macaranga denticulate showed potential inhibitory activities against PTP1B in vitro with an IC50 value of 22.7, 14.0, 15.2, 48.8, 19.3, and 20.7µM, respectively (Zhang et al. 2016). 166, cudraflavone C (167), cudraflavanone D (472), and euchrestaflavanone C (510) derived from the roots of Cudrania tricuspidate, showed PTP1B inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 13.6, 9.4, 5.7, and 12.3 µM, respectively (Quang et al. 2015). Five prenylated flavonoids, morunigrol A (174), 204, cudraflavone B (228), and morunigrols C (248) and B (249), from Morus nigra exhibited PTP1B inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 12.5, 22.1, 20.0, 7.7 and 5.3 µM, respectively (Qu et al. 2021).
Aldose reductase mediates the first step of the “polyol pathway” by reducing glucose to sorbitol through a NADPH-dependent reaction. Under hyperglycemic conditions, it tended to cause excessive accumulation of sorbitol which might finally promote the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) by decrease the cell’s antioxidative capabilities. The AGEs could lead to diabetic complications, such as microangiopathies, nephropathies, retinopathies, peripheral neuropathies and cataract. Aldose reductase inhibitors possessed the potential to prevent or control the onset of these diabetic complications. 280, 281, and 579 are potent tight-binding inhibitors of human aldose reductase AKR1B1 with IC50 values of 0.81, 0.57, and 9.11 µM and Ki values of 0.30, 0.17, and 5.29 µM, respectively, using glyceraldehyde as a generic substrate. The IC50 and Ki values of three inhibitors against AKR1B1 were 1.87, 0.88, and 29.17µM, and 0.71, 0.34, and 15.08 µM, respectively, when applied glucose as a generic substrate. 280 and 579 inhibited AKR1B1 in a non-competitive fashion, whereas 281 displayed the typical pattern of an uncompetitive inhibitor. All three inhibitors exhibit a 4′-OH group which indicated a 4′-OH group is crucial for the inhibition of AKR1B1. 280 (IC50 = 0.81 µM) exhibited an inhibitory potency that is 7.6 times greater as compared to that of 267 (IC50 = 6.2 µM), applying glyceraldehyde as substrate. It suggested that prenyl moiety at the C-8 position played an important role in aldose reductase inhibition. The efficacy of 280 (IC50 = 1.87 µM) and 281 (IC50 = 0.88 µM) is 15–34 times greater than that of 579 (IC50 = 29.17 µM), which indicated that the C-ring structure is an important determinant for aldose reductase inhibition, opening C-ring results in remarkably lower activity (Seliger et al. 2018; Shim et al. 2009). A series of prenylated isoflavoinds (698, 705, 727, 745, 760, 799, 808, 809, 832–834, and 835) from M. tricuspidata leaves efficiently inhibited methylglyoxal- or glyoxal-induced AGEs formation, which can be considered as promising candidates for the treatment of several diabetic complications (Jo et al. 2021).
Prenylated flavonoids with antioxidant activity
6-Prenylated-3,5,7,4′-tetrahydroxy-2′-methoxyflavonol (69), isolated from Chlorophora regia, exhibited remarkable free radical scavenging properties with an IC50 value of 2.8 µg/mL (Kyekyeku et al. 2016). 70, 5′-prenylquercetin (102), 266, 312, and 8-[(E)-3-hydroxymethyl-2-butenyl]-eriodictyol (323) from Glycyrrhiza uralensis leaves scavenged DPPH radicals with an EC50 value of 2.4, 3.6, 5.2, 8.7, and 2.3 µg/mL (Fan et al. 2019). 72 exhibited weak DPPH scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 0.34 mg/mL (ascorbic acid as a positive control, IC50 = 0.07 mg/mL) (Kırmızıbekmez et al. 2015). The prenylated flavnoids (84, 267, 308, and 332) and several non-prenylated flavonoids isolated from Eleocharis tuberosa were evaluated for antioxidant activity by the reducing power assay and DPPH radical scavenging assay. The result indicated that the flavonoids, 84, eleocharins C (308), and B (332), with a 3′,4′-dihydroxylated B ring had strong antioxidant activity, and the activity decreased when the hydroxyl of B-ring was substituted with methoxy. The prenylation of flavonoids did not affect the antioxidant activity of flavonoids (Luo et al. 2014). Elastixanthone (97), 202, and cycloartobiloxanthone (217) identified in the bark of Artocarpus elasticus, displayed significant scavenging activity for DPPH with an IC50 value of 21.6, 11.5, and 40.0 µg/mL (Ramli et al. 2016). Artocarpin (169), 3′-hydroxycycloartocarpin (182), and pyranocycloartobiloxanthone A (232) are from the leaves and heartwoods of Artocarpus anisophyllus and showed DPPH radical scavenging activity with SC50 values of 140.0, 152.9, and 20.2 µg/mL, respectively. (Abdul Lathiff et al. 2015). The antioxidant activities of sixteen prenylated flavonoids from Artocarpus altilis were assessed to scavenge DPPH, ABST, and superoxide anions. Artogomezianon (179) and isocycloartobiloxanthone (230) exhibited ABTS activities with IC50 values of 36.9 and 7.2 µM, respectively, while 179 had an IC50 value of 39.7 for superoxide anion scavenging activity. Artoflavone A (209), hydroxyartoflavone A (210), and 230 showed DPPH scavenging activities, with IC50 values of 53.5, 20.9, and 33.9 µM, respectively (Lan et al. 2013). A diprenylflavone, 3,5,2′,4′-tetrahydroxy-6′′,6′′-dimethylpyrano(2′′,3′′:7,6)-8-(3′′′,3′′′-dimethylallyl) flavone (195), from the roots of Eriosema chinense show strong DPPH scavenging activities with an IC50 value of 35 µM (Thongnest et al. 2013). Cycloheterophyllin (258) and 2′,4′-dihydroxy-3,4-(2′′,2′′-dimethylchromeno)-3′-prenyldihydrochalcone (688) showed antioxidant activity towards DPPH with SC50 value of 102.8 and 223.8 µM (Abdullah et al. 2017). Mildbone (341) and mildbenone (593) were from Erythrina mildbraedii and showed potent DPPH scavenging activities with IC50 values of 20.2 and 28.5 µM, stronger than the positive control (BHA, IC50 value: 44.2) (Ali et al. 2012). Two derivatives, 1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-[8-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-2 H-1-benzopyran-5-yl]-1-propanone (672) and 2-geranyl-2′,3,4,4′-tetrahydroxydihydrochalcone (673), from Artocarpus altilis showed DPPH scavenging activities with IC50 values of 82.2 and 82.4 µM, respectively (Huong et al. 2012). Excelsanone (694) and 6,8-diprenylgenistein (805) from Erythrina excelsa possessed actives for DPPH radical scavenging with IC50 values of 1.31 and 0.07 mg/mL, respectively (Gbaweng et al. 2020). Thonningiisoflavone (781) is from Ficus thonningii and showed strong DPPH radical scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 65.5 µM (Fongang et al. 2015). Iconisoflavan (945), iconisoflaven (952), licorisoflavan A (961), (3 S)-licoricidin (962), and glycycoumarin (995), isolated from the roots of Glycyrrhiza iconica, exhibited weak DPPH scavenging activity with IC50 values of 0.29, 0.18, 0.56, 0.32, and 0.47 mg/mL, respectively (ascorbic acid as a positive control, IC50: 0.07 mg/mL) (Kırmızıbekmez et al. 2015).
Sophoflavanones A (539) and B (540) from the roots of Sophora flavescens exhibited antioxidant activities against Fe2+/cysteine-induced toxicity at a concentration of 0.1 µM with inhibitory values of 71.65% and 72.49%, respectively (vitamin C as a positive control:87.83%) (Zhu et al. 2018). The diprenylisoflavones 5,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy-6,8-diprenylisoflavone (807) and 818 from Flemingia philippinensis showed antioxidant activities with ferric reducing antioxidant power values of 4338 and 2977 µmol/g, respectively (Fu et al. 2012).
In general, the antioxidant activity of prenylated flavonoids shows a close relationship with the number and position of hydroxyl groups. The catechol motif of B ring had strong antioxidant activity, and the activity decreased when the hydroxyl of B-ring was substituted with methoxy. Additionally, the prenylation of flavonoids did not affect the antioxidant activity of flavonoids.
Prenylated flavonoids with antibacterial activity
Compound 204 showed a potent antibacterial effect by disrupting the phospholipid-repair system and inhibiting the phosphatidic acid biosynthesis pathway of Staphylococcus aureus (Pang et al. 2019). (±)-5,4′-dihydroxy-2′-methoxy-6′,6′′-dimethypyraro-(2′′,3′′:7,8)-6-methylflavanone (338) from the traditional Chinese medicine Tripterygium wilfordii showed significant antimicrobial activities against S. aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus, with IC50 values of 2.60 and 2.07 µg/mL, respectively. Another compound 467 exhibited antimicrobial activities against Cryptococcus neoformans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis, and methicillin-resistant S. aureus with IC50 values of 2.95, 8.59, 4.32, and 4.47 µg/mL, respectively (Chen et al. 2017). 501 inhibited the growth of S. aureus with MIC and MBC values of 8 and 16 µg/mL, respectively, by damaging the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane (Yusook et al. 2017). 501 resisted the activity of multidrug resistant enterococci with antibiofilm-producing activity, increasing membrane permeability and causing loss of salt tolerance (Sianglum et al. 2019). 579 possessed antimicrobial activities against S. aureus (T28.1, T25.10, T26A4, 08143), Trypanosoma brucei, and Leishmania mexicana with MIC values of 6.8–55.0 µM (Bocquet et al. 2019).
Several monoprenylated isoflavonoids exhibited potent natural antifungal against Z. parabailii acting by severely compromising the membrane integrity, fifteen (690, 734, 735, 777, 778, 949, 951–953, 968–970, 975, 978, and 989) of which showed moderate to good antifungal activity against Z. parabailii (MIC ≤ 50 µg/mL) at pH 6.5. Wighteone (734), luteone (735), and glabridin (949) showed the highest antifungal activities with MICs of 3.13–6.25, 12.5, and 6.25–12.5 µg/mL. The fungicidal activity of 734 and 949 was 4–8 times higher than that of polygodial (MIC 50 µg/mL) at pH 6.5, the most potent natural agent against Z. parabailii reported so far. However, the diprenylated isoflavones (805 and 854) and diprenylated flavonone (466) did not exert any antifungal activity (MIC ≫ 25 µg/mL). A brief SARs of prenylated flavonoids was shown in Fig. 18 (Kalli et al. 2022). The isoflavans licoricidin (956), 961, and licorisoflavans C − E (958–960) showed marked antibacterial activities against P. gingivalis with MIC value range of 1.56 − 12.5 µg/mL. Cyclization of a single prenyl group could reduce the activity against P. gingivalis by comparing the MIC values of 958–960 with those of 956 and 961 (Villinski et al. 2014). The prenylated isoflavans (945, 952, 962, and 961) from the roots of Glycyrrhiza iconica showed antimicrobial activity against Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 13,311 with MIC values of 2–16 µg/mL (Kırmızıbekmez et al. 2015).
Prenylated flavonoids with antimalarial activity
The prenylated flavonoid scaffolds can be considered as promising skeletons for antiplasmodial activity. Monoprenylated flavonones, 4′-O-Methyl-sigmoidin B (290), abyssinin II (291), sigmoidin B (292), abyssinoflavone IV (322), exhibited antiplasmodial activity with IC50 values of 4.37, 6.87, 7.14, and 7.96 µM, respectively. Diprenylated flavonone, sigmoidin A (477), abyssinin III (489), sigmoidin F (513) and abyssinoflavone V (514), exhibited antiplasmodial activity with IC50 values 3.02, 2.32, 2.29, and 9.51 µM, respectively. However, sigmoidins C (345) and D (346), and erylatissin G (347) show weak antiplasmodial activity, indicating that cyclization of the prenyl side chain would dramatically decrease the antiplasmodial activity (Tuenter et al. 2019). Tripteryols B (467) and A (508) from Tripterygium wilfordii were active against chloroquine-sensitive D6 and resistant W2 clones of Plasmodium falciparum with IC50 values in the range of 3.15–4.63 µg/mL. A novel flavan-4-ol analogue rhodiflavan C (548) bearing an unprecedented five-membered A-ring bearing two prenyl groups at C8 and a pair of rare diastereomers rhodiflavans A (549) and B (550) possessing a chromene-5,7-dione unit and three prenyl substitutions at the A ring were isolated from Tephrosia rhodesica. They exhibited antiplasmodial activity against the 3D7 strain of Plasmodium falciparum with an IC50 values of 7.0, 7.3, and 5.7 µg/mL (Atilaw et al. 2020).
Other active prenylated flavonoids
Methoxycyclocommunol (113) and cudraflavone C (167), isolated from the bark of Artocarpus integer, exhibited strong PGE2 inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 4.3 and 0.07 µM, respectively, in LPS-treated human whole blood (Shah et al. 2016). Kushenol X (141), Kurarinone (522) and kushenol C (523), 2-[(2′-(1-Hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-7′-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-2′,3′-dihydrobenzofuran)-5-yl]-7-hydroxy-8-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)chroman-4-one (558) exhibited dose-dependently inhibitory activities of hCE 2 with IC50 values of 3.05, 1.46, 2.61, and 1.13 µM, respectively, and were proven to be uncompetitive inhibitors with Ki values of 1.72, 1.73, 0.79, and 1.59 µM and Km values of 5.41, 2.08 3.10, and 2.74 µM, respectively. Comparison of their structures and molecular docking results suggested the hydroxy groups of C-4′ and C-7 and ketone carbonyl group at C-4 in flavonoids were important for their inhibitor activities. (Song et al. 2019).
Tyrosinase inhibitors are important substances to treat abnormal pigmentation disorders, such as melasma, age spots and sites of actinic damage, arising from the accumulation of an excessive level of epidermal pigmentation. Artogomezianone (179) and cudraflavone A (231) repressed melanin production by suppressing tyrosinase activity with IC50 values of 84.8 and 88.4 µM, respectively (Lan et al. 2013). 232 inhibited tyrosinase activity with an IC50 value of 60.5 µg/mL (Abdul Lathiff et al. 2015). Artonin M (261) is from the dried heartwood of Artocarpus altilis and repressed melanin production by suppressing tyrosinase activity with an IC50 value of 74.1 µM (Lan et al. 2013). 279 is from the leaves of Morus alba and significantly inhibited tyrosinase activity, with an IC50 value of 0.26 µM (Yang et al. 2012). Morusyunnansins E (911) and F (912) from the leaves of Morus yunnanensis significantly inhibited mushroom tyrosinase with IC50 values of 1.43 and 0.15 µM, respectively (Hu et al. 2012). Sigmoidin B (292) and 477 are from the stem barks of Erythrina latissimi and exhibited antigenotoxic activity with IC50 values of 52.5 and 44.1 µM, respectively. (Zarev et al. 2017). (2 S)-2′,4′-Dihydroxy-5′-(1′′′,1′′′-dimethylallyl)-8-prenylpinocembrin (492) exhibited strong anti-tyrosinase activity with an IC50 value of 2.32 µM (Peralta et al. 2014). 579 was proven to have a protective effect against HUVEC injury caused by Ang II by improving cell viability from 53.9 to 74.9% (Zhang et al. 2017).
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are enzymes that cleave acetyl groups from acetyl-lysine residues in histones and various nonhistone proteins. Both acetylation and deacetylation of histones play a fundamental role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression, and disruption of the balance between histone acetyltransferases and HDACs causes many disorders and metabolic diseases. Alopecurone J (1011) exerted strong histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitory activity in HeLa and HCT116 cells with IC50 values of 3.85 and 0.08 µM, respectively. The molecular docking results indicated that 1011 could bind to the active pocket of HDAC8, and the resveratrol group of 1011 had hydrophobic interactions with residues Phe 152 and His 143, whose hydroxyl moieties bear metal coordination with Zn2+ (Soltani et al. 2020).
