Abstract
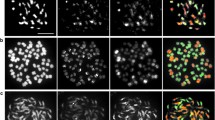
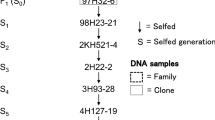
Haploids have often been used to simplify the genetic complexity of potato due to its high heterozygosity and autotetraploidy. We maintained some haploid plants of wild potato species in vitro that were produced through anther culture almost a half century ago. Among them, a diploid Solanum bulbocastanum and its monohaploid, three monohaploids of S. verrucosum, a disomic tetraploid S. stoloniferum and its dihaploid (all Mexican species) and a dihaploid of the disomic tetraploid S. acaule (South American species) were analyzed morphologically, cytologically and by molecular markers. Their species identity and ploidy levels were confirmed to be correct except for those of a monoploid S. bulbocastanum, which had already experienced natural chromosome doubling. The monohaploids and chromosome-doubled monohaploid were all homozygous in 19,889 SNP loci surveyed. Two of three monohaploids of S. verrucosum were morphologically different but similar by SNP analysis. Most of the heterozygous loci of the tetraploid S. stoloniferum were in a duplex condition. The heterozygous loci of the dihaploid S. stoloniferum were mostly duplexed in the tetraploid S. stoloniferum, suggesting that the alleles are fixed in homoeologous loci. Therefore, each of these haploid-plant genomes is homozygous and is suitable for whole-genome sequencing.
Resumen
Los haploides se han utilizado con frecuencia para simplificar la complejidad genética de la papa debido a su alta heterocigosidad y autotetraploidía. Mantuvimos algunas plantas haploides de especies silvestres de papa in vitro que se produjeron a través del cultivo de anteras hace casi medio siglo. Entre ellas, un diploide de Solanum bulbocastanum y su monohaploide, tres monohaploides de S. verrucosum, un tetraploide disómico de S. stoloniferum y su dihaploide (todas especies mexicanas) y un dihaploide del tetraploide disómico S. acaule (especie sudamericana). Se analizaron morfológicamente, citológicamente y por marcadores moleculares. Se confirmó que su identidad de especie y sus niveles de ploidía eran correctos, excepto los de una monoploide de S. bulbocastanum, que ya había experimentado la duplicación natural de cromosomas. Los monohaploides y el monohaploide doblado cromosómico fueron todos homocigotos en 19,889 loci SNP analizados. Dos de los tres monohaploides de S. verrucosum eran morfológicamente diferentes pero similares según el análisis de SNP. La mayoría de los loci heterocigotos del tetraploide S. stoloniferum estaban en una condición de duplicidad. Los loci heterocigotos del dihaploide S. stoloniferum fueron en su mayoría duplicados en el tetraploide S. stoloniferum, sugiriendo que los alelos se fijan en loci homólogos. Por lo tanto, cada uno de estos genomas de plantas haploides es homocigoto y es adecuado para la secuenciación completa del genoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All data are included in the manuscript. Plant materials are available upon request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aversano, R., F. Contaldi, M.R. Ercolano, V. Grosso, M. Iorizzo, F. Tatino, L. Xumerle, A. Dal Molin, C. Avanzato, A. Ferrarini, M. Delledonne, W. Sanseverino, R.A. Cigliano, S. Capella-Gutierrez, T. Gabaldón, L. Frusciante, J.M. Bradeen, and D. Carputo. 2015. The Solanum commersonii genome sequence provides insights into adaptation to stress conditions and genome evolution of wild potato relatives. The Plant Cell 27: 954–968.
Bamberg, J.B., and A. del Rio. 2020. Assessing under-estimation of genetic diversity within wild potato (Solanum) species populations. American Journal of Potato Research 97: 547–553.
Bamberg, J., A. Kielar, A. del Rio, and D. Douches. 2021. Making hybrids with the wild potato Solanum jamesii. American Journal of Potato Research 98: 187–193.
