Abstract
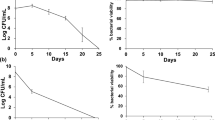
Antibiotics are powerful and reliable substances that can control microorganism growth. However, microbes employ several countermeasures to adapt to external stresses such as extreme salt concentrations and antibiotics. Among them, microbes can regulate the fatty acid composition of their cell membrane. Our previous study reported that Halomonas socia CKY01, a various hydrolase producing halophilic bacterium, exhibited NaCl concentration-dependent kanamycin resistance. In this study, kanamycin, which is known to interfere with protein synthesis by targeting bacterial ribosomes, was unexpectedly found to inhibit cyclopropane fatty acid (CFA) synthesis in the cell membrane of this microbe. As a result, the aim of the current study was to elucidate the mechanism underlying this unique function of kanamycin. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to examine cfa expression, which encodes cyclopropane-fatty acid-acyl-phospholipid synthase, and it was found that the mRNA expression of cfa was not significantly affected by kanamycin treatment. Inhibition of CFA production was also observed when oleic acid, a CFA precursor, was supplied to cells. Additionally, inhibition of CFA synthase was monitored in cfa-overexpressing Escherichia coli, and CFA production did not differ significantly, suggesting that this phenomenon is specific to H. socia CKY01. Although the exact mechanism of CFA inhibition by kanamycin remains unclear, the study findings demonstrate the impact of kanamycin on the cell membrane composition of H. socia CKY01, suggesting possible synergetic effects with membrane-targeted antibiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 December 2022
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-022-1111-8
References
Park, Y. L., T. R. Choi, Y. H. Han, H. S. Song, J. Y. Park, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, K. Y. Choi, Y. G. Kim, and Y. H. Yang (2020) Effects of osmolytes on salt resistance of Halomonas socia CKY01 and identification of osmolytes-related genes by genome sequencing. J. Biotechnol. 322: 21–28.
Ghazaei, C. (2017) Role and mechanism of the Hsp70 molecular chaperone machines in bacterial pathogens. J. Med. Microbiol. 66: 259–265.
Burg, M. B. and J. D. Ferraris (2008) Intracellular organic osmolytes: function and regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 7309–7313.
Giuliodori, A. M., C. O. Gualerzi, S. Soto, J. Vila, and M. M. Tavío (2007) Review on bacterial stress topics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1113: 95–104.
Cronan, J. E., Jr., R. Reed, F. R. Taylor, and M. B. Jackson (1979) Properties and biosynthesis of cyclopropane fatty acids in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 138: 118–121.
Schweizer, H. P. (2004) Fatty acid biosynthesis and biologically significant acyl transfer reactions in pseudomonads. pp. 83–109. In: J.-L. Ramos (ed.). Pseudomonas. Springer, Boston, MA, USA.
Choi, T.-R., H.-S. Song, Y.-H. Han, Y.-L. Park, J. Y. Park, S.-Y. Yang, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, H. J. Kim, Y. K. Lee, K. Y. Choi, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Enhanced tolerance to inhibitors of Escherichia coli by heterologous expression of cyclopropane-fatty acid-acyl-phospholipid synthase (cfa) from Halomonas socia. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 43: 909–918.
Taylor, F. R. and J. E. Cronan Jr. (1979) Cyclopropane fatty acid synthase of Escherichia coli. Stabilization, purification, and interaction with phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 18: 3292–3300.
Wang, A. Y., D. W. Grogan, and J. E. Cronan Jr. (1992) Cyclopropane fatty acid synthase of Escherichia coli: deduced amino acid sequence, purification, and studies of the enzyme active site. Biochemistry 31: 11020–11028.
Loffhagen, N., C. Härtig, W. Geyer, M. Voyevoda, and H. Harms (2007) Competition between cis, trans and cyclopropane fatty acid formation and its impact on membrane fluidity. Eng. Life Sci. 7: 67–74.
Kuchta, T. and N. J. Russell (1994) Glycinebetaine stimulates, but NaCl inhibits, fatty acid biosynthesis in the moderately halophilic eubacterium HX. Arch. Microbiol. 161: 234–238.
Smittle, R. B., S. E. Gilliland, M. L. Speck, and W. M. Walter Jr. (1974) Relationship of cellular fatty acid composition to survival of Lactobacillus bulgaricus in liquid nitrogen. Appl. Microbiol. 27: 738–743.
