Abstract
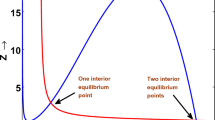
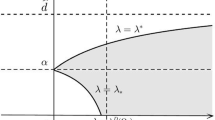
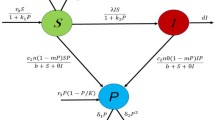
In this paper, a predator–prey model with fear-induced group defense and Monod–Haldane functional response is considered. We establish a connection between fear effect and group defense by incorporating anti-predator sensitivity and emphasizing their impact on the dynamics of the model. Our analysis shows that increasing anti-predator sensitivity lowers the threshold for initiating group defense, leading to faster adoption of prey defense strategies. The preliminary results include positivity, boundedness, and persistence. We find that under certain thresholds, anti-predator sensitivity can sustain species persistence; otherwise, predators may face extinction. Changes in anti-predator sensitivity significantly influence system dynamics, notably affecting the quantity and stability of equilibrium points. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the global properties of both boundary and interior equilibrium points. Additionally, the system undergoes Transcritical, Saddle-node and Hopf bifurcation by considering the anti-predator sensitivity as a bifurcation parameter and Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation with respect to the prey birth rate and the anti-predator sensitivity. Numerical simulations support our theoretical findings. Our study highlights the complex interplay of fear effect, group defense, and anti-predator sensitivity in predator–prey dynamics. These results may provide valuable biological insights into predator–prey interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molla, H., Sarwardi, S., Haque, M.: Dynamics of adding variable prey refuge and an Allee effect to a predator–prey model. Alex. Eng. J. 61(6), 4175–4188 (2022)
Prasad, B., Banerjee, M., Srinivasu, P.D.N.: Dynamics of additional food provided predator–prey system with mutually interfering predators. Math. Biosci. 246(1), 176–190 (2013)
Souna, F., Lakmeche, A., Djilali, S.: Spatiotemporal patterns in a diffusive predator–prey model with protection zone and predator harvesting. Chaos Solitons Fract. 140, 110180 (2020)
Ryu, K., Ko, W., Haque, M.: Bifurcation analysis in a predator–prey system with a functional response increasing in both predator and prey densities. Nonlinear Dyn. 94, 1639–1656 (2018)
Colon, C., Claessen, D., Ghil, M.: Bifurcation analysis of an agent-based model for predator–prey interactions. Ecol. Model. 317, 93–106 (2015)
Seo, G., DeAngelis, D.L.: A predator–prey model with a Holling type I functional response including a predator mutual interference. J. Nonlinear Sci. 21, 811–833 (2011)
Holling, C.S.: The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 97(S45), 5–60 (1965)
Liu, X., Huang, Q.: The dynamics of a harvested predator–prey system with Holling type IV functional response. Biosystems 169–170, 26–39 (2018)
Andrews, J.F.: A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 10(6), 707–723 (1968)
Freedman, H.I., Wolkowicz, G.S.: Predator–prey systems with group defence: the paradox of enrichment revisited. Bull. Math. Biol. 48, 493508 (1986)
Ajraldi, V., Pittavino, M., Venturino, E.: Modeling Herd behavior in population systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12(4), 2319–2338 (2011)
Braza, P.A.: Predator–prey dynamics with square root functional responses. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 13(4), 1837–1843 (2012)
Xu, C., San, Y., Tong, Z.: Global dynamics of a predator–prey model with defense mechanism for prey. Appl. Math. Lett. 62, 42–48 (2016)
Bulai, I.M., Venturino, E.: Shape effects on herd behavior in ecological interacting population models. Math. Comput. Simul. 141, 40–55 (2017)
Salman, S.M., Yousef, A.M., Elsadany, A.A.: Stability, bifurcation analysis and chaos control of a discrete predator–prey system with square root functional response. Chaos Solitons Fract. 93, 20–31 (2016)
Bi, Z., Liu, S., Ouyang, M.: Three-dimensional pattern dynamics of a fractional predator–prey model with cross-diffusion and herd behavior. Appl. Math. Comput. 421, 126955 (2022)
Yao, W., Li, X.: Complicate bifurcation behaviors of a discrete predator–prey model with group defense and nonlinear harvesting in prey. Appl. Anal. 102(9), 2567–2582 (2023)
Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Xiao, Y.: Canard phenomena for a slow-fast predator–prey system with group defense of the prey. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 527(1), 127418 (2023)
Suleman, A., Ahmed, R., Alshammari, F.S., Shah, N.A.: Dynamic complexity of a slow-fast predator–prey model with herd behavior. AIMS Math. 8(10), 24446–24472 (2023)
Li, Y., He, M., Li, Z.: Dynamics of a ratio-dependent Leslie–Gower predator–prey model with Allee effect and fear effect. Math. Comput. Simul. 201, 417–439 (2022)
Chen, M., Xu, Y., Zhao, J.: Turing–Hopf bifurcation analysis in a diffusive ratio-dependent predator–prey model with Allee effect and predator harvesting. Entropy 26(1), 18 (2023)
Wang, J.G., Meng, X.Y., Lv, L.: Stability and bifurcation analysis of a Beddington–DeAngelis prey–predator model with fear effect, prey refuge and harvesting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 33(01), 2350013 (2023)