Camadro, E.L., R.W. Masuelli, and M.C. Cortés. 1992. Haploids of the wild tetraploid potato Solanum acaule ssp. acaule: Generation, meiotic behavior, and electrophoretic pattern for the aspartate aminotransferase system. Genome 35: 431–435.
Cappadocia, M., D.S.K. Cheng, and R. Ludlum-Simonette. 1984. Plant regeneration from in vitro culture of anthers of Solanum chacoense Bitt. and interspecific diploid hybrids S. tuberosum L. × S. chacoense Bitt. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 69: 139–143.
Dinu, I.I., R.J. Hayes, R.G. Kynast, R.L. Phillips, and C.A. Thill. 2005. Novel inter-series hybrids in Solanum, section Petota. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 110: 403–415.
Eijlander, R., W. ter Laak, J.G.Th. Hermsen, M.S. Ramanna, and E. Jacobsen. 2000. Occurrence of self-compatibility, self-incompatibility and unilateral incompatibility after crossing diploid S. tuberosum (SI) with S. verrucosum (SC): I. Expression and inheritance of self-compatibility. Euphytica 115: 127–139.
Foroughi-Wehr, B., H.M. Wilson, G. Mix, and H. Gaul. 1977. Monohaploid plants from anthers of a dihaploid genotype of Solanum tuberosum L. Euphytica 26: 361–367.
Hamernik, A.J., M. Ramon, and R.E. Hanneman Jr. 2001. Modified conventional breeding methods to efficiently transfer unique late blight resistance from 2x (1EBN) Mexican species to 2x (2EBN) and 4x (4EBN) breeding lines. American Journal of Potato Research 78: 456.
Hamilton, J.P., C.N. Hansey, B.R. Whitty, K. Stoffel, A.N. Massa, A. Van Deynze, W.S. De Jong, D.S. Douches, and C.R. Buell. 2011. Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in elite North American potato germplasm. BMC Genomics 12: 302.
Hardigan, M.A., J. Bamberg, C.R. Buell, and D.S. Douches. 2015. Taxonomy and genetic differentiation among wild and cultivated germplasm of Solanum sect. Petota. The Plant Genome 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2014.06.0025.
Hardigan, M.A., F.P.E. Laimbeer, L. Newton, E. Crisovan, J.P. Hamilton, B. Vaillancourt, K. Wiegert-Rininger, J.C. Wood, D.S. Douches, E.M. Farré, R.E. Veilleux, and C.R. Buell. 2017. Genome diversity of tuber-bearing Solanum uncovers complex evolutionary history and targets of domestication in the cultivated potato. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114: E9999–E10008.
Hawkes, J.G. 1990. The potato - evolution, biodiversity and genetic resources. London: Belhaven Press.
Hermsen, J.G.Th., and M.S. Ramanna. 1969. Meiosis in different F1-hybrids of Solanum acaule Bitt. × S. bulbocastanum Dun. and its bearing on genome relationship, fertility and breeding behaviour. Euphytica 18: 27–35.
Hermsen, J.G.Th., and M.S. Ramanna. 1976. Barriers to hybridization of Solanum bulbocastanum Dun. and S. verrucosum Schlechtd. and structural hybridity in their F1 plants. Euphytica 25: 1–10.
Hermsen, J.G.Th., and J. Verdenius. 1973. Selection from Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja of genotypes combining high-frequency haploid induction with homozygosity for embryo-spot. Euphytica 22: 244–259.
Hosaka, K., and R.E. Hanneman Jr. 1998. Genetics of self-compatibility in a self-incompatible wild diploid potato species Solanum chacoense. 2. Localization of an S locus inhibitor (Sli) gene on the potato genome using DNA markers. Euphytica 103: 265–271.
Hosaka, K., and R. Sanetomo. 2012. Development of a rapid identification method for potato cytoplasm and its use for evaluating Japanese collections. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 125: 1237–1251.
Hosaka, K., and R. Sanetomo. 2014. Application of a PCR-based cytoplasm genotyping method for phylogenetic analysis in potato. American Journal of Potato Research 91: 246–253.
