Abstract
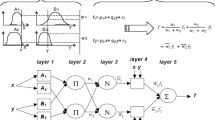
In this article, the accuracy of a soft computing technique is evaluated in terms of discharge coefficient prediction of an improved triangular side weir. The process includes simulating the discharge coefficient with the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). Matlab software is used for ANFIS modeling. To identify the most appropriate input variables, eight different input combinations with various numbers of inputs are examined. The performance of the proposed system is confirmed by comparing the ANFIS and experimental results for the testing dataset. The performance evaluation demonstrates that the ANFIS model with five inputs (Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.014) is more accurate than the ANFIS model with one input (RMSE = 0.088). The ANFIS model results are also compared with the results obtained from previous regression and soft computing studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin, M. C. and Emiroglu, M. E. (2013). “Determination of capacity of labyrinth side weir by CFD.” Flow. Meas. Instrum., Vol. 29, No. 2013, pp. 1–8, DOI: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2012.09.008.
Bilhan, O., Emiroglu, M. E., and Kisi, O. (2010). “Application of two different neural network techniques to lateral outflow over rectangular side weirs located on a straight channel.” Adv. Eng. Software, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 831–837, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2010.03.001.
Bilhan, O., Emiroglu, M. E., and Kisi, O. (2011). “Use of artificial neural networks for prediction of discharge coefficient of triangular labyrinth side weir in curved channels.” Adv. Eng. Software, Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 208–214, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.02.006.
Borghei, S. M. and Parvaneh, A. (2011). “Discharge characteristics of a modified oblique side weir in subcritical flow.” Flow. Meas. Instrum., Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 370–376, DOI: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2011.04.009.
Cosar, A. and Agaccioglu, H. (2004). “Discharge coefficient of a triangular side-weir located on a curved channel.” J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., Vol. 130, No. 5, pp. 410–423, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2004)130:5(410).
Dastorani, M. T., Afkhami, H., Sharifidarani, H., and Dastorani, M. (2010). “Application of ANN and ANFIS models on dryland precipitation prediction (case study: Yazd in central Iran).” J. Appl. Sci., Vol. 10, No. 20, pp. 2387–2394, DOI: 10.3923/jas.2010.2387.2394.
De Marchi, G. (1934). “Saggio di teoria del funzionamento degli stramazzi laterali.” L’Energia Elettrica, Vol. 11, No. 11, pp. 849–860.
Dursun, O. F., Kaya, N., and Firat, M. (2012). “Estimating discharge coefficient of semi-elliptical side weir using ANFIS.” J. Hydrol., Vols. 426–427, No. 2012, pp. 55–62, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.01.010.
Ebtehaj, I. and Bonakdari, H. (2014). “Performance evaluation of adaptive neural fuzzy inference system for sediment transport in sewers.” Water. Resour. Manage., Vol. 28, No. 13, pp. 4765–4779, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-014-0774-0.
El-Shafie, A., Jaafer, O., and Seyed, A. (2011). “Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system based model for rainfall forecasting in Klang River, Malaysia.” Int. J. Phys. Sci., Vol. 6, No. 12, pp. 2875–2888.
Emiroglu, M. E. and Kisi, O. (2013). “Prediction of discharge coefficient for trapezoidal labyrinth side weir using a neuro-fuzzy approach.” Water. Resour. Manage., Vol. 27, No. 5, pp. 1473–1488, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-012-0249-0.
Emiroglu, M. E., Kisi, O., and Bilhan, O. (2010). “Predicting discharge capacity of triangular labyrinth side weir located on a straight channel by using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy technique.” Adv. Eng. Software, Vol. 41, No. 2, pp. 154–160, DOI: 0.1016/j.advengsoft. 2009.09.006.
Ghodsian, M. (2003). “Supercritical flow over a rectangular side weir.” Can. J. Civ. Eng., Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 596–600, DOI: 10.1139/L03-004.
Ghodsian, M. (2004). “Flow over triangular side weir.” Sci. Iranica, Vol. 11, Nos. 1-2, pp. 114-120.
Jang, J. S. R. (1993). “ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system.” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern., Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 665–685, DOI: 10.1109/21.256541.
Khajeh, A., Modarress, H., and Rezaee, B. (2009). “Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for solubility prediction of carbon dioxide in polymers.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 36, No. 3 PART 1, pp. 5728–5732, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.06.051.
Kisi, O., Bilhan, O., and Emiroglu, M. E. (2013). “Anfis to estimate discharge capacity of rectangular side weir.” Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manage., Vol. 166, No. 9, pp. 479–487, DOI: 10.1680/ wama.11.00095.
Kisi, O., Emin Emiroglu, M., Bilhan, O., and Guven, A. (2012). “Prediction of lateral outflow over triangular labyrinth side weirs under subcritical conditions using soft computing approaches.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 39, No. 3, pp. 3454–3460, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.09.035.