Yumoto, I., K. Hirota, H. Iwata, M. Akutsu, K. Kusumoto, N. Morita, Y. Ezura, H. Okuyama, and H. Matsuyama (2004) Temperature and nutrient availability control growth rate and fatty acid composition of facultatively psychrophilic Cobetia marina strain L-2. Arch. Microbiol. 181: 345–351.
Annous, B. A., M. F. Kozempel, and M. J. Kurantz (1999) Changes in membrane fatty acid composition of Pediococcus sp. strain NRRL B-2354 in response to growth conditions and its effect on thermal resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 2857–2862.
Pini, C. V., P. Bernal, P. Godoy, J. L. Ramos, and A. Segura (2009) Cyclopropane fatty acids are involved in organic solvent tolerance but not in acid stress resistance in Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E. Microb. Biotechnol. 2: 253–261.
Chang, Y. Y. and J. E. Cronan Jr. (1999) Membrane cyclopropane fatty acid content is a major factor in acid resistance of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 33: 249–259.
Zhao, Y., L. A. Hindorff, A. Chuang, M. Monroe-Augustus, M. Lyristis, M. L. Harrison, F. B. Rudolph, and G. N. Bennett (2003) Expression of a cloned cyclopropane fatty acid synthase gene reduces solvent formation in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69: 2831–2841.
Choi, T.-R., Y.-L. Park, H.-S. Song, S. M. Lee, S. L. Park, H. S. Lee, H.-J. Kim, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, Y. K. Lee, C. Sung, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Effects of a Δ-9-fatty acid desaturase and a cyclopropane-fatty acid synthase from the novel psychrophile Pseudomonas sp. B14-6 on bacterial membrane properties. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47: 1045–1057.
Arahal, D. R., R. H. Vreeland, C. D. Litchfield, M. R. Mormile, B. J. Tindall, A. Oren, V. Bejar, E. Quesada, and A. Ventosa (2007) Recommended minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Halomonadaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57: 2436–2446. (Erratum published 2008, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58: 2673)
Argandoña, M., C. Vargas, M. Reina-Bueno, J. Rodríguez-Moya, M. Salvador, and J. J. Nieto (2012) An extended suite of genetic tools for use in bacteria of the Halomonadaceae: an overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 824: 167–201.
Park, Y.-L., S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, T.-R. Choi, H. J. Kim, H.-S. Song, J.-Y. Park, Y.-H. Han, S. M. Lee, S. L. Park, H. S. Lee, Y.-G. Kim, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Fructose based hyper production of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate from Halomonas sp. YLGW01 and impact of carbon sources on bacteria morphologies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 154: 929–936.
Park, Y.-L., H.-S. Song, T.-R. Choi, S. M. Lee, S. L. Park, H. S. Lee, H.-J. Kim, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, K. Park, and Y.-H. Yang (2021) Revealing of sugar utilization systems in Halomonas sp. YLGW01 and application for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production with low-cost medium and easy recovery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 167: 151–159.
Park, Y.-L., T.-R. Choi, H. J. Kim, H.-S. Song, H. S. Lee, S. L. Park, S. M. Lee, S. H. Kim, S. Park, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, C. Sung, S.-O. Seo, and Y.-H. Yang (2021) NaCl concentration-dependent aminoglycoside resistance of Halomonas socia CKY01 and identification of related genes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31: 250–258.
Aston, J. E. and B. M. Peyton (2007) Response of Halomonas campisalis to saline stress: changes in growth kinetics, compatible solute production and membrane phospholipid fatty acid composition. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 274: 196–203.
Suzuki, J., T. Kunimoto, and M. Hori (1970) Effects of kanamycin on protein synthesis: inhibition of elongation of peptide chains. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 23: 99–101.
Bligh, E. G. and W. J. Dyer (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37: 911–917.
Buyer, J. S. and M. Sasser (2012) High throughput phospholipid fatty acid analysis of soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 61: 127–130.
Lee, H. S., H.-S. Song, H.-J. Lee, S. H. Kim, M. J. Suh, J. Y. Cho, S. Ham, Y.-G. Kim, H.-S. Joo, W. Kim, S. H. Lee, D. Yoo, S. K. Bhatia, and Y.-H. Yang (2021) Comparative study of the difference in behavior of the accessory gene regulator (Agr) in USA300 and USA400 community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31: 1060–1068.
Song, H.-S., T.-R. Choi, Y.-H. Han, Y.-L. Park, J. Y. Park, S.-Y. Yang, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, Y.-G. Kim, J.-S. Kim, H.-S. Joo, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Increased resistance of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Δagr mutant with modified control in fatty acid metabolism. AMB Express 10: 64.
