Abstract
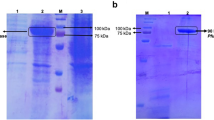
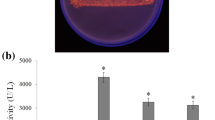
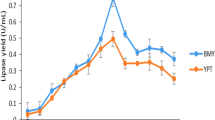
Lipases are industrially important enzymes having vast applications in various fields. Cloning and expression of lipase enzyme-encoding genes in suitable host lead to their widespread use in different fields. The present study represents the first attempt towards the expression of the synthetic lipase gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. An alkalophilic lipase gene (GenBank accession number: NP_388152) from Bacillus subtilis was synthetically designed and introduced in the pJN105 vector and subsequently cloned in Pseudomonas aeruginosa SDK-6. Agarose gel electrophoresis confirmed the transformation of SDK-6, exhibiting a band difference of ~ 700 bp between native and recombinant pJN105. Further amplification of cloned lipase gene was confirmed using PCR amplification with Lip 1 and Lip 2 primers respectively, followed by restriction analysis. Approximately 15-fold increase in lipase production was observed in recombinant Pseudomonas as compared to the native strain. One factor at a time (OFAT) analysis revealed L-arabinose, inoculum size (0.5%; v/v), and agitation (120 rpm) as significant factors affecting the over-expression of lipase enzyme. Optimization of enzyme induction conditions by central composite design (CCD) led to 1.60-fold increase in the production of lipase at 0.65% (w/v) inducer concentration, OD600—1.075 before induction and 35 °C post induction temperature with overall lipase production of 50.50 IU/mL. Statistical validation of observed value via ANOVA showed an F-value of 138.70 at p < 0.01 with R2 of 0.9921.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acikel U, Ersan M, Acikel YS (2010) Optimization of critical medium components using response surface methodology for lipase production by Rhizopus delemar. Food and Bioprod Process 88:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2009.08.003
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO (2018) Optimization of culture conditions for enhanced lipase production by an indigenous Bacillus aryabhattai SE3-PB using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32:1514–1526. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2018.1514985
Aulakh SS, Prakash R (2010) Optimization of medium and process parameters for the production of lipase from an oil-tolerant Aspergillus sp. (RBD-01). J Basic Microbiol 50:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200900361
Baharum SN, Razak ABS, Basri MC, Rahman MBA, Rahman RNZRA (2003) Organic solvent tolerant lipase by Pseudomonas sp. strain S5: stability of enzyme in organic solvent and physical factors affecting its production. Ann Microbiol 53:75–83
Batumalaie K, Khalili E, Mahat NA, Huyop FZ, Wahab RA (2018) A statistical approach for optimizing the protocol for overexpressing lipase KV1 in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1407670
Chen PT, Chen YC, Lin YY, Su HH (2015) Strategy for efficient production of recombinant Staphylococcus epidermidis lipase in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Eng J 103:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.008
Dartois V, Baulard A, Schanck K, Colson C (1992) Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of a lipase gene from Bacillus subtilis 168. BBA-Gene Struct Expr 1131:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4781(92)90023-S
Elena C, Ravasi P, Castelli ME, Peir S, Menzella HG (2014) Expression of codon optimized genes in microbial systems: current industrial applications and perspectives. Front Microbiol 5:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00021
Emtenani S, Asoodeh A, Emtenani S (2013) Molecular cloning of a thermo-alkaliphilic lipase from Bacillus subtilis DR8806: expression and biochemical characterization. Process Biochem 48:1679–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.08.016
Francis DM, Page R (2010) Strategies to optimize protein expression in E. coli. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 61:5.24.1–5.24.29. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140864.ps0524s61
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:763–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1568-8
Gupta N, Sahai V, Gupta R (2007) Alkaline lipase from a novel strain Burkholderia multivorans: statistical medium optimization and production in a bioreactor. Proc Biochem 42:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2006.10.006
Gustafsson C, Govindarajan S, Minshull J (2004) Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol 22:346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.04.006