Pharmacological activity
Members of the prenylated flavonoids, such as icariin, icaritin, and xanthohumol, are promising candidates for diverse diseases. The pharmacological activities of the active prenylated flavonoids obtained from plant sources are summarized in this review.
Anticancer activity
Glabratephrin (58) was proposed as an effective and safe compound able to reverse doxorubicin resistance mediated by Pgp in triple negative breast cancers. It increased doxorubicin accumulation and cytotoxicity in triple negative breast cancer cells with high levels of Pgp, without adding significant additional toxicities to doxorubicin treatment. Glycine 185 of Pgp was identified as a critical residue mediating the reduced catalytic efficacy of Pgp elicited by compound 58 in a site-directed mutagenesis experiment. In addition, 58 was predicted to bind two residues, Pha 322 and Gln 721, by in silico molecular docking (Abd–Ellatef et al. 2022). 6-Prenylapigenin (64) suppressed the proliferation of HeLa cells via the MAPK and Akt signaling pathways. Compound 64 increased the protein levels of p-JNK and p-p38, and reduced the expression of p-Akt and p-ERK (Ye et al. 2021). 2-methoxy-2′,4′,4,6-tetrahydroxy-5-lavanduly dihydrochalcone (671) could significantly activate autophagic flux and trigger ROS release in HepG2 cells. However, it did not affect the main proteins of the apoptosis signaling pathway (Yang et al. 2021). A new prenylated flavone (165), isolated from Daphne giraldii, selectively inhibited the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells by activating the p38/MAPK pathway without apparent cytotoxicity to normal human cells. It also repressed tumor growth in a nude mouse xenograft model without significantly affecting body weight or pathology characteristics. Mechanistically, 165 resulted in G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis by downregulating the expression of cyclin E1, CDK2, and CDK4 and promoting the cleavage of caspase 3 and PARP in HCC cells. It aggravated p38 phosphorylation and attenuated JNK phosphorylation which were abrogated by SB203580, a p38/MAPK-specific inhibitor, and exacerbated by SP600125, a JNK/MAPK-specific inhibitor, indicating 165-induced apoptosis in a p38/MAPK dependent manner (Wang et al. 2017a). A further mechanistic study indicated that 165-induced p38-dependent apoptosis was related to oxidative and nitrosative stress in HCC cells (Shang et al. 2018). 169-induced primary glioblastoma cell apoptosis was mediated by the activation of the mitochondrial pathway involving mitochondrial depolarization, ROS production, cytochrome c release, Bad and Bax upregulation, and Bcl-2 downregulation. The 169-induced ROS generation activated Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation which resulted in PARP cleavage and caspase-3, -7, and − 9 activation (Lee et al. 2018). Norartocarpin (173) was identified as an Nrf2 activator and prevented oxidative insults in human lung epithelial cells. 173 upregulated the protein levels of Nrf2 and its downstream genes NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) and γ-glutamyl cysteine synthetase (GCLM) by facilitating the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and enhancing Nrf2 protein stability (Yang et al. 2019). 204 is from the root bark of Morus australis and effectively inhibited the proliferation and survival of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cells in vitro and repressed tumor growth in vivo. It resulted in paraptosis-like cell death, a novel mode of nonapoptotic programmed cell death that is characterized by extensive cytoplasmic vacuolation due to dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria and lack of apoptotic hallmarks. 204 also resulted in an obvious enhancement of mitochondrial Ca2+ levels, accumulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers, generation of ROS, and depletion of Δψm in EOC cells. 204-induced paraptosis-like cell death was supposed to relate to overloaded mitochondrial Ca2+ causing mitochondrial swelling and dysfunction for the treatment of voltage-dependent anion channel inhibitor, 4,4′-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid, which reversed the aforementioned effect in vitro and in vivo (Xue et al. 2018). In addition, 204 was found to be a promising candidate for cancer treatment, including lung cancer. It induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis through chromatin condensation, PARP cleavage, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) loss, cytochrome c release, Bax/Bcl-2 dysregulation, and caspase-3 cleavage. It also caused a pro-autophagic effect, accompanied by an increased level of LC3-II and a decreased level of SQSTM1/p62. 204 enhanced intracellular ROS levels, inhibited PI3K/Akt signaling and activated the JNK and ERK pathways, which was confirmed by treatment with the corresponding enzyme inhibitors (Wang et al. 2020c). 202, derived from the stem bark of Artocarpus elasticus, suppressed breast cancer cell viability by inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis. 202 enhanced the release of total ROS and polarized the mitochondrial membrane. It upregulated the expression of cytochrome c, Bax, caspase-7 and -9, and p21 and downregulated the expression of MAPK and cyclin D at the transcriptional and translational levels. 202 also repressed an inhibitor of apoptosis, livin, to avoid preceding chemotherapeutic resistance and apoptosis evasion (Etti et al. 2017a, b). 267 inhibited the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 with an estimated value of the half-blocking concentration of 5.76 µM in Jurkat T cells and exhibited more effective inhibition of Kv1.3 channels than the nonprenylated compounds, acacetin, chrysin, baicalein, wogonin, and luteolin. 266 showed low cytotoxicity to Jurkat T cells, which indicated that the channel inhibition might be involved in its anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects (Teisseyre et al. 2018). 281 can diminish melanoma cell viability due to autophagy and caspase-dependent apoptosis in the B16-F10 murine melanoma model. 281 abolished the metastatic potential of a melanoma subclone by disrupting integrin signaling and inhibited the development of lung metastatic foci in tumor-challenged animals (Krajnović et al. 2019). In addition, 281 was identified as a noncompetitive inhibitor with a different binding site than acarbose. It bound to α-glucosidase in allosteric sites via hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, van der Waals, and electrostatic forces. The binding of 281 to α-glucosidase affected the tertiary structure of α-glucosidase by changing the hydrophobicity around Tyr and Trp residues. After binding 281, the binding sites of α-glucosidase formed a stable α-helix, which is involved in forming stable hydrogen bonds with the Asn241 residue (Wang et al. 2022). 460 inhibited autophagy-modulating activity by exhibiting autophagosome maturation by blocking the degradation of EGFP puncta in HeLa cells stably expressing EGFP-mRFP-LC3B. It also reduced lysosomal activity and cathepsin maturation by disrupting lysosomal positioning, subsequently inducing apoptosis. Valosin-containing protein (VCP)/p97 was proven to be a potential target protein of 460 in regulating lysosomal positioning for autophagy maturation (Kwon et al. 2020). 522 suppressed the TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of lung epithelial cells. 522 suppressed the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 and Akt induced by TGF-β1 in lung epithelial cells and lung tissues treated with BLM. Oral administration of 522 attenuated fibrotic changes in lung tissues, including the accumulation of collagen, and improved mechanical pulmonary functions (Park et al. 2021).
579, a prenylated chalcone from hops, exhibited diverse anti-cancer activities, such as anti-chronic myelogenous leukemia, anti-breast cancer, and anti-glioma cell activities, but the anti-cancer mechanisms are different. 579 inhibited the proliferation, induced S phase cell cycle arrest, and stimulated apoptosis in K562 cells. It degraded BCR-ABL in a concentration- and time-dependent manner involving the activation of caspase and inhibition of autophagy and the ubiquitin proteasome system in K562 cells (Lu et al. 2019). 579 inhibited the survival of breast cancer cells by modulating the Notch signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. It not only downregulated cell viability and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, but also reduced the activation of the Notch signaling pathway and apoptotic regulators Bcl-2, Bcl-extra large, and caspase 3 (Liu et al. 2016; Sun et al. 2018b). 579 induced reversal of drug resistance via the inhibition of ABCB1-mediated transport of doxorubicin, stimulating ABCB1 ATPase activity and acting as a substrate of ABCB1. 579 bound to the ABCB1 transmembrane domain, which resulted in less protein and ligand position fluctuation, and 579 synergized with the ABCB1 substrate colchicine (Liu et al. 2018a). 579 induced glioma cell autophagy and inhibited tumor growth in vivo through the Akt/mTOR/S6K pathway and MAPK cascade (Lu et al. 2015). 579 induced apoptosis in human malignant glioblastoma cells and the mechanism was related to the increase in ROS species and activation of MAPK pathways, and 579 activated caspase-3 and − 9 and PARP cleavage (Festa et al. 2011). 579 decreased the proliferation of TPC1 cancer cells by inducing DNA fragmentation and promoting cell cycle arrest (Carvalho et al. 2018). The chemoprotective effect of 579 was investigated in vitro in the metabolically competent HepG2 cell line. The results indicated that 579 could act as a scavenger of AFBO, preventing DNA adduct formation and DNA damage induction (Štern et al. 2021). 579 impaired the PMA-driven migratory and invasive capacity of A549 cells by decreasing the level of MMP-9 expression and concomitantly increasing TIMP-1 protein expression, a specific blocker of PRO-MMP-9 activation. 579 decreased the PMA-induced production of VEGF and TGF-β. Furthermore, 579-treatment counteracted the PMA-induced EMT of A549 cells by upregulating of E-cadherin and α-E-catenin and downregulating of N-cadherin, vimentin, and snail-l expression (Slawinska-Brych et al. 2021). 579 significantly induced glioblastoma multiforme cell death and enhanced temozolomide cytotoxicity. Mechanistically, 579 downregulated replication factor C subunit 2 (RFC2), a DNA repair-related gene, which was overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme patients and tumors. MicroRNA-4749-5p, a 579-upregulated microRNA, was identified to target the RFC2 3′ UTR and inhibit RFC2 expression (Ho et al. 2020). 579 inhibited esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by targeting keratin (KRT)-18, which was highly expressed in patient ESCC tissues. Knockdown or overexpression of KRT18 protein abrogated or enhanced the anti-proliferative activity of 579, respectively. 579 could attenuate KRT18 protein expression. However, it did not change the KRT18 mRNA levels. 579 also induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase, which was associated with the modulation of the expression of related markers, including cyclin D1, cyclin D3, cleaved-PARP, Bcl-2, cytochrome c, and Bax (Yin et al. 2020).
818, isolated from Flemingia philippinensis, promoted apoptosis and diminished tumor growth by suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling through an ROS-mediated caspase-independent pathway. It caused selective apoptotic cell death in LNCaP prostate cancer cells by elevating DNA fragmentation, the sub-G1 cell population, c-PARP, the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, AIF and endonuclease G. 818 decreased the phosphorylation of Akt, mTOR and PI3K. However, auriculasin-induced apoptosis did not result in caspase-3, -8, and − 9 activation (Cho et al. 2018). Isoangustone A (845) was proven to be an agonist of AMPK, an important signaling molecule that regulates cell energy homeostasis and autophagy. 845 inhibited mitochondrial respiratory capacity, activated autophagic signaling and induced a complete autophagic flux in colorectal cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner. It also enhanced AMPK and ACC phosphorylation and increased LC3-I&II protein levels in vivo and in vitro in a concentration- and time-dependent manner (Tang et al. 2021). BAS-4, isolated from Brosimum acutifolium, showed potential activity against glioma through the apoptosis pathway mediated by ΔΨm loss and Akt pathway disruption. It inhibited migration and invasion and induced apoptosis via mitochondrial damage, ΔΨm loss, cell cycle arrest, and Akt phosphorylation suppression in glioma cells. However, it did not induce cytotoxicity in primary glial cells (Maués et al. 2019). 949 suppressed the tumor formation in the hepatoma xenograft model in vivo without statistically significant changes in body weight. It was proven to restrain the migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and JNK1/2 rather than inhibiting their proliferation. 949 suppressed the protein and mRNA expression of MMP9 by affecting the expression of the NF-κB and AP-1 transcription factors (Hsieh et al. 2014). Two prenylated dihydroisoflavones, sigmoidin I (883) and bidwillon A (904), and two prenylated pterocarpans, 6α-hydroxyphaseollidin (982) and sophorapterocarpan A (990), exhibited promising cytotoxic effects to diverse sensitive cell lines (CCRF-CEM, MDA-MB-231-pcDNA, HCT116, U87MG, and HepG2) with an IC50 value range of 3.36–29.48 µM and drug-resistant cancer cell lines [CEM/ADR5000, MDA-MB-231-BCRP, HCT116 (p53−/−), U87MG, and ΔEGFR] with an IC50 value range of 4.60-30.98 µM, and did not exhibit obvious cytotoxicity to the normal cell line AML12, with the IC50 values greater than 98.02 µM (Kuete et al. 2014). 982 induced apoptosis in CCRF-CEM cells mediated by the activation of effector and initiator caspases, including caspase-3, -7, -8, and − 9, breakdown of MMP and increase in ROS production, whereas the apoptotic process induced by abyssinone IV (483), 883, and 990 was alleviated by the loss of MMP and the increase in ROS production (Kuete et al. 2014). A brief summary of the anti-cancer mechanisms of the active ingredients is listed in Table 5..
Anti-inflammatory activity
169 prevented skin damage from UVB irradiation-induced photodamage in hairless mice, probably due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Treatment with 169 at topical doses of 0.05% and 0.1% showed a significant photoprotective effect by decreasing histopathological changes, such as desquamation, epidermal thickening and sunburn cell formation. It exhibited a significant effect by decreasing levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation which have been used as markers of oxidative stress for evaluating UVB irradiation induced skin damage. In addition, 169 downregulated the inflammatory proteins cPLA2 and COX-2 to decrease the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β (Lee et al. 2013). 169 had a potential therapeutic effect on skin wounds by accelerating the inflammatory phase and increasing myofibroblast differentiation, proliferation and migration of fibroblasts and keratinocytes, collagen synthesis and maturation, re-epithelialization, and angiogenesis. It accelerated inflammatory progression and subsequently decreased persistent inflammation. 169 increased collagen production and increased human fibroblast proliferation and migration by activating the p38 and JNK pathways, whereas it increased the proliferation and migration of human keratinocytes through the ERK and p38 pathways and augmented human endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation through the Akt and p38 pathways (Yeh et al. 2017). 190 exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and may be a potential Nrf2 activator. It inhibited the LPS-induced production of NO, TNF-α, and IL-1β in vitro in RAW264.7 and mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. 190 suppressed the expression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Mechanistically, 190 induced OH-1 mRNA and protein expression by activating Nrf2 through the p38 MAPK pathway. When HO-1 was inhibited, the anti-inflammatory effect of 190 was significantly abrogated (Tran et al. 2018). 228, a large amount of prenylated flavonoid in the roots of Morus alba, was identified as a COX-2 and COX-1 inhibitor and decreased the expression and secretion of TNF-α by blocking the translocation of the NF-κB in THP-1 human monocytic leukemia cells (Hošek et al. 2011). Cudraflavanone B (275) suppressed the production of IL-6 and TNF-α and inhibited NF-κB signaling pathway by restraining the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 and BV2 cells. In addition, 275 inhibited the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase, an extracellular signal-regulated kinase, signaling pathways in these LPS-stimulated cells (Ko et al. 2021). Sophoraflavanone M (286) reduced LPS-induced production of inflammatory mediators NO, IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1, and the expression of these mediators at the mRNA level in the LPS-primed RAW264.7 cell line. 286 inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway by suppressing the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα and the translocation of p65. 286 also suppressed JNK phosphorylation to dampen AP-1 transcriptional activity (Han et al. 2021). Neougonin A (416) from Helminthostachys zeylanica reduced the production of the inflammatory mediators TNF-α, PGE2, NO, IL-1β, and IL-6 and the inflammation-related proteins iNOS and COX-2 via the suppression of the NF-κB signal transduction pathway in LPS-induced macrophage RAW264.7 cells. 416 inhibited the phosphorylation of IκBα and blocked the translocation of NF-κB/p65 into the nucleus. However, it had no effect on JNK, ERK1/2, or p38MAPK phosphorylation (Cao et al. 2016). 472 exhibited a potential antineuroinflammatory effect and inhibited NO production activity with an IC50 value of 6.28 in LPS-treated BV2 microglial cells. Mechanistically, it remarkably suppressed the protein expression of iNOS and COX-2. 472 also decreased the production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-12, and IL-1β), blocked the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p50 and p65 by interrupting the degradation and phosphorylation of IκB-α, and inhibited NF-κB binding. In addition, 472 suppressed the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 (Kim et al. 2016). 523 dose-dependently suppressed the production of inflammatory mediators, including NO, PGE2, IL-6, IL1β, MCP-1, and IFN-β, in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages, demonstrating the inhibition of STAT1, STAT6, and NF-κB activation. It augmented the activity of Nrf2 transcription, which was responsible for the upregulation of HO-1 expression and its activity. 523 activated the endogenous antioxidant defense system involving glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase in tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBHP)-induced oxidative stress HaCaT cells, which was relative to upregulated activation of Nrf2 and Akt in the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (Cho et al. 2020). Sophoraflavanone G (527) inhibited LPS-induced production of NO and PGE2 by downregulating the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. It also decreased the mRNA and protein expression levels of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Mechanistically, 527 decreased the levels of phosphorylated PI3K and Akt, and attenuated the expression of phosphorylated JAK and STAT. In addition, it upregulated HO-1 expression via nuclear translocation of Nrf2 (Guo et al. 2016b). Compared with the chronic, unpredictable, mild stress-exposed group, the levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the hippocampus were significantly reduced, and the quantity of 5-HT and NE was increased considerably in the 527-treatment model. 527 upregulated the expression of PI3K, Akt, mTOR, 70S6K, BDNF, and Trkb (Wang et al. 2020b). SPF1 was identified as a potent ligand for RXR, a target related to Alzheimer’s disease. SPF1 potentiated the effect of T0901317, a liver X receptor ligand, on reducing proinflammatory cytokine mRNA levels. It efficiently reduced the mRNA expression levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in vitro. SPF1 increased ATF3 mRNA levels in RAW264.7 cells. However, SPF1 did not affect ATF3 mRNA induction in LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells since ATF3 is also induced by LPS (Wang et al. 2019).