Song, H.-S., S. K. Bhatia, T.-R. Choi, R. Gurav, H. J. Kim, S. M. Lee, S. L. Park, H. S. Lee, H.-S. Joo, W. Kim, S.-O. Seo, and Y.-H. Yang (2021) Increased antibiotic resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Δpsm mutants and a complementation study of Δpsm mutants using synthetic phenol-soluble modulins. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31: 115–122.
Choi, T.-R., J.-M. Jeon, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, Y. H. Han, Y. L. Park, J.-Y. Park, H.-S. Song, H. Y. Park, J.-J. Yoon, S.-O. Seo, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Production of low molecular weight P(3HB-co-3HV) by butyrateacetoacetate CoA-transferase (cftAB) in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 279–286.
Royce, L. A., P. Liu, M. J. Stebbins, B. C. Hanson, and L. R. Jarboe (2013) The damaging effects of short chain fatty acids on Escherichia coli membranes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97: 8317–8327.
Lee, S. M., H.-J. Lee, S. H. Kim, M. J. Suh, J. Y. Cho, S. Ham, R. Gurav, S. H. Lee, S. K. Bhatia, and Y.-H. Yang (2022) Selective recovery of L-pipecolic acid from L-lysine bioconversion mixture by liquid-liquid extraction. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 27: 286–293.
Mykytczuk, N. C., J. T. Trevors, L. G. Leduc, and G. D. Ferroni (2007) Fluorescence polarization in studies of bacterial cytoplasmic membrane fluidity under environmental stress. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 95: 60–82.
Han, Y.-H., T.-R. Choi, Y.-L. Park, J. Y. Park, H.-S. Song, H. J. Kim, S. M. Lee, S. L. Park, H. S. Lee, S. K. Bhatia, R. Gurav, and Y.-H. Yang (2020) Enhancement of pipecolic acid production by the expression of multiple lysine cyclodeaminase in the Escherichia coli whole-cell system. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 140: 109643.
Yang, S.-Y., T.-R. Choi, H.-R. Jung, Y.-L. Park, Y.-H. Han, H.-S. Song, S. K. Bhatia, K. Park, J.-O. Ahn, W.-Y. Jeon, J.-S. Kim, and Y.-H. Yang (2019) Production of glutaric acid from 5-aminovaleric acid by robust whole-cell immobilized with polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 128: 72–78.
Hong, Y.-G., Y.-M. Moon, J.-W. Hong, S.-Y. No, T.-R. Choi, H.-R. Jung, S.-Y. Yang, S. K. Bhatia, J.-O. Ahn, K.-M. Park, and Y.-H. Yang (2018) Production of glutaric acid from 5-aminovaleric acid using Escherichia coli whole cell bio-catalyst overexpressing GabTD from Bacillus subtilis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 118: 57–65.
Kim, J., H.-M. Seo, S. K. Bhatia, H.-S. Song, J.-H. Kim, J.-M. Jeon, K.-Y. Choi, W. Kim, J.-J. Yoon, Y.-G. Kim, and Y.-H. Yang (2017) Production of itaconate by whole-cell bioconversion of citrate mediated by expression of multiple cis-aconitate decarboxylase (cadA) genes in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 7: 39768.
Jiang, X., Y. Duan, B. Zhou, Q. Guo, H. Wang, X. Hang, L. Zeng, J. Jia, and H. Bi (2019) The cyclopropane fatty acid synthase mediates antibiotic resistance and gastric colonization of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 201: e00374–19.
Liu, Q., M. Li, Y. Teng, H. Yang, Y. Xi, S. Chen, and G. Duan (2019) The role of cfa gene in ampicillin tolerance in Shigella. Infect. Drug Resist. 12: 2765–2774.
Guianvarc’h, D., E. Guangqi, T. Drujon, C. Rey, Q. Wang, and O. Ploux (2008) Identification of inhibitors of the E. coli cyclopropane fatty acid synthase from the screening of a chemical library: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1784: 1652–1658.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Research Program to solve social issues with the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (grant number 2017M3A9E4077234), National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (grant numbers NRF-2022 R1A2C2003138 and NRF-2019M3E6A1103979). W.K. was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant (2020R1C1C1008842, 2018R1A5A2025286).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.S., Lee, HJ., Kim, B. et al. Inhibition of Cyclopropane Fatty Acid Synthesis in the Membrane of Halophilic Halomonas socia CKY01 by Kanamycin. Biotechnol Bioproc E 27, 788–796 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-022-0086-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-022-0086-9