Abstract
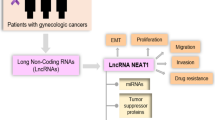
Gynecologic cancers are reproductive disorders characterized by pelvic pain and infertility. The identification of new predictive markers and therapeutic targets for the treatment of gynecologic cancers is urgently necessary. One of the recent successes in gynecologic cancers research is identifying the role of signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of the disease. Recent experiments showed long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) can be novel therapeutic approaches for the diagnosis and treatment of gynecologic cancers. LncRNA are transcribed RNA molecules that play pivotal roles in multiple biological processes by regulating the different steps of gene expression. Metastasis‐associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript‐1 (MALAT1) is a well-known lncRNA that plays functional roles in gene expression, RNA processing, and epigenetic regulation. High expression of MALAT1 is closely related to numerous human diseases. It is generally believed that MALAT1 expression is associated with cancer cell growth, autophagy, invasion, and metastasis. MALAT1 by targeting multiple signaling pathways and microRNAs (miRNAs) could contribute to the pathogenesis of gynecologic cancers. In this review, we will summarize functional roles of MALAT1 in the most common gynecologic cancers, including endometrium, breast, ovary, and cervix.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
5'-AMP‑activated protein kinase
- CDK2:
-
Cyclin dependent kinase 2
- CREB1:
-
Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein 1
- DIE:
-
Deep infiltrating endometriosis
- EEC:
-
Endometrioid endometrial carcinoma
- EMs:
-
Endometriosis
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- E2:
-
17β-Estradiol
- GCs:
-
Granulosa cells
- HESCs:
-
Endometrial stromal cells
- HCN:
-
Hepcarcin
- HIF‐1α:
-
Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1α
- LC3:
-
Microtubule‑associated protein 1A/1B‑light chain 3
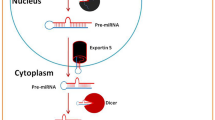
- LncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis‐associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript‐1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- mascRNA:
-
MALAT1-associated small cytoplasmic RNA
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- NEAT2:
-
Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 2
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OMA:
-
Ovarian endometrioma
- PCDH10:
-
Protocadherin 10
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2
- p-JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal protein kinase
- SR:
-
Serine- and arginine-rich
- 3‐MA:
-
3‐Methyladenine
- CREB1:
-
Cyclic AMP response element-(CRE-) binding protein 1
- CYP1B1:
-
Cytochrome P450 1B1
- CYP19A1:
-
Cytochrome P450
- E2:
-
Estradiol
- GCs:
-
Granulosa cells
- LIF:
-
Leukemia inhibitory factor
- LncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- LOD:
-
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis‐associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript‐1
- mascRNA:
-
MALAT1-associated small cytoplasmic RNA
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- NEAT2:
-
Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 2
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PRC:
-
Polycomb repressive complex
- P4:
-
Progesterone
- TGFBR1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta receptor 1
References
Malla RR, Patnala K, Kumar DKG, Marni R. Drug resistance in gynecologic cancers: emphasis on noncoding RNAs and drug efflux mechanisms. In: Riyaz B, Safraz A, editors. Overcoming drug resistance in gynecologic cancers. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2021.
Maheshwari A, Kumar N, Mahanshetty U. Gynecological cancers: a summary of published Indian data. South Asian J Cancer. 2016;5:112–20.
Saha P, Kumar A, Bhanja J, Shaik R, Kawale AL, Kumar R: A Review of Immune Blockade Safety and Antitumor Activity of Dostarlimab Therapy in Endometrial Cancer. International Journal for Research in Applied Sciences and Biotechnology 2022, 9:201-209.
Lin K-T, Sun S-P, Wu J-I, Wang L. Low-dose glucocorticoids suppresses ovarian tumor growth and metastasis in an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0178937.
Almadrones-Cassidy LA. Gynecologic cancers. Pittsburgh: Oncology Nursing Society; 2010.
Gilchrist RB, Ritter LJ, Myllymaa S, Kaivo-Oja N, Dragovic RA, Hickey TE, Ritvos O, Mottershead DG. Molecular basis of oocyte-paracrine signalling that promotes granulosa cell proliferation. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:3811–21.
Di Fiore R, Suleiman S, Ellul B, O’toole SA, Savona-Ventura C, Felix A, Napolioni V, Conlon NT, Erson-Bensan AE, Kahramanoglu IJC. Gynocare update: modern strategies to improve diagnosis and treatment of rare gynecologic tumors—current challenges and future directions. Cancers. 2021;13:493.