Hosaka, K., and R. Sanetomo. 2020. Creation of a highly homozygous diploid potato using the S locus inhibitor (Sli) gene. Euphytica 216: 169.
Hougas, R.W., S.J. Peloquin, and A.C. Gabert. 1964. Effect of seed-parent and pollinator on frequency of haploids in Solanum tuberosum. Crop Science 4: 593–595.
Irikura, Y. 1975a. Induction of haploid plants by anther culture in tuber-bearing species and interspecific hybrids of Solanum. Potato Research 18: 133–140.
Irikura, Y. 1975b. Cytogenetic studies on the haploid plants of tuber-bearing Solanum species. 1. Induction of haploid plants of tuber-bearing Solanums (in Japanese). Research Bulletin of the Hokkaido National Agricultural Experiment Station 112: 1–67.
Irikura, Y. 1976. Cytogenetic studies on the haploid plants of tuber-bearing Solanum species. 2. Cytological investigations on haploid plants and interspecific hybrids by utilizing haploidy (in Japanese). Research Bulletin of the Hokkaido National Agricultural Experiment Station 115: 1–80.
Irikura, Y., and S. Sakaguchi. 1972. Induction of 12-chromosome plants from anther culture in a tuberous Solanum. Potato Research 15: 170–173.
Jansky, S., and A. Hamernik. 2009. The introgression of 2x 1EBN Solanum species into the cultivated potato using Solanum verrucosum as a bridge. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 56: 1107–1115.
Kyriakidou, M., H.H. Tai, N.L. Anglin, D. Ellis, and M.V. Stromvik. 2018. Current strategies of polyploid plant genome sequence assembly. Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 1660.
Kyriakidou, M., S.R. Achakkagari, J.H.G. López, X. Zhu, C.Y. Tang, H.H. Tai, N.L. Anglin, D. Ellis, and M.V. Strömvik. 2020. Structural genome analysis in cultivated potato taxa. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 133: 951–966.
Leisner, C.P., J.P. Hamilton, E. Crisovan, N.C. Manrique-Carpintero, A.P. Marand, L. Newton, M. Gina, G.M. Pham, J. Jiang, D.S. Douches, S.H. Jansky, and C.R. Buell. 2018. Genome sequence of M6, a diploid inbred clone of the high-glycoalkaloid-producing tuber-bearing potato species Solanum chacoense, reveals residual heterozygosity. The Plant Journal 94: 562–570.
Li, Y., C. Colleoni, J. Zhang, Q. Liang, Y. Hu, H. Ruess, R. Simon, Y. Liu, H. Liu, G. Yu, E. Schmitt, C. Ponitzki, G. Liu, H. Huang, F. Zhan, L. Chen, Y. Huang, D. Spooner, and B. Huang. 2018. Genomic analyses yield markers for identifying agronomically important genes in potato. Molecular Plant 11: 473–484.
Lightbourn, G.J., and R.E. Veilleux. 2007. Production and evaluation of somatic hybrids derived from monoploid potato. American Journal of Potato Research 84: 425–435.
Lokossou, A.A., H. Rietman, M. Wang, P. Krenek, H. van der Schoot, B. Henken, R. Hoekstra, V.G.A.A. Vleeshouwers, E.A.G. van der Vossen, R.G.F. Visser, E. Jacobsen, and B. Vosman. 2010. Diversity, distribution, and evolution of Solanum bulbocastanum late blight resistance genes. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 23: 1206–1216.
MacKey, J. 1970. Significance of mating systems for chromosome and gametes in polyploids. Hereditas 66: 165–176.
Magoon, M.L., D.C. Cooper, and R.W. Hougas. 1958. Cytogenetic studies of some diploid Solanums section Tuberarium. American Journal of Botany 45: 207–221.
Matsubayashi, M. 1955. Studies on the species differentiation in the section Tuberarium of Solanum. III. Behavior of meiotic chromosomes in F1 hybrid between S. longipedicellatum and S. schickii, in relation to its parent species. Science Report, Hyogo University of Agriculture 2: 25–31.
