Abstract
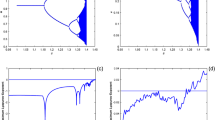
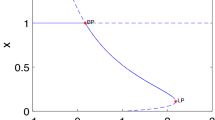
This paper presents a qualitative study of a predator–prey interaction system with the functional response proposed by Cosner et al. (Theor Popul Biol 56:65–75, 1999). The response describes a behavioral mechanism which a group of predators foraging in linear formation searches, contacts and then hunts a school of prey. On account of the response, strong Allee effects are induced in predators. In the system, we determine the existence of all feasible nonnegative equilibria; further, we investigate the stabilities and types of the equilibria. We observe the bistability and paradoxical phenomena induced by the behavior of a parameter. Moreover, we mathematically prove that the saddle-node, Hopf and Bogdanov–Takens types of bifurcations can take place at some positive equilibrium. We also provide numerical simulations to support the obtained results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso, D.M., Paolini, E.E., Moiola, J.L.: Bifurcation theory in mechanical systems. Mecánica Computacional 21, 1232–1247 (2002)
Alves, M.T., Hilker, F.M.: Hunting cooperation and Allee effects in predators. J. Theor. Biol. 419, 13–22 (2017)
Arditi, R., Ginzburg, L.R., Akcakaya, H.R.: Variation in plankton densities among lakes: a case for ratio-dependent models. Am. Nat. 138, 1287–1296 (1991)
Ascher, U., Ruuth, S., Wetton, B.: Implicit-explicit methods for time-dependent partial differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32, 797–823 (1995)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 331–340 (1975)
Berec, I.: Impacts of foraging facilitation among predators on predator-prey dynamics. Bull. Math. Biol. 72, 94–121 (2010)
Chen, J., Huang, J., Ruan, S., Wang, J.: Bifurcations of invariant tori in predator-prey models with seasonal prey harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 73, 1876–1905 (2013)
Cheng, K.S., Hsu, S.B., Lin, S.S.: Some results on global stability of a predator-prey system. J. Math. Biol. 12, 115–126 (1981)
Cosner, C., DeAngelis, D.L., Ault, J.S., Olson, D.B.: Effects of spatial grouping on the functional response of predators. Theor. Popul. Biol. 56, 65–75 (1999)
Cantrell, R.S., Cosner, C.: On the dynamics of predator-prey models with the Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 257, 206–222 (2001)
DeAngelis, D.L., Goldstein, R.A., O’Neill, R.V.: A model for trophic interaction. Ecology 56, 881–892 (1975)
Freedman, H.I., Wolkowicz, G.S.K.: Predator-prey systems with group defence: the paradox of enrichment revisited. Bull. Math. Biol. 48, 493–508 (1986)
Gao, Y., Li, B.: Dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with a strong allee effect. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 18, 2283–2313 (2013)
Haque, M.: A detailed study of the Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model. Math. Biosci. 234, 1–16 (2011)
Holling, C.S.: Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 91, 385–398 (1959)
Holling, C.S.: The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 46, 1–60 (1995)
Huang, J., Gong, Y., Ruan, S.: Bifurcation analysis in a predator-prey model with constant yield predator harvesting. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 18, 2101–2121 (2013)
Kuznetsov, Y.A.: Elements of applied bifurcation theory, Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 112. Springer, New York, (1995)
Liu, X., Wang, C.: Bifurcation of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Nonlinear Dyn. 62, 841–850 (2010)
Perko, L.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2001)
Rosenzweig, M.L.: Paradox of enrichment: destabilization of exploitation ecosystems in ecological time. Science 171, 385–387 (1971)
Ruan, S., Xiao, D.: Global analysis in a predator-prey system with nonmonotonic functional response. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61, 1445–1472 (2001)
Sakellaridis, N.G., Karystianos, M.E., Vournas, C.D.: Homoclinic loop and degenerate Hopf bifurcations introduced by load dynamics. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 24, 1892–1893 (2009)
Serajian, R.: Parameters’ changing influence with different lateral stiffnesses on nonlinear analysis of hunting behavior of a bogie. J. Meas. Eng. 1, 195–206 (2013)
Voorn, G.A.K., Hemerik, L., Boer, M.P., Kooi, B.W.: Heteroclinic orbits indicate overexploitation in predator-prey systems with a strong Allee effect. Math. Biosci. 209, 451–469 (2007)
Xiao, D., Jennings, L.S.: Bifurcations of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with constant rate harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65, 737–753 (2005)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J. Math. Biol. 43, 268–290 (2001)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Bogdanov-Takens bifurcations in predator-prey systems with constant rate harvesting. Fields Inst. Commun. 21, 493–506 (1999)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Codimension two bifurcations in a predator-prey system with group defense. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 11, 2123–2131 (2001)
Younesian, D., Jafari, A.A., Serajian, R.: Effects of the bogie and body inertia on the nonlinear wheel-set hunting recognized by the Hopf bifurcation theory. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 3(1), 186–196 (2011)
Zhang, Z., Ding, T., Huang, W., Dong, Z.: Qualitative theory of differential equations, Translations of Mathematical Monographs, vol. 101, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI (1992)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT [NRF-2017R1A2B1011902 to W. Ko]. The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions which helped to improve the quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in publishing this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, K., Ko, W. & Haque, M. Bifurcation analysis in a predator–prey system with a functional response increasing in both predator and prey densities. Nonlinear Dyn 94, 1639–1656 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4446-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4446-0