Abstract
Gynecologic cancers are a worldwide problem among women. Recently, molecular targeted therapy opened up an avenue for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are RNA molecules (> 200 nt) that are not translated into protein, and interact with DNA, RNA, and proteins. LncRNAs were found to play pivotal roles in cancer tumorigenesis and progression. Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) is a lncRNA that mediates cell proliferation, migration, and EMT in gynecologic cancers by targeting several miRNAs/mRNA axes. Therefore, NEAT1 may function as a potent biomarker for the prediction and treatment of breast, ovarian, cervical, and endometrial cancers. In this narrative review, we summarized various NEAT1-related signaling pathways that are critical in gynecologic cancers.
Graphical abstract

Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) by targeting various signaling pathways involved in its target genes can regulate the occurrence of gynecologic cancers
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Gynecologic cancers, including endometrium, ovaries, cervix, fallopian tubes, and breast are a worldwide problem in women at any age (Kataki et al. 2023). Several factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and exposure to carcinogens may influence the frequency of gynecologic cancers (Razavi et al. 2021). Recently, the molecular biology of cancer has opened a new area of biomedical research (Fiore et al. 2021). The concept of RNA-based cancer therapies has gradually evolved into reality (Zhu et al. 2022). Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been shown to play important roles in the pathophysiology of different diseases such as cancer by targeting coding information (Balihodzic et al. 2022). ncRNA is classed as either small non-coding RNA (sncRNA) with less than 200 nucleotides (Beg et al. 2022) or long ncRNA (lncRNAs) with more than 200 nucleotides in length. LncRNAs play a significant role in gene transcription, post-transcription, translation, and epigenetic modification (Grammatikakis and Lal 2022). Abnormal expression or malfunction of lncRNAs has been linked to various illnesses (Ni et al. 2022). LncRNAs can influence cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion during cancer formation (Yuan et al. 2021). Nuclear enriched autosomal transcript 1 (NEAT1) is a newly discovered lncRNA that plays functional role in cancer carcinogenesis (Zhong et al. 2019). NEAT1 dysregulation has been linked to a poor prognosis in various malignancies (Chen et al. 2017; Thankachan et al. 2021). NEAT1 can bind with multiple downstream miRNAs (sncRNA with approximately 22 nts) and regulate tumor growth and progression (Knutsen et al. 2020). Therefore, targeting NEAT1-miRNAs suggests novel therapeutic targets in gynecologic cancers (Venkatesh et al. 2021; Gu et al. 2022; Hussein et al. 2022). In this review, we summarized several NEAT1/miRNA/mRNA pathways that are critical in the pathogenesis of gynecologic cancers.
Biological characteristics of NEAT1
-
Structure of NEAT1
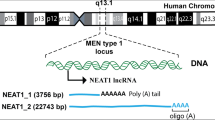
NEAT1 which is known as Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript belongs to the lncRNA families and was first defined in 2007 as a thoroughly numerous nuclear RNA (Klec et al. 2019). In humans, the encoded NEAT1 gene is transcribed via RNA polymerase II from the multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type I locus on Chr 11q13.1, and gives rise into two transcriptional isoforms, including a 3756 bp variant as short NEAT1-1 and a 22,743 bp variant as long NEAT1-2 (Zhang et al. 2021; Ronchetti et al. 2020). Both variants share a similar promoter at the 5ʹ-end and a distinct 3ʹ-end which forms two different subtypes (Gu et al. 2022). In opposition to high expression of long NEAT1-2 in the adult mice stomach and intestine, short NEAT1-1 exerts high abundance in a variety of tissues (Prinz et al. 2019a). The main localization site for NEAT1 is the nucleus but it can be detected in the cytoplasm (An et al. 2018).
-
NEAT1 functions in normal tissues
NEAT1 has been implicated in the formation of nuclear architecture known as paraspeckles for gene transcriptional and splicing programs (Kopp and Mendell 2018). Nuclear speckles constitutes active punctate sections in the nucleus that possess parts of the pre-mRNA spliceosome such as subunits of RNA Pol II, proteins of 3' end processing, small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), SRSFs, m6A writers METTL3/14 and reader YTHDC1, and diverse protein kinases that modulate the protein pool in the speckles (Klinge 2018). NEAT1 in correlation with paraspeckle proteins, splicing factor proline/glutamine rich, 54 kDa nuclear RNA- and DNA-binding protein (p54nrb), and paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) can provide a structural scaffold (Li et al. 2021a). In contrast to the tendency of NEAT1-1 in microspeckle formation, NEAT1-2 contains a limiting factor to form paraspeckles, thereby nucleus tendency for paraspeckle formation is dependent on NEAT1-2 concentration (Pisani and Baron 2020). The recent knowledge exhibits an overview by which NEAT1 and paraspeckles are associated with cancer. In some instances, NEAT1 could reduce chemoresistance in several biological contents (Pisani and Baron 2020; Shin et al. 2019a). NEAT1 by interaction with gene modulatory signals can induce some variations in gene expression, and stimulate or reduce effective immune responses. Hence, NEAT1 could be a possible predictive or prognostic biomarker (Pisani and Baron 2020). Moreover, the pivotal function of NEAT1 and paraspeckles in the control and modulation of DNA damage repair is well documented, which illustrated a crucial step to preserve cells against genetic damages. Therefore, NEAT1 can indirectly participate in DNA damage repair (Taiana et al. 2020). Also, NEAT1 modulates target genes through assigning and/or arresting transcriptional factors and affecting gene transcription, splicing, RNA stability, and translation (Wang et al. 2020). NEAT1 has been implicated in extracellular matrix remodeling (Wang et al. 2019a; Ruan et al. 2018) and the epigenetic modulatory functions of NEAT1 was reported in different studies (Wang et al. 2019a, b; Dilmaghnai et al. 2021). NEAT1 can regulate histone 3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) at the promoter or interact with DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) to control cellular behavior (Thankachan et al. 2021; Butler et al. 2019). Given the vital function of paraspeckle in governing gene expression within diverse cellular processes including homeostasis, differentiation, viral infection, immune and stress response along with organ development, NEAT1 may function a necessary role in the specific cellular processes and normal embryonic development (Dong et al. 2018; Bu et al. 2020). During mammary gland development and mammary gland branching morphogenesis, NEAT1-containing paraspeckles is necessary (Standaert et al. 2014).
NEAT1 as a guide can bind with RNA-binding proteins and chromatin-modifying complexes, and help them localize at their transcriptional loci (Statello et al. 2021; Fang and Fullwood 2016). Recent studies have identified that NEAT1 as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) can sponge or suppress miRNAs and prevent their effect on mRNAs (Meng et al. 2021; López-Urrutia et al. 2019). Therefore, NEAT1 can function as a scaffold, paraspeckle, guide, and ceRNA. Figure 1 shows the structure and functions of NEAT1.