Compound 579 alleviated oxidative damage and accelerated diabetic wound healing via Nrf2 activation in vitro and in vitro. It augmented Nrf2 expression and accelerated diabetic wound healing. 579 caused AMPKα activation and covalent modification of Keap1, which were related to the stabilization and translocation of Nrf2 (Lu et al. 2022). 579 possessed a potential protective effect on LPS-treated depressive-like symptoms mediated by inflammation and oxidative stress. Pretreatment with 579 at doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg reversed the behavioral impairments prophylactically, as was obvious in the forced swimming test and tail suspension test, without affecting locomotion, and the 20 mg/kg dose improved anhedonic behavior, as observed in the sucrose preference test. 579 prevented LPS-induced neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress in a dose-dependent manner. It reduced activated gliosis via attenuation of Iba-1 and GFAP, and the expression of phosph-NF-κB and caspase-3 and enhanced the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 in the hippocampus (Rahman et al. 2021). A brief summary of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the active ingredients is listed in Table 6.
Neuroprotective activity
Neurons are damaged following prolonged exposure to high concentrations of corticosterone and one of the main mechanisms underlying neuronal injury is apoptosis. Icariin (26) protected neurons from damage in hippocampal neuronal cells by protecting them against apoptosis. 26 blocked p38 MAPK phosphorylation, improved mitochondrial membrane potential, and inhibited caspase-3 activation. 26 stimulated mitochondrial activity by upregulating the cortical expression of SIRT1 and PGC-1α and prevented brain ischemic nerve injury (Zhu et al. 2010; Liu et al. 2011). 26 could be used to treat poststroke dementia. It ameliorated the damage in central cholinergic circuit histone acetylation homeostasis by enhancing CREB phosphorylation in the central cholinergic circuits. 26 decreased the levels of acetylcholine and choline acetyltransferase compared with those without 26-treatment (Wang et al. 2013). 522 alleviated the clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and some other neurodegenerative diseases. It was proven that 522 played a functional role in dopamine receptor subtypes, V1AR, 5-HT1AR, and hMAOs. 522 could bind well to dopamine receptor subtypes, unfolding antagonist behavior on D1R (IC50: 42.1 µM) and agonist effects on D2LR and D4R (EC50 22.4 and 71.3 µM, respectively). 522 suppressed hMAO isoenzymes in a modest and nonspecific manner (Prajapati et al. 2021). 579 acted at GABAA receptors in the hippocampal nerve terminals to downregulate the Ca2+ influx by N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels, which subsequently suppressed the Ca2+-calmodulin/PKA cascade to reduce the evoked glutamate release. 579 reduced the frequency of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents without affecting their amplitude (Chang et al. 2016). In addition, 579 reduced infarct volume and improved neurobehavior, mediated by inhibition of inflammatory responses, apoptosis, and platelet activation. 579 decreased the expression of HIF-1α, TNF-α, iNOS, and caspase-3, which were associated with middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal cerebral ischemia (Yen et al. 2012). Morachalcone D (586) and morachalcone E (610), two prenylated flavonoids with similar structures isolated from mulberry leaves, exerted protective effects against glutamate- and erastin-induced HT22 cell death. 586 had more potential than 610 in preventing oxytosis and ferroptosis. 586 attenuated glutamate- and erastin-induced neurotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner at concentrations between 20 µM and 50 µM. However, it had no significant protective effect against neurotoxicity below 15 µM. Mechanistically, the protective effect of 586 was related to the prevention of ROS production, glutathione depletion, and active Fe2+ iron accumulation. 586 upregulated the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, including GPx4, CAT, SOD2, Nrf2, HMOX1 and SLC7A11. The activation of Nrf2 and HO-1 might play an important role in the neuroprotective effect of 586 against oxidative stress (Wen et al. 2020). A brief summary of the neuroprotective mechanisms of the active ingredients was listed in Table 7..
Anti-diabetic and anti-obesity activity
(3,5,4′-trihydroxy-8,3′-dimethoxy-7-(3-methylbut-2-enoxy)flavone (121), a 7-O-prenylated flavonoid from the leaves of Melicope lunuankenda, induces insulin release by acting on pancreatic β-cells in STZ-induced diabetic rats. It ameliorated the derailed blood glucose levels, liver glycogen, and serum biological parameters at a dose of 10 mg/kg in STZ-induced diabetic rats. In vitro, 121 induced insulin release in RIN 5 F cells, which supported its action on pancreatic β-cells. Moreover, 121 did not show any conspicuous toxic symptoms at a dose of 500 mg/kg in the acute toxicity test. (George et al. 2015). 949 stimulated glucose uptake through the AMPK pathway in L6 myotubes. It increased glucose uptake accompanied by the translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane. 949 required at least 4 h to increase glucose uptake, whereas it significantly decreased glycogen and increased lactic acid within 15 min. The 949-induced glucose uptake was abrogated by an AMPK inhibitor or siRNA. However, the inhibitors of PI3K and Akt did not block this progress. Therefore, 949 alleviated the effect of glucose intolerance by AMPK-dependent GLUT4 translocation in the plasma membrane of mouse skeletal muscle (Sawada et al. 2014). 579 had anti-obesity benefits. It decreased the production of dysfunctional fatty acid oxidation and ROS, through mitochondrial uncoupling and stress response induction, and inhibited respiration in a ROS-dependent manner at higher concentrations (Kirkwood et al. 2013). 579 also significantly decreased plasmic purine metabolites, glucose levels, energy metabolites, and body weight in vivo (Legette et al. 2013; Paraiso et al. 2021). The seed extract of Psoralea corylifolia was rich in prenylated flavonoids, which reduced body weight and fat mass in a dose-dependent manner. It prevented obesity by increasing browning and activating thermogenic genes to increase energy expenditure and stimulating thermogenesis in subcutaneous white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue. It induced browning in white adipose tissue, increased p-AMPKα1/2 and p38, and increased brown adipose tissue activity and the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by increasing the expression of uncoupling protein 1 and other thermogenic genes. In addition, it improved insulin sensitivity and prevented hepatic steatosis by increasing lipid oxidation and secretion in HFD-fed mice (Liu et al. 2019a). A brief summary of the anti-diabetic and anti-obesity mechanisms of the active ingredients was listed in Table 7..
Cardioprotective activity
26 ameliorated left ventricular dysfunction and cardiac remodeling by downregulating the activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in rats with congestive heart failure. It could alleviate apoptosis by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax axis, inhibiting the levels of TNF-α, noradrenaline, angiotensin II and brain natriuretic peptide, and blocking the expression and activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 (Song et al. 2011). 26 protected cardiomyocytes and apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK and p38 pathways. It prevented the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 and the protein expression levels of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in Ang II-treated H9c2 cells but upregulated the expression of Bcl-2 (Zhou et al. 2014). 579 inhibited TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation by mediating the PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway. It inhibited the TGF-β1-induced proliferation, differentiation, and collagen overproduction of cardiac fibroblasts by inducing the expression of PTEN and phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR (Jiang et al. 2020). Moreover, 579 exerted a cardioprotective effect by upregulating PTEN expression and inhibiting the phosphorylation of Akt/mTOR in vivo (Sun et al. 2021). 579 was also identified as a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor that regulates cholesterol transfer between lipoproteins, leading to an increase in HDL cholesterol levels and decreasing the risk of atherosclerosis (Hirata et al. 2012). A brief summary of the cardioprotective mechanisms of the active ingredients is listed in Table 7..
Anti-osteoclastogenesis activity
26 inhibited osteoclastogenesis through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated MAPK/TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway and suppressed the activation of the p38 and JNK pathways. 26 suppressed bone resorption, ERK phosphorylation, IL-6, TNF-α, HIF-1α, and COX-2 and PGE2 synthesis. 26 also reduced the size of osteoclast formation and diminished the activity of TRAP and ACP (Hsieh et al. 2011; Kim et al. 2018a). 579 inhibited osteoclastogenesis by modulating the RANKL signaling pathway. It inhibited multinucleated osteoclast formation and transcription factor expression of c-Fos and NFATc1 and suppressed RANKL-induced expression of TRAF6, GAB2, ERK, c-Src, PI3K, and Akt genes, as well as RANKL-induced activity of TRAP (Suh et al. 2013). On the other hand, it stimulated osteoblast differentiation through the p38 MAPK and ERK signaling pathways by modulating ALP activity and the expression of RUNX2 in a mesenchymal stem cell line (Jeong et al. 2011). A brief summary of the anti-osteoclastogenesis mechanisms of the active ingredients was listed in Table 7..
Other activities
949 inhibited dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy via directly binding to the glucocorticoid receptor and inhibiting nuclear translocation of the glucocorticoid receptor. Moreover, 949 inhibited dexamethasone-induced phosphorylation of p38 and FoxO3a (Yoshioka et al. 2019).
492 exerted its antifungal activity on biofilms due to its antioxidant activity. It inhibited Candida albicans strain fluconazole-sensitive and C. albicans strain azole-resistant biofilms, with a prooxidant effect leading to the accumulation of endogenous oxidative metabolites and increased antioxidant defenses. COMSTAT analysis showed that biofilms treated with higher concentrations exhibited different diffusion distances that could change the flow inside the biofilm matrix (Peralta et al. 2018).
579 inhibited porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus proliferation and decreased viral-induced oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2–HMOX1 pathway. It stimulated genes associated with the antioxidant response in the Nrf2 signaling pathway and upregulated the expression of Nrf2, HMOX1, GCLC, GCLM, and NQO1 in marc-145 cells (Liu et al. 2019b).
Safety
281 display none or remarkably low toxic effect on various non-cancerous cells (Krajnović et al. 2019). 579 exhibited a good safety profile without adverse effects on major organ function and homoeostasis and hepatotoxic effects in mice (Albini et al. 2006; Dorn et al. 2010). A safety study of oral 579 administration was carried out to evaluate the influence on fertility in Sprague Dawley rats. Treatment of 579 (100 mg/kg body weight per day or 0.5% xanthohumol in the diet) by gavage for 28 days did not cause any adverse effects on female reproduction and the development of offspring (Hussong et al. 2005). 820 and 895 can inhibit cancer cell proliferation at < 10 µM with no cytotoxicities to normal cells (Bueno Perez et al. 2013; Venturelli et al. 2016). It is worthy to mention that many functional foods and traditional herbal medicines are rich in prenylated flavonoids, indicating the safety of prenylated flavonoids.
Conclusion
In this review, the research progress on phytochemistry and pharmacological activity of prenylated flavonoids and plant resources in the past decade were comprehensively summarized. Prenylated flavonoids showed great potential in anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, cardioprotective, and anti-osteoclastogenic activities. Due to the presence of the prenyl group, the bioavailability of prenylated flavonoids was improved and they had more potential in drug development than nonprenylated flavonoids. Several studies have confirmed that prenylation can increase the bioactivities of flavonoids. In this review, we made the best possible effort to summarize the available information and evidence. This review could be a useful tool in assisting researchers in discovering the new medicinal value of prenylated flavonoids.