Matsubayashi, M. 1982. Species differentiation in Solanum, sect. Petota. XI. Genomic relationships between S. acaule and certain diploid Commersoniana species. Science Report, Faculty of Agriculture, Kobe University 15: 23–33.
Matsubayashi, M. 1991. Phylogenetic relationships in the potato and its related species. In Chromosome engineering in plants: Genetics, breeding, evolution Part B, ed. T. Tsuchiya and P.K. Gupta, 93–118. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Meyer, R., F. Salamini, and H. Uhrig. 1992. Biotechnology and plant breeding: relevance of cell genetics in potato improvement. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section B: Biological Sciences 99: 11–21.
Mix, G. 1983. Production of dihaploid plantlets from anthers of autotetraploid genotypes of Solanum tuberosum L. Potato Research 26: 63–67.
Nakagawa, K., and K. Hosaka. 2002. Species relationships between a wild tetraploid species, Solanum acaule Bitter, and its related species as revealed by RFLPs of chloroplast and nuclear DNA. American Journal of Potato Research 79: 85–98.
Ortiz, R., and S.J. Peloquin. 1994. Use of 24-chromosome potatoes (diploids and dihaploids) for genetical analysis. In Potato genetics, ed. J.E. Bradshaw and G.R. Mackay, 133–154. Wallingford: CAB International.
Pendinen, G., T. Gavrillenko, J. Jiang, and D.M. Spooner. 2008. Allopolyploid speciation of the Mexican tetraploid potato species Solanum stoloniferum and S. hjertingii revealed by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 51: 714–730.
Peterson, B.A., S.H. Holt, R.E. Laimbeer, A.G. Doulis, J. Coombs, D.S. Douches, M.A. Hardigan, C.R. Buell, and R.E. Veilleux. 2016. Self-fertility in a cultivated diploid potato population examined with the Infinium 8303 potato single-nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Genome 9: 3.
Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium. 2011. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 475: 189–195.
Rodríguez, F., and D.M. Spooner. 2009. Nitrate reductase phylogeny of potato (Solanum sect. Petota) genomes with emphasis on the origins of the polyploid species. Systematic Botany 34: 207–219.
Sanetomo, R., and K. Hosaka. 2013. A recombination-derived mitochondrial genome retained stoichiometrically only among Solanum verrucosum Schltdl. and Mexican polyploid wild potato species. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 60: 2391–2404.
Sopory, S.K., E. Jacobsen, and G. Wenzel. 1978. Production of monohaploid embryoids and plantlets in cultured anthers of Solanum tuberosum. Plant Science Letters 12: 14–54.
Spooner, D.M., and R.T. Castillo. 1997. Reexamination of series relationships of South American wild potatoes (Solanaceae: Solanum sect. Petota): Evidence from chloroplast DNA restriction site variation. American Journal of Botany 84: 671–685.
Spooner, D.M., R.G. van den Berg, A. Rodríguez, J. Bamberg, R.J. Hijmans, and S.I.L. Cabrera. 2004. Wild potatoes (Solanum section Petota; Solanaceae) of North and Central America. Systematic Botany Monographs Vol 68. Ann Arbor: The American Society of Plant Taxonomists.
Swaminathan, M.S. 1954. Nature of polyploidy in some 48-chromosome species of the genus Solanum section Tuberarium. Genetics 39: 59–76.
Swaminathan, M.S., and H.W. Howard. 1953. The cytology and genetics of the potato (Solanum tuberosum) and related species. Bibliographia Genetica 16: 1–192.
Tiwari, J.K., S. Rawat, S.K. Luthra, R. Zinta, S. Sahu, S. Varshney, V. Kumar, D. Dalamu, N. Mandadi, M. Kumar, S.K. Chakrabarti, A.R. Rao, and A. Rai. 2021. Genome sequence analysis provides insights on genomic variation and late blight resistance genes in potato somatic hybrid (parents and progeny). Molecular Biology Reports 48: 623–635.
Uhrig, H. 1985. Genetic selection and liquid medium conditions improve the yield of androgenetic plants from diploid potatoes. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 71: 455–460.
