Abstract
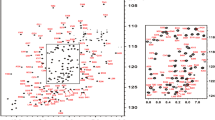
Musashi1 (Msi1) is an RNA-binding protein that is involved in cell fate determination. Here, we report the 1H, 15N, and 13C resonance assignments of Msi1 second RNA-binding domain in free form and in complex with RNA. The assignments can be utilized for NMR structure and dynamics analyses of the Msi1:RNA complex, and moreover, for chemical shift perturbation analyses to evaluate the binding of potential small molecule inhibitors against Msi1:RNA interaction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charlesworth A, Wilczynska A, Thampi P et al (2006) Musashi regulates the temporal order of mRNA translation during Xenopus oocyte maturation. EMBO J 25:2792–2801. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601159
Clingman CC, Deveau LM, Hay SA et al (2014) Allosteric inhibition of a stem cell RNA-binding protein by an intermediary metabolite. Elife 3:e02848. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02848
Cragle C, MacNicol AM (2014) Musashi protein-directed translational activation of target mRNAs is mediated by the poly(A) polymerase, germ line development defective-2. J Biol Chem 289:14239–14251. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548271
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW et al (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00197809
Imai T, Tokunaga A, Yoshida T et al (2001) The neural RNA-binding protein Musashi1 translationally regulates mammalian numb gene expression by interacting with its mRNA. Mol Cell Biol 21:3888–3900. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.3888-3900.2001
Iwaoka R, Nagata T, Tsuda K, Imai T, Okano H, Kobayashi N, Katahira M (2017) Structural insight into the recognition of r(UAG) by musashi-1 RBD2, and construction of a model of musashi-1 RBD1-2 bound to the minimum target RNA. Molecules 22(7):1207. doi:10.3390/molecules22071207
Johnson BA (2004) Using NMRView to visualize and analyze the NMR spectra of macromolecules. Methods Mol Biol 278:313–352. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-809-9:313
Kawahara H, Imai T, Imataka H et al (2008) Neural RNA-binding protein Musashi1 inhibits translation initiation by competing with eIF4G for PABP. J Cell Biol 181:639–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200708004
Kobayashi N, Iwahara J, Koshiba S et al (2007) KUJIRA, a package of integrated modules for systematic and interactive analysis of NMR data directed to high-throughput NMR structure studies. J Biomol NMR 39:31–52. doi: 10.1007/s10858-007-9175-5
Kobayashi N, Harano Y, Tochio N et al (2012) An automated system designed for large scale NMR data deposition and annotation: application to over 600 assigned chemical shift data entries to the BioMagResBank from the Riken Structural Genomics/Proteomics Initiative internal database. J Biomol NMR 53:311–320. doi: 10.1007/s10858-012-9641-6
Lan L, Appelman C, Smith AR et al (2015) Natural product (−)-gossypol inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting RNA-binding protein Musashi-1. Mol Oncol 9:1406–1420. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.03.014
Miyanoiri Y, Kobayashi H, Imai T et al (2003) Origin of higher affinity to RNA of the N-terminal RNA-binding domain than that of the C-terminal one of a mouse neural protein, Musashi1, as revealed by comparison of their structures, modes of interaction, surface electrostatic potentials, and backbone. J Biol Chem 278:41309–41315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306210200
Nagata T, Kanno R, Kurihara Y et al (1999) Structure, backbone dynamics and interactions with RNA of the C-terminal RNA-binding domain of a mouse neural RNA-binding protein, Musashi1. J Mol Biol 287:315–330. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2596
Nagata T, Suzuki S, Endo R et al (2008) The RRM domain of poly(A)-specific ribonuclease has a noncanonical binding site for mRNA cap analog recognition. Nucleic Acids Res 36:4754–4767. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn458
Ohyama T, Nagata T, Tsuda K et al (2012) Structure of Musashi1 in a complex with target RNA: the role of aromatic stacking interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 40:3218–3231. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1139
Shen Y, Bax A (2013) Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J Biomol NMR 56:227–241. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9741-y
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI to M.K. (#15H01256, #16H00833, and #16K14678) and to T.N. (#15H01634 and #26440026). The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Mikako Shirouzu for fruitful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwaoka, R., Nagata, T., Tsuda, K. et al. Backbone and side chain assignments of the second RNA-binding domain of Musashi-1 in its free form and in complex with 5-mer RNA. Biomol NMR Assign 11, 265–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-017-9760-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-017-9760-9