-
NEAT1 functions in cancer cells
Biogenesis and function of lncRNA NEAT1: In humans, the encoded NEAT1 gene is transcribed via RNA polymerase II from the multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type I locus on Chr 11q13.1 and gives rise into two transcriptional isoforms, including a 3756 bp variant as short NEAT1-1 and a 22,743 bp variant as long NEAT1-2. NEAT1 can function as a scaffold for multiple RNA-binding proteins (RBP), paraspeckle, guide, and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA). NEAT1 as a ceRNA prevents miRNAs interactions with their downstream targets. Besides, NEAT1 as a guide can bind with RNA-binding proteins to help their correct localization at a specific gene locus
NEAT1 shows typical features of tumor drivers because it can be involved in cancer initiation and progression, and its abnormal expression is associated with clinical characteristics including metastasis, therapy resistance, and patient survival (Snyder et al. 2022; Knutsen et al. 2022). Evidence accumulation revealed that NEAT1 can promote stem cell properties and mediate the oncogenic phenotype in different malignancies (Li et al. 2021a; Moreno-García et al. 2020). In reproductive system tumors, this lncRNA appears to regulate EMT processes and tumor metastasis by targeting various miRNAs, RNA binding proteins, mature mRNAs, and non-protein coding genes (Li et al. 2021b; Luo et al. 2020).
-
NEAT1 in non-cancerous disorders
There is emerging proof that NEAT1 can function as a miRNA sponge and interact with target mRNAs during the progression of non-cancerous disorders (Prinz et al. 2019a, b). It has been confirmed that direct binding of NEAT1 to miR-27b-3p repressed diabetic nephropathy (Wang et al. 2019a). NEAT1 by interaction with miR-339-5p has been implicated in mesangial gene expression and functions in diverse diabetic-correlated injury models (Reichelt-Wurm et al. 2022). A recent study on acute kidney injury (AKI) observed that high expression of Neat1-2 by suppressing miR-129-5p induced kidney injury and apoptosis (Ma et al. 2022). In a study on patients with acute ischemic stroke, high expression of NEAT1 was found to inhibit miRNA‐124 and miRNA‐125, and triggered the expression of TNF‐α, IL‐6, IL‐8, and IL‐22 (Li et al. 2020a). Another study observed that NEAT1 had the capacity to target miRNAs in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Direct binding of NEAT1 to miR-128 promoted inflammation and oxidative stress in atherosclerosis progression (Chen et al. 2019). In diabetic animal models, high expression of NEAT1 deteriorated myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through induction of apoptosis and autophagy (Ma et al. 2018). Recent finding confirmed the role of NEAT1 in modulating the immune responses of retinal Müller cell to Toxoplasma gondii (Rochet et al. 2019). In a viral infection, gel containing NEAT1-siRNA reduced the activity of inflammatory macrophage and promoted HTNV propagation (Yang et al. 2022). Therefore, NEAT1 has a pivotal function in chronic diseases and future researches will assist to figure out the complete story of such intriguing lncRNA.
Functional roles of NEAT1 in gynecologic cancers
It has been reported that NEAT1 by targeting various axes plays a role in the pathogenesis of gynecologic cancers (Table 1). Here, we listed several NEAT1/miRNA/mRNA axes that are essential in breast, cervical, ovarian, and endometrial cancers (Fig. 2).
Breast cancer
-
NEAT1/miR-204
A study suggested that serum levels of NEAT1 along with lncRNA H19 were upregulated in plasma samples of breast cancer patients compared with healthy women. In lymph node‐positive and TNBC patients, high expression of NEAT1 was observed. The inhibition of NEAT1.1 and NEAT1.2 strongly suppressed cell proliferation and enhanced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. miR‐204 as a tumor suppressor was found to reduce the stimulatory effect of NEAT1 on cell proliferation. Therefore, siRNA NEAT1.1 and miR-204 mimic enhanced cell apoptosis. Also, the apoptosis-inductive effect of miR-204 overexpression increased in the presence of Camptothecin (CPT) treatment (Müller et al. 2019).
-
NEAT1/miR-129-5p/WNT4
Upregulation of NEAT1 was reported to stimulate breast tumorigenicity by targeting the breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) protein. BRCA1 is a tumor suppressor protein that regulate cell differentiation and tumorigenesis. Besides, NEAT1 could block miR-129-5p expression and upregulate WNT4 levels as a target of miR-129-5p. WNT4 is an oncogenic factor through the WNT signaling. Therefore, NEAT1 was necessary for the malignancies of breast cancer cells (Lo et al. 2016).
-
NEAT1/miR-448/ZEB1
Jiang et al. (2018) showed that NEAT1 by sponging miR-448 downregulated its levels, and consequently increased the expression of zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1). ZEB1 is a pivotal transcription factor during EMT process and breast cancer progression (Wu et al. 2020). NEAT1 downregulation was shown to suppress cell proliferation in MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-231, and SKBR3 breast cancer cells. Also, miR-448 mimic showed the same effect on the proliferative potentials of cancer cells. Consistent with the silencing results, NEAT1 overexpression promoted cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through repressing miR-448 and enhancing ZEB1 expression.
-
NEAT1/miR-218-5p/TPD52
Ren et al. (2021) demonstrated that NEAT1 suppressed miR-218-5p and accelerated the expression of tumor protein D52 (TPD52), which is already known to be upregulated in breast cancer (Wang et al. 2022), and is correlated with worse clinicopathological features in breast cancer patients (Roslan et al. 2014). The NEAT1/miR-218-5p/TPD52 axis was shown to promote cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. TPD52 overexpression has the same effects on the proliferative and migratory capacities of cancer cells, while its downregulation inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
-
NEAT1/miR-218
Zhao et al. (2017) evaluated the stimulatory effects of NEAT1 on breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion via repressing miR-218. NEAT1 knockdown reduced the proliferation of MCF-7 or SK-BR-3 cells in colony formation assay, while simultaneous transfection of cancer cells with small interfering RNA against NEAT1 (si-NEAT1) and miR-218 inhibitor showed an opposite effect on cell proliferation. The transwell cell invasion assay showed that NEAT1 knockdown inhibited the invasive capacity of cancer cells, while co-transfection revealed reverse impact.