Gutarra ML, de Godoy MG, Silva JN, Guedes IA, Lins U, Castilho LR, Freire DM (2009) Lipase production and Penicillium simplicissimum morphology in solid-state and submerged fermentations. Biotechnol J 4:1450–1459. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.200800298
Guzman LM, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J (1995) Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose pBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 177:4121–4130. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.177.14.4121-4130.1995
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Tech 39:235–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016
Hirose I, Sano K, Shioda I, Kumano M, Nakamura K, Yamane K (2000) Proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis extracellular proteins: a two-dimensional protein electrophoretic study. Microbiology 146:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-1-65
Jaeger KE, Eggert T (2002) Lipases for biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:390–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00341-5
Jaeger KE, Dijkstra BW, Reetz MT (1999) Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:315–351. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.315
Kai W, Peisheng Y (2016) Optimization of lipase production from a novel strain Thalassospira permensis M35–15 using response surface methodology. Bioengineered 7:298–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2016.1197713
Kanmani P, Kumaresan K, Aravind J (2015) Gene cloning, expression, and characterization of the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PS35 lipase. Braz J Microbiol 46:1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246420141068
Kaur B, Chakraborty D, Kumar B (2014) Metabolic engineering of Pediococcus acidilactici BD16 for production of vanillin through ferulic acid catabolic pathway and process optimization using response surface methodology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8539–8551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5950-x
Kaur D, Singh RP, Gupta S (2022) Screening and characterization of next-generation biofuels producing bacterial strains. Curr Microbiol 79:85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02781-0
Khurana J, Pratibha C, Kaur J (2017) Studies on recombinant lipase production by E. coli effect of media and bacterial expression system optimization. Int J Mol Biol 2:17–23. https://doi.org/10.15406/ijmboa.2017.02.00008
Kumar S, Kikon K, Upadhyay A, Kanwar SS, Gupta R (2005) Production, purification, and characterization of lipase from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus coagulans BTS-3. Protein Expr Purif 41:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2004.12.010
Kumar R, Sharma M, Singh R, Kaur J (2013) Characterization and evolution of a metagenome-derived lipase towards enhanced enzyme activity and thermostability. Mol Cell Biochem 373:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1483-8
Larentis AL, Argondizzo AP, Esteves Gdos S, Jessouron E, Galler R, Medeiros MA (2011) Cloning and optimization of induction conditions for mature PsaA (pneumococcal surface adhesin A) expression in Escherichia coli and recombinant protein stability during long-term storage. Protein Expr Purif 78:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2011.02.013
Lesuisse E, Schanck K, Colson C (1993) Purification and preliminary characterization of the extracellular lipase of Bacillus subtilis 168, an extremely basic tolerant enzyme. Eur J Biochem 216:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18127.x
Ma RJ, Wang YH, Liu L, Bai LL, Ban R (2018) Production enhancement of the extracellular lipase LipA in Bacillus subtilis: effects of expression system and Sec pathway components. Protein Expr Purif 142:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2017.09.011
Ma J, Zhang Z, Wang B, Kong X, Wang Y, Cao S, Feng Y (2006) Over-expression and characterization of a lipase from Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr Purif 45:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2005.06.004
Montgomery DC (1997) Response surface methods and other approaches to process optimization. In: Montgomery DC (ed) Design and analysis of experiments. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 427–510
Moradi S, Razavi SH, Mousavi SM (2018) Isolation of lipase producing bacteria from olive extract to improve lipase production using a submerge fermentation technique. J Food Bioprocess Eng 1–8.
