Abstract
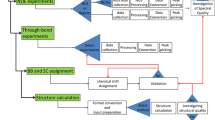
The recent expansion of structural genomics has increased the demands for quick and accurate protein structure determination by NMR spectroscopy. The conventional strategy without an automated protocol can no longer satisfy the needs of high-throughput application to a large number of proteins, with each data set including many NMR spectra, chemical shifts, NOE assignments, and calculated structures. We have developed the new software KUJIRA, a package of integrated modules for the systematic and interactive analysis of NMR data, which is designed to reduce the tediousness of organizing and manipulating a large number of NMR data sets. In combination with CYANA, the program for automated NOE assignment and structure determination, we have established a robust and highly optimized strategy for comprehensive protein structure analysis. An application of KUJIRA in accordance with our new strategy was carried out by a non-expert in NMR structure analysis, demonstrating that the accurate assignment of the chemical shifts and a high-quality structure of a small protein can be completed in a few weeks. The high completeness of the chemical shift assignment and the NOE assignment achieved by the systematic analysis using KUJIRA and CYANA led, in practice, to increased reliability of the determined structure.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum coherence
- SASA:
-
Solvent accessible surface area
- TOCSY:
-
Total correlated spectroscopy
References
Altieri AS, Byrd RA (2004) Automation of NMR structure determination of proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14(5):547–553
Andrec M, Levy RM (2002) Protein sequential resonance assignments by combinatorial enumeration using 13C alpha chemical shifts and their (i, i-1) sequential connectivities. J Biomol NMR 23(4):263–270
Atreya HS, Sahu SC, Chary KV, Govil G (2000) A tracked approach for automated NMR assignments in proteins (TATAPRO). J Biomol NMR 17(2):125–136
Baran MC, Moseley HN, Sahota G, Montelione GT (2002) SPINS: standardized protein NMR storage. A data dictionary and object-oriented relational database for archiving protein NMR spectra. J Biomol NMR 24(2):113–121
Baran MC, Huang YJ, Moseley HN, Montelione GT (2004) Automated analysis of protein NMR assignments and structures. Chem Rev 104(8):3541–3556
Bartels C, Xia TH, Billeter M, Güntert P, Wüthrich K (1995) The program XEASY for computer-supported NMR spectral analysis of biological macromolecules. J Biomol NMR 6:1–10
Bartels C, Billeter M, Güntert P, Wüthrich K (1996a) Automated sequence-specific NMR assignment of homologous proteins using the program GARANT. J Biomol NMR 7:207–213
Bartels C, Billeter M, Güntert P, Wüthrich K (1996b) GARANT-A general algorithm for resonance assignment of multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. J Comput Chem 18:139–149
Buchler NE, Zuiderweg ER, Wang H, Goldstein RA (1997) Protein heteronuclear NMR assignments using mean-field simulated annealing. J Magn Reson 125(1):34–42
Coggins BE, Zhou P (2003) PACES: protein sequential assignment by computer-assisted exhaustive search. J Biomol NMR 26(2):93–111
Cornilescu G, Marquardt JL, Ottiger M, Bax A (1998) Validation of protein structure from anisotropic carbonyl chemical shifts in a dilute liquid crystalline phase. J Am Chem Soc 120(27):6836–6837
Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 13(3):289–302
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6(3):277–293
Fogh R, Ionides J, Ulrich E, Boucher W, Vranken W, Linge JP, Habeck M, Rieping W, Bhat TN, Westbrook J, Henrick K, Gilliland G, Berman H, Thornton J, Nilges M, Markley J, Laue E (2002) The CCPN project: an interim report on a data model for the NMR community. Nat Struct Biol 9(6):416–418
Fogh RH, Boucher W, Vranken WF, Pajon A, Stevens TJ, Bhat TN, Westbrook J, Ionides JM, Laue ED (2005) A framework for scientific data modeling and automated software development. Bioinformatics 21(8):1678–1684
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (2001) Sparkey 3. University of California, San Francisco
Gronwald W, Kalbitzer HR (2004) Automated structure determination of proteins by NMR spectroscopy. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 44:33–96
Gronwald W, Kirchfofer R, Gorler A, Kremer W, Ganslmeier B, Neidig KP, Kalbitzer HR (1998) CAMRA: chemical shift based computer aided protein NMR assignments. J Biomol NMR 12:395–405
Güntert P (2003) Automated NMR protein structure calculation. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 43:105–125
Güntert P, Mumenthaler C, Wüthrich K (1997) Torsion angle dynamics for NMR structure calculation with the new program DYANA. J Mol Biol 273(1):283–298
Güntert P, Salzmann M, Braun D, Wüthrich K (2000) Sequence-specific NMR assignment of proteins by global fragment mapping with the program MAPPER. J Biomol NMR 18(2):129–137
Helgstrand M, Kraulis P, Allard P, Hard T (2000) Ansig for Windows: an interactive computer program for semiautomatic assignment of protein NMR spectra. J Biomol NMR 18(4):329–336
Herrmann T, Güntert P, Wüthrich K (2002) Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE assignment using the new software CANDID and the torsion angle dynamics algorithm DYANA. J Mol Biol 319(1):209–227
Hooft RW, Vriend G, Sander C, Abola EE (1996) Errors in protein structures. Nature 381(6580):272