-
NEAT1/miR-133b/TIMM17A
Li et al. (2019) demonstrated that miR-133b expression was significantly decreased in more than 92% of breast cancer tissues. This miRNA was also higher in tissues of breast cancer patients compared to the normal adjacent tissues, and induced worse clinicopathological features such as tumor histological and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. miR-133b can interact with NEAT1 and overexpression of miR-133b and NEAT1 silencing inhibited migration and invasion of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. In contrast, miR-133b silencing or NEAT1 overexpression repressed the inhibitory effects on migratory and invasive capacity of cancer cells. Additionally, miR-133b silencing was shown to enhance the oncogenic features of cancer cells and tumor metastasis in vivo via targeting the mitochondrial protein translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 17 homolog A (TIMM17A), which is already known to promote aggressiveness in the breast cancer cells (Yang et al. 2016).
-
NEAT1/miR-141-3p/KLF12
Zhou et al. (2021) demonstrated high levels of NEAT1 in extracellular vesicles (EVs) extracted from serum samples of breast cancer patients compared to healthy subjects. NEAT1 was shown to enhance the proliferation, migration, and invasion, and promote the chemoresistance of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells to cisplatin, paclitaxel, and 5-fluorouracil in vitro, while NEAT1 silencing reversed these effects. NEAT1 was found to sponge miR-141-3p and consequently upregulated the expression of Krüppel-like factor 12 (KLF12) to regulate breast cancer progression.
-
NEAT1/miR‑124/STAT3
NEAT1 was shown by Pang et al. to be upregulated in breast cancer cells and tissues, and inhibited miR-124 expression (Pang et al. 2019). NEAT1 overexpression enhanced the proliferation of MCF-7 cells and accelerated cell cycle progression. NEAT1 knockdown inhibited proliferation and caused G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in cancer cells. miR-124 was shown to target the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). To assess the effect of miR-124 on the malignant features of cancer cells, MTT assay and cell cycle analysis revealed that miR-124 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation and the G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest, while STAT3 overexpression reversed this effect in breast cancer cells.
-
NEAT1/miR-146b-5p
Li et al. (2020b) found that NEAT1 is upregulated in BT474, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-453, and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells relative to MCF10A human breast cell line and in 56 breast cancer tissues compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues. High expression level of NEAT1 was significantly associated with decreased overall survival. NEAT1 silencing was found to reduce cell proliferation and colony formation, decrease EMT, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-453 cells. By contrast, NEAT1 overexpression enhanced these oncogenic features. Furthermore, miR-146b-5p was shown to be negatively regulated by NEAT1 and its overexpression reversed the oncogenic impacts of NEAT1 on cell proliferation and EMT.
-
NEAT1/miR-410-3p/CCND1
Liu et al. (2020) revealed that miR-410-3p (among 5 screened miRNAs) expression downregulated in BT549, MDA-MB-231, ZR- 229 75-30, SKBR3, and MCF7 cells compared to MCF-10A cells, and also in breast cancer tissues compared to normal adjacent tissues. NEAT1 was observed to block miR-410-3p and stimulate cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT. Among 5 screened target genes for miR-410-3p (HMGB1, STAT3, IRS1, SOX2, and CCND1), the oncogene encoding cyclin D1 (CCND1) had the most expression level in breast cancer tissues. CCND1-encoded cyclin D1 was known to be upregulated in breast cancer tissues (Adorno-Cruz et al. 2021). Therefore, NEAT1 by targeting the miR-410-3p/CCND1 axis could improve the progression of breast cancer.
-
NEAT1/miR-548ar-3p/FUS
Ke et al. (2016) reported that NEAT1 knockdown suppressed proliferation of MDA-MB231 cells, and induced apoptosis and increased the percentage of apoptotic cells. RNA immunoprecipitation revealed that NEAT1 interacted with the RNA binding protein (RBP) Fused in Sarcoma (FUS) and repressed miR-548ar-3p. Therefore, miR-548ar-3p overexpression downregulated NEAT1 and triggered apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
-
NEAT1/miR-23a-3p/FOXA1
Zhu et al. (2021) demonstrated that NEAT1 was upregulated in breast cancer cell lines and tissues compared to MCF10A benign breast cell line and non-tumorous tissues. NEAT1 silencing suppressed cell proliferation in MDA-MD-231 and SKBR3 cells, and enhanced chemosensitivity to Taxol. RNA-pull down and luciferase assays demonstrated that NEAT1 could bind with miR-23a-3p and trigger the expression of Forkhead Box A1 (FOXA1). miR-23a-3p expression was observed to be downregulated in 40 breast cancer tissues compared with adjacent non-cancerous tissues.
-
NEAT1/miR-211/HMGA2
Li et al. (2017) illustrated that NEAT1 upregulation was associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. NEAT1 knockdown suppressed proliferation, migration, and invasion, and reversed the EMT phenotype of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells, and induced apoptosis. Additionally, NEAT1 downregulation improved chemosensitivity to 5-FU in breast cancer cells. Among several predicated miRNAs with potential interaction with NEAT1, miR-211 was confirmed in the luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, the high mobility group A2 (HMGA2) gene was found as a downstream gene of NEAT1. miR-211 mimic inhibited cell migration, invasion, and EMT phenotype of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. Besides, HMGA2 knockdown showed the same effect with NEAT1 silencing. NEAT1 knockdown decreased metastasis through the smaller number of lung metastatic colonies compared with the control animals.
-
NEAT1/ miR-138-5p/ZFX
Yao et al. (2020) reported that NEAT1 expression was increased in breast cancer tissues and SUM-185, MCF-7, and T47D breast cancer cells. Bioinformatics evaluations using the starBase v3.0 tool predicted miR-138-5p as a target of NEAT1. NEAT1 by blocking miR-138-5p enhanced the proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells, and inhibited apoptosis. Zinc finger protein X-linked (ZFX) was identified as a target gene of miR-138-5p, which can be overexpressed by NEAT1 in breast cancer cells. Overexpression of miR-138-5p demonstrated the same effects as NEAT1 knockdown..
-
NEAT1/miR-21/RRM2
Quan et al. (2020) suggested that the NEAT1/miR‐21/RRM2 axis can be involved in breast cancer progression. The Kaplan–Meier curve revealed that breast cancer patients with high expression levels of NEAT1, miR‐21, and ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2 (RRM2) had a worse prognosis compared with those with low levels. Importantly, overexpression of miR‐21 was found to promote tumor cell proliferation and migration.