References
Abd-Ellatef GEF, Gazzano E, El-Desoky AH, Hamed AR, Kopecka J, Belisario DC, Costamagna C, Marie S, Fahmy MA, Abdel-Hamid SR, Riganti AZ C (2022) Glabratephrin reverses doxorubicin resistance in triple negative breast cancer by inhibiting P-glycoprotein. Pharmacol Res 175:105975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105975
Abdul Lathiff SM, Jemaon N, Abdullah SA, Jamil S (2015) Flavonoids from Artocarpus anisophyllus and their bioactivities. Nat Prod Commun 10(3):1934578X1501000305. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1501000305
Abdullah SA, Jamil S, Basar N, Abdul Lathiff SM, Mohd Arriffin N (2017) Flavonoids from the leaves and heartwoods of Artocarpus lowii King and their bioactivities. Nat Prod Res 31(10):1113–1120. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1222387
Abdullah I, Phongpaichit S, Voravuthikunchai SP, Mahabusarakam W (2018) Prenylated biflavonoids from the green branches of Garcinia dulcis. Phytochem Lett 23:176–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.12.004
Abourashed EA, Abraha A, Khan SI, McCants T, Awan S (2015) Potential of horse apple isoflavones in targeting inflammation and tau protein fibrillization. Nat Prod Commun 10(9):1934578X1501000923. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1501000923
Adam Suleiman MH (2015) Prenylated flavonoids from the stem wood of Commiphora opobalsamum (L.) Engl. (Burseraceae). J King Saud Univ Sci 27(1):71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2014.04.005
Ahn J, Kim Y-M, Chae H-S, Choi YH, Ahn H-C, Yoo H, Kang M, Kim J, Chin Y-W (2019) Prenylated flavonoids from the roots and rhizomes of Sophora tonkinensis and their effects on the expression of inflammatory mediators and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. J Nat Prod 82(2):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00748
Akashi T, Sasaki K, Aoki T, Ayabe S, Yazaki K (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cdna for pterocarpan 4-dimethylallyltransferase catalyzing the key prenylation step in the biosynthesis of glyceollin, a soybean phytoalexin1,[w]. Plant Physiol 149(2):683–693. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.123679
Akihisa T, Motoi T, Seki A, Kikuchi T, Fukatsu M, Tokuda H, Suzuki N, Kimura Y (2012) Cytotoxic activities and anti-tumor-promoting effects of microbial transformation products of prenylated chalcones from Angelica keiskei. Chem Biodivers 9(2):318–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201100255
Albini A, Dell’Eva R, Venè R, Ferrari N, Buhler DR, Noonan DM, Fassina G (2006) Mechanisms of the antiangiogenic activity by the hop flavonoid xanthohumol: NF-κB and akt as targets. FASEB J 20:527–529. http://www.fasebj.org/cgi/doi/https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-5128fje
Ali MS, Ali MI, Ahmed G, Afza N, Lateef M, Iqbal L, Waffo AFK, Ahmed Z (2012) Potent antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory flavanone and chalcone from Erythrina mildbraedii Harms (Fabaceae) of cameroon. Z Naturforsch B 67(1):98–102. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2012-0116
Anh HLT, Tuan DT, Trang DT, Tai BH, Nguyen XN, Yen PH, Kiem PV, Minh CV, Duc TM, Kang HK, Kim YC, Kim YH (2017) Prenylated isoflavones from Cudrania tricuspidata inhibit NO production in RAW 264.7 macrophages and suppress HL-60 cells proliferation. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19(5):510–518. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2016.1232253
Araya-Cloutier C, Vincken J-P, van de Schans MGM, Hageman J, Schaftenaar G, den Besten HMW, Gruppen H (2018) QSAR-based molecular signatures of prenylated (iso)flavonoids underlying antimicrobial potency against and membrane-disruption in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. Sci Rep 8(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27545-4
Ateba SB, Njamen D, Ukowitz K, Zehl M, Kählig H, Hobiger S, Jungbauer A, Krenn L (2016) New flavonoids from the underground parts of Eriosema laurentii. Phytochem Lett 18:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2016.10.003
Atilaw Y, Muiva-Mutisya L, Bogaerts J, Duffy S, Valkonen A, Heydenreich M, Avery VM, Rissanen K, Erdélyi M, Yenesew A (2020) Prenylated Flavonoids from the roots of Tephrosia rhodesica. J Nat Prod 83(8):2390–2398. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00245
Bao S, Luo L, Wan Y, Xu K, Tan G, Fan J, Li S-M, Yu X (2021) Regiospecific 7-O-prenylation of anthocyanins by a fungal prenyltransferase. Bioorg Chem 110:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104787
Bartmańska A, Tronina T, Poplonski J, Milczarek M, Filip-Psurska B, Wietrzyk J (2018) Highly cancer selective antiproliferative activity of natural prenylated flavonoids. Molecules 23(11):29221–292214. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112922
Bartmańska A, Tronina T, Poplonski J (2019) Biotransformation of a major beer prenylflavonoid - isoxanthohumol. Z naturforsch C. J Biosci 74(1–2):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2018-0101
Belofsky G, Aronica M, Foss E, Diamond J, Santana F, Darley J, Dowd PF, Coleman CM, Ferreira D (2014) Antimicrobial and antiinsectan phenolic metabolites of Dalea searlsiae. J Nat Prod 77(5):1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1021/np401083g
Bocquet L, Sahpaz S, Bonneau N, Beaufay C, Mahieux S, Samaillie J, Roumy V, Jacquin J, Bordage S, Hennebelle T, Chai F, Quetin-Leclercq J, Neut C, Rivière C (2019) Phenolic compounds from Humulus lupulus as natural antimicrobial products: new weapons in the fight against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Leishmania mexicana and Trypanosoma brucei strains. Molecules 24(6):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061024
Boozari M, Nejad Ebrahimi S, Soltani S, Tayarani-Najaran Z, Emami SA, Asili J, Iranshahi M (2019a) Absolute configuration and anti-cancer effect of prenylated flavonoids and flavonostilbenes from Sophora pachycarpa: possible involvement of wnt signaling pathway. Bioorg Chem 85:498–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.01.051
Boozari M, Soltani S, Iranshahi M (2019) Biologically active prenylated flavonoids from the genus Sophora and their structure-activity relationship-a review. Phytother Res 33(3):546–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6265
Bueno Perez L, Li J, Lantvit DD, Pan L, Ninh TN, Chai H-B, Soejarto DD, Swanson SM, Lucas DM, Kinghorn AD (2013) Bioactive constituents of Indigofera spicata. J Nat Prod 76(8):1498–1504. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400567c
Cao L, Li R, Chen X, Xue Y, Liu D (2016) Neougonin A inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses via downregulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Inflammation 39(6):1939–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0429-9
Cao Y-G, Zheng X-K, Yang F-F, Li F, Qi M, Zhang Y-L, Zhao X, Kuang H-X, Feng W-S (2018) Two new phenolic constituents from the root bark of Morus alba L. and their cardioprotective activity. Nat Prod Res 32(4):391–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1309535
Carvalho DO, Freitas J, Nogueira P, Henriques SN, Carmo AM, Castro MA, Guido LF (2018) Xanthohumol inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human thyroid cells. Food Chem Toxicol 121:450–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.021
Chang Y, Lin TY, Lu CW, Huang SK, Wang YC, Wang SJ (2016) Xanthohumol-induced presynaptic reduction of glutamate release in the rat hippocampus. Food Funct 7(1):212–226. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo01005e
Chang Y-S, Jin H-G, Lee H, Lee D-S, Woo E-R (2019) Phytochemical constituents of the root bark from Morus alba and their Il-6 inhibitory activity. Nat Prod Sci 25(3):268–274. https://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.3.268
Chen L, Duan Y, Li C, Wang Y, Tong X, Dai Y, Yao X (2013) Four new prenylated flavonoids from the roots of Cudrania tricuspidata. Magn Reson Chem 51(12):842–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.4020
Chen R, Xiao L, Zou J, Yin Y, Ou B, Li J, Wang R, Xie D, Zhang P, Dai J (2013) Regio- and stereospecific prenylation of flavonoids by Sophora flavescens. prenyltransferase Adv Synthesis Catal 355(9):1817–1828. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201300196
Chen R, Gao B, Liu X, Ruan F, Zhang Y, Lou J, Feng K, Wunsch C, Li S-M, Dai J, Sun F (2016) Molecular insights into the enzyme promiscuity of an aromatic prenyltransferase. Nat Chem Biol 13:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2263
Chen Y, Zhao J, Qiu Y, Yuan H, Khan SI, Hussain N, Iqbal Choudhary M, Zeng F, Guo D-A, Khan IA, Wang W (2017) Prenylated flavonoids from the stems and roots of Tripterygium wilfordii. Fitoterapia 119:64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2017.04.003
Chien TV, Nguyen TA, Nguyen TT, Thao TTP, Loc TV, Sung TV (2019) Two new prenylated isoflavones from Maclura cochinchinensis collected in Hoa Binh province Vietnam. Nat Prod Res 33(2):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1443096
Cho H-D, Lee J-H, Moon K-D, Park K-H, Lee M-K, Seo K-I (2018) Auriculasin-induced ROS causes prostate cancer cell death via induction of apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 111:660–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.12.007
Cho BO, Che DN, Kim JS, Kim JH, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Jang SI (2020) In vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress activities of Kushenol C isolated from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081768
Cuca-Suarez LE, Della-Monache F, Coy-Barrera E (2015) Cytotoxic constituents from bark and leaves of Amyris pinnata Kunth. Rec. Nat Prod 9(3):441–445
Darmawan A, Megawati, Lotulung PDN, Fajriah S, Primahana G, Meiliawati L (2015) A new flavonoid derivative as cytotoxic compound isolated from ethyl acetate extract of Macaranga gigantifolia Merr. Leaves. Procedia Chem 16:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2015.12.021
Daus M, Chaithada P, Phongpaichit S, Watanapokasin R, Carroll AR, Mahabusarakam W (2017) New prenylated dihydrochalcones from the leaves of Artocarpus elasticus. Phytochem Lett 19:226–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.01.007
Derese S, Barasa L, Akala HM, Yusuf AO, Kamau E, Heydenreich M, Yenesew A (2014) 4′-Prenyloxyderrone from the stem bark of Millettia oblata ssp. teitensis and the antiplasmodial activities of isoflavones from some Millettia species. Phytochem Lett 8:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2014.02.001
Desta ZY, Majinda RRT (2014) Three new isoflavonoids from Erythrina caffra. Nat Prod Commun 9(6):817–820. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1400900622
Ding W-J, Zhang S-Q, Wang J-H, Lin Y-X, Liang Q-X, Zhao W-J, Li C-Y (2013) A new di-O-prenylated flavone from an actinomycete Streptomyces sp. MA-12. J Asian Nat Prod Res 15(2):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2012.751979
Dizamatova A, Zhumanova K, Zhusupova GE, Zhussupova AI, Srivedavyasasri R, Ibrahim MA, Ross SA (2019) A new prenylated isoflavonoid from Limonium leptophyllum. Nat Prod Commun. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x19844137
Domínguez-Villegas V, Domínguez-Villegas V, García ML, Calpena A, Clares-Naveros B, Garduño-Ramírez ML (2013) Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities of methanolic extract and prenylated flavanones isolated from leaves of Eysehardtia platycarpa. Nat Prod Commun 8(2):177–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0612-9
Dorn C, Bataille F, Gaebele E, Heilmann J, Hellerbrand C (2010) Xanthohumol feeding does not impair organ function and homoeostasis in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 48(7):1890–1897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.04.030
Dzoyem JP, Nkuete AHL, Ngameni B, Eloff JN (2017) Anti-inflammatory and anticholinesterase activity of six flavonoids isolated from Polygonum and Dorstenia species. Arch Pharm Res 40(10):1129–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0612-9
El-Gamal AA, Al-Massarani SM, Abdel-Mageed WM, El-Shaibany A, Al-Mahbashi HM, Basudan OA, Badria FA, Al-Said MS, Abdel-Kader MS (2017) Prenylated flavonoids from Commiphora opobalsamum stem bark. Phytochemistry 141:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.05.014
Etti IC, Rasedee A, Hashim NM, Abdul AB, Kadir A, Yeap SK, Waziri P, Malami I, Lim KL, Etti CJ (2017b) Artonin E induces p53-independent G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and livin suppression in MCF-7 cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 11:865–879. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S124324
Fan Y-H, Ye R, Xu H-Y, Feng X-H, Ma C-M (2019) Structures and in vitro antihepatic fibrosis activities of prenylated dihydrostilbenes and flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Leaves. J Food Sci 84(5):1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14592
Fareza MS, Syah YM, Mujahidin D, Juliawaty LD, Kurniasih I (2014) Antibacterial flavanones and dihydrochalcones from Macaranga trichocarpa. Z Naturforsch C: J Biosci 69(9/10):375–380. https://doi.org/10.5560/znc.2014-0066
Fei W-T, Zhang J-J, Tang R-Y, Yue N, Zhou X, Wang L-Y (2020) Two new prenylated flavonoids from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia with their inhibitory activity on α-glucosidase. Phytochem Lett 39:64–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2020.07.005
Feng K-P, Chen R-D, Li J-H, Tao X-Y, Liu J-M, Zhang M, Dai J-G (2016) Flavonoids from the cultured cells of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. J Asian Nat Prod Res 18(3):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2015.1074573
Festa M, Capasso A, D′Acunto CW, Masullo M, Rossi AG, Pizza C, Piacente S (2011) Xanthohumol induces apoptosis in human malignant glioblastoma cells by increasing reactive oxygen species and activating MAPK pathways. J Nat Prod 74(12):2505–2513. https://doi.org/10.1021/np200390x
Fongang YSF, Bankeu JJK, Ali MS, Awantu AF, Zeeshan A, Assob CN, Mehreen L, Lenta BN, Ngouela SA, Tsamo E (2015) Flavonoids and other bioactive constituents from Ficus thonningii Blume (Moraceae). Phytochem Lett 11:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2014.11.012
Fu M, Feng S, Zhang N, Zhou X, Huang R, Huang H, Xu Z, Li X, Qiu SX (2012) A new prenylated isoflavone and a new flavonol glycoside from Flemingia philippinensis. Helv Chim Acta 95(4):598–605. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.201100360
Gao S, Sun D, Wang G, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Li G, Zhang K, Wang L, Huang J, Chen L (2016) Growth inhibitory effect of paratocarpin E, a prenylated chalcone isolated from Euphorbia humifusa Wild., by induction of autophagy and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Bioorg Chem 69:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.10.005
Gbaweng AJY, Daïrou H, Zingué S, Emmanuel T, Tchinda AT, Frédérich M, Mbafor JT (2020) Excelsanone, a new isoflavonoid from Erythrina excelsa (Fabaceae), with in vitro antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxic effects on prostate cancer cells lines. Nat Prod Res 34(5):659–667
George S, Ajikumaran Nair S, Johnson AJ, Venkataraman R, Baby S (2015) O-prenylated flavonoid, an antidiabetes constituent in Melicope lunu-ankenda. J Ethnopharmacol 168:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.060
Grienke U, Richter M, Walther E, Hoffmann A, Kirchmair J, Makarov V, Nietzsche S, Schmidtke M, Rollinger JM (2016) Discovery of prenylated flavonoids with dual activity against influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sci Rep 6:27156. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27156
Gumula I, Heydenreich M, Derese S, Ndiege IO, Yenesew A (2012) Four isoflavanones from the stem bark of Platycelphium voense. Phytochem Lett 5(1):150–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2011.11.012
Guo C, Yang L, Luo J, Zhang C, Xia Y, Ma T, Kong L (2016a) Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 38:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.06.021
Guo Z, Li X, Li J, Yang X, Zhou Y, Lu C, Shen Y (2016b) Licoflavonol is an inhibitor of the type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477(4):998–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.018
Han F, Lee I-S (2017) A new flavonol glycoside from the aerial parts of Epimedium koreanum. Nakai Nat Prod Res 31(3):320–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1239092
Han Y, Zhang X, Kang Y, Gao Y, Li X, Qi R, Cai R, Qi Y (2021) Sophoraflavanone M, a prenylated flavonoid from Sophora flavescens Ait., suppresses pro-inflammatory mediators through both NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 signaling pathways in LPS-primed macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 907:174246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174246