Tu J, Chen Y, Li Z, Yang H, Chen H, Yu Z. Long non-coding RNAs in ovarian granulosa cells. J Ovarian Res. 2020;13:1–12.
Ji Z, Song R, Regev A, Struhl K. Many lncRNAs, 5’UTRs, and pseudogenes are translated and some are likely to express functional proteins. Elife. 2015;4:e08890.
Chew G-L, Pauli A, Rinn JL, Regev A, Schier AF, Valen EJD. Ribosome profiling reveals resemblance between long non-coding RNAs and 5′ leaders of coding RNAs. Development. 2013;140:2828–34.
Anbiyaiee A, Ramazii M, Bajestani SS, Meybodi SM, Keivan M, Khoshnam SE, Farzaneh M. The function of LncRNA-ATB in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02848-1.
Xu W-W, Jin J, Wu X-Y, Ren Q-L, Farzaneh M. MALAT1-related signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22:1–9.
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin K-J. The long noncoding RNA Malat 1: Its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1705–14.
Farzaneh M, Najafi S, Anbiyaee O, Azizidoost S, Khoshnam SE. LncRNA MALAT1-related signaling pathways in osteosarcoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02876-x.
Amodio N, Raimondi L, Juli G, Stamato MA, Caracciolo D, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P. MALAT1: a druggable long non-coding RNA for targeted anti-cancer approaches. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:1–19.
Amodio N, Raimondi L, Juli G, Stamato MA, Caracciolo D, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P. MALAT1: a druggable long non-coding RNA for targeted anti-cancer approaches. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:63–63.
Zhang X-Z, Liu H, Chen S-R. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancers and their dynamic regulations. Cancers. 2020;12:1245.
Zhao K, Jin S, Wei B, Cao S, Xiong Z. Association study of genetic variation of lncRNA MALAT1 with carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:6257–61.
Yan W, Hu H, Tang B. Progress in understanding the relationship between long noncoding RNA and endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2020;5: 100067.
Liang Z, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Xu C, Zhang A, Zhang Q, Wang D, He J, Hua W, Duan P. miR-200c suppresses endometriosis by targeting MALAT1 in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:1–11.
Du Y, Zhang Z, Xiong W, Li N, Liu H, He H, Li Q, Liu Y, Zhang L. Estradiol promotes EMT in endometriosis via MALAT1/miR200s sponge function. Reproduction. 2019;157:179–88.
Li Y, Liu Y-d, Chen S-l, Chen X, Ye D-s, Zhou X-y, Zhe J, Zhang J. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 inhibits granulosa cell proliferation in endometriosis by up-regulating P21 via activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. MHR Basic Sci Reprod Med. 2019;25:17–29.
Zhu M, Chen L, Hu M, Shi Z, Liu Y. Effects of lncRNA BANCR on endometriosis through ERK/MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:6806–12.
Chen G, Zhang M, Liang Z, Chen S, Chen F, Zhu J, Zhao M, He J, Hua W, Duan P. Association of polymorphisms in MALAT1 with the risk of endometrial cancer in Southern Chinese women. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34: e23146.
Jao T-M, Fang W-H, Ciou S-C, Yu S-L, Hung Y-L, Weng W-T, Lin T-Y, Tsai M-H, Yang Y-C. PCDH10 exerts tumor-suppressor functions through modulation of EGFR/AKT axis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021;499:290–300.
Zhao Y, Yang Y, Trovik J, Sun K, Zhou L, Jiang P, Lau T-S, Hoivik EA, Salvesen HB, Sun H. A novel wnt regulatory axis in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Can Res. 2014;74:5103–17.
Amenyogbe E, Chen G, Wang Z, Lu X, Lin M, Lin AY. A Review on sex steroid hormone estrogen receptors in mammals and fish. Int J Endocrinol. 2020;2020:5386193–5386193.
Li Q, Zhang C, Chen R, Xiong H, Qiu F, Liu S, Zhang M, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhou X, et al. Disrupting MALAT1/miR-200c sponge decreases invasion and migration in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016;383:28–40.
Wang Y-W, Chen X, Gao J-W, Zhang H, Ma R-R, Gao Z-H, Gao P. High expression of cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (CREB1) is associated with metastasis, tumor stage and poor outcome in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:10646–57.
