Abstract
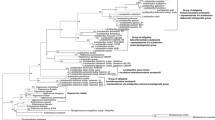
The order Lactobacillales represents a morphologically, metabolically, and physiologically diverse group of bacteria. Lactic acid bacteria represent the core of this phylogenetic group. They are a part of epiphytic microflora, fermented dairy, meat, fruit and vegetable products, and the digestive tract of humans and animals. Despite the fact that these bacteria form a phenotypically and genotypically heterogeneous group, their phylogenetic relationship enables to propose a common genetic marker usable in classification, typing, and phylogeny. By creation of consensus sequence based on available genomic sequences of some representatives of order Lactobacillales, a specific primer-pair binding variable region of aspS gene (length of 615 nts) encoding the aspartyl-tRNA synthetase was designed. This gene has not yet been used in classification and phylogeny of the order Lactobacillales, although it meets the requirements of molecular markers (distribution and single copy in bacterial genomes, functional constancy and genetic stability, sequence variability among taxonomic units, irreplaceable role in proteosynthesis). Primers were applied on 54 type and wild Lactobacillales strains. Obtained sequences allowed to provide alignments for purpose of phylogenetic tree reconstructions that uncovered particular phylogenetic clusters of vagococci/enterococci, obligately homofermentative and heterofermentative lactobacilli. Although a relatively short fragment of the aspS gene (approximately 33% of the complete gene sequence) was evaluated, much higher sequence variability (61.8% of pairwise identity) among strains examined compared with 16S rRNA gene (90.7%, length of 1318 nt) provides a relatively simple and effective tool for classification and typing of selected representatives of the order Lactobacillales.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carr FJ, Chill D, Maida N (2002) The lactic acid bacteria: a literature survey. Crit Rev Microbiol 28:281–370
Claesson MJ, van Sinderen D, O'Toole PW (2008) Lactobacillus phylogenomics-towards a reclassification of the genus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2945–2954
Ehrmann MA, Müller MR, Vogel RF (2003) Molecular analysis of sourdough reveals Lactobacillus mindensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:7–13
Glaeser SP, Kämpfer P (2015) Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) in prokaryotic taxonomy. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:237–245
Goh SH, Facklam RR, Chang M, Hill JE, Tyrrell GJ, Burns EC, Chan D, He C, Rahim T, Shaw C, Hemmingsen SM (2000) Identification of Enterococcus species and phenotypically similar Lactococcus and Vagococcus species by reverse checkerboard hybridization to chaperonin 60 gene sequences. J Clin Microbiol 38:3953–3959
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Hammes WP, Hertel C (2009) Genus Lactobacillus. In: de Vos P, Garrity GM, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd edn, vol. 3 (The Firmicutes). Springer, New York, pp 466–467
Killer J, Havlík J, Vlková E, Rada V, Pechar R, Benada O, Kopečný J, Kofroňová O, Sechovcová H (2014) Lactobacillus rodentium sp. nov., from the digestive tract of wild rodents. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1526–1533
Killer J, Mekadim C, Pechar R, Bunešová V, Mrázek J, Vlková E (2018) Gene encoding the CTP synthetase as an appropriate molecular tool for identification and phylogenetic study of the family Bifidobacteriaceae. Microbiologyopen. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.579 (in press)
Killer J, Švec P, Sedláček I, Cernohlávková J, Benada O, Hroncová Z, Havlík J, Vlková E, Rada V, Kopecny J, Kofronová O (2014) Vagococcus entomophilus sp. nov., from the digestive tract of a wasp (Vespula vulgaris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:731–737
Killer J, Votavová A, Valterová I, Vlková E, Rada V, Hroncová Z (2014) Lactobacillus bombi sp. nov., from the digestive tract of laboratory-reared bumblebee queens (Bombus terrestris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2611–2617
Klein G, Pack A, Bonaparte C, Reuter G (1998) Taxonomy and physiology of probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 41:103–125
Loy A, Lehner A, Lee N, Adamczyk J, Meier H, Ernst J, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (2002) Oligonucleotide microarray for 16S rRNA gene-based detection of all recognized lineages of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5064–5081
Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB (2009) Order II. Lactobacillales ord. nov. In: de Vos P, Garrity GM, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed, vol. 3 (The Firmicutes). Springer, New York, p 464
Makarova KS, Koonin EV (2007) Evolutionary genomics of lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol 189:1199–1208
Makarova K, Slesarev A, Wolf Y, Sorokin A, Mirkin B, Koonin E, Pavlov A, Pavlova N, Karamychev V, Polouchine N, Shakhova V, Grigoriev I, Lou Y, Rohksar D, Lucas S, Huang K, Goodstein DM, Hawkins T, Plengvidhya V, Welker D, Hughes J, Goh Y, Benson A, Baldwin K, Lee JH, Díaz-Muñiz I, Dosti B, Smeianov V, Wechter W, Barabote R, Lorca G, Altermann E, Barrangou R, Ganesan B, Xie Y, Rawsthorne H, Tamir D, Parker C, Breidt F, Broadbent J, Hutkins R, O'Sullivan D, Steele J, Unlu G, Saier M, Klaenhammer T, Richardson P, Kozyavkin S, Weimer B, Mills D (2006) Comparative genomics of the lactic acid bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15611–15616