Kumar, C. P. and Pathak, S. K. (1987). “Triangular side weirs.” J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., Vol. 113, No. 1, pp. 98–105, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE) 0733-9437(1987)113:1(98).
Mirnaseri, M. and Emadi, A. (2013). “Hydraulic performance of combined flow rectangular labyrinth weir-gate.” Middle. East. J. Sci. Res., Vol. 18, No. 9, pp. 1335–1342, DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr. 2013.18.9.12374.
Muslu, Y. (2001). “Numerical analysis of lateral weir flow.” J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., Vol. 127, No. 4, pp. 246–253, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE) 0733-9437(2001)127:4(246).
Muslu, Y., Tozluk, H., and Yuksel, E. (2003). “Effect of lateral water surface profile on side weir discharge.” J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., Vol. 129, No. 5, pp. 371–375, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2003) 129:5(371).
Nadesamoorthy, T. and Thomson, A. (1972). “Discussion of “Spatially Varied Flow over Side-Weirs”.” J. Hydraul. Div., Vol. 98, No. 12, pp. 2234–2235.
Onen, F. (2014a). “GEP prediction of scour around a side weir in curved channel.” J. Environ Eng. Landsc. Manage., Vol. 22, No. 3, pp. 161–170, DOI: 10.3846/16486897.2013.865632.
Onen, F. (2014b). “Prediction of scour at a side-weir with GEP, ANN and Regression Models.” Arab. J. Sci. Eng., Vol. 39, No. 8, pp. 6031–6041, DOI: 10.1007/s13369-014-1244-y.
Petković, D. and Ćojbašić, Z. (2011). “Adaptive neuro-fuzzy estimation of automatic nervous system parameters effect on heart rate variability.” Neural. Comput. Appl., Vol. 21, No. 8, pp. 2065–2070. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-011-0629-z.
Petković, D., Ćojbašić, Ž., and Lukić, S. (2013a). “Adaptive neuro fuzzy selection of heart rate variability parameters affected by autonomic nervous system.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 40, No. 11, pp. 4490–4495, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.01.055.
Petković, D., Issa, M., Pavlović, N. D., Pavlović, N. T., and Zentner, L. (2012). “Adaptive neuro-fuzzy estimation of conductive silicone rubber mechanical properties.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 39, No. 10, pp. 9477–9482, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.111.
Petković, D., Pavlović, N. D., Ćojbašić, Ž., and Pavlović, N. T. (2013b). “Adaptive neuro fuzzy estimation of underactuated robotic gripper contact forces.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 281–286, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.07.076.
Ranga Raju, K. G., Prasad, B., and Gupta, S. K. (1979). “Side weir in rectangular channel.” J. Hydraul. Div., Vol. 105, No. 5, pp. 547–554.
Seyedian, S. M., Ghazizadeh, M. J., and Tareghian, R. (2014). “Determining side-weir discharge coefficient using Anfis.” Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manage., Vol. 167, No. 4, pp. 230–237, DOI: 10.1680/wama. 12.00102.
Singh, R., Manivannan, D., and Satyanarayana, T. (1994). “Discharge coefficients of rectangular side weirs.” J. Irrig Drain. Eng., Vol. 120, No. 4, pp. 814–819, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1996)122:2(132).
Swamee, P. K., Pathak, S. K., and Ali, M. S. (1994). “Side weir analysis using elementary discharge coefficient.” J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., Vol. 120, No. 4, pp. 742–755, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1994)120:4 (742).
Talei, A., Chua, L. H. C., and Quek, C. (2010). “A novel application of a neuro-fuzzy computational technique in event-based rainfall-runoff modeling.” Expert. Sys. Appl., Vol. 37, No. 12, pp. 7456–7468, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.04.015.
Wahida Banu, R. S. D., Shakila Banu, A., and Manoj, D. (2011). “Identification and control of nonlinear systems using soft computing techniques.” Int. J. Model. Optimiz., Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 24–28, DOI: 10.7763/IJMO.2011.V1.5.
Wu, C. L. and Chau, K. W. (2012). “Prediction of rainfall time series using modular soft computing methods.” Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., Vol. 26, No. 3, pp. 997–1007, DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2012.05.
Yuksel, E. (2004). “Effect of specific energy variation on lateral overflows.” Flow Meas Instrum, Vol. 15, Nos. 5-6, pp. 259–269, DOI: 10.1016/ j.flowmeasinst.2004.06.005.
Zaji, A. H. and Bonakdari, H. (2014). “Performance evaluation of two different neural network and particle swarm optimization methods for prediction of discharge capacity of modified triangular side weirs.” Flow. Meas. Instrum., Vol. 40, pp. 149–156, DOI: 10.1016/ j.flowmeasinst.2014.10.002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamshirband, S., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H. et al. Improved side weir discharge coefficient modeling by adaptive neuro-fuzzy methodology. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 2999–3005 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-1723-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-1723-7