Allavena G, Carrarelli P, Del Bello B, Luisi S, Petraglia F, Maellaro E. Autophagy is upregulated in ovarian endometriosis: a possible interplay with p53 and heme oxygenase-1. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:1244-1251.e1241.
Liu H, Zhang Z, Xiong W, Zhang L, Xiong Y, Li N, He H, Du Y, Liu Y. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α promotes endometrial stromal cells migration and invasion by upregulating autophagy in endometriosis. Reproduction. 2017;153:809–20.
Liu H, Zhang Z, Xiong W, Zhang L, Du Y, Liu Y, Xiong X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT 1 mediates hypoxia-induced pro-survival autophagy of endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:439–52.
Feng Y, Tan B-Z. LncRNA MALAT1 inhibits apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells through miR-126-5p-CREB1 axis by activating PI3K-AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;475:185–94.
Sun L, Zhang P, Lu W. lncRNA MALAT1 regulates mouse granulosa cell apoptosis and 17β-estradiol synthesis via regulating miR-205/CREB1 axis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:667.
Liu X, Zhang P, Li Y, Zhao N, Han H. The AMPK-mTOR axis requires increased MALAT1 expression for promoting granulosa cell proliferation in endometriosis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21:1–1.
Venkatesh J, Wasson M-CD, Brown JM, Fernando W, Marcato P. LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: novel points of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett. 2021;509:81–8.
Shih C-H, Chuang L-L, Tsai M-H, Chen L-H, Chuang EY, Lu T-P, Lai L-C. Hypoxia-induced MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells by sponging MiR-3064-5p. Front Oncol. 2021;11:658151–658151.
Wang N, Cao S, Wang X, Zhang L, Yuan H, Ma X. lncRNA MALAT1/miR-26a/26b/ST8SIA4 axis mediates cell invasion and migration in breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 2021;46:181.
Zhao C, Ling X, Xia Y, Yan B, Guan Q. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of breast cancer through the MALAT1/miR-26b/HMGA2 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:441.
Zeng C, Huang W, Li Y, Weng H. Roles of METTL3 in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:117.
Shao J, Zhang Q, Wang P, Wang Z. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes breast cancer progression by sponging miR101-3p to mediate mTOR/PKM2 signal transmission. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13:10262–75.
Sun Q, Chen X, Ma J, Peng H, Wang F, Zha X, Wang Y, Jing Y, Yang H, Chen R, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin up-regulation of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 is critical for aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:4129–34.
Zheng L, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Gong H, Guo J, Wu K, Jia Q, Ding X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates BLCAP mRNA expression through binding to miR-339-5p and promotes poor prognosis in breast cancer. Biosci Rep. 2019;39:BSR20181284.
Zhao M, Zhang L, Qiu X, Zeng F, Chen W, An Y, Hu B, Wu X, Wu X. BLCAP arrests G1/S checkpoint and induces apoptosis through downregulation of pRb1 in HeLa cells. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:3050–8.
Chou J, Wang B, Zheng T, Li X, Zheng L, Hu J, Zhang Y, Xing Y, Xi T. MALAT1 induced migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by competitively binding miR-1 with cdc42. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;472:262–9.
Zuo Y, Li Y, Zhou Z, Ma M, Fu K. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and invasion via targeting miR-129-5p in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:922–8.
Jin C, Yan B, Lu Q, Lin Y, Ma L. Reciprocal regulation of Hsa-miR-1 and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer development. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:7383–94.
Li Y, Wu Y, Abbatiello TC, Wu WL, Kim JR, Sarkissyan M, Sarkissyan S, Chung SS, Elshimali Y, Vadgama JV. Slug contributes to cancer progression by direct regulation of ERα signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 2015;46:1461–72.
Barsoum FS, Awad AS, Hussein NH, Eissa RA, El Tayebi HM. MALAT-1: LncRNA ruling miR-182/PIG-C/mesothelin triad in triple negative breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2020;216: 153274.
Wang Y, Wang L, Li D, Wang HB, Chen QF. Mesothelin promotes invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells. J Int Med Res. 2012;40:2109–16.
Nakakido M, Tamura K, Chung S, Ueda K, Fujii R, Kiyotani K, Nakamura Y. Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class X containing complex promotes cancer cell proliferation through suppression of EHD2 and ZIC1, putative tumor suppressors. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:868–76.