-
NEAT1/miR-101/EZH2
Qian et al. (2017) demonstrated upregulation of NEAT1 in 43 paired breast cancer samples cell lines. They showed that NEAT1 knockdown reduced the proliferation and DNA synthesis of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-453 cells compared to the control group. Also, among several miRNAs with abnormal expression in the past studies (miR-34a, miR-101, miR-761, miR-320b, miR-9, miR-214, and miR-107), miR-101 showed the most significant change by 7.5 times compared to the control group. Consistent with this result in breast cancer cells, patients’ tissues also demonstrated significant downregulation of miR-101 compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues. miR-101 is a target of NEAT1 in breast cancer cells and Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Subunit (EZH2) was identified as a downstream target of miR-101. The expression of EZH2 was positively correlated with NEAT1 levels. NEAT1 knockdown reduced proliferation of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-453 cells, unlike miR-101 knockdown promoted cancer cell growth. Also, the BrdU assay revealed reduced DNA synthesis upon NEAT1 knockdown, unlike miR-101 inhibition.
-
NEAT1/miR-107/CPT1A
Xiong et al. (2019) primarily analyzed the expression levels of NEAT1 and miR-107 in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells compared with MCF-10A cells. The results showed increased expression of NEAT1 versus downregulated miR-107 in breast cancer cells. NEAT1 knockdown increased miR-107 expression, and suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer cells. Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A) was identified as the downstream target gene of miR-107. miR-107 was shown to negatively regulate NEAT1 expression and regulate breast cancer progression through affecting the tumor development-associated genes, including TIMP-1, PDGF-A, SERPINB2, cyclin D1, CDK4, and CPA1A in breast cancer cells. In breast cancer cells, NEAT1 can interact with miR-107 and regulate the expression of CPT1A.
Cervical cancer
-
NEAT1/miR-193b-3p/CCND1
High expression of NEAT1 was identified in non-sensitive and radio-resistant cervical cell lines. NEAT1 was found to enhance cell proliferation and colony formation. While the knockdown of NEAT1 triggered apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. NEAT1 by sponging miR-193b-3p could regulate CCND1 expression. Therefore, NEAT1 induced cervical cancer cell radio-resistance of via competitively binding miR-193b-3p to up-regulate the expression of CCND1 (Han et al. 2018).
-
NEAT1/AKT/PI3K
It has been shown that high expression of NEAT1 increased the proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells by targeting cyclin D1, CDK4, AKT/PI3K, and matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP2). NEAT1-siRNA transfection was reported to suppress cell proliferation and trigger apoptosis by targeting caspase 3. Therefore, NEAT1 through regulating the AKT/PI3K signaling may play important role in cervical cancer diagnosis and treatment (Guo et al. 2018).
-
NEAT1/miR-9-5p/PTEN/POU2F1
A recent study revealed that NEAT1 participated in initiation and progression of both cervical cancer tissues and cell lines by binding to miR-9-5p and suppressing its expression. High expression of NEAT1 stimulated cervical cancer cells proliferation and migration by targeting the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and POU class 2 homeobox 1 (POU2F1) protein coding genes (Xie et al. 2019).
-
NEAT1/miR-133a/SOX4
NEAT1 was explored to stimulate cervical cancer development by blocking miR-133a expression. that NEAT1 via targeting SRY-Box transcription factor 4 (SOX4) as a downstream target of miR-133a can induce colony formation, cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in cervical cancer cells. SOX4 plays essential roles in cancer progression and metastasis (Pan et al. 2022). Knockdown of NEAT1 by siRNA reduced cervical cancer cell migration and invasion capacity. Therefore, the NEAT1/miR-133a/SOX4 axis presented an important role in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer (Wang et al. 2019c).
-
NEAT1/miR-124/NF-κB
An experiment reported that NEAT1 expression was increased in cervical cancer tissues and HeLa and SiHa cell lines. NEAT1 could accelerate tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis. Overexpression of NEAT1 stimulated the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway by blocking miR-124. NF-κB is a transcriptional factor that plays a crucial role in cell proliferation and migration. miR-124 was found to reduce tumor cell migration, invasion, and EMT by suppressing N-cadherin, MMP-2, MMP-9, Vimentin, and p-NF-κB p65 (Shen et al. 2020).
-
NEAT1/miR-361/HSP90
A recent study detected that NEAT1 functions as an oncogene in patients with cervical cancer and induced worse survival. NEAT1 could stimulate invasion, sphere formation, and EMT in cervical cells by sponging miR-361. miR-361 by targeting E-cadherin and Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) was positively associated with patient survival. NEAT1 was shown to increase heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) expression as a downstream target of miR-361 and a key EMT activator (Xu et al. 2020a).
-
NEAT1/miR-34a/LDHA
NEAT1 was shown to be upregulated considerably in cervical cancer tissues and cell lines. NEAT1 was found to be linked to 5-Fu resistance. Furthermore, in 5-Fu resistant CaSki cervical cancer cells, NEAT1 expression was considerably increased. NEAT1 knockdown by shRNA significantly improved the sensitivity of 5-Fu resistant CaSki cells. Furthermore, in cervical cancer patient tissues, there was a negative connection between NEAT1 and miR-34a. Therefore, NEAT1 suppression increased the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to 5-Fu through the miR-34a/LDHA pathway (Shao et al. 2021).
-
NEAT1/miR-377/FGFR1
In cervical cancer cells, NEAT1 and FGFR1 expression levels were significantly higher, whereas miR-377 expression was significantly reduced. After NEAT1 knockdown, miR-377 expression was elevated, cell viability and migration were decreased, and apoptosis was triggered in HeLa and C33A cells. Low expression of FGFR1 decreased cell survival and migration, and caused apoptosis. Through regulation of the miR377/FGFR1 axis, inhibition of NEAT1 decreased cell survival and migration, and accelerated apoptosis in cervical cancer cells (Geng et al. 2022).
Ovarian cancer
-
NEAT1/miR-1321/TJP3
In ovarian cancer, high expression of NEAT1 as an independent factor was positively correlated with tumor grade, distant metastasis, and poor prognosis (Chen et al. 2016). NEAT1 was reported to mediate the expression of tight junction protein three (TJP3) and repress the function of miR-1321, thereby promoting EMT, invasion, and migration of ovarian cancer cells (Luo et al. 2020).
-
NEAT1/miR-124-3p/HuR
In ovarian cancer patients and cell lines, overexpression of NEAT1 induced the FIGO stage and lymph node metastasis. It has been displayed that NEAT1 by sponging miR-124-3p and binding to the human antigen R (HuR) protein could stimulate tumor cell proliferation and invasion. HuR as a specific RBP can stabilize p21, p53, and TNF-α for mRNA degradation (Chai et al. 2016).
-
NEAT1/miR-34a-5p/BCL2
It has been observed that NEAT1 overexpression induced cell proliferation and reduced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by suppressing caspase-3 activity. NEAT1 can negatively regulate miR-34a-5p and trigger B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL2) expression. High expression of NEAT1 could reduce the G0/G1 phase and accelerate the proportion of cells in the S phase. Therefore, knockdown of NEAT1 decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis (Ding et al. 2017).