Huang YJ, Powers R, Montelione GT (2005) Protein NMR recall, precision, and F-measure scores (RPF scores): structure quality assessment measures based on information retrieval statistics. J Am Chem Soc 127(6):1665–1674
Hyberts SG, Wagner G (2003) IBIS—a tool for automated sequential assignment of protein spectra from triple resonance experiments. J Biomol NMR 26(4):335–344
Jee J, Güntert P (2003) Influence of the completeness of chemical shift assignments on NMR structures obtained with automated NOE assignment. J Struct Funct Genomics 4(2–3):179–189
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) NMRView: a computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Kabsch W, Sander C (1983) Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 22(12):2577–2637
Kigawa T, Yabuki T, Yoshida Y, Tsutsui M, Ito Y, Shibata T, Yokoyama S (1999) Cell-free production and stable-isotope labeling of milligram quantities of proteins. FEBS Lett 442(1):15–19
Kigawa T, Yabuki T, Matsuda N, Matsuda T, Nakajima R, Tanaka A, Yokoyama S (2004) Preparation of Escherichia coli cell extract for highly productive cell-free protein expression. J Struct Funct Genomics 5(1–2):63–68
Kirby NI, DeRose EF, London RE, Mueller GA (2004) NvAssign: protein NMR spectral assignment with NMRView. Bioinformatics 20(7):1201–1203
Kraulis PJ (1989) ANSIG-a program for the assignment of protein H-1 2D NMR spectra by interactive computer graphics. J Magn Reson 24:627–633
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM (1996) AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol NMR 8(4):477–486
Lee B, Richards FM (1971) The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol 55:379–400
Leutner M, Gschwind RM, Liermann J, Schwarz C, Gemmecker G, Kessler H (1998) Automated backbone assignment of labeled proteins using the threshold accepting algorithm. J Biomol NMR 11(1):31–43
Li KB, Sanctuary BC (1997) Automated resonance assignment of proteins using heteronuclear 3D NMR. 2. Side chain and sequence-specific assignment. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 37(3):467–477
Lovell SC, Word JM, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2000) The penultimate rotamer library. Proteins 40(3):389–408
Lukin JA, Gove AP, Talukdar SN, Ho C (1997) Automated probabilistic method for assigning backbone resonances of (13C,15N)-labeled proteins. J Biomol NMR 9(2):151–166
Moseley HN, Sahota G, Montelione GT (2004) Assignment validation software suite for the evaluation and presentation of protein resonance assignment data. J Biomol NMR 28(4):341–355
Nabuurs SB, Spronk CA, Krieger E, Maassen H, Vriend G, Vuister GW (2003) Quantitative evaluation of experimental NMR restraints. J Am Chem Soc 125(39):12026–12034
Neidig KP, Geyer M, Görler A, Antz C, Saffrich R, Beneicke W, Kalbitzer HR (1995) Automated peak integration in multidimensional NMR spectra by an optimized iterative segmentation procedure. J Biol NMR 6:255–270
Nilges M, O’Donoghue SI (1998) Ambiguous NOEs and automated NOE assignment. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 32:107–139
Rodriguez R, Chinea G, Lopez N, Pons T, Vriend G (1998) Homology modeling, model and software evaluation: three related resources. Bioinformatics 14(6):523–528
Slupsky CM, Boyko RF, Booth VK, Sykes BD (2003) Smartnotebook: a semi-automated approach to protein sequential NMR resonance assignments. J Biomol NMR 27(4):313–321
Spronk CA, Nabuurs SB, Krieger E, Vriend G, Vuister GW (2004) Validation of protein structures derived by NMR spectroscopy. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrrosc 45(3–4):315–337
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59(4):687–696
Vriend G (1990) WHAT IF: a molecular modeling and drug design program. J Mol Graph 8(1):52–56, 29
Wei Y, Werner MH (2006) iDC: a comprehensive toolkit for the analysis of residual dipolar couplings for macromolecular structure determination. J Biomol NMR 35(1):17–25
Zimmerman D, Kulikowski C, Wang L, Lyons B, Montelione GT (1994) Automated sequencing of amino acid spin systems in proteins using multidimensional HCC(CO)NH-TOCSY spectroscopy and constraint propagation methods from artificial intelligence. J Biomol NMR 4(2):241–256
Zimmerman DE, Kulikowski CA, Huang Y, Feng W, Tashiro M, Shimotakahara S, Chien C, Powers R, Montelione GT (1997) Automated analysis of protein NMR assignments using methods from artificial intelligence. J Mol Biol 269(4):592–610
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Toshio Yamazaki, Yutaka Muto, Fumiaki Hayashi, Takashi Nagata, Fahu He, Yufeng Wei and Prof. Milton, H. Werner for their valuable comments and discussions, and Prof. Yo Matsuo for his helpful advice regarding the algorithm for the calculation of the solvent accessible surface area. We also thank Mr. Masatomo Tanaka and Dr. Takuma Kasai for providing the information from the structural analyses of human ubiquitin. This work was supported by the RIKEN Structural Genomics/Proteomics Initiative (RSGI), the National Project on Protein Structural and Functional Analyses, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, N., Iwahara, J., Koshiba, S. et al. KUJIRA, a package of integrated modules for systematic and interactive analysis of NMR data directed to high-throughput NMR structure studies. J Biomol NMR 39, 31–52 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9175-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9175-5