Feng T, Shao F, Wu Q, Zhang X, Xu D, Qian K, Xie Y, Wang S, Xu N, Wang Y, Qi C. miR-124 downregulation leads to breast cancer progression via LncRNA-MALAT1 regulation and CDK4/E2F1 signal activation. Oncotarget. 2016;7:16205–16.
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yang Z, Chen B, Huang W, Liu Y, Zhang Y. MiR-204/ZEB2 axis functions as key mediator for MALAT1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017;39:1010428317690998.
Guo C, Wang X, Chen L, Li M, Li M, Hu Y, Ding W, Wang X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:3703–12.
Wang Z, Li B, Zhou L, Yu S, Su Z, Song J, Sun Q, Sha O, Wang X, Jiang W. Prodigiosin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exerts anticancer activity in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113:13150–5.
Pei C, Gong X, Zhang Y. LncRNA MALAT-1 promotes growth and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer via sponging microrna-22. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:6977.
Paliwal N, Vashist M, Chauhan M. Evaluation of miR-22 and miR-21 as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 3 Biotech. 2020;10:1–6.
Xiong J, Du Q, Liang Z. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-22 inhibits the transcription of E-box-containing c-Myc target genes by silencing c-Myc binding protein. Oncogene. 2010;29:4980–8.
Zhang K, Li X, Wang Z, Han Z, Zhao Y. MiR-22 inhibits lung cancer cell EMT and invasion through targeting Snail. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:3598–604.
Wang Y, Wang X, Han L, Hu D. LncRNA MALAT1 regulates the progression and cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells via modulating miR-1271-5p/E2F5 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:9999.
Li Q, Shi J, Xu X. MicroRNA-1271–5p inhibits the tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer through targeting E2F5 and negatively regulates the mTOR signaling pathway. Panminerva Med. 2020;63:336.
Hu J, Meng Y, Yu T, Hu L, Mao M. Ubiquitin E3 ligase MARCH7 promotes ovarian tumor growth. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12174.
Hu J, Zhang L, Mei Z, Jiang Y, Yi Y, Liu L, Meng Y, Zhou L, Zeng J, Wu H. Interaction of E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH7 with long noncoding RNA MALAT1 and autophagy-related protein ATG7 promotes autophagy and invasion in ovarian cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47:654–66.
Chen P, Cescon M, Bonaldo P. Autophagy-mediated regulation of macrophages and its applications for cancer. Autophagy. 2014;10:192–200.
Zhang S-F, Wang X-Y, Fu Z-Q, Peng Q-H, Zhang J-Y, Ye F, Fu Y-F, Zhou C-Y, Lu W-G, Cheng X-D. TXNDC17 promotes paclitaxel resistance via inducing autophagy in ovarian cancer. Autophagy. 2015;11:225–38.
Zhang X, Wang L-L, Wang B, Liu H-L, Zhang J, Li Y-H, Wang L-H. Effect of siRNA-induced Atg7 gene silencing on the sensitivity of ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells to cisplatin. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:2052.
Gajewska M, Gajkowska B, Motyl T. Apoptosis and autophagy induced by TGF-B1 in bovine mammary epithelial BME-UV1 cells. J Physiol Pharmacol Official J Polish Physiol Soc. 2005;56:143–57.
Kiyono K, Suzuki HI, Matsuyama H, Morishita Y, Komuro A, Kano MR, Sugimoto K, Miyazono K. Autophagy is activated by TGF-β and potentiates TGF-β–mediated growth inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Can Res. 2009;69:8844–52.
Zhou Y, Xu X, Lv H, Wen Q, Li J, Tan L, Li J, Sheng X. The long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is highly expressed in ovarian cancer and induces cell growth and migration. PLoS ONE. 2016;11: e0155250.
Wu L, Wang X, Guo Y. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 is upregulated and involved in cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in ovarian cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13:3055–60.
Mao T-L, Fan M-H, Dlamini N, Liu C-L. LncRNA MALAT1 facilitates ovarian cancer progression through promoting chemoresistance and invasiveness in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10201.
Liu S, Jiang X, Li W, Cao D, Shen K, Yang J. Inhibition of the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 suppresses tumorigenicity and induces apoptosis in the human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cell line. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:3686–92.
Chen Q, Su Y, He X, Zhao W, Wu C, Zhang W, Si X, Dong B, Zhao L, Gao Y. Plasma long non-coding RNA MALAT1 is associated with distant metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 2016;12:1361–6.