Hanáková Z, Hošek J, Babula P, Dall′Acqua S, Václavík J, Šmejkal K (2015) C-Geranylated flavanones from Paulownia tomentosa fruits as potential anti-inflammatory compounds acting via inhibition of TNF-α production. J Nat Prod 78(4):850–863. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00005
Hanáková Z, Hošek J, Kutil Z, Temml V, Landa P, Vaněk T, Schuster D, Dall’Acqua S, Cvačka J, Polanský O, Šmejkal K (2017) Anti-inflammatory activity of natural geranylated flavonoids: cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibitory properties and proteomic analysis. J Nat Prod 80(4):999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b01011
Harish V, Haque E, Smiech M, Taniguchi H, Jamieson S, Tewari D, Bishayee A (2021) Xanthohumol for human malignancies: Chemistry, pharmacokinetics and molecular targets. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094478
He Q-F, Wu Z-L, Huang X-J, Zhong Y-L, Li M-M, Jiang R-W, Li Y-L, Ye W-C, Wang Y (2018) Cajanusflavanols A – C, three pairs of flavonostilbene enantiomers from Cajanus cajan. Org Lett 20:876–879. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00010
Herlina T, Aloanis AA, Kurnia D, Harneti D, Maharani R, Supratman U (2017) Prenylated isoflavanones from the stem bark of Erythrina poeppigiana (Leguminosae) and its Antimalarial Properties. Nat Prod Commun 12(8):1934578X1701200825. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1701200825
Hiep NT, Kwon J, Kim D-W, Hwang BY, Lee H-J, Mar W, Lee D (2015) Isoflavones with neuroprotective activities from fruits of Cudrania tricuspidata. Phytochemistry 111:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.10.021
Higa M, Imamura M, Shimoji K, Ogihara K, Suzuka T (2012) Isolation of six new flavonoids from Melicope triphylla. Chem Pharm Bull 60(9):1112–1117. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c12-00213
Hikita K, Yamada S, Shibata R, Katoh M, Murata T, Kato K, Tanaka H, Kaneda N (2015) Inhibitory effect of isoflavones from Erythrina poeppigiana on the growth of HL-60 human leukemia cells through inhibition of glyoxalase I. Nat Prod Commun 10(9):1934578X1501000924. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1501000924
Hirata H, Takazumi K, Segawa S, Okada Y, Kobayashi N, Shigyo T, Chiba H (2012) Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone from Humulus lupulus L. inhibits cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Food Chem 134(3):1432–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.043
Ho K-H, Kuo T-C, Lee Y-T, Chen P-H, Shih C-M, Cheng C-H, Liu A-J, Lee C-C, Chen K-C (2020) Xanthohumol regulates miR-4749-5p-inhibited RFC2 signaling in enhancing temozolomide cytotoxicity to glioblastoma. Life Sci 254:117807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117807
Hošek J, Bartos M, Chudík S, Dall′Acqua S, Innocenti G, Kartal M, Kokoška L, Kollár P, Kutil Z, Landa P, Marek R, Závalová V, Žemlička M, Šmejkal K (2011) Natural compound cudraflavone B shows promising anti-inflammatory properties in vitro. J Nat Prod 74(4):614–619. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100638h
Hossain MA, Mizanur Rahman SM (2015) Isolation and characterisation of flavonoids from the leaves of medicinal plant Orthosiphon stamineus. Arab J Chem 8(2):218–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.06.016
Hsieh T-P, Sheu S-Y, Sun J-S, Chen M-H (2011) Icariin inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppression of MAPKs/NF-κB regulated HIF-1α and PGE2 synthesis. Phytomedicine 18(2–3):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2010.04.003
Hsieh M-J, Lin C-W, Yang S-F, Chen M-K, Chiou H-L (2014) Glabridin inhibits migration and invasion by transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through modulation of NF-κB and AP-1 activity in human liver cancer cells. Br J Pharmacol 171(12):3037–3050. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12626
Hu X, Wu J-W, Wang M, Yu M-H, Zhao Q-S, Wang H-Y, Hou A-J (2012) 2-Arylbenzofuran, flavonoid, and tyrosinase inhibitory constituents of Morus yunnanensis. J Nat Prod 75(1):82–87. https://doi.org/10.1021/np2007318
Huang Y-L, Shen C-C, Shen Y-C, Chiou W-F, Chen C-C (2017) Anti-inflammatory and antiosteoporosis flavonoids from the rhizomes of Helminthostachys zeylanica. J Nat Prod 80(2):246–253. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01164
Hudcová T, Bryndová J, Fialová K, Fiala J, Karabín M, Jelínek L, Dostálek P (2014) Antiproliferative effects of prenylflavonoids from hops on human colon cancer cell lines. J Inst Brew 120(3):225–230. https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.139
Huong TT, Nguyen XC, Tram LH, Quang TT, Duong LV, Nguyen HN, Nguyen TD, Huong PTT, Diep CN, Kiem PV, Minh CV (2012) A new prenylated aurone from Artocarpus altilis. J Asian Nat Prod Res 14(9):923–928. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2012.702758
Huonga DTM, Vu LTN, The Anh L, Cuc NT, Nhiem NX, Tai BH, Van Kiem P, Litaudon M, Dang Thach T, Van Minh C, Pham VC (2019) Cytotoxic prenylated flavonoids from the leaves of Macaranga indica. Phytochem Lett 34:39–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.09.001
Hussain N, Adhikari A, Ahmad MS, Wahab AT, Ali M, Choudhary MI (2017) Two new prenylated flavonoids from the roots of Berberis thunbergii DC. Nat Prod Res 31(7):785–790. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1244195
Hussong R, Frank N, Knauft J, Ittrich C, Owen R, Becker H, Gerhäuser H (2005) A safety study of oral xanthohumol administration and its influence on fertility in Sprague Dawley rats Molecular Nutrition &. Food Res 49:861–867. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200500089
IC Etti, R Abdullah, A Kadir, NM Hashim, SK Yeap, MU Imam, F Ramli, I Malami, KL Lam, U Etti, P Waziri, M Rahman (2017) The molecular mechanism of the anticancer effect of artonin E in MDA-MB 231 triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0182357
Indran IR, Liang RL, Min TE, Yong EL (2016) Preclinical studies and clinical evaluation of compounds from the genus Epimedium for osteoporosis and bone health. Pharmacol Ther 162:188–205
Inoue M, Hitora Y, Kato H, Losung F, Mangindaan REP, Tsukamoto S (2018) New geranyl flavonoids from the leaves of Artocarpus communis. J Nat Med 72(3):632–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1192-z
Jakimiuk K, Gesek J, Atanasov AG, Tomczyk M (2021) Flavonoids as inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 36(1):1016–1028. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2021.1927006
Jeong HM, Han EH, Jin YH, Choi YH, Lee KY, Jeong HG (2011) Xanthohumol from the hop plant stimulates osteoblast differentiation by RUNX2 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 409(1):82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.113
Ji S, Liang W-F, Li Z-W, Feng J, Wang Q, Qiao X, Ye M (2016) Efficient and selective glucosylation of prenylated phenolic compounds by Mucor hiemalis. RSC Adv 6(25):20791–20799. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra00072j
Jiang C, Liu S, He W, Luo X, Zhang S, Xiao Z, Qiu X, Yin H (2012) A new prenylated flavanone from Derris trifoliata Lour. Molecules 17:657–663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010657
Jiang C, Xie N, Sun T, Ma W, Zhang B, Li W (2020) Xanthohumol inhibits TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblasts activation via mediating PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:5431–5439. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S282206
Jo YH, Kim SB, Liu Q, Lee JW, Hwang BY, Lee MK (2015) Benzylated and prenylated flavonoids from the root barks of Cudrania tricuspidata with pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25(17):3455–3457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.017
Jo YH, Lee S, Yeon SW, Turk A, Lee JH, Hong S-M, Han YK, Lee KY, Hwang BY, Kim SY, Lee MK (2021) Anti-diabetic potential of Masclura tricuspidata leaves: Prenylated isoflavonoids with α-glucosidase inhibitory and anti-glycation activity. Bioorg Chem 114:105098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105098
Jung J-W, Ko W-M, Park J-H, Seo K-H, Oh E-J, Lee D-Y, Lee D-S, Kim Y-C, Lim D-W, Han D, Baek N-I (2015) Isoprenylated flavonoids from the root bark of Morus alba and their hepatoprotective and neuroprotective activities. Arch Pharmacal Res 38(11):2066–2075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0613-8
Kalli S, Araya-Cloutier C, Chapman J, Sanders J-W, Vincken J-P (2022) Prenylated (iso)flavonoids as antifungal agents against the food spoiler Zygosaccharomyces parabailii. Food Control 132:108434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108434
Kamel EM, Mahmoud AM, Ahmed SA, Lamsabhi AM (2016) A phytochemical and computational study on flavonoids isolated from Trifolium resupinatum L. and their novel hepatoprotective activity. Food Funct 7(4):2094–2106. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo00194g
Kang W-J, Li D-H, Han T, Sun L, Fu Y-B, Sai C-M, Li Z-L, Hua H-M (2016) New chalcone and pterocarpoid derivatives from the roots of Flemingia philippinensis with antiproliferative activity and apoptosis-inducing property. Fitoterapia 112:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2016.06.003
Khamthong N, Hutadilok-Towatana N (2017) Phytoconstituents and biological activities of Garcinia Dulcis (Clusiaceae): a review. Nat Prod Commun 12(3):1934578X1701200337. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1701200337
Kim D-C, Yoon C-S, Quang TH, Ko W, Kim J-S, Oh H, Kim Y-C (2016) Prenylated flavonoids from Cudrania tricuspidata suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory activities in BV2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Sci 17(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020255
Kim JH, Cho CW, Kim HY, Kim KT, Choi G-S, Kim H-H, Cho IS, Kwon SJ, Choi S-K, Yoon J-Y, Yang SY, Kang JS, Kim YH (2017) α-Glucosidase inhibition by prenylated and lavandulyl compounds from Sophora flavescens roots and in silico analysis. Int J Biol Macromol 102:960–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.092
Kim B, Lee KY, Park B (2018a) Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine 51:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.06.020
Kim JY, Wang Y, Uddin Z, Song YH, Li ZP, Jenis J, Park KH (2018b) Competitive neutrophil elastase inhibitory isoflavones from the roots of Flemingia philippinensis. Bioorg Chem 78:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.03.024
Kim E, Kim Y-M, Ahn J, Chae H-S, Chin Y-W, Kim J (2021) Prenylated flavonoid glycosides with PCSK9 mRNA expression inhibitory activity from the aerial parts of Epimedium koreanum. Molecules 26(12):3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123590
Kirkwood JS, Legette LL, Miranda CL, Jiang Y, Stevens JF (2013) A metabolomics-driven elucidation of the anti-obesity mechanisms of xanthohumol. J Biol Chem 288(26):19000–19013. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.445452
Kırmızıbekmez H, Uysal GB, Masullo M, Demirci F, Bağcı Y, Kan Y, Piacente S (2015) Prenylated polyphenolic compounds from Glycyrrhiza iconica and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Fitoterapia 103:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.05.003
Ko W, Kim K-W, Quang T-H, Yoon C-S, Kim N, Lee H, Kim S-C, Woo E-R, Kim Y-C, Oh H, Lee D-S (2021) Cudraflavanone B isolated from the root bark of Cudrania tricuspidata alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by downregulating NF-κB and ERK MAPK signaling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages and BV2 microglia. Inflammation 44(1):104–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01312-y
Koch K, Schulz G, Doring W, Bučhter C, Havermann S, Mutiso PC, Passreiter C, Watjen W (2019) Abyssinone V, a prenylated flavonoid isolated from the stem bark of Erythrina melanacantha increases oxidative stress and decreases stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Pharm Pharmacol 71(6):1007–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.13074
Kollar P, Bárta T, Hošek J, Souček K, Závalová VM, Artinian S, Talhouk R, Šmejkal K, Suchý P Jr, Hampl A (2013) Prenylated flavonoids from Morus alba L. cause inhibition of G1/S transition in THP-1 human leukemia cells and prevent the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013
Krajnović T, Drača D, Kaluđerović GN, Dunđerović D, Mirkov I, Wessjohann LA, Maksimović-Ivanić D, Mijatović S (2019) The hop-derived prenylflavonoid isoxanthohumol inhibits the formation of lung metastasis in B16-F10 murine melanoma model. Food Chem Toxicol 129:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.04.046
Kuete V, Sandjo LP, Djeussi DE, Zeino M, Kwamou GMN, Ngadjui B, Efferth T (2014) Cytotoxic flavonoids and isoflavonoids from Erythrina sigmoidea towards multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells. Invest New Drugs 32(6):1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0137-y
Kumano T, Richard S-B, Noel J-P, Nishiyama M, Kuzuyama T (2008) Chemoenzymatic syntheses of prenylated aromatic small molecules using streptomyces prenyltransferases with relaxed substrate specificities. Bioorg Med Chem 16:8117–8126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2008.07.052
Kwon M, Jang M, Kim G-H, Oh T, Ryoo I-J, Ryu HW, Oh S-R, Kim BY, Jang J-H, Ko S-K, Ahn JS (2020) Kushenol E inhibits autophagy and impairs lysosomal positioning via VCP/p97 inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol 175:113861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113861
Kyekyeku JO, Kusari S, Adosraku RK, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2016) Prenylated 2-arylbenzofuran derivatives with potent antioxidant properties from Chlorophora regia (Moraceae). Fitoterapia 108:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.11.013
Lai W-C, Tsui Y-T, Singab ANB, El-Shazly M, Du Y-C, Hwang T-L, Wu C-C, Yen M-H, Lee C-K, Hou M-F, Wu Y-C, Chang F-R (2013) Phyto-SERM constitutes from Flemingia macrophylla. Int J Mol Sci 14(8):15578–15594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140815578
Lan W-C, Tzeng C-W, Lin C-C, Yen F-L, Ko H-H (2013) Prenylated flavonoids from Artocarpus altilis: antioxidant activities and inhibitory effects on melanin production. Phytochemistry 89:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.01.011
Lee C-W, Ko H-H, Lin C-C, Chai C-Y, Chen W-T, Yen F-L (2013) Artocarpin attenuates ultraviolet B-induced skin damage in hairless mice by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect. Food Chem Toxicol 60:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.029
Lee SM, Song YH, Uddin Z, Ban YJ, Park KH (2017) Prenylated flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum Nakai and their human neutrophil elastase inhibitory effects. Rec Nat Prod 11(6):514–520. https://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.66.17.05.090
Lee C-W, Hsu L-F, Lee M-H, Lee I-T, Liu J-F, Chiang Y-C, Tsai M-H (2018) Extracts of Artocarpus communis induce mitochondria-associated apoptosis via pro-oxidative activity in human glioblastoma cells. Front Pharmacol 9:411. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00411
Legette LL, Luna AYM, Reed RL, Miranda CL, Bobe G, Proteau RR, Stevens JF (2013) Xanthohumol lowers body weight and fasting plasma glucose in obese male Zucker fa/fa rats. Phytochemistry 91:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.04.018
Lemes BB, da Silva Miguez L, Santos RL, da Rocha Bastos Serafim JC, Figueiredo JMR, Tavares IF, de Godoi Pereira M, de Jesus Marques E, da Silva Ramos F, El-Bacha RS, Ribeiro AI, das Gracas Fernandes da Silva MF, de Souza Neta LC, (2019) Two new prenylated isoflavones from Deguelia costata. Phytochem Lett 30:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.02.018
Li H, Zhai F, Yang M, Li X, Wang P, Ma X (2012) A new benzofuran derivative from Flemingia philippinensis Merr. et Rolfe Molecules 17(7):7637–7644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17077637
Li J, Chen R, Wang R, Liu X, Xie D, Zou J, Dai J (2014) Gua6dt, a regiospecific prenyltransferase from glycyrrhiza uralensis, catalyzes the 6-prenylation of flavones. Chembiochem: A Eu J Chem Biol 15:1673–1681. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402160
Li Y-P, Yang Y-C, Li Y-K, Jiang Z-Y, Huang X-Z, Wang W-G, Gao X-M, Hu Q-F (2014a) Five new prenylated chalcones from Desmodium renifolium. Fitoterapia 95:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.03.026
Li Y-P, Yang Y-C, Li Y-K, Jiang Z-Y, Huang X-Z, Wang W-G, Gao X-M, Hu Q-F (2014b) Prenylated chalcones from Desmodium renifolium. Phytochem Lett 9:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2014.04.003
