Abstract
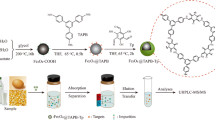
In this study, core-shell magnetic covalent organic framework nanoparticles (Fe3O4@COF) were prepared as solid-phase extraction (SPE) sorbents for simultaneous determination of five benzimidazole (BZD) residues in fruits and commercially available juices. Fe3O4@COF was prepared using the controllable in situ growth strategy and then fully characterized. This sensitive and selective analytical method was developed by combining the rapid magnetic SPE procedure and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The large surface area and suitable pore size of Fe3O4@COF facilitated the selective absorption of BZDs free from macromolecular interference. Several experimental parameters affecting the extraction efficiency were investigated, including adsorption isotherms, kinetics, pH and salt strength of sample solution, desorption eluents, and time. Furthermore, under the optimized conditions, the limit of detection and the limit of quantification were found to be less than 2.9 and 9.7 ng mL−1, respectively, along with good linearity at 0.01–0.2 μg mL−1 for all the five BZDs. When the proposed method was applied to fruits and juice samples, the recoveries ranged from 85.3 to 102.3%, with relative standard deviations always being < 8.6%. These results prove that the established method was fast, convenient, and feasible for the detection of BZDs in commercial food samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin LA, Crowe JW, Pyles DA, McGrier PL (2016) Metalation of a mesoporous three-dimensional covalent organic framework. J Am Chem Soc 138:15134–15137
Cai Y, He X, Cui PL, Liu J, Li ZB, Jia BJ, Zhang T, Wang JP, Yuan WZ (2019) Preparation of a chemiluminescence sensor for multi-detection of benzimidazoles in meat based on molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem 280:103–109
Chang QY, Zang XH, Wu T, Wang MT, Pang YC, Wang C, Wang Z (2019) Use of functionalized covalent organic framework as sorbent for the solid-phase extraction of biogenic amines from meat samples followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods 12:1–11
Chen D, Tao Y, Liu Z, Liu Z, Huang L, Wang Y, Pan Y, Peng D, Dai M, Yuan Z (2010) Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography method to monitor the residues of benzimidazoles in bovine milk. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 878:2928–2932
Chen DM, Tao YF, Zhang HH, Pan YH, Liu Z, Huang LL, Wang YL, Peng DP, Wang X, Dai MH, Yuan ZH (2011) Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with pressurized liquid extraction method for the determination of benzimidazole residues in edible tissues. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:1659–1667
Chen L, Wu Q, Gao J, Li H, Dong S, Shi X, Zhao L (2019) Applications of covalent organic frameworks in analytical chemistry. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 113:182–193
Deng YH, Qi DW, Deng CH, Zhang XM, Zhao DY (2008) Superparamagnetic highmagnetization microspheres with an Fe3O4@SiO2 core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130:28–29
Díaz-Álvarez M, Martín-Esteban A (2018) Hollow fiber membrane-protected molecularly imprinted microspheres for micro solid-phase extraction and clean-up of thiabendazole in citrus samples. J Chromatogr A 1531:39–45
Dong YY, Yang LJ, Zhang L (2017) Simultaneous electrochemical detection of benzimidazole fungicides carbendazim and thiabendazole using a novel nanohybrid material-modified electrode. J Agric Food Chem 65:727–736
Dowling G, Cantwell H, O’Keeffe M, Smyth MR (2005) Multiresidue method for the determination of benzimidazoles in bovine liver. Anal Chim Acta 529:285–292
Dreassi E, Zanfini A, Zizzari AT, La Rosa C, Botta M, Corbini G (2010) LC/ESI/MS/MS determination of postharvest fungicide residues in citrus juices. Lwt-Food Sci Technol 43:1301–1306
García-Fernández M, Díaz-Álvarez M, Martín-Esteban A (2017) Molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for the micro solid-phase extraction of thiabendazole from citrus samples. J Sep Sci 40:2638–2644
Guo LL, Wu XL, Liu LQ, Kuang H, Xu CL (2018) Gold nanoparticle-based paper sensor for simultaneous detection of 11 benzimidazoles by one monoclonal antibody. Small 14:1701782
Huang N, Zhai L, Xu H, Jiang D (2017) Stable covalent organic frameworks for exceptional mercury removal from aqueous solutions. J Am Chem Soc 139:2428–2434
Karak S, Kandambeth S, Biswal BP, Sasmal HS, Kumar S, Pachfule P, Banerjee R (2017) Constructing ultraporous covalent organic frameworks in seconds via an organic terracotta process. J Am Chem Soc 139:1856–1862
Li H, Pan Q, Ma Y, Guan X, Xue M, Fang Q, Yan Y, Valtchev V, Qiu S (2016) Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with dual linkages for bifunctional cascade catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 138:14783–14788
Li Y, Yang CX, Yan XP (2017) Controllable preparation of core–shell magnetic covalent-organic framework nanospheres for efficient adsorption and removal of bisphenols in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 53:2511–2514
Li WX, Huang L, Guo DD, Zhao YG, Zhu Y (2018) Self-assembling covalent organic framework functionalized poly(styrene-divinylbenzene-glycidylmethacrylate) composite for the rapid extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1571:76–83
Lin G, Ding H, Yuan D, Wang B, Wang C (2016) A pyrenebased, fluorescent three-dimensional covalent organic framework. J Am Chem Soc 138:3302–3305