Qiu J-J, Lin X-J, Tang X-Y, Zheng T-T, Lin Y-Y, Hua K-Q. Exosomal metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 promotes angiogenesis and predicts poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 1960;2018:14.
Lei R, Xue M, Zhang L, Lin Z. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1-regulated microRNA 506 modulates ovarian cancer growth by targeting iASPP. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:35.
Zheng Y, Yin L, Chen H, Yang S, Pan C, Lu S, Miao M, Jiao B. miR-376a suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:2396–403.
Fellenberg J, Sähr H, Kunz P, Zhao Z, Liu L, Tichy D, Herr I. Restoration of miR-127-3p and miR-376a-3p counteracts the neoplastic phenotype of giant cell tumor of bone derived stromal cells by targeting COA1, GLE1 and PDIA6. Cancer Lett. 2016;371:134–41.
Li Y, Ahmad A, Sarkar F. ASPP and iASPP: implication in cancer development and progression. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015;61:2–8.
Jiang L, Siu MK, Wong OG, Tam K-F, Lu X, Lam EW, Ngan HY, Le X-F, Wong ES, Monteiro LJ. iASPP and chemoresistance in ovarian cancers: effects on paclitaxel-mediated mitotic catastrophe. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6924–33.
Mak CS, Yung MM, Hui L, Leung LL, Liang R, Chen K, Liu SS, Qin Y, Leung TH, Lee K-F. MicroRNA-141 enhances anoikis resistance in metastatic progression of ovarian cancer through targeting KLF12/Sp1/survivin axis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:1–17.
Lin Q, Guan W, Ren W, Zhang L, Zhang J, Xu G. MALAT1 affects ovarian cancer cell behavior and patient survival. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:2644–52.
Gordon MA, Babbs B, Cochrane DR, Bitler BG, Richer JK. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating RBFOX2-mediated alternative splicing. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58:196–205.
Venables JP, Brosseau J-P, Gadea G, Klinck R, Prinos P, Beaulieu J-F, Lapointe E, Durand M, Thibault P, Tremblay K. RBFOX2 is an important regulator of mesenchymal tissue-specific splicing in both normal and cancer tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:396–405.
Bai L, Wang A, Zhang Y, Xu X, Zhang X. Knockdown of MALAT1 enhances chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through inhibiting the Notch1 signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;366:161–71.
Ma S-l, Hu Y-P, Wang F, Huang Z-C, Chen Y-F, Wang X-K, Fu L-W. Lapatinib antagonizes multidrug resistance-associated protein 1-mediated multidrug resistance by inhibiting its transport function. Mol Med. 2014;20:390–9.
Li X, Wang H, Wang J, Chen Y, Yin X, Shi G, Li H, Hu Z, Liang X. Emodin enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells through ROS elevation and MRP1 downregulation. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:1–10.
Jin Y, Feng S, Qiu S, Shao N, Zheng J. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer via the PI3K-AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:3176–84.
Xu W, Yang Z, Lu N. A new role for the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9:317–24.
Sun Q, Li Q, Xie F. LncRNA-MALAT1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells by targeting miR-503-5p. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:6297.
Ruiz‐Manriquez LM, Estrada‐Meza C, Benavides‐Aguilar JA, Ledesma‐Pacheco SJ, Torres‐Copado A, Serrano‐Cano FI, Bandyopadhyay A, Pathak S, Chakraborty S, Srivastava A: Phytochemicals mediated modulation of microRNAs and long non coding RNAs in cancer prevention and therapy. Phytotherapy Research 2022, 36:705-729.
Abubaker K, Luwor RB, Zhu H, McNally O, Quinn MA, Burns CJ, Thompson EW, Findlay JK, Ahmed N. Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in ovarian cancer results in the loss of cancer stem cell-like characteristics and a reduced tumor burden. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:1–22.
Rosen DG, Mercado-Uribe I, Yang G, Bast RC Jr, Amin HM, Lai R, Liu J. The role of constitutively active signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in ovarian tumorigenesis and prognosis. Cancer Interdiscip Int J Am Cancer Soc. 2006;107:2730–40.
Kim H-C, Kim E, Bae JI, Lee KH, Jeon Y-T, Hwang J-W, Lim Y-J, Min S-W, Park H-P. Sevoflurane postconditioning reduces apoptosis by activating the JAK-STAT pathway after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2017;29:37–45.