-
NEAT1/miR-382-3p/ROCK1
A recent study illustrated that high expression of NEAT1 in ovarian patients was correlated to poor prognosis and shorter survival rate. NEAT1 by sponging miR-382-3p and targeting the expression of Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) as a metastasis-related gene could enhance ovarian cell migration and invasion. Therefore, miR-382-3p reduced tumor metastasis by targeting the 3′-UTR of ROCK1 (Gan et al. 2018).
-
LIN28B/NEAT1/miR-506
The aberrant expression of NEAT1 was found in high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC). LIN28B as an oncogene can bind and stabilize NEAT1 expression. Thus, NEAT1 by suppressing miR-506 could regulate tumor cell growth, proliferation, progression, and cell–cell adhesion. Therefore, NEAT1 combined with LIN28B can be potent biomarkers for HGSOC (Yong et al. 2018).
-
NEAT1/miR-194/ZEB1
NEAT1 was reported to decrease miR-194 in paclitaxel (PTX)-resistant ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines. NEAT1 was discovered to sponge miR-194, stimulate ZEB1 expression, and induce EMT and drug-resistant phenotype. NEAT1 knockdown accelerated cell sensitivity to PTX via promoting PTX-induced apoptosis in vitro. Furthermore, NEAT1 knockdown decreased resistance to drug treatment in vivo (An et al. 2017).
-
NEAT1/miR‑4500/BZW1
It has been invested that high expression of NEAT1 can inhibit miR‑4500 and stimulate basic leucine zipper and W2 domain‑containing protein 1 (BZW1) in ovarian cancer cells. NEAT1 knockdown was reported to suppress ovarian cancer cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and glycolysis, and trigger apoptosis (Xu et al. 2020b).
-
NEAT1/miR-365/FGF9
It has been demonstrated that NEAT1 and FGF9 are overexpressed in ovarian cancer cells. NEAT1 was found to target VEGF, Ang-1, and MMP2 to induce angiogenesis. Overexpression of miR-365 or knockdown of NEAT1 or FGF9 decreased cell proliferation, colony formation, and angiogenesis. The effect of FGF9 knockdown can be reversed by overexpression of NEAT1 or knockdown of miR-365 (Yuan et al. 2021).
-
NEAT1/let-7/ATGL/MEST
In ovarian cancer cells, NEAT1 expression was upregulated, whereas let-7 g was decreased. NEAT1 is competitively binding to let-7 g and thereby downregulating its expression. Let-7 g suppressed the expression of mesoderm specific transcript (MEST), increased adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) production, and decreased cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, silencing of NEAT1 reduced the xenograft tumor growth (Yin and Wang 2021).
Endometrial cancer
-
NEAT1/IGF1
In endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma (EEC), high expression of NEAT1 was correlated with FIGO stage and lymph node metastasis. Besides, NEAT1 increased cell growth, colony formation, migration, and invasion by increasing the S-phase cells and suppressing apoptosis. This lncRNA was found to enhance the expression of MMP-2, MMP-7, c-myc, and insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1). NEAT1 also reduced the expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2) and Cadherin 1. Therefore, siNEAT1 could induced G0/G1 arrest and stimulate cell apoptosis and tumor development (Li et al. 2016).
-
NEAT1/miR-124-3p
It has been reported that the expression of NEAT1 in endometrial cancer is elevated. NEAT1 by targeting miR-124-3p presented an essential role in tumor development. Therefore, silencing of NEAT1 reduced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and promoted apoptosis (Yuan et al. 2022).
-
NEAT1/miR-146b-5p/Wnt3a/HMGA1
In endometrial cancer cells, the expression level of NEAT1 increased and positively interacted with lymphoid enhancing factor 1 (LEF1), c-myc, and MMP9 through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. NEAT1 was found to suppress miR-146b-5p, increase the number of cells in the S stage, and decrease the activation of G0/G1 phase-related cycle regulators. Therefore, NEAT1 by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhanced cell growth and colony formation in endometrial cancer cells (Huang et al. 2019).
-
NEAT1/miR-144-3p/EZH2
High expression of NEAT1 was found in endometrial cancer tissues and cell lines. NEAT1 by sponging miR-144-3p can interact with EZH2 as a target gene of miR-144-3p to induce cell growth, colony formation, and invasion. NEAT1 knockdown has been shown to reduce cell proliferating, migrating, and invading. Besides, overexpression of miR-144-3p inhibited tumor cell growth and invasion (Wang et al. 2019c).
-
NEAT1/miR-361/STAT3
NEAT1 expression was significantly increased in early-stage endometrial cancer tissue samples, and high NEAT1 expression was associated with poor prognosis. NEAT1 was invested to inhibit miR-361 and mediate the expression of STAT3 as an oncogene to stimulate cell proliferation, invasion, and sphere formation. Besides, NEAT1 was reported to stimulate several tumor microenvironment-related genes such as MEF2D, ROCK1, WNT7A, VEGFA, PDE4B and KPNA4. In aggressive endometrial cancer cells, NEAT1 suppression using shRNAs reduced cell proliferation, invasion, sphere formation, and xenograft tumor growth while improving TX responsiveness (Dong et al. 2019).
-
NEAT1/miR-214-3p/Wnt/β-catenin
In endometrial cancer tissues, NEAT1, HMGA1, and β-catenin were all considerably elevated, while miR-214-3p was dramatically downregulated. NEAT1 increased the mRNA levels of Wnt/β-catenin to stimulate the expression of c-myc and MMP9, thereby accelerating cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in HEC-1A cells. Overexpression of miR-214-3p decreased HEC-1A cell proliferation, motility, and invasion, whereas overexpression of NEAT1 restored these effects. Overexpression of miR-214-3p decreased the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, whereas overexpression of NEAT1 reversed this effect (Wang et al. 2017).
-
NEAT1/miR-202-3p/TIMD4
In endometrial tumor and cell lines, overexpression of NEAT1 was related to cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by suppressing miR-202-3p. Depletion of NEAT1 was reported to improve apoptosis and reduce cell progression. NEAT1 could facilitate T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 4 (TIMD4) expression as a downstream target of miR-202-3p. Therefore, NEAT1 may provide a potential method for patients with endometrial tumor (Xu et al. 2020c).