Liu YH, Yuan SK, Hu XR, Zhang CQ (2019) Shift of sensitivity in botrytis cinerea to benzimidazole fungicides in strawberry greenhouse ascribing to the rising-lowering of E198A subpopulation and its visual on-site monitoring by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Sci Rep 9:11644
Matsumoto M, Dasari RR, Ji W, Feriante CH, Parker TC, Marder SR, Dichtel WR (2017) Rapid, low temperature formation of imine-linked covalent organic frameworks catalyzed by metal triflates. J Am Chem Soc 139:4999–5002
Msagati TA, Nindi MM (2006) Comparative study of sample preparation methods; supported liquid membrane and solid phase extraction in the determination of benzimidazole anthelmintics in biological matrices by liquid chromatography-electrospray-mass spectrometry. Talanta 69:243–250
Pulgarín JAM, Bermejo LFG, Rodríguez SB (2018) Simultaneous determination of 1-naphthylacetic acid and thiabendazole in strawberry tree berries and citrus fruits by fluorescence spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 11:394–402
Qian HL, Li Y, Yan XP (2018) A building block exchange strategy for the rational fabrication of de novo unreachable aminofunctionalized imine-linked covalent organic frameworks. J Mater Chem A 6:17307–17311
Reuter S, Jensen B, Buttenschoen K, Kratzer W, Kern P (2000) Benzimidazoles in the treatment of alveolar echinococcosis: a comparative study and review of the literature. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:451–456
Sharma A, Babarao R, Medhekar NV, Malani A (2018) Methane adsorption and separation in slipped and functionalized covalent organic frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:4767–4778
Silva GR, Lima JA, Souza LF, Santos FA, Lana MAG, Assis DCS, Cançado SV (2017) Multiresidue method for identification and quantification of avermectins, benzimidazoles and nitroimidazoles residues in bovine muscle tissue by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) using a QuEChERS approach. Talanta 171:307–320
Sun H, Yu QW, He HB, Lu Q, Shi ZG, Feng YQ (2016) Nickel oxide nanoparticle-deposited silica composite solid-phase extraction for benzimidazole residue analysis in milk and eggs by liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 64:356–363
Tejada-Casado C, Moreno-González D, Lara FJ, García-Campaña AM, Olmo-Iruela M (2017) Determination of benzimidazoles in meat samples by capillary zone electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry following dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1490:212–219
Thuan NH, Pandey RP, Sohng JK (2014) Recent advances in biochemistry and biotechnological synthesis of avermectins and their derivatives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7747–7759
Wang HQ, Li Z, Feng W, Jia Q (2017) Polymer monolith containing an embedded covalent organic framework for the effective enrichment of benzophenones. New J Chem 41:13043–13050
Wu MX, Chen G, Liu P, Zhou WH, Jia Q (2016) Polydopamine-based immobilization of a hydrazone covalent organic framework for headspace solid-phase microextraction of pyrethroids in vegetables and fruits. J Chromatogr A 1456:34–41
Xu X, Long N, Lv JN, Wang LL, Zhang MH, Qi XY, Zhang L (2016) Functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube as dispersive solid-phase extraction materials combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for thiabendazole analysis in environmental and food samples. Food Anal Methods 9:30–37
Xu Q, Tang YP, Zhang XB, Oshima Y, Chen QH, Jiang DL (2018) Template conversion of covalent organic frameworks into 2D conducting nanocarbons for catalyzing oxygen reduction reaction. Adv Mater 30:789–794
Yu QW, Sun H, Wang K, He HB, Feng YQ (2017) Monitoring of carbendazim and thiabendazole in fruits and vegetables by SiO2@NiO-based solid-phase extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detector. Food Anal Methods 10:2892–2901
Zeng Y, Zou R, Zhao Y (2016) Covalent organic frameworks for CO2 capture. Adv Mater 28:2855–2873
Zhang Y, Huang XJ, Yuan DX (2015) Determination of benzimidazole anthelmintics in milk and honey by monolithic fiber-based solid-phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:557–567
Zhang SH, Yang Q, Li Z, Wang WC, Wang C, Wang Z (2017) Covalent organic frameworks as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of volatile benzene homologues. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:3429–3439
Zhuang GL, Gao YF, Zhou X, Tao XY, Luo JM, Gao YJ, Yan YL, Gao PY, Zhong X, Wang JG (2017) ZIF-67/COF-derived highly dispersed Co3O4/N-doped porous carbon with excellent performance for oxygen evolution reaction and Li-ion batteries. Chem Eng J 330:1255–1264
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi, China (Grant No. 2018JM2039) and Science and Technology Program of Xi’an, China (Grant No. 2019216914GXRC005CG006-GXYD5.3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Shuming Li declares that she has no conflict of interest. Qian Liang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Shadi Ali Hassen Ahmed declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jing Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 172 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Liang, Q., Ahmed, S.A.H. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Five Benzimidazoles in Agricultural Foods by Core-Shell Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Nanoparticle–Based Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 13, 1111–1118 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01708-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01708-4