Bayoumi AS, Sayed A, Broskova Z, Teoh J-P, Wilson J, Su H, Tang Y-L, Kim I-M. Crosstalk between long noncoding RNAs and microRNAs in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:356.
Pa M, Naizaer G, Seyiti A, Kuerbang G. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 functions as a sponge of MiR-200c in ovarian cancer. Oncol Res Featur Preclin Clin Cancer Ther. 2021;28:7–8.
Lee JE, Park HS, Lee D, Yoo G, Kim T, Jeon H, Yeo M-K, Lee C-S, Moon JY, Jung SS. Hippo pathway effector YAP inhibition restores the sensitivity of EGFR-TKI in lung adenocarcinoma having primary or acquired EGFR-TKI resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474:154–60.
Yao Q, Yang J, Liu T, Zhang J, Zheng Y. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes the stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by enhancing YAP transcriptional activity. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9:1392–402.
Wu X, Wang Y, Zhong W, Cheng H, Tian Z. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 enhances ovarian cancer cell stemness by inhibiting YAP translocation from nucleus to cytoplasm. Med Sci Monitor Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2020;26:e922012–e922011.
Li Z-X, Zhu Q-N, Zhang H-B, Hu Y, Wang G, Zhu Y-S. MALAT1: a potential biomarker in cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:6757.
Yang L, Bai H, Deng Y, Fan L. High MALAT1 expression predicts a poor prognosis of cervical cancer and promotes cancer cell growth and invasion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:3187–93.
Pontillo A, Bricher P, Leal V, Lima S, Souza P, Crovella S. Role of inflammasome genetics in susceptibility to HPV infection and cervical cancer development. J Med Virol. 2016;88:1646–51.
Wang T, Zhang W, Huang W, Hua Z, Li S. LncRNA MALAT1 was regulated by HPV16 E7 independently of pRB in cervical cancer cells. J Cancer. 2021;12:6344.
Hao Y, Yan Z, Zhang A, Hu S, Wang N, Luo X-G, Ma W, Zhang T-C, He H. IL-6/STAT3 mediates the HPV18 E6/E7 stimulated upregulation of MALAT1 gene in cervical cancer HeLa cells. Virus Res. 2020;281: 197907.
Jiang Y, Li Y, Fang S, Jiang B, Qin C, Xie P, Zhou G, Li G. The role of MALAT1 correlates with HPV in cervical cancer. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:2135–41.
Wang N, Hou M, Zhan Y, Shen X, Xue H. MALAT1 promotes cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:7653–9.
Lu H, He Y, Lin L, Qi Z, Ma L, Li L, Su Y. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 modulates radiosensitivity of HR-HPV+ cervical cancer via sponging miR-145. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:1683–91.
Guo C, Zhao D, Zhang Q, Liu S, Sun M-Z. miR-429 suppresses tumor migration and invasion by targeting CRKL in hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting Raf/MEK/ERK pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1–18.
Shen F, Zheng H, Zhou L, Li W, Xu X. Overexpression of MALAT1 contributes to cervical cancer progression by acting as a sponge of miR-429. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:11219–26.
Tie W, Ge F. MALAT1 inhibits proliferation of HPV16-positive cervical cancer by sponging miR-485-5p to promote expression of MAT2A. DNA Cell Biol. 2021;40:1407–17.
Xu Y, Zhang Q, Lin F, Zhu L, Huang F, Zhao L, Ou R. Casiopeina II-gly acts on lncRNA MALAT1 by miR-17-5p to inhibit FZD2 expression via the Wnt signaling pathway during the treatment of cervical carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2019;42:1365–79.
Gujral TS, Chan M, Peshkin L, Sorger PK, Kirschner MW, MacBeath G. A noncanonical Frizzled2 pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell. 2014;159:844–56.
Fu Y, Zheng Q, Mao Y, Jiang X, Chen X, Liu P, Lv B, Huang T, Yang J, Cheng Y. WNT2-mediated FZD2 stabilization regulates esophageal cancer metastasis via STAT3 signaling. Front oncol. 2020;10:1168.
Han X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Hu B, Dong X, Zhang H, Wang W. Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1/microRNA-202-3p/periostin axis modulates invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:14170–80.
Liang T, Wang Y, Jiao Y, Cong S, Jiang X, Dong L, Zhang G, Xiao D. LncRNA MALAT1 accelerates cervical carcinoma proliferation by suppressing miR-124 expression in cervical tumor cells. J Oncol. 2021;2021:8836078.