-
NEAT1/miR-26a/b-5p/STAT3/YKL-40
A recent study revealed that cancer-associated fibroblast cells (CAFs)-derived exosomal NEAT1 can target the growth, metastasis, and progression of endometrial cancer. NEAT1 was found to inhibit miR-26a/b-5p and accelerate STAT3 and Chitinase 3-like 1 (YKL-40/CHI3L1) expression levels in endometrial tissues. YKL-40 acts as an oncogene that can be positively regulated by STAT3. Therefore, NEAT1 promoted tumor growth and tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo (Fan et al. 2021).
Clinical potential of the lncRNA NEAT1 in gynecologic cancers
In order to enhance therapeutic rates and decrease mortality, early detection, diagnosis along with early therapy are suggested for patients suffering from cancer. Since the evolution of imaging techniques, numerous screening tools have been used to figure out and recognize gynecologic cancers, including mammography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (Jafari et al. 2018). Nonetheless, the susceptibility and specificity of such imaging methods have faced some challenges for clinical application. Interestingly, a considerable number of lncRNAs are shown with promising potential for helping diagnosis, prediction of prognosis, and treatment of gynecologic cancers (Hashemipour et al. 2021). Among them, the clinical significance of NEAT1 is evaluated in several studies and the findings have suggested this lncRNA with applications in diagnosis and treatment of patients with gynecological cancers.
Aberrant expression of NEAT1 in serum samples of breast cancer patients is correlated with clinicopathological characteristics, including pathological types, tumor size, histological grading, TNM stage, and hormonal status. Therefore, NEAT1 serum upregulation can predict lower survival rates and poor prognosis in those patients (Zhao et al. 2017; Liu et al. 2020; Swellam et al. 2021; El-Fattah et al. 2021; Zhang et al. 2017; Li et al. 2017). Moreover, NEAT1 sensitivity was shown to be more pronounce for identification of those patients with high-risk factors. Notably, serum expression level of NEAT1 has shown acceptable diagnostic power in differentiation of breast cancer patients from healthy individuals with an area under curve (AUC) value of 0.83 (CI = 0.73 to 0.93, p < 0.0001) (El-Fattah et al. 2021). Therefore, lncRNA detection in body fluid is recommended for high-risk patients who were shown to be correlated with hormonal receptors (Swellam et al. 2021; Wang et al. 2021).
Recently, chemoresistance-correlated lncRNAs might be possible markers to speculate cancer cell chemotherapeutic response (Ye et al. 2022). NEAT1 knockdown is implicated in cancer cell sensitization to chemotherapy, and attenuation of SOX2+ cancer cell population (Shin et al. 2019a). SOX2 stands as a stemness gene, which modulated cancer initiating and drug-resistant behavior (Song et al. 2016). This is also shown for resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), cisplatin and Taxol, where NEAT1 downregulation using specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) improved chemosensitivity (Li et al. 2017; Shin et al. 2019b). Thereby, the role of NEAT1 in chemoresistance and cancer stemness proposed that NEAT1 could be applied as a promising clinical curative target for patients with drug resistance (Shin et al. 2019a). Moreover, NEAT1 in combination with specific pathways, such as miR-129/ZEB2 and miR-211/HMGA2 are participated in the chemotherapy drug resistance in cancer cells (Jin et al. 2021). Novel diagnostic technologies, such as microarrays, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and qRT-PCR have been used to quantify lncRNAs (Bolha et al. 2017). Currently, investigating the novel drugs targeting lncRNAs has made some advance. Some small molecule inhibitors, siRNAs, antisense oligonucleotides, and CRISPR-Cas9 have been progressed, and indirect regulators of lncRNAs are also pointed out a new window in drug advancement (Malih et al. 2016). Accumulating researches indicate that the CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technology can be applied to silence lncRNAs (Jin et al. 2021; Zhu et al. 2016). This technology can omit genomes at accurate locations with a special size and high fidelity (Najafi et al. 2022). NEAT1 expression translationally modulated NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 expression in radiation-resistant cancer cells. Suppression of NEAT1 expression by CRISPR-Cas9 has been shown to induce the radiation-resistant cancer cell sensitivity to radiation and decrease cancer cell proliferation and the expression of stem cell markers (Lin et al. 2020). These findings suggest that CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing can be applied for targeting of deregulated NEAT1 in gynecologic cancers (Jin et al. 2021). Taken together, along with an increasing number of lncRNAs, NEAT1 is also suggested with potentials in prediction of prognosis, helping diagnosis and a therapeutic target for patients with gynecologic cancers.
Conclusion
Considering the above-mentioned examples, we highlighted the recently reported function of NEAT1 in gynecologic cancers. Although the expression of NEAT1 was found to be increased in cancer cells, the exact roles of NEAT1 remain largely unknown and further studies are required to confirm this hypothesis. Based on the literature, it has been suggested that some miRNAs such as miR-124, miR-146b-5p, and miR-34a may be potent targets for gynecologic cancer diagnosis and pre-treatment. Besides, targeting some transcription factors, including STAT3, Wnt, β-catenin, and ZEB1 might be a suitable strategy against gynecologic cancers. Taken together, NEAT1 can be used as a potential biomarker for the treatment of gynecologic cancers.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ATGL:
-
Adipose triglyceride lipase
- BZW1:
-
Basic leucine zipper and W2 domain‑containing protein 1
- BCL2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- BRCA1:
-
Breast cancer susceptibility gene 1
- CAFs:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast cells
- CHI3L1:
-
Chitinase 3-like 1
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CPT:
-
Camptothecin
- CCND1:
-
Cyclin D1
- CPT1A:
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- EZH2:
-
Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit
- EEC:
-
Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma
- FUS:
-
Sarcoma
- FOXA1:
-
Forkhead box A1
- HGSOC:
-
High-grade serous ovarian cancer
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group A2
- IGF1:
-
Insulin like growth factor 1
- KLF12:
-
Krüppel-like factor 12
- LEF1:
-
Lymphoid enhancing factor 1
- LncRNAs:
-
Long ncRNA
- MEST:
-
Mesoderm specific transcript
- MMP2:
-
Metallopeptidase 2
- MEN:
-
Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- NEAT1:
-
Nuclear enriched autosomal transcript 1
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- POU2F1:
-
POU class 2 homeobox 1