Li F-F, Sun Q, Wang D, Liu S, Lin B, Liu C-T, Li L-Z, Huang X-X, Song S-J (2016) Chiral separation of cytotoxic flavan derivatives from Daphne giraldii. J Nat Prod 79(9):2236–2242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00305
Li Y, Wu ZH, Zeng KW, Zhao MB, Jiang Y, Li J, Tu PF (2017) A new prenylated flavone from Pleione bulbocodioides. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19(7):738–743. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2017.1311871
Li M, Wu X, Wang X, Shen T, Ren D (2018) Two novel compounds from the root bark of Morus alba L. Nat Prod Res 32(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1327862
Lima NM, Cursino LMC, Lima AM, Souza JVB, de Oliveira AC, Marinho JVN, Nunez CV (2018) Antifungal activity of extracts and phenolic compounds from Deguelia duckeana. Rev Bras Farmacogn 28(6):697–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2018.08.004
Liu B, Zhang H, Xu C, Yang G, Tao J, Huang J, Wu J, Duan X, Cao Y, Dong J (2011) Neuroprotective effects of icariin on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 1375:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.12.053
Liu M, Yin H, Qian X, Dong J, Qian Z, Miao J (2016) Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone from hops, inhibits the viability and stemness of doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7/ADR cells. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010036
Liu F, Hoag H, Wu C, Liu H, Yin H, Dong J, Qian Z, Miao F, Liu M, Miao J (2018a) Experimental and simulation identification of xanthohumol as an inhibitor and substrate of ABCB1. Appl Sci 8(5):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050681. /1-861-11
Liu X, Kuang X-D, He X-R, Ren G, Wang Y, Xu L-Y, Feng L-H, Wang B, Zhou Z-W (2018b) Prenylflavonoids from the twigs of Artocarpus nigrifolius. Chem Pharm Bull 66(4):434–438. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c17-00958
Liu Y, Zhang J, Wen R, Tu G-Z, Chen H-B, Liang H, Zhao Y-Y (2018c) Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative prenylated chalcones from Hedysarum gmelinii. J Asian Nat Prod Res 20(11):1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2018.1450390
Liu J, Zhao Y, Huang C, Li Y, Guo F (2019a) Prenylated flavonoid-standardized extract from seeds of Psoralea corylifolia L. activated fat browning in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Phytother Res 33(7):1851–1864. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6374
Liu X, Song Z, Bai J, Nauwynck H, Zhao Y, Jiang P (2019b) Xanthohumol inhibits PRRSV proliferation, alleviates oxidative stress induced by PRRSV via the Nrf2-HMOX1 axis. Vet Res 50(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-019-0679-2
Liu Y-P, Guo J-M, Yan G, Zhang M-M, Zhang W-H, Qiang L, Fu Y-H (2019c) Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative prenylated isoflavone derivatives from the fruits of Ficus carica. J Agric Food Chem 67(17):4817–4823. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00865
Liu Y-P, Yu X-M, Zhang W, Wang T, Jiang B, Tang H-X, Su Q-T, Fu Y-H (2020) Prenylated chromones and flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus with their potential antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg Chem 101:104030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104030
Long G-Q, Hu G-S, Gao X-X, Jia J-M, Wang A-H (2022) Sophoranone A and B: two new cytotoxic prenylated metabolites and their analogs from the root bark of Sophora flavescens. Nat Prod Res 36(6):1515–1521. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2021.1894562
Lu W-J, Chang C-C, Lien L-M, Yen T-L, Chiu H-C, Huang S-Y, Sheu J-R, Lin K-H (2015) Xanthohumol from Humulus lupulus L. induces glioma cell autophagy via inhibiting Akt/mTOR/S6K pathway. J Funct Foods 18:538–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.08.020
Lu X, Geng J, Zhang J, Miao J, Liu M (2019) Xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops, induces caspase-dependent degradation of oncoprotein BCR-ABL in K562 cells. Antioxidants 8(9):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090402
Lu X, Liu M, Dong H, Miao J, Stagos D, Liu M (2022) Dietary prenylated flavonoid xanthohumol alleviates oxidative damage and accelerates diabetic wound healing via Nrf2 activation. Food Chem Toxicol 160:112813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112813
Luo Y, Li X, He J, Su J, Peng L, Wu X, Du R, Zhao Q (2014) Isolation, characterisation, and antioxidant activities of flavonoids from chufa (Eleocharis tuberosa) peels. Food Chem 164:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.04.103
Ma S, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Du G, Feng L, Huang C, Li Y, Guo F (2016) Prenylflavone derivatives from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia exhibited PPAR-γ agonist activity. Phytochem Lett 16:213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2016.04.016
Mai HDT, Toan TP, Huu GT, Le TN, Oanh VTK, Hang NTM, Thu HT, Chau VM, Litaudon M, Pham VC (2020) New flavonoid and stilbene derivatives from the fruits of Macaranga balansae. Nat Prod Res 34(19):2772–2778. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1587425
Maués LAL, Alves GM, Couto NMG, da Silva BJM, Arruda MSP, Macchi BM, Sena CBC, Prado AF, Crespo-Lopez ME, Silva EO, do Nascimento JLM (2019) Flavonoids from the Amazon plant Brosimum acutifolium induce C6 glioma cell line apoptosis by disrupting mitochondrial membrane potential and reducing AKT phosphorylation. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108728
Milella L, Milazzo S, De Leo M, Vera Saltos MB, Faraone I, Tuccinardi T, Lapillo M, De Tommasi N, Braca A (2016) α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors from Arcytophyllum thymifolium. J Nat Prod 79(8):2104–2112. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00484
Minakawa T, Toume K, Arai MA, Koyano T, Kowithayakorn T, Ishibashi M (2013) Prenylflavonoids isolated from Artocarpus champeden with TRAIL-resistance overcoming activity. Phytochemistry 96:299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.08.015
Molčanová L, Kauerová T, Dall′Acqua S, Maršík P, Kollár P, Šmejkal K (2021) Antiproliferative and cytotoxic activities of C-Geranylated flavonoids from Paulownia tomentosa Steud. Fruit. Bioorg Chem 111:104797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104797
Morel S, Helesbeux J-J, Séraphin D, Derbré S, Gatto J, Aumond M-C, Abatuci Y, Grellier P, Beniddir MA, Le Pape P, Pagniez F, Litaudon M, Landreau A, Richomme P (2013) Anti-AGEs and antiparasitic activity of an original prenylated isoflavonoid and flavanones isolated from Derris ferruginea. Phytochem Lett 6(3):498–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2013.06.002
Mouffouk S, Marcourt L, Benkhaled M, Boudiaf K, Wolfender J-L, Haba H (2017) Two new prenylated isoflavonoids from Erinacea anthyllis with antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Nat Prod Commun 12(7):1934578X1701200716. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1701200716
Muiva-Mutisya LM, Atilaw Y, Heydenreich M, Koch A, Akala HM, Cheruiyot AC, Brown ML, Irungu B, Okalebo FA, Derese S, Mutai C, Yenesew A (2018) Antiplasmodial prenylated flavanonols from Tephrosia subtriflora. Nat Prod Res 32(12):1407–1414. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1353510
Munikishore R, Rammohan A, Padmaja A, Gunasekar D, Deville A, Bodo B (2013) A new O-prenylated flavonol from the roots of Sophora interrupta. Nat Prod Res 27(20):1823–1826. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2012.761622
Na Z, Fan Q-F, Song Q-S, Hu H-B (2017) Three new flavonoids from Millettia pachyloba. Phytochem Lett 19:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.02.002
Nago RDT, Nayim P, Mbaveng AT, Mpetga JDS, Bitchagno GTM, Garandi B, Tane P, Lenta BN, Sewald N, Tene M, Kuete V, Ngouela AS (2021) Prenylated flavonoids and C-15 isoprenoid analogues with antibacterial properties from the whole plant of Imperata cylindrica (L.) Raeusch (Gramineae). Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164717
Navrátilová A, Schneiderová K, Veselá D, Hanáková Z, Fontana A, Dall′Acqua S, Cvacka J, Innocenti G, Novotná J, Urbanová M, Pelletier J, Čížek A, Žemličková H, Šmejkal K (2013) Minor C-geranylated flavanones from Paulownia tomentosa fruits with MRSA antibacterial activity. Phytochemistry 89:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.01.002
Nenaah GE (2014) Toxic and antifeedant activities of prenylated flavonoids isolated from Tephrosia apollinea L. against three major coleopteran pests of stored grains with reference to their structure-activity relationship. Nat Prod Res 28(24):2245–2252. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.932788
Nguyen MTT, Le TH, Nguyen HX, Dang PH, Do TNV, Abe M, Takagi R, Nguyen NT (2017) Artocarmins G-M, prenylated 4-chromenones from the stems of Artocarpus rigida and their tyrosinase inhibitory activities. J Nat Prod 80(12):3172–3178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00453
Nur-e-Alam M, Yousaf M, Parveen I, Hafizur RM, Ghani U, Ahmed S, Hameed A, Threadgill MD, Al-Rehaily AJ (2019) New flavonoids from the saudi arabian plant Retama raetam which stimulates secretion of insulin and inhibits α-glucosidase. Org Biomol Chem 17(5):1266–1276. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ob02755b
Nyandoro SS, Munissi JJE, Kombo M, Mgina CA, Pan F, Gruhonjic A, Fitzpatrick P, Lu Y, Wang B, Rissanen K, Erdélyi M (2017) Flavonoids from Erythrina schliebenii. J Nat Prod 80(2):377–383. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00839
Ohara K, Muroya A, Fukushima N, Yazaki K (2009) Functional characterization of LePGT1, a membrane-bound prenyltransferase involved in the geranylation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Biochem J 421:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081968
Okoth DA, Chenia HY, Koorbanally NA (2013) Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of flavonoids from Lannea alata (Engl) Engl (Anacardiaceae). Phytochem Lett 6(3):476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2013.06.003
Ombito JO, Majinda RRT, Masesane IB, Bojase G, Schuffler A, Opatz T (2018) Prenylated isoflavones from the stem bark of Erythrina sacleuxii. Phytochem Lett 26:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2018.05.026
Orazbekov Y, Ibrahim MA, Srivedavyasasri R, Chaurasiya ND, Tekwani BL, Ross SA, Orazbekov Y, Makhatov B, Ibrahim MA, Mombekov S, Datkhayev U, Tekwani BL, Ross SA (2018) Isolation and biological evaluation of prenylated flavonoids from Maclura pomifera. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:1370368. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1370368
Oyama M, Nakashima K-I, Kamiya T, Haba M, Ito T, Murata H, Tanaka T, Adachi T, Iinuma M, Kinoshita T (2013a) Flavonoids isolated from the leaves of Melicope triphylla and their extracellular-superoxide dismutase-inducing activity. Phytochem Lett 6(2):215–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2013.01.007
Oyama SdO, de Souza LA, Baldoqui DC, Sarragiotto MH, Silva AA (2013b) Prenylated flavonoids from Maclura tinctoria fruits. Quim Nova 36(6):800–802. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422013000600010
Ozaki T, Mishima S, Nishiyama M, Kuzuyama T (2009) NovQ is a prenyltransferase capable of catalyzing the addition of a dimethylallyl group to both phenylpropanoids and flavonoids. J Antibiot 62(7):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.48
Pang X, Yin S-S, Yu H-Y, Zhang Y, Wang T, Hu L-M, Han L-F (2018) Prenylated flavonoids and dihydrophenanthrenes from the leaves of Epimedium brevicornu and their cytotoxicity against HepG2 cell. Nat Prod Res 32(19):2253–2259. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1405410
Pang D, Liao S, Wang W, Mu L, Li E, Shen W, Liu F, Zou Y (2019) Destruction of the cell membrane and inhibition of cell phosphatidic acid biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus: an explanation for the antibacterial mechanism of morusin. Food Funct 10(10):6438–6446. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo01233h
Paraiso IL, Mattio LM, Alcazar Magana A, Choi J, Plagmann LS, Redick MA, Miranda CL, Maier CS, Dallavalle S, Kioussi C, Blakemore PR, Stevens JF (2021) Xanthohumol pyrazole derivative improves diet-induced obesity and induces energy expenditure in high-fat diet-fed mice. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 4(6):1782–1793. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.1c00161
Park S-J, Kim T-H, Lee K, Kang M-A, Jang H-J, Ryu H-W, Oh S-R, Lee H-J (2021) Kurarinone attenuates BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting TGF-β signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168388
Passreiter CM, Suckow-Schnitker A-K, Kulawik A, Addae-Kyereme J, Wright CW, Waetjen W (2015) Prenylated flavanone derivatives isolated from Erythrina addisoniae are potent inducers of apoptotic cell death. Phytochemistry 117:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.04.002
Peng J, Hartley RM, Fest GA, Mooberry SL (2012) Amyrisins A-C, O-Prenylated flavonoids from Amyris madrensis. J Nat Prod 75(3):494–496. https://doi.org/10.1021/np200796e
Peralta MA, Santi MD, Agnese AM, Cabrera JL, Ortega MG (2014) Flavanoids from Dalea elegans: Chemical reassignment and determination of kinetics parameters related to their anti-tyrosinase activity. Phytochem Lett 10:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2014.10.012
Peralta MA, Ortega MG, Cabrera JL, Paraje MG (2018) The antioxidant activity of a prenyl flavonoid alters its antifungal toxicity on Candida albicans biofilms. Food Chem Toxicol 114:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.02.042
Polbuppha I, Suthiphasilp V, Maneerat T, Charoensup R, Limtharakul T, Cheenpracha S, Pyne SG, Laphookhieo S (2021) Macluracochinones A-E, antimicrobial flavonoids from Maclura cochinchinensis. (Lour) Corner Phytochemistry 187:112773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112773
Popoola OK, Marnewick JL, Rautenbach F, Ameer F, Iwuoha EI, Hussein AA (2015) Inhibition of oxidative stress and skin aging-related enzymes by prenylated chalcones and other flavonoids from Helichrysum teretifolium. Molecules 20(4):7143–7155. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20047143
Prajapati R, Seong SH, Paudel P, Park SE, Jung HA, Choi JS (2021) In vitro and In Silico characterization of kurarinone as a dopamine D1A Receptor Antagonist and D2L and D4 receptor agonist. ACS Omega 6(49):33443–33453. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c04109
Qin J, Fan M, He J, Wu X-D, Peng L-Y, Su J, Cheng X, Li Y, Kong L-M, Li R-T, Zhao Q-S (2015a) New cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory compounds isolated from Morus alba L. Nat Prod Res 29(18):1711–1718. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.999333
Qin Y, Yang Y-C, Meng Y-L, Xia C-F, Gao X-M, Hu Q-F (2015b) Chalcones from Desmodium podocarpum and their cytotoxicity. Chem Nat Compd 51(6):1062–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-015-1492-4
Qu K-J, Wang B, Jiang C-S, Xie B-G, Liu A-H, Li S-W, Guo Y-W, Li J, Mao S-C (2021) Rearranged diels-alder adducts and prenylated flavonoids as potential PTP1B inhibitors from Morus nigra. J Nat Prod 84(8):2303–2311. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00403
Quang TH, Ngan NTT, Yoon C-S, Cho K-H, Kang DG, Lee HS, Kim Y-C, Oh H (2015) Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from the roots of Cudrania tricuspidata. Molecules 20(6):11173–11183. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200611173
Rahman SU, Ali T, Hao Q, He K, Li W, Ullah N, Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Li S (2021) Xanthohumol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive like behavior in mice: involvement of NF-κB/Nrf2 signaling pathways. Neurochem Res 46(12):3135–3148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03396-w
Raksat A, Maneerat W, Andersen RJ, Pyne SG, Laphookhieo S (2018) Antibacterial prenylated isoflavonoids from the stems of Millettia extensa. J Nat Prod 81(8):1835–1840. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00321
Ramli F, Rahmani M, Ismail IS, Sukari MA, Abd Rahman M, Zajmi A, Akim AM, Hashim NM, Go R (2016) A new bioactive secondary metabolite from Artocarpus elasticus. Nat Prod Commun 11(8):1934578X1601100818. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1601100818
Rea K-A, Casaretto J-A, Al-Abdul-Wahid M-S, Sukumaran A, Geddes-Mcalister J, Rothstein S-J, Akhtar T-A (2019) Biosynthesis of cannflavins a and B from Cannabis sativa L. Phytochemistry 164:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.05.009
Rees KA, Bermudez C, Edwards DJ, Elliott AG, Ripen JE, Seta C, Huang JX, Cooper MA, Fraser JA, Yeo TC, Butler MS (2015) Flemingin-type prenylated chalcones from the Sarawak Rainforest Plant Desmodium congestum. J Nat Prod 78(8):2141–2144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00410