Muntari B, Amid A, Mel M, Jami MS, Salleh HM (2012) Recombinant bromelain production in Escherichia coli: process optimization in shake flask culture by response surface methodology. AMB Express 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-0855-2-12
Newman JR, Fuqua C (1999) Broad-host-range expression vectors that carry the L-arabinose-inducible Escherichia coli araBAD promoter and the araC regulator. Gene 227:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00601-5
Nguyen VDH, Huynh TNP, Nguyen TTT, Ho HH, Trinh LTP, Nguyen AQ (2024) Expression and characterization of a lipase EstA from Bacillus subtilis KM-BS for application in bio-hydrolysis of waste cooking oil. Protein Expr Purif 215:106419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2023.106419
Nthangeni MB, Patterton HG, Tonder AV, Vergeer WP, Litthauer D (2001) Over-expression and properties of a purified recombinant Bacillus licheniformis lipase: a comparative report on Bacillus lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 28:705–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-0229(01)00316-7
Obeng DP, Morrell S, Napier-Munn TJ (2005) Application of central composite rotatable design to modeling the effect of some operating variables on the performance of three-product cyclone. Int J Miner Process 76:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2005.01.002
Olusesan AT, Azura LK, Forghani B, Bakar FA, Mohamed AK, Radu S, Manap MY, Saari N (2011) Purification, characterization and thermal inactivation kinetics of a non-regioselective thermostable lipase from a genotypically identified extremophilic Bacillus subtilis NS 8. New Biotechnol 28:738–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.01.002
Packiam KAR, Ramanan RN, Ooi CW, Krishnaswamy L, Tey BT (2020) Stepwise optimization of recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli utilizing computational and experimental approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:3253–3266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10454-w
Pahoja WM, Sethar MA (2002) A review of enzymatic properties of lipase in plants, animals and microorganisms. J Appl Sci 2:474–484. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2002.474.484
Pandey A, Benjamin S, Soccol CR, Poonam N, Krieger N, Soccols VT (1999) The realm of microbial lipases in biotechnology. Biotechnol Applied Biochem 29:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-8744.1999.tb00541.x
Papaneophytou CP, Kontopidis GA (2012) Optimization of TNF-α over-expression in Escherichia coli using response surface methodology: purification of the protein and oligomerization studies. Protein Expr Purif 86:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2012.09.002
Papaneophytou CP, Rinotas V, Douni E, Kontopidis G (2013) A statistical approach for optimization of RANKL over-expression in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization of the protein. Protein Expr Purif 90:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2013.04.005
Pinsirodom P, Parkin KL (2001) Lipase assays. Curr Protoc Food Anal Chem 1:C3.1.1-C3.1.13. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142913.fac0301s00
Salihu A, Alam MZ (2015) Solvent tolerant lipases: a review. Process Biochem 50:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.10.019
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shi B, Wu W, Wen J, Shi Q, Wu S (2010) Cloning and expression of a lipase gene from Bacillus subtilis FS1403 in Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60:399–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0055-y
Shojaosadati SA, Kolaei SMV, Babaeipour V, Farnoud AM (2008) Recent advances in high cell density cultivation for production of recombinant protein. Iran J Biotechnol 6:63–84
Sinchaikul S, Sookkheo B, Phutrakul S, Pan F, Chen S (2001) Optimization of a thermostable lipase from Bacillus stearothermophilus P1: over-expression, purification, and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 22:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1006/prep.2001
Swalley SE, Fulghum JR, Chambers SP (2006) Screening factors effecting a response in soluble protein expression: formalized approach using design of experiments. Anal Biochem 351:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.11.046
Tripathi NK, Shrivastava A (2019) Recent developments in bioprocessing of recombinant proteins: expression hosts and process development. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00420
Wang Y, Wang Z, Xu Q, Du G, Hua Z, Liu J, Li J, Chen J (2009) Lowering induction temperature for enhanced production of polygalacturonate lyase in recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem 44:949–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.04.019
Zafar A, Rahman Z, Hamid A, Sughra F, Makhdoom M, Fatima S, Ahmed H, Mehmood Z, Khan M, Aftab MN (2024) Heterologous expression and characterization of a novel thermostable and alkali stable recombinant lipase enzyme from Bacillus thuringensis into E. coli BL21 (DE3) for detergent formulation. J Surfact Deterg. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsde.12731
Zhou Y, Han LR, He HW, Sang B, Yu DL, Feng JT, Zhang X (2018) Effects of agitation, aeration and temperature on production of a novel glycoprotein GP-1 by Streptomyces kanasenisi ZX01 and scale-up based on volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient. Molecules 23:125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010125
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly obliged to Prof. Caroline S. Harwood (Department of Microbiology, University of Washington, Seattle, USA) for providing the plasmid pJN105 to accomplish this research. The authors would also like to acknowledge the Faculty and Head, Department of Biotechnology and Food Technology, Punjabi University, Patiala, India, for their help and suggestions during this work.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Saurabh Gupta designed the study. Ms. Damanjeet Kaur performed the experiments. Dr. Saurabh Gupta analyzed the data. Dr. Rupinder Pal Singh designed the CCD model. Ms. Damanjeet Kaur prepared the first draft of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, D., Singh, R.P. & Gupta, S. Construction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa SDK-6 with synthetic lipase gene cassette and optimization of different parameters using response surface methodology for over-expression of recombinant lipase. Folia Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01167-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01167-y