- PET:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PTX:
-
Paclitaxel
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- RRM2:
-
Ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2
- ROCK1:
-
Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1
- RBP:
-
RNA binding protein
- SPECT:
-
Single-photon emission computed tomography
- SOX4:
-
SRY-Box transcription factor 4
- si-NEAT1:
-
Small interfering RNA against NEAT1
- sncRNA:
-
Small non-coding RNA
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TJP3:
-
Tight junction protein three
- TPD52:
-
Tumor protein D52
- TIMP2:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2
- TIMD4:
-
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 4
- TIMM17A:
-
Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 17 homolog A
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens-1
- ZFX:
-
Zinc finger protein X-linked
- ZEB1:
-
Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1
References
Adorno-Cruz V, Hoffmann AD, Liu X, Dashzeveg NK, Taftaf R, Wray B, Keri RA, Liu H (2021) ITGA2 promotes expression of ACLY and CCND1 in enhancing breast cancer stemness and metastasis. Genes Dis 8:493–508
An J, Lv W, Zhang Y (2017) LncRNA NEAT1 contributes to paclitaxel resistance of ovarian cancer cells by regulating ZEB1 expression via miR-194. Onco Targets Ther 10:5377
An H, Williams NG, Shelkovnikova TA (2018) NEAT1 and paraspeckles in neurodegenerative diseases: a missing lnc found? Non-Coding RNA Res 3:243–252
Balihodzic A, Prinz F, Dengler MA, Calin GA, Jost PJ, Pichler M (2022) Non-coding RNAs and ferroptosis: potential implications for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ 29(6):1–13
Beg A, Parveen R, Fouad H, Yahia M, Hassanein AS (2022) Role of different non-coding RNAs as ovarian cancer biomarkers. J Ovarian Res 15:1–11
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M, Glavač D (2017) Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7243968
Bu FT, Wang A, Zhu Y, You HM, Zhang YF, Meng XM, Huang C, Li J (2020) LncRNA NEAT1: shedding light on mechanisms and opportunities in liver diseases. Liver Int 40:2612–2626
Butler AA, Johnston DR, Kaur S, Lubin FD (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 mediates neuronal histone methylation and age-related memory impairment. Sci Signal 12:eaaw9277
Chai Y, Liu J, Zhang Z, Liu L (2016) HuR-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 stability in tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Med 5:1588–1598
Chen Z, Zhang Z, Xie B, Zhang H (2016) Clinical significance of up-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 in prognosis of ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:3373–3377
Chen T, Wang H, Yang P, He ZY (2017) Prognostic role of long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in various carcinomas: a meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 10:993–1000
Chen DD, Hui LL, Zhang XC, Chang Q (2019) NEAT1 contributes to ox-LDL-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in macrophages through inhibiting miR-128. J Cell Biochem 120:2493–2501
Di Fiore R, Suleiman S, Ellul B, Otoole SA, Savona-Ventura C, Felix A, Napolioni V, Conlon NT, Kahramanoglu I, Azzopardi MJ (2021) Gynocare update: modern strategies to improve diagnosis and treatment of rare gynecologic tumors—current challenges and future directions. Cancers 13:493
Dilmaghnai NA, Shoorei H, Sharifi G, Mohaqiq M, Majidpoor J, Dinger ME, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2021) Non-coding RNAs modulate function of extracellular matrix proteins. Biomed Pharmacother 136:111240
Ding N, Wu H, Tao T, Peng E (2017) NEAT1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer by miR-34a-5p/BCL2. Onco Targets Ther 10:4905–4915
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Hanley SJ, Kobayashi N, Todo Y, Watari H (2018) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1: a novel target for diagnosis and therapy in human tumors. Front Genet 9:471
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Xu D, Ihira K, Konno Y, Kobayashi N, Todo Y, Watari H (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 drives aggressive endometrial cancer progression via miR-361-regulated networks involving STAT3 and tumor microenvironment-related genes. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:1–15
El-Fattah AAA, Sadik NAH, Shaker OG, Mohamed Kamal A, Shahin NN (2021) Serum long non-coding RNAs PVT1, HOTAIR, and NEAT1 as potential biomarkers in Egyptian women with breast cancer. Biomolecules 11:301
Fan J-T, Zhou Z-Y, Luo Y-L, Luo Q, Chen S-B, Zhao J-C, Chen Q-R (2021) Exosomal lncRNA NEAT1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates endometrial cancer progression via miR-26a/b-5p-mediated STAT3/YKL-40 signaling pathway. Neoplasia 23:692–703
Fang Y, Fullwood MJ (2016) Roles, functions, and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Genom Proteom Bioinform 14:42–54
Gan L, Yang Y, Li Q, Feng Y, Liu T, Guo W (2018) Epigenetic regulation of cancer progression by EZH2: from biological insights to therapeutic potential. Biomark Res 6:10
Geng F, Jia W-C, Li T, Li N, Wei W (2022) Knockdown of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses proliferation and migration, and induces apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by regulating the miR-377/FGFR1 axis. Mol Med Rep 25:1–11
Grammatikakis I, Lal A (2022) Significance of lncRNA abundance to function. Mamm Genome 33:271–280
Gu J, Zhang B, An R, Qian W, Han L, Duan W, Wang Z, Ma Q (2022) Molecular interactions of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in cancer. Cancers 14:4009
Guo H, Yang S, Zhao S, Li L, Yan M, Fan M (2018) LncRNA NEAT1 regulates cervical carcinoma proliferation and invasion by targeting AKT/PI3K. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:4090–4097
Han D, Wang J, Cheng G (2018) LncRNA NEAT1 enhances the radio-resistance of cervical cancer via miR-193b-3p/CCND1 axis. Oncotarget 9:2395–2409
Hashemipour M, Boroumand H, Mollazadeh S, Tajiknia V, Nourollahzadeh Z, Borj MR, Pourghadamyari H, Rahimian N, Hamblin MR, Mirzaei H (2021) Exosomal microRNAs and exosomal long non-coding RNAs in gynecologic cancers. Gynecol Oncol 161:314–327
Huang X, Zhong R, He X, Deng Q, Peng X, Li J, Luo X (2019) Investigations on the mechanism of progesterone in inhibiting endometrial cancer cell cycle and viability via regulation of long noncoding RNA NEAT1/microRNA-146b-5p mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. IUBMB Life 71:223–234
Hussein NH, Eissa RA, de Bruyn M, El Tayebi HM (2022) NEAT1: culprit lncRNA linking PIG-C, MSLN, and CD80 in triple-negative breast cancer. Life Sci 299:120523
Jafari SH, Saadatpour Z, Salmaninejad A, Momeni F, Mokhtari M, Nahand JS, Rahmati M, Mirzaei H, Kianmehr M (2018) Breast cancer diagnosis: imaging techniques and biochemical markers. J Cell Physiol 233:5200–5213
Jiang X, Zhou Y, Sun AJ, Xue JL (2018) NEAT1 contributes to breast cancer progression through modulating miR-448 and ZEB1. J Cell Physiol 233:8558–8566