Uijtewaal, B.A., G.J. Huigen, and J.G.Th. Hermsen. 1987. Production of potato monohaploids (2n=x=12) through prickle pollination. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 73: 751–758.
van Breukelen, E.W.M., M.S. Ramanna, and J.G.Th. Hermsen. 1975. Monohaploids (n=x=12) from autotetraploid Solanum tuberosum (2n=4x=48) through two successive cycles of female parthenogenesis. Euphytica 24: 567–574.
van Lieshout, N., A. van der Burgt, M.E. de Vries, M. ter Maat, D. Eickholt, D. Esselink, M.P.W. van Kaauwen, L.P. Kodde, R.G.F. Visser, P. Lindhout, and R. Finkers. 2020. Solyntus, the new highly contiguous reference genome for potato (Solanum tuberosum). G3 Genes Genomics Genetics 10: 3489–3495.
Veilleux, R.E., J. Booze-Daniels, and E. Pehu. 1985. Anther culture of a 2n pollen producing clone of Solanum phureja Juz. & Buk. Canadian Journal of Genetics and Cytology 27: 559–564.
Vos, P.G., J.G.A.M.L. Uitdewilligen, R.E. Voorrips, R.G.F. Visser, and H.J. van Eck. 2015. Development and analysis of a 20K SNP array for potato (Solanum tuberosum): An insight into the breeding history. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 128: 2387–2401.
Wang, M., S. Allefs, R.G. van den Berg, V.G.A.A. Vleeshouwers, E.A.G. van der Vossen, and B. Vosman. 2008. Allele mining in Solanum: Conserved homologues of Rpi-blb1 are identified in Solanum stoloniferum. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 116: 933–943.
Wenzel, G., O. Schieder, T. Przewozny, S.K. Sopory, and G. Melchers. 1979. Comparison of single cell culture derived Solanum tuberosum L. plants and a model for their application in breeding programs. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 55: 49–55.
Yamada, T., S. Misoo, T. Ishii, Y. Ito, K. Takaoka, and O. Kamijima. 1997. Characterization of somatic hybrids between tetraploid Solanum tuberosum L. and dihaploid S. scaule. Breeding Science 47: 229–236.
Yamada, T., K. Hosaka, K. Nakagawa, N. Kaide, S. Misoo, and O. Kamijima. 1998a. Nuclear genome constitution and other characteristics of somatic hybrids between dihaploid Solanum acaule and tetraploid S. tuberosum. Euphytica 102: 239–246.
Yamada, T., K. Hosaka, N. Kaide, K. Nakagawa, S. Misoo, and O. Kamijima. 1998b. Cytological and molecular characterization of BC1 progeny from two somatic hybrids between dihaploid Solanum acaule and tetraploid S. tuberosum. Genome 41: 743–750.
Zhou, Q., D. Tang, W. Huang, Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, J.P. Hamilton, R.G.F. Visser, C.W.B. Bachem, C.R. Buell, Z. Zhang, C. Zhang, and S. Huang. 2020. Haplotype-resolved genome analyses of a heterozygous diploid potato. Nature Genetics 52: 1018–1023.
Acknowledgements
I thank E. Kakuta and W. Takenaka for the maintenance of the in vitro plants. This research was financially supported in part by a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research for Young Scientists (Grant Number JP19K15813) and by Calbee Inc., Hokkaido Potato Growers Association, Kewpie Corp., KENKO Mayonnaise Co., Ltd., and the Japan Snack Cereal Foods Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS and KH conducted entire experiments and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to late Dr. Yukio Irikura (died at the age of 72 on June 1, 2002), who created most of the plant materials used in this study. The Hawkes (1990) classification system is tentatively adopted throughout the text.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanetomo, R., Hosaka, K. Re-evaluation of Monohaploid Solanum verrucosum and S. bulbocastanum (2n = x = 12) and Dihaploid S. stoloniferum and S. acaule (2n = 2x = 24), All Derived from Anther Culture. Am. J. Potato Res. 98, 333–343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-021-09847-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-021-09847-y