Mao Y, Chen M, Horvath P (2015) Lactobacillus herbarum sp. nov., a species related to Lactobacillus plantarum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4682–4688
Martin DP, Lemey P, Lott M, Moulton V, Posada D, Lefeuvre P (2010) RDP3: a flexible and fast computer program for analyzing recombination. Bioinformatics 26:2462–2463
Martinez-Murcia AJ, Monera A, Saavedra MJ, Oncina R, Lopez-Alvarez M, Lara E, Figueras MJ (2011) Multilocus phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:189–199
Mayo B, van Sinderen D, Ventura M (2008) Genome analysis of food grade lactic acid-producing bacteria: from basics to applications. Curr Genomics 9:169–183
Naser SM, Dawyndt P, Hoste B, Gevers D, Vandemeulebroecke K, Cleenwerck I, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2007) Identification of lactobacilli by pheS and rpoA gene sequence analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2777–2789
Naser SM, Thompson FL, Hoste B, Gevers D, Dawyndt P, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2005) Application of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) for rapid identification of Enterococcus species based on rpoA and pheS genes. Microbiology 151:2141–2150
Nuñez H, Loyola D, Cárdenas JP, Holmes DS, Johnson DB, Quatrini R (2014) Multi locus sequence typing scheme for Acidithiobacillus caldus strain evaluation and differentiation. Res Microbiol 165:735–742
Oguntoyinbo FA, Narbad A (2012) Molecular characterization of lactic acid bacteria and in situ amylase expression during traditional fermentation of cereal foods. Food Microbiol 31:254–262
Palakawong Na Ayudthaya S, Hilderink LJ, Oost JV, Vos WM, Plugge CM (2017) Streptococcus caviae sp. nov., isolated from guinea pig faecal samples. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1551–1556
Rahkila R, Johansson P, Säde E, Paulin L, Auvinen P, Björkroth J (2015) Multilocus sequence typing of Leuconostoc gelidum subsp. gasicomitatum, a psychrotrophic lactic acid bacterium causing spoilage of packaged perishable foods. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2474–2480
Roux S, Enault F, Bronner G, Debroas D (2011) Comparison of 16S rRNA and protein-coding genes as molecular markers for assessing microbial diversity (Bacteria and Archaea) in ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78:617–628
Satokari RM, Vaughan EE, Smidt H, Saarela M, Mättö J, de Vos WM (2003) Molecular approaches for the detection and identification of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the human gastrointestinal tract. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:572–584
Talavera G, Castresana J (2007) Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst Biol 56:564–577
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tatusov RL, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Kiryutin B, Koonin EV, Krylov DM, Mazumder R, Mekhedov SL, Nikolskaya AN, Rao BS, Smirnov S, Sverdlov AV, Vasudevan S, Wolf YI, Yin JJ, Natale DA (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4:41
Tindall BJ, Rosselló-Móra R, Busse HJ, Ludwig W, Kämpfer P (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:249–266
Tomasini N, Lauthier JJ, Llewellyn MS, Diosque P (2013) MLSTest: novel software for multi-locus sequence data analysis in eukaryotic organisms. Infect Genet Evol 20:188–196
Větrovský T, Baldrian P (2013) The variability of the 16S rRNA gene in bacterial genomes and its consequences for bacterial community analyses. PLoS One 8:e57923
Woese CR, Olsen GJ, Ibba M, Söll D (2000) Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, the genetic code, and the evolutionary process. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:202–236
Wu D, Jospin G, Eisen JA (2013) Systematic identification of gene families for use as “markers” for phylogenetic and phylogeny-driven ecological studies of bacteria and archaea and their major subgroups. PLoS One 8:e77033
Xing Z, Geng W, Li C, Sun Y, Wang Y (2017) Comparative genomics of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens ZW3 and related members of Lactobacillus spp. reveal adaptations to dairy and gut environments. Sci Rep 7(1):12827
Xu H, Liu W, Zhang W, Yu J, Song Y, Menhe B, Zhang H, Sun Z (2015) Use of multilocus sequence typing to infer genetic diversity and population structure of Lactobacillus plantarum isolates from different sources. BMC Microbiol 15:241
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Zhang ZG, Ye ZQ, Yu L, Shi P (2011) Phylogenomic reconstruction of lactic acid bacteria: an update. BMC Evol Biol 11:1
Zheng J, Ruan L, Sun M, Gänzle MA (2015) Genomic view of lactobacilli and pediococci demonstrates that phylogeny matches ecology and physiology. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:7233–7243
Funding
This study was funded by the Project Excellence (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000460), the Czech Health Research Council (Project No. 16-27449A), and the Institution research project No. RO 0318 of the Food Research Institute Prague (Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(ODP 752 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mekadim, C., Killer, J., Pechar, R. et al. Fragment of the aspartyl-tRNA synthetase applicable as a shared classification and phylogenetic marker in particular representatives of the order Lactobacillales. Folia Microbiol 64, 113–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0638-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0638-8