Rueda DC, De Mieri M, Hering S, Hamburger M (2014) HPLC-based activity profiling for GABAA receptor modulators in Adenocarpus cincinnatus. J Nat Prod 77(3):640–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/np500016z
Ryu HW, Park YJ, Lee SU, Lee S, Yuk HJ, Seo K-H, Kim Y-U, Hwang BY, Oh S-R (2017) Potential anti-inflammatory effects of the fruits of Paulownia tomentosa. J Nat Prod 80(10):2659–2665. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00325
S Maneechai, W De-Eknamkul, K Umehara, H Noguchi, K Likhitwitayawuid (2012) Flavonoid and stilbenoid production in callus cultures of Artocarpus lakoocha. Phytochemistry 81:42–49
Saelee A, Phongpaichit S, Mahabusarakam W (2015) A new prenylated biflavonoid from the leaves of Garcinia dulcis. Nat Prod Res 29(20):1884–1888. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1010087
Sasaki K, Mito K, Ohara K, Yamamoto H, Yazaki K (2008) Cloning and characterization of naringenin 8-prenyltransferase, a flavonoid-specific prenyltransferase of Sophora flavescens. Plant Physiol 146(3):1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.110544
Sasaki K, Tsurumaru Y, Yamamoto H, Yazaki K (2011) Molecular characterization of a membrane-bound prenyltransferase specific for isoflavone from Sophora flavescens. J Biol Chem 286(27):24125–24134. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.244426
Sasaki H, Kashiwada Y, Shibata H, Takaishi Y (2012) Prenylated flavonoids from Desmodium caudatum and evaluation of their anti-MRSA activity. Phytochemistry 82:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.06.007
Sasaki T, Li W, Higai K, Quang TH, Kim YH, Koike K (2014) Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activity of lavandulyl flavonoids from roots of Sophora flavescens. Planta Med 80(7):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368400
Sawada K, Yamashita Y, Zhang T, Nakagawa K, Ashida H (2014) Glabridin induces glucose uptake via the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in muscle cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 393(1–2):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.06.009
Schneiderova K, Slapetova T, Hrabal R, Dvorakova H, Prochazkova P, Novotna J, Urbanova M, Cvacka J, Smejkal K (2013) Tomentomimulol and mimulone B: two new C-geranylated flavonoids from Paulownia tomentosa fruits. Nat Prod Res 27(7):613–618. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2012.683002
Segun PA, Ogbole OO, Ismail FMD, Nahar L, Evans AR, Ajaiyeoba EO, Sarker SD (2019) Bioassay-guided isolation and structure elucidation of cytotoxic stilbenes and flavonols from the leaves of Macaranga barteri. Fitoterapia 134:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.02.019
Seliger JM, Misuri L, Maser E, Hintzpeter J (2018) The hop-derived compounds xanthohumol, isoxanthohumol and 8-prenylnaringenin are tight-binding inhibitors of human aldo-keto reductases 1B1 and 1B10. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 33(1):607–614. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2018.1437728
Selim Y, El-Sharkawy E, Abd El-Azim MHM (2020) New cytotoxic flavonoids from aerial parts of Platycladus orientalis L. Nat Prod Res 34(12):1763–1771. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1530234
Shaffer CV, Cai S, Peng J, Robles AJ, Hartley RM, Powell DR, Du L, Cichewicz RH, Mooberry SL (2016) Texas native plants yield compounds with cytotoxic activities against prostate cancer cells. J Nat Prod 79(3):531–540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00908
Shah MKK, Sirat HM, Jamil S, Jalil J (2016) Flavonoids from the bark of Artocarpus integer var. Silvestris and their anti-inflammatory properties. Nat Prod Commun 11(9):1934578X1601100921. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1601100921
Shahinozzaman M, Taira N, Ishii T, Halim MA, Hossain MA, Tawata S (2018) Anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and anti-alzheimer′s effects of prenylated flavonoids from okinawa propolis: an investigation by experimental and computational studies. Molecules 23(10):24792471–24792418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102479
Shang X-Y, Chen J-J, Song X-Y, Wang W, Chen Y, Yao G-D, Song S-J (2018) Daphnegiravone D from Daphne giraldii nitsche induces p38-dependent apoptosis via oxidative and nitrosative stress in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1426–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.141
Sheliya MA, Rayhana B, Ali A, Pillai KK, Aeri V, Sharma M, Mir SR (2015) Inhibition of α-glucosidase by new prenylated flavonoids from euphorbia hirta L. herb. J Ethnopharmacol 176:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.018
Shen G, Huhman D, Lei Z, Snyder J, Sumner L-W, Dixon R-A (2012) Characterization of an isoflavonoid-specific prenyltransferase from Lupinus albus. Plant Physiol 159(1):70–80. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.195271
Shen G, Huhman D, Lei Z, Snyder J, Sumner L-W, Dixon R-A (2017) Characterization of an isoflavonoid-specific prenyltransferase from Lupinus albus1[w]. Plant Physiol 159:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.195271
Shi S, Li J, Zhao X, Liu Q, Song S (2021) A comprehensive review: biological activity, modification and synthetic methodologies of prenylated flavonoids. Phytochemistry 191:112895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112895
Shim S-H, Kim Y, Lee J-Y, Song D-G, Pan C-H, Jung S-H (2009) Aldose reductase inhibitory activity of the compounds from the seed of Psoralea corylifolia. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 52:568–572. https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.096
Shimomura K, Sugiyama Y, Nakamura J, Ahn M-R, Kumazawa S (2013) Component analysis of propolis collected on Jeju Island, Korea. Phytochemistry 93:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.02.018
Shindo K, Tachibana A, Tanaka A, Toba S, Yuki E, Ozaki T, Kumano T, Nishiyama M, Misawa N, Kuzuyama T (2011) Production of novel antioxidative prenyl naphthalen-ols by combinational bioconversion with dioxygenase phnA1A2A3A4 and prenyltransferase NphB or SCO7190. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:505–510. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.100731
Shour S, Iranshahy M, Pham N, Quinn RJ, Iranshahi M (2017) Dereplication of cytotoxic compounds from different parts of Sophora pachycarpa using an integrated method of HPLC, LC-MS and 1H-NMR techniques. Nat Prod Res 31(11):1270–1276. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1239095
Sianglum W, Muangngam K, Joycharat N, Voravuthikunchai SP (2019) Mechanism of action and biofilm inhibitory activity of lupinifolin against multidrug-resistant enterococcal cinical isolates. Microb Drug Resist 25(10):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2018.0391
Slawinska-Brych A, Mizerska-Kowalska M, Krol SK, Stepulak A, Zdzisinska B (2021) Xanthohumol impairs the PMA-Driven invasive behaviour of lung cancer cell line A549 and exerts anti-EMT action. Cells 10(6):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061484
Smadi A, Ciavatta ML, Bitam F, Carbone M, Villani G, Gavagnin M (2018) Prenylated flavonoids and phenolic compounds from the rhizomes of marine phanerogam Cymodocea nodosa. Planta Med 84(9/10):704–709. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-122747
Soltani S, Boozari M, Nejad Ebrahimi S, Amin GR, Iranshahi M (2020) Histone deacetylase inhibitory and cytotoxic activities of the constituents from the roots of Sophora Pachycarpa. Iran J Pharm Res 19(4):51–58. https://doi.org/10.22037/ijpr.2020.112442.13760
Song Y-H, Cai H, Gu N, Qian C-F, Cao S-P, Zhao Z-M (2011) Icariin attenuates cardiac remodelling through down-regulating myocardial apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinase activity in rats with congestive heart failure. J Pharm Pharmacol 63(4):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01241.x
Song S-S, Sun C-P, Zhou J-J, Chu L (2019) Flavonoids as human carboxylesterase 2 inhibitors: inhibition potentials and molecular docking simulations. Int J Biol Macromol 131:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.060
Song M, Liu Y, Li T, Liu X, Hao Z, Ding S, Panichayupakaranant P, Zhu K, Shen J (2021) Plant natural flavonoids against multidrug resistant pathogens. Adv Sci 8(15):e2100749. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202100749
Sritularak B, Tantrakarnsakul K, Lipipun V, Likhiwitayawuid K (2013) Flavonoids with anti-HSV activity from the root bark of Artocarpus Lakoocha. Nat Prod Commun 8(8):1079–1080. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1300800811
Stec E, Li S-M (2012) Mutagenesis and biochemical studies on AuaA confirmed the importance of the two conserved aspartate-rich motifs and suggested difference in the amino acids for substrate binding in membrane-bound prenyltransferases. Arch Microbiol 194(7):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-012-0795-0
Štern A, Furlan V, Novak M, Štampar M, Kolenc Z, Kores K, Filipič M, Bren U, Žegura B (2021) Chemoprotective effects of xanthohumol against the carcinogenic mycotoxin aflatoxin B1. Foods 10(6):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061331
Su X-H, Li C-Y, Zhong Y-J, Yuan Z-P, Li Y-F, Liang B (2012) A new prenylated chalcone from the seeds of Millettia pachycarpa. Chin J Nat Medicines 10(3):222–225. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1009.2012.00222
Suh KS, Rhee SY, Kim YS, Lee YS, Choi EM (2013) Xanthohumol modulates the expression of osteoclast-specific genes during osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 62:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.08.047
Sukumaran A, McDowell T, Chen L, Renaud J, Dhaubhade S (2018) Isoflavonoid-specific prenyltransferase gene family in soybean: GmPT01, a pterocarpan 2-dimethylallyltransferase involved in glyceollin biosynthesis. Plant J 96:966–981. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14083
Sun Y-J, Hao Z-Y, Si J-G, Wang Y, Zhang Y-L, Wang J-M, Gao M-L, Chen H (2015) Prenylated flavonoids from the fruits of Sinopodophyllum emodi and their cytotoxic activities. RSC Adv 5(101):82736–82742. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra16136c
Sun Q, Li F-F, Wang D, Wu J, Yao G-D, Li X, Li L-Z, Liu Q-B, Huang X-X, Song S-J (2016a) Flavans with cytotoxic activity from the stem and root bark of Daphne giraldii. RSC Adv 6(61):55919–55929. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA08537G
Sun Y-J, Pei L-X, Wang K-B, Sun Y-S, Wang J-M, Zhang Y-L, Gao M-L, Ji B-Y (2016b) Preparative isolation of two prenylated biflavonoids from the roots and rhizomes of Sinopodophyllum emodi by sephadex LH-20 column and high-speed counter-current chromatography. Molecules 21(1):101–1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010010
Sun F, Li Q, Xu J (2017) Chemical composition of roots Flemingia philippinensis and their inhibitory kinetics on aromatase. Chem Biodivers. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201600193
Sun Y, Shi B, Gao M, Fu L, Chen H, Hao Z, Zhang Y, Feng W (2018a) Two new biflavonoids from the roots and rhizomes of Sinopodophyllum emodi. Chem Nat Compd 54(4):649–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-018-2438-4
Sun Z, Zhou C, Liu F, Zhang W, Chen J, Pan Y, Ma L, Liu Q, Du Y, Yang J, Wang Q (2018b) Inhibition of breast cancer cell survival by xanthohumol via modulation of the notch signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Oncol Lett 15(1):908–916. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7434
Sun Y, Chen H, Wang J, Gao M, Zhao C, Han R, Chen H, Li M, Xue G, Feng W (2019) Sixteen new prenylated flavonoids from the fruit of Sinopodophyllum hexandrum. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173196
Sun T-L, Li W-Q, Tong X-L, Liu X-Y, Zhou W-H (2021) Xanthohumol attenuates isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulating PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 891:173690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173690
Tang S, Huang W, Ji S, Wang Y, Pei D, Ye M, Yu S (2016) Prenylated flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza uralensis as promising anti-cancer agents: a preliminary structure-activity study. J Chin Pharm Sci 25(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.5246/jcps.2016.01.003
Tang S, Cai S, Ji S, Yan X, Zhang W, Qiao X, Zhang H, Ye M, Yu S (2021) Isoangustone a induces autophagic cell death in colorectal cancer cells by activating AMPK signaling. Fitoterapia 152:104935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2021.104935
Tchamgoue J, Hafizur RM, Tchouankeu JC, Kouam SF, Adhikari A, Hameed A, Green IR, Choudhary MI (2016) Flavonoids and other constituents with insulin secretion activity from Pseudarthria hookeri. Phytochem Lett 17:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2016.07.015
Teisseyre A, Palko-Labuz A, Uryga A, Michalak K (2018) The influence of 6-prenylnaringenin and selected non-prenylated flavonoids on the activity of Kv1.3 channels in human jurkat T cells. J Membrane Biol 251(5–6):695–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-018-0046-7
Thai QD, Tchoumtchoua J, Makropoulou M, Boulaka A, Meligova AK, Mitsiou DJ, Mitakou S, Michel S, Halabalaki M, Alexis MN, Skaltsounis LA (2016) Phytochemical study and biological evaluation of chemical constituents of Platanus orientalis and Platanus x acerifolia buds. Phytochemistry 130:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.04.006
Thongnest S, Lhinhatrakool T, Wetprasit N, Sutthivaiyakit P, Sutthivaiyakit S (2013) Eriosema chinense: a rich source of antimicrobial and antioxidant flavonoids. Phytochemistry 96:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.06.004
Toume K, Habu T, Arai MA, Koyano T, Kowithayakorn T, Ishibashi M (2015) Prenylated flavonoids and resveratrol derivatives isolated from Artocarpus communis with the ability to overcome TRAIL resistance. J Nat Prod 78(1):103–110. https://doi.org/10.1021/np500734t
Tran HNK, Nguyen VT, Kim JA, Rho SS, Woo MH, Choi JS, Lee JH, Min BS (2017) Anti-inflammatory activities of compounds from twigs of Morus alba. Fitoterapia 120:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2017.05.004
Tran PL, Tran PT, Tran HNK, Lee S, Kim O, Min BS, Lee JH (2018) A prenylated flavonoid, 10-oxomornigrol F, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by activating the Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway in macrophage cells. Int Immunopharmacol 55:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.12.015
Tsurumaru Y, Sasaki K, Miyawaki T, Uto Y, Momma T, Umemoto N, Momose M, Yazaki K (2012) HlPT-1, a membrane-bound prenyltransferase responsible for the biosynthesis of bitter acids in hops. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 417(1):393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.125
Tu Y, Xiao T, Gong G, Bian Y, Li Y (2020) A new isoflavone with anti-inflammatory effect from the seeds of Millettia pachycarpa. Nat Prod Res 34(7):981–987. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1547294
Tuenter E, Zarev Y, Matheeussen A, Elgorashi E, Pieters L, Foubert K (2019) Antiplasmodial prenylated flavonoids from stem bark of Erythrina latissima. Phytochem Lett 30:169–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.02.001
Umereweneza D, Atilaw Y, Rudenko A, Gutlin Y, Bourgard C, Gupta AK, Orthaber A, Muhizi T, Sunnerhagen P, Erdelyi M, Gogoll A (2021) Antibacterial and cytotoxic prenylated dihydrochalcones from Eriosema montanum. Fitoterapia 149:104809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104809
van de Schans MGM, Bovee TFH, Stoopen GM, Lorist M, Gruppen H, Vincken J-P (2015a) Prenylation and backbone structure of flavonoids and isoflavonoids from licorice and hop influence their phase I and II metabolism. J Agric Food Chem 63(49):10628–10640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04703
van de Schans MGM, Ritschel T, Bovee TFH, Sanders MG, de Waard P, Gruppen H, Vincken J-P (2015b) Involvement of a hydrophobic pocket and helix 11 in determining the modes of action of prenylated flavonoids and isoflavonoids in the human estrogen receptor. ChemBioChem 16(18):2668–2677. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201500343
Venturelli S, Burkard M, Biendl M, Lauer UM, Frank J, Busch C (2016) Prenylated chalcones and flavonoids for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutrition 32(11–12):1171–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.03.020
Veselova MV, Fedoreyev SA, Tarbeeva DV, Kulesh NI, Kalinovskiy AI, Kuzmich AS, Kim NY, Grigorchuk VP (2017) Cytotoxic prenylated polyphenolic compounds from Maackia amurensis root bark. Nat Prod Commun 12(7):1934578X1701200709. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x1701200709