Cui, M., Shao, Y., Xue, R.: Dynamic behavior of a predator–prey model with double delays and Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Axioms 12(1), 73 (2023)
Debnath, S., Majumdar, P., Sarkar, S.: Memory effect on prey–predator dynamics: exploring the role of fear effect, additional food and anti-predator behaviour of prey. J. Comput. Sci. 66, 101929 (2023)
Li, H., Tian, Y.: Dynamic behavior analysis of a feedback control predator–prey model with exponential fear effect and Hassell–Varley functional response. J. Frankl. Inst. 360(4), 3479–3498 (2023)
Chen, X., Du, Z.: Existence of positive periodic solutions for a neutral delay predator–prey model with Hassell–Varley type functional response and impulse. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 17, 67–80 (2018)
Taylor, R.J.: Predation. Chapman & Hall, New York (1984)
Lima, S.L.: Nonlethal effects in the ecology of predator–prey interactions. Bioscience 48(1), 25–34 (1998)
Creel, S., Christianson, D.: Relationships between direct predation and risk effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23(4), 194–201 (2008)
Lima, S.L.: Predators and the breeding bird: behavioural and reproductive flexibility under the risk of predation. Biol. Rev. 84(3), 485–513 (2009)
Maerz, J.C., Panebianco, N.L., Madison, D.M.: Effects of predator chemical cues and behavioral biorhythms on foraging, activity of terrestrial salamanders. J. Chem. Ecol. 27(7), 1333–1344 (2001)
Sheriff, M.J., Krebs, C.J., Boonstra, R.: The sensitive hare: sublethal effects of predator stress on reproduction in snowshoe hares. J. Anim. Ecol. 78(6), 1249–1258 (2009)
Cresswell, W.: Predation in bird populations. J. Ornithol. 152(Suppl 1), 251–263 (2011)
Zanette, L.Y., White, A.F., Allen, M.C., Clinchy, M.: Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year. Science 334(6061), 1398–1401 (2011)
Wang, X., Zanette, L., Zou, X.: Modelling the fear effect in predator–prey interactions. J. Math. Biol. 73, 1179–1204 (2016)
Pal, S., Pal, N., Samanta, S.: Effect of hunting cooperation and fear in a predator–prey model. Ecol. Complex. 39, 100770 (2019)
Mondal, S., Samanta, G.P.: Impact of fear on a predator–prey system with prey-dependent search rate in deterministic and stochastic environment. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(3), 2931–2959 (2021)
Panday, P., Pal, N., Samanta, S.: Dynamics of a stage-structured predator–prey model: cost and benefit of fear-induced group defense. J. Theor. Biol. 528, 110846 (2021)
Thirthar, A.A., Majeed, S.J., Alqudah, M.A.: Fear effect in a predator–prey model with additional food, prey refuge and harvesting on super predator. Chaos Solitons Fract. 159, 112091 (2022)
Sarkar, K., Khajanchi, S.: Spatiotemporal dynamics of a predator–prey system with fear effect. J. Frankl. Inst. 6, 66 (2023)
Rao, F., Kang, Y.: Dynamics of a stochastic prey–predator system with prey refuge, predation fear and its carry-over effects. Chaos Solitons Fract. 175, 113935 (2023)
Pal, D., Kesh, D., Mukherjee, D.: Cross-diffusion mediated Spatiotemporal patterns in a predator–prey system with hunting cooperation and fear effect. Math. Comput. Simul. 96, 66 (2024)
Sarkar, K., Khajanchi, S.: Impact of fear effect on the growth of prey in a predator–prey interaction model. Ecol. Complex. 42, 100826 (2020)
Dong, Y., Wu, D., Shen, C.: Influence of fear effect and predator-taxis sensitivity on dynamical behavior of a predator–prey model. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 73(1), 25 (2022)
Chen, F.: On a nonlinear nonautonomous predator–prey model with diffusion and distributed delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 180(1), 33–49 (2005)
Gard, T.C., Hallam, T.G.: Persistence in food webs-I Lotka–Volterra food chains. Bull. Math. Biol. 41(6), 877–891 (1979)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology I. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Verhulst, F.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems. Henri Poincaré, Springer (2012)
Perko, L.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems. Springer, New York (2013)
Zhang, Z.: Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations. American Mathematical Society, Philadelphia (1992)
Majumdar, P., Debnath, S., Mondal, B., Sarkar, S., Ghosh, U.: Complex dynamics of a prey–predator interaction model with Holling type-II functional response incorporating the effect of fear on prey and non-linear predator harvesting. Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo Series 72(2), 1017–1048 (2023)
Pal, S., Karmakar, S., Pal, S., Pal, N., Misra, A.K., Chattopadhyay, J.: Impact of fear and group defense on the dynamics of a predator–prey system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 34(02), 2450019 (2024)
Kuznetsov, Y.A., Kuznetsov, I.A., Kuznetsov, Y.: Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory. Springer, New York (1998)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (11672074), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2022J01192)and the Young Lecturer Education Research Project of Fujian Province (JAT220043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Yang, W. Impact of fear-induced group defense in a Monod–Haldane type prey–predator model. J. Appl. Math. Comput. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02101-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02101-8