Jin H, Du W, Huang W, Yan J, Tang Q, Chen Y, Zou Z (2021) lncRNA and breast cancer: Progress from identifying mechanisms to challenges and opportunities of clinical treatment. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids 25:613–637
Kataki AC, Tiwari P, Thilagavthi R, Krishnatreya M (2023) Epidemiology of Gynaecological Cancers. In Fundamentals in Gynaecologic Malignancy. Springer, 1–8
Ke H, Zhao L, Feng X, Xu H, Zou L, Yang Q, Su X, Peng L, Jiao B (2016) NEAT1 is required for survival of breast cancer cells through FUS and miR-548. Gene Regul Syst Biol 10:11–17
Klec C, Prinz F, Pichler M (2019) Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT 1 in carcinogenesis. Mol Oncol 13:46–60
Klinge CM (2018) Non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: intracellular and intercellular communication. Non-Coding RNA 4:40
Knutsen E, Lellahi SM, Aure MR, Nord S, Fismen S, Larsen KB, Gabriel MT, Hedberg A, Bjørklund SS, Bofin AM et al (2020) The expression of the long NEAT1_2 isoform is associated with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancers. Sci Rep 10:1277
Knutsen E, Harris AL, Perander M (2022) Expression and functions of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and isoforms in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 126:551–561
Kopp F, Mendell JT (2018) Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 172:393–407
Li Z, Wei D, Yang C, Sun H, Lu T, Kuang D (2016) Overexpression of long noncoding RNA, NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion and migration in endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother 84:244–251
Li X, Wang S, Li Z, Long X, Guo Z, Zhang G, Zu J, Chen Y, Wen L (2017) The lncRNA NEAT1 facilitates cell growth and invasion via the miR-211/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Int J Biol Macromol 105:346–353
Li X, Deng S, Pang X, Song Y, Luo S, Jin L, Pan Y (2019) LncRNA NEAT1 silenced miR-133b promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 20:3616
Li P, Duan S, Fu A (2020a) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 correlates with higher disease risk, worse disease condition, decreased miR-124 and miR-125a and predicts poor recurrence-free survival of acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Lab Anal 34:e23056
Li S, Hao J, Hong Y, Mai J, Huang W (2020b) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and metastasis of human breast-cancer cells by inhibiting miR-146b-5p expression. Cancer Manag Res 12:6091–6101
Li K, Yao T, Zhang Y, Li W, Wang Z (2021a) NEAT1 as a competing endogenous RNA in tumorigenesis of various cancers: role, mechanism and therapeutic potential. Int J Biol Sci 17:3428
Lin L-C, Lee H-T, Chien P-J, Huang Y-H, Chang M-Y, Lee Y-C, Chang W-W (2020) NAD (P) H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 determines radiosensitivity of triple negative breast cancer cells and is controlled by long non-coding RNA NEAT1. Int J Med Sci 17:2214
Liu X, Yao W, Xiong H, Li Q, Li Y (2020) LncRNA NEAT1 accelerates breast cancer progression through regulating miR-410-3p/ CCND1 axis. Cancer Biomark 29:277–290
Lo P-K, Zhang Y, Wolfson B, Gernapudi R, Yao Y, Duru N, Zhou Q (2016) Dysregulation of the BRCA1/long non-coding RNA NEAT1 signaling axis contributes to breast tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 7:65067
López-Urrutia E, Bustamante Montes LP, de Guevara Cervantes DL, Pérez-Plasencia C, Campos-Parra AD (2019) Crosstalk between long non-coding RNAs, micro-RNAs and mRNAs: deciphering molecular mechanisms of master regulators in cancer. Front Oncol 9:669
Luo M, Zhang L, Yang H, Luo K, Qing C (2020) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration by interacting with miR-1321 and regulating tight junction protein 3 expression. Mol Med Rep 22:3429–3439
Ma M, Hui J, Zhang Q-Y, Zhu Y, He Y, Liu X-J (2018) Long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 inhibition blunts myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury via autophagic flux arrest and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Atherosclerosis 277:113–122
Ma T, Li H, Liu H, Peng Y, Lin T, Deng Z, Jia N, Chen Z, Wang P (2022) Neat1 promotes acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease by facilitating tubular epithelial cells apoptosis via sequestering miR-129-5p. Mol Ther 30:3313–3332
Malih S, Saidijam M, Malih N (2016) A brief review on long noncoding RNAs: a new paradigm in breast cancer pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Tumor Biol 37:1479–1485
Meng X, Li A, Yu B, Li S (2021) Interplay between miRNAs and lncRNAs: mode of action and biological roles in plant development and stress adaptation. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:2567–2574
Moreno-García L, López-Royo T, Calvo AC, Toivonen JM, de la Torre M, Moreno-Martínez L, Molina N, Aparicio P, Zaragoza P, Manzano R (2020) Competing endogenous RNA networks as biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 21:9582
Müller V, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Steinbach B, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H (2019) Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer. Mol Oncol 13:1137–1149
Najafi S, Tan SC, Aghamiri S, Raee P, Ebrahimi Z, Jahromi ZK, Rahmati Y, Sadri Nahand J, Piroozmand A, Jajarmi V, Mirzaei H (2022) Therapeutic potentials of CRISPR-Cas genome editing technology in human viral infections. Biomed Pharmacother 148:112743
Ni J, Lu J, Lu D (2022) Abnormal expression and clinical value analysis of long noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 2 in children with severe pneumonia complicated with respiratory failure. Clin Respir J 16(6):460–466
Pan Q, Meng X, Li J, Qin X, Chen H, Li Y (2022) CircSAMD11 facilitates progression of cervical cancer via regulating miR-503/SOX4 axis through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 49:175–187
Pang Y, Wu J, Li X, Wang C, Wang M, Liu J, Yang G (2019) NEAT1/miR-124/STAT3 feedback loop promotes breast cancer progression. Int J Oncol 55:745–754
Pisani G, Baron B (2020) NEAT1 and paraspeckles in cancer development and chemoresistance. Non-Coding RNA 6:43
Prinz F, Kapeller A, Pichler M, Klec C (2019a) The implications of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in non-cancerous diseases. Int J Mol Sci 20:627
Prinz F, Kapeller A, Pichler M, Klec C (2019b) The implications of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in non-cancerous diseases. Int J Mol Sci 20:627
Qian K, Liu G, Tang Z, Hu Y, Fang Y, Chen Z, Xu X (2017) The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 interacted with miR-101 modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2. Arch Biochem Biophys 615:1–9
Quan D, Chen K, Zhang J, Guan Y, Yang D, Wu H, Wu S, Lv L (2020) Identification of lncRNA NEAT1/miR-21/RRM2 axis as a novel biomarker in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 235:3372–3381
Razavi ZS, Tajiknia V, Majidi S, Ghandali M, Mirzