Abstract
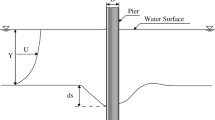
Side-weir is known as a lateral intake structure, which is widely used in irrigation, land drainage, and urban sewerage system by flow diversion device. Local scour in-/volves the removal of material around piers, abutments, side-weir, spurs, and embankments. Clear-water scour depth based on four dimensional parameters: approach flow velocity (V 1/ V c ), water head ratio (h 1 − p)/h 1, side-weir length (L/b) and sediment size (d 50/p). The equilibrium depth of scour increases by the increase of the dimensionless parameters of approach flow velocity, water head ratio, side-weir length and sediment size. This study presents artificial neural network (ANN) and gene expression programming (GEP) models, which is an algorithm based on genetic algorithms and genetic programming, for prediction of the clear-water scour depth at side-weir. The explicit formulations of the GEP models are developed. The GEP-based formulation and ANN approach are compared with experimental results, multiple linear/nonlinear regressions (MLR/MNLR). The performance of GEP is found in slightly more influential than ANN approach and MNLR for predicting the clear-water scour depth at side-weir.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu-Tech L.: Discussion of spatially varied flow over side-weir. ASCE J. Hydraul. Eng. 98(11), 2046–2048 (1972)
Ramamurthy A.S.: Lateral weirs in trapezoidal channels. J.Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 112(2), 130–137 (1986)
Cheong H.F.: Discharge coefficient of lateral diversion from trapezoidal channel. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 117(4), 461–475 (1991)
Singh R., Manivannan D., Satyanarayana T.: Discharge coefficient of rectangular side weirs. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 120(4), 814–819 (1994)
Agaccioglu H., Yuksel Y.: Side-weir flow in curved channels. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 124(3), 163–175 (1998)
Muslu Y.: Numerical analysis for lateral weir flow. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 127(4), 246–253 (2001)
Fares Y.R.: Changes of bed topography in meandering rivers at a neck cutoff intersection. J. Environ. Hydrol. 8(13), 1–18 (2000)
Onen, F.: Hareketli tabanli akarsularda yanal akimin hidrodinamiğinin incelenmesi. (An investigation of hydrodynamic of lateral flows in movable bed rivers). PhD thesis presented to Yildiz Tecnical University, Istanbul. Turkey (in Turkish) (2005)
Onen F., Agaccioglu H.: Scour at a side weir intersection located on an alluvial river. Nord. Hydrol. 38(2), 165–176 (2007)
Chow, V.T.: Open Channel Hydraulics, pp. 439–460. Mcgraw Hill, Chap. 16, (1959)
Raudkivi A.J.: Functional trends of scour at bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 112(1), 1–13 (1986)
Melville B.W., Chiew Y.M.: Time scale for local scour at bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 125(1), 59–65 (1999)
Harris E.L., Babovic V., Falconer R.A.: Velocity predictions in compound channels with vegetated floodplains using genetic programming. Int. J. River Mang. 1(2), 117–123 (2003)
Dorado J., Rabunal J.R., Pazos A., Rivero D., Santos A., Puertas J.: Prediction and modeling of the rainfall–runoff transformation of a typical urban basin using ANN and GP. Appl. Artif. Intell. 17, 329–343 (2003)
Khorchani M., Blanpain O.: Development of a discharge equation for side weirs using artificial neural networks. J. Hydroinform. 7(1), 31–39 (2005)
Srinivasulu S., Jain A.: A comparative analysis of training methods for artificial neural network rainfall–runoff models. Appl. Soft Comput. 6, 295–306 (2006)
Aytek A., Kisi O.: A genetic programming approach to suspended sediment modeling. J. Hydrol. 351, 288–298 (2008)
Guven A., Gunal M.: Genetic programming approach for prediction of local scour downstream hyraulic structures. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 134(2), 241–249 (2008)
Guven A., Aytek A.: New approach for stage-discharge relationship: gene-expression programming. J. Hydrol. Eng. 14(8), 812–820 (2009)
Azamathulla H.M.D., Ghani A.A.B., Zakaria N.A., Lai S.H., Chang C.K., Leow C.S., Abuhasan Z.: Genetic programming to predict ski-jump bucket spill-way scour. J. Hydrodyn. 20(4), 477–484 (2008)
Azamathulla H.M.D., Ghani A.A.B., Zakaria N.A., Guven A.: Genetic programming to predict bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. 136(3), 165–169 (2010)
Eldrandaly K.: Integrating gene expression programming and geographic information systems for solving a multi site land use allocation problem. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 6(5), 1021–1027 (2009)
Bilhan O., Emiroglu M.E., Emiroglu M.E.: Use of artificial neural networks for prediction of discharge coefficient of triangular labyrinth side-weir in curved channels. Adv. Eng. Softw. 42(4), 208–214 (2011)
Baylar A., Unsal M., Ozkan F.: GEP Modeling of oxygen transfer efficiency prediction in aeration cascades. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 15(5), 799–804 (2011)
Unsal M.: GEP Modeling of penetration depth in sharp crested weirs. Arab. J. sci.Eng. 37(8), 2163–2174 (2012)
Toth E., Brandimarte L.: Prediction of local scour depth at bridge under piers under clear-water and live-bed condition: comparison of literature formulae and artificial neural networks. J. Hydroinform. 13(4), 812–824 (2011)
Azamathulla H.M.D.: Gene-expression programming to predict scour at a bridge abutment. J. Hydroinform. 14(2), 324–331 (2012)
Karami H., Ardeshir A., Saneie M., Salamation A.: Prediction of time variation of scour depth around spur dikes using neural networks. J. Hydrodyn. 14(1), 180–191 (2012)
Esmaeili, T.: Hydraulic and geometric numerical simulation of scouring around concrete bridge piers (case study), M.S. thesis, Dept. Hydr. Eng, Islamic Azad Univ-South Tehran Branch., Iran (2009)
Richardson J.E., Panchang V.G.: Three-dimensional simulation of scour-inducing flow at bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 124(5), 530–540 (1998)
Olsen, N.R.B.; Jimenes, O.F.; Abrahamsen, L.; Lovoll, A.: 3D CFD modeling of water and sediment flow in a hydropower reservoir. J. Sedimet. Res. 14(1), 1–8 (1999)
Tseng M.H., Yen C.L., Song C.S.: Computation of three dimensional flow around square and circular piers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 122, 120–128 (2000)
Esmaeili T., Dehghani A.A., Zahiri A.R, Suzuki K.: 3D Numerical simulation of scouring around bridge piers, World Academy of Science. Eng. Technol. 34, 1028–1032 (2009)
Taskiran T.: Prediction of California bearing ratio (CBR) of fine grained soils by AI methods. Adv. Eng. Softw. 41(9), 1115–1123 (2010)
Ferreira C.: Gene expression programming and the evolution of computer programs. In: de Castro, L.N., Zuben, F.J. (eds) Recent Developments in Biologically Inspired Computing, pp. 82–103. Idea Group Publishing, Hershey (2004)
Ferreira C.: Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Syst. 13, 87–129 (2001)
Ferreira C.: Gene Expression Programming: Mathematical Modeling by an Artificial Intelligence. Angra do Heroismo, Portugal (2002)
Jacomino V.M.F., Fields D.E.: A critical approach to the calibration of a watershed model. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 33(1), 143–154 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onen, F. Prediction of Scour at a Side-Weir with GEP, ANN and Regression Models. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6031–6041 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1244-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1244-y