Guo F, Li Y, Liu Y, Wang J, Li Y, Li G. Inhibition of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 in CaSki human cervical cancer cells suppresses cell proliferation and invasion. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2010;42:224–9.
Liu S, Song L, Zeng S, Zhang L. MALAT1-miR-124-RBG2 axis is involved in growth and invasion of HR-HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:633–40.
Giubellino A, Burke TR, Bottaro DP. Grb2 signaling in cell motility and cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12:1021–33.
Sun R, Qin C, Jiang B, Fang S, Pan X, Peng L, Liu Z, Li W, Li Y, Li G. Down-regulation of MALAT1 inhibits cervical cancer cell invasion and metastasis by inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Mol BioSyst. 2016;12:952–62.
Zhang J, Liu SC, Luo XH, Tao GX, Guan M, Yuan H, Hu DK. Exosomal Long noncoding RNA s are differentially expressed in the Cervicovaginal lavage samples of cervical cancer patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 2016;30:1116–21.
Xia C, Liang S, He Z, Zhu X, Chen R, Chen J. Metformin, a first-line drug for type 2 diabetes mellitus, disrupts the MALAT1/miR-142-3p sponge to decrease invasion and migration in cervical cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;830:59–67.
Qiao F-H, Tu M, Liu H-Y. Role of MALAT1 in gynecological cancers: pathologic and therapeutic aspects. Oncol Lett. 2021;21:1–8.
Liao H, Chen Q, Xiao J. Reflections on the role of Malat1 in gynecological cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:13489.
Liu R, Li J, Lai Y, Liao Y, Liu R, Qiu W. Hsa-miR-1 suppresses breast cancer development by down-regulating K-ras and long non-coding RNA MALAT1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;81:491–7.
Zhu P, Wang F, Li Q. Correlation study between long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and radiotherapy efficiency on cervical carcinoma and generation of radiotherapy resistant model of cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:7564–7564.
Li Z, Xu L, Liu Y, Fu S, Tu J, Hu Y, Xiong Q. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes relapse of breast cancer patients with postoperative fever. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:3186.
Huang XJ, Xia Y, He GF, Zheng LL, Cai YP, Yin Y, Wu Q. MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis of breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2018;40:2683–9.
Arun G, Diermeier S, Akerman M, Chang K-C, Wilkinson JE, Hearn S, Kim Y, MacLeod AR, Krainer AR, Norton L. Differentiation of mammary tumors and reduction in metastasis upon Malat1 lncRNA loss. Genes Dev. 2016;30:34–51.
Li J, Liu X, Zang S, Zhou J, Zhang F, Sun B, Qi D, Li X, Kong J, Jin D. Small extracellular vesicle-bound vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promotes angiogenesis in a bevacizumab-resistant manner. Cancer Lett. 2020;492:71–83.
Zhang Y, Hu M, Liu L, Cheng X-L, Cai J, Zhou J, Wang T. Anticancer effects of Rosmarinic acid in OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cells are mediated via induction of apoptosis, suppression of cell migration and modulation of lncRNA MALAT-1 expression. J BUON. 2018;23:763–8.
Goyal B, Yadav SRM, Awasthee N, Gupta S, Kunnumakkara AB, Gupta SC. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Rev Cancer. 2021;1875:188502.
Zhou L-J, Yang D-W, Ou L-N, Guo X-R, Wu B-L. Circulating expression level of lncrna malat1 in diabetic kidney disease patients and its clinical significance. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:4729019.
Gong X, Zhu Y, Chang H, Li Y, Ma F. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial infarction via targeting miR-144-3p. Biosci Rep. 2019;39:BSR20191103.
Guo D, Ma J, Yan L, Li T, Li Z, Han X, Shui S. Down-regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 attenuates neuronal cell death through suppressing Beclin1-dependent autophagy by regulating Mir-30a in cerebral ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43:182–94.
Yu J, Chen L, Zhang B, Zheng Q. The modulation of endometriosis by lncRNA MALAT1 via NF-kappaB/iNOS. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:4073–80.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all our colleagues in Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Medical Basic Sciences Research Institute, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran (Ethical No. IR.AJUMS.REC.1401.124).
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MF, SN, MA, and DD have been involved in drafting the manuscript. MCH, MSHS, and SHA have made substantial contributions to the revising of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farzaneh, M., Najafi, S., Dari, M.A.G. et al. Functional roles of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in gynecologic cancers. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 48–65 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02914-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02914-8