Villinski JR, Bergeron C, Cannistra JC, Gloer JB, Coleman CM, Ferreira D, Azelmat J, Grenier D, Gafner S (2014) Pyrano-isoflavans from Glycyrrhiza uralensis with antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans, Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Nat Prod 77(3):521–526. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400788r
Vu LTN, Anh LT, Cuc NT, Nhiem NX, Tai BH, Van Kiem P, Litaudon M, Thach TD, Van Minh C, Mai HDT, Van Cuong P (2021a) Prenylated flavonoids and other constituents from Macaranga indica. Nat Prod Res 35(13):2123–2130. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1662007
Vu NK, Ha MT, Kim CS, Gal M, Kim JA, Woo MH, Lee J-H, Min BS (2021b) Structural characterization of prenylated compounds from Broussonetia kazinoki and their antiosteoclastogenic activity. Phytochemistry 188:112791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112791
Wang X, Li J, Qian L, Zang X-F, Zhang S-Y, Wang X-Y, Jin J-L, Zhu X-L, Zhang X-B, Wang Z-Y, Xu Y (2013) Icariin promotes histone acetylation and attenuates post-stroke cognitive impairment in the central cholinergic circuits of mice. Neuroscience 236:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.074
Wang R, Chen R, Li J, Liu X, Xie K, Chen D, Yin Y, Tao X, Xie D, Zou J, Yang L, Dai J (2014) Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of two novel regio-specific flavonoid prenyltransferases from Morus alba and Cudrania tricuspidata. J Biol Chem 289(52):35815–35825. http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.608265
Wang D, Sun Q, Wu J, Wang W, Yao G, Li T, Li X, Li L, Zhang Y, Cui W, Song S (2017a) A new prenylated flavonoid induces G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis through p38/JNK MAPK pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci Rep 7(1):5736. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05955-0
Wang L-X, Zheng H-R, Ren F-C, Chen T-G, Li X-M, Jiang X-J, Wang F (2017b) Polysubstituted Isoflavonoids from Spatholobus suberectus, Flemingia macrophylla, and Cudrania cochinchinensis. Nat Prod Bioprospect 7(2):201–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-017-0121-2
Wang Q-H, Guo S, Yang X-Y, Zhang Y-F, Shang M-Y, Shang Y-H, Xiao J-J, Cai S-Q (2017c) Flavonoids isolated from sinopodophylli fructus and their bioactivities against human breast cancer cells. Chin J Nat Med 15(3):225–233. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1009.2017.00225
Wang W, Nakashima K-I, Hirai T, Inoue M (2019) Anti-inflammatory effects of naturally occurring retinoid X receptor agonists isolated from Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. Via retinoid X receptor/liver X receptor heterodimers. J Nat Med 73(2):419–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-01277-1
Wang C-Y, Ai G-F, Zhang Y-F (2020a) Two new isoflavones from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia with diacylglycerol acyltransferase inhibitory activity. J Asian Nat Prod Res 22(4):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2019.1570159
Wang H, Tong Y, Xiao D, Xia B (2020b) Involvement of mTOR-related signaling in antidepressant effects of sophoraflavanone G on chronically stressed mice. Phytother Res 34(9):2246–2257. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6675
Wang J, Liu X, Zheng H, Liu Q, Zhang H, Wang X, Shen T, Wang S, Ren D (2020c) Morusin induces apoptosis and autophagy via JNK, ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling in human lung carcinoma cells. Chem Biol Interact 331:109279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109279
Wang L, Zhang Y, Johnpaul IA, Hong K, Song Y, Yang X, Lv C, Ma C (2022) Exploring two types of prenylated bitter compounds from hop plant (Humulus lupulus L.) against α-glucosidase in vitro and in silico. Food Chem 370:130979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130979
Wen L, Shi D, Zhou T, Tu J, He M, Jiang Y, Yang B (2020) Identification of two novel prenylated flavonoids in mulberry leaf and their bioactivities. Food Chem 315:126236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126236
Wen L, Zhou T, Jiang Y, Chang SK, Yang B (2021) Prenylated flavonoids in foods and their applications on cancer prevention. Crit Rev Food Sci 62(18):5067–5080
Win T, Htwe TT, Shwe HH, Heilmann J (2012) Lavandulyl flavanones from the stems of Hypericum calycinum L. Chem Biodivers 9(6):1198–1204. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201100310
Won TH, Song I-H, Kim K-H, Yang W-Y, Lee SK, Oh D-C, Oh W-K, Oh K-B, Shin J (2015) Bioactive metabolites from the fruits of Psoralea corylifolia. J Nat Prod 78(4):666–673. https://doi.org/10.1021/np500834d
Xiao Y, Lee I-S (2018) Microbial transformation of quercetin and its prenylated derivatives. Nat Prod Res 32(8):902–908. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1367780
Xiao C-Y, Li W-Y, Zhai X-X, Zhu L-Z, Zhou Y-F, Yao P-C, Shu Q-X, Gang R (2018) Prenylated flavonoids from the roots of Artocarpus heterophyllus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 53(4):592–597. https://doi.org/10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-1305
Xie G, Lin B, Qin X, Wang G, Wang Q, Yuan J, Li C, Qin M (2015) New flavonoids with cytotoxicity from the roots of Flemingia latifolia. Fitoterapia 104:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.05.015
Xu Y-L, He J-L, Jiang S-P, Wang Y-J, Zhu W-P (2020) A new prenylated flavonoid glycoside from Sinopodophyllum hexandrum. Chin Tradit Herbal Drugs 51(17):4388–4392
Xue J, Li R, Zhao X, Ma C, Lv X, Liu L, Liu P (2018) Morusin induces paraptosis-like cell death through mitochondrial calcium overload, dysfunction in epithelial ovarian cancer. Chem Biol Interact 283:59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.003
Yan H-W, Zhu H, Yuan X, Yang Y-N, Feng Z-M, Jiang J-S, Zhang P-C (2019) Eight new biflavonoids with lavandulyl units from the roots of Sophora flavescens and their inhibitory effect on PTP1B. Bioorg Chem 86:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.01.058
Yang Z, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2012) Bioassay-guided screening and isolation of α-glucosidase and tyrosinase inhibitors from leaves of Morus alba. Food Chem 131(2):617–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.040
Yang D-S, Wei J-G, Peng W-B, Wang S-M, Sun C, Yang Y-P, Liu K-C, Li X-L (2014) Cytotoxic prenylated bibenzyls and flavonoids from Macaranga kurzii. Fitoterapia 99:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.10.003
Yang D-S, Li Z-L, Peng W-B, Yang Y-P, Wang X, Liu K-C, Li X-L, Xiao W-L (2015a) Three new prenylated flavonoids from Macaranga denticulata and their anticancer effects. Fitoterapia 103:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.04.001
Yang D-S, Wang S-M, Peng W-B, Yang Y-P, Liu K-C, Li X-L, Xiao W-L (2015b) Minor prenylated flavonoids from the twigs of Macaranga adenantha and their cytotoxic activity. Nat Prod Bioprospect 5(2):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-015-0059-1
Yang D-S, Peng W-B, Yang Y-P, Liu K-C, Li X-L, Xiao W-L (2015c) Cytotoxic prenylated flavonoids from Macaranga indica. Fitoterapia 103:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.04.002
Yang X, Jiang Y, Yang J, He J, Sun J, Chen F, Zhang M, Yang B (2015) Prenylated flavonoids, promising nutraceuticals with impressive biological activities. Trends Food Sci Technol 44(44):93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.03.007
Yang Z, Ma X, Tan W, Zhou L, Zhuang X, Yang S, Qian Z, Zhou Z (2015d) Two new chalcones from Shuteria sinensis. Nat Prod Res 29(20):1909–1913. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1012718
Yang X, Yang J, Jiang Y, Yang H, Yun Z, Rong W, Yang B (2016) Regiospecific synthesis of prenylated flavonoids by a prenyltransferase cloned from Fusarium oxysporum. Sci Rep 6:24819. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24819
Yang W-J, He J-X, Zhou M-X, Huang M, Wang S-Q, Wang X-N, Lou H-X, Ren D-M, Shen T (2019) An isopentenyl-substituted flavonoid norartocarpin activates Nrf2 signalling pathway and prevents oxidative insults in human lung epithelial cells. Free Radic Res 53(3):348–358. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2019.1582769
Yang J, Zhou T, Jiang Y, Yang B (2020) Substrate specificity change of a flavonoid prenyltransferase AhPT1 induced by metal ion. Int J Biol Macromol 153:264–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.005
Yang Y-N, Zhu H, Yuan X, Zhang X, Feng Z-M, Jiang J-S, Zhang P-C (2021) Seven new prenylated flavanones from the roots of Sophora flavescens and their anti-proliferative activities. Bioorg Chem 109:104716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104716
Yao J, Wang Z, Wang R, Wang Y, Xu J, He X (2021) Anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory prenylated isoflavones and coumaronochromones from the fruits of Ficus altissima. Bioorg Chem 113:104996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104996
Ye X-S, Tian W-J, Zhou M, Zeng D-Q, Lin T, Wang G-H, Yao X-S, Chen H-F (2021) Prenylated flavonoids from Ficus hirta induces HeLa cells apoptosis via MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 38:127859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.127859
Yeh C-J, Chen C-C, Leu Y-L, Lin M-W, Chui M-M, Wang H-W (2017) The effects of artocarpin on wound healing: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15876-7
Yen T-L, Hsu C-K, Lu W-J, Hsieh C-Y, Hsiao G, Chou D-S, Wu G-J, Sheu J-R (2012) Neuroprotective effects of xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus lupulus), in ischemic stroke of rats. J Agric Food Chem 60(8):1937–1944. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf204909p
Yim D, Kim MJ, Shin Y, Lee S-J, Shin JG, Kim DH (2019) Inhibition of cytochrome P450 activities by Sophora flavescens extract and its prenylated flavonoids in human liver microsomes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019:2673769
Yin H, Zhang S, Wu J, Nan H, Long L, Yang J, Li Q (2006) Pongaflavanol: a prenylated flavonoid from Pongamia pinnata with a modified ring A. Molecules 11(10):786–791. https://doi.org/10.3390/11100786
Yin S, Song M, Zhao R, Liu X, Kang W-K, Lee J-M, Kim Y-E, Zhang C, Shim J-H, Liu K, Dong Z, Lee M-H (2020) Xanthohumol inhibits the growth of keratin 18-overexpressed esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:366. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00366
Yoneyama K, Akashi T, Aoki T (2016) Molecular characterization of soybean pterocarpan 2-dimethylallyltransferase in glyceollin biosynthesis: local gene and whole-genome duplications of prenyltransferase genes led to the structural diversity of soybean prenylated isoflavonoids. Plant Cell Physiol 57(12):2497–2509. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw178
Yoshioka Y, Kubota Y, Samukawa Y, Yamashita Y, Ashida H (2019) Glabridin inhibits dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy. Arch Biochem Biophys 664:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.006
Yu X, Li S-M (2011) Prenylation of flavonoids by using a dimethylallyltryptophan synthase, 7-DMATS, from Aspergillus fumigatus. ChemBioChem 12:2280–2283. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201100413
Yu Q, Cheng N, Ni X (2013) Identifying 2 prenylflavanones as potential hepatotoxic compounds in the ethanol extract of Sophora flavescens. J Food Sci 78(11):T1830–T1834. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12275
Yusook K, Weeranantanapan O, Hua Y, Kumkrai P, Chudapongse N (2017) Lupinifolin from Derris reticulata possesses bactericidal activity on Staphylococcus aureus by disrupting bacterial cell membrane. J Nat Med 71(2):357–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-016-1065-2
Zakaria I, Ahmat N, Jaafar FM, Widyawaruyanti A (2012) Flavonoids with antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activities of Macaranga triloba. Fitoterapia 83(5):968–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.04.020
Zarev Y, Foubert K, Lucia de Almeida V, Anthonissen R, Elgorashi E, Apers S, Ionkova I, Verschaeve L, Pieters L (2017) Antigenotoxic prenylated flavonoids from stem bark of Erythrina latissima. Phytochemistry 141:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.06.003
Zelová H, Hanáková Z, Čermáková Z, Šmejkal K, Dall Acqua S, Babula P, Cvačka J, Hošek J (2014) Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of prenylated substances isolated from Morus alba and Morus nigra. J Nat Prod 77(6):1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1021/np401025f
Zeutsop JF, Nono RN, Frese M, Chouna JR, Lenta BN, Nkeng-Efouet-Alango P, Sewald N (2021) Phytochemical, antibacterial, antioxidant and cytoxicity investigation of Tarenna grandiflora. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 76(7–8):285–290. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2020-0187
Zhang N-L, Zhu Y-H, Huang R-M, Fu M-Q, Su Z-W, Cai J-Z, Hu Y-J, Qiu S-X (2012) Two new stilbenoids from Cajanus cajan. Z Naturforsch B 67:1314–1318. https://doi.org/10.5560/znb.2012-0184
Zhang L-B, Lei C, Gao L-X, Li J-Y, Li J, Hou A-J (2016) Isoprenylated flavonoids with PTP1B inhibition from Macaranga denticulata. Nat Prod Bioprospect 6(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-015-0082-2
Zhang N, Tian B, Zhao S, Zhang X, Pan D, Shen X, Zhang Y (2017) A new formylated chalcone from Humulus lupulus with protective effect on HUVECs injury by angiotensin II. Nat Prod Res 33(5):617–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1402318
Zhang H, Wu X, Wang J, Wang M, Wang X, Shen T, Wang S, Ren D (2020) Flavonoids from the leaves of Epimedium Koreanum Nakai and their potential cytotoxic activities. Nat Prod Res 34(9):1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1560283
Zheng Z-P, Tan H-Y, Chen J, Wang M (2013) Characterization of tyrosinase inhibitors in the twigs of Cudrania tricuspidata and their structure-activity relationship study. Fitoterapia 84:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.12.006
Zheng Y, Xie Y-G, Zhang Y, Li T, Li H-L, Yan S-K, Jin H-Z, Zhang W-D (2016) New norlignans and flavonoids of Dysosma versipellis. Phytochem Lett 16:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2016.03.001
Zheng Y, Wang H, Yang M, Peng G, Dong TTX, Xu ML, Tsim KWK (2018) Prenylated flavonoids from roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis induce differentiation of B16–F10 melanoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082422
Zhou H, Yuan Y, Liu Y, Deng W, Zong J, Bian Z-Y, Dai J, Tang Q-Z (2014) Icariin attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy and apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes by inhibiting reactive oxygen species-dependent JNK and p38 pathways. Exp Ther Med 7(5):1116–1122. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1598
Zhou K, Xia Y, Xie X, Li S-M (2015) Complementary flavonoid prenylations by fungal indole prenyltransferases. J Nat Prod 78(9):2229–2235. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00422
Zhu H-R, Wang Z-Y, Zhu X-L, Er-guang Li, Xu Y (2010) Icariin protects against brain injury by enhancing SIRT1-dependent PGC-1α expression in experimental stroke. Neuropharmacol 59:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.03.017
Zhu H, Yang Y-N, Feng Z-M, Jiang J-S, Zhang P-C (2018) Sophoflavanones A and B, two novel prenylated flavanones from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Bioorg Chem 79:122–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.04.019
Zoofishan Z, Kúsz N, Csorba A, Tóth G, Hajagos-Tóth J, Kothencz A, Gáspár R, Hunyadi A (2019) Antispasmodic activity of prenylated phenolic compounds from the root bark of Morus nigra. Molecules 24(13):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132497
Zulfiqar F, Khan SI, Ross SA, Ali Z, Khan IA (2017) Prenylated flavonol glycosides from Epimedium grandiflorum: cytotoxicity and evaluation against inflammation and metabolic disorder. Phytochem Lett 20:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.04.027
Zuo B, Liao Z-X, Xu C, Liu C (2016) Two novel prenylated kaempferol derivatives from fresh bud’s fur of Platanus acerifolia and their anti-proliferative activities. Nat Prod Res 30(22):2523–2528. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1118632
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Grant Numbers: 81603255), grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China. (Grant Numbers: 2022YFC2804204) and High-Level Talent Special Support Plan of Zhejiang Province (Grant Numbers: 2019R52009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Confict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, HW., Wang, QL., Luo, M. et al. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of natural prenylated flavonoids. Arch. Pharm. Res. 46, 207–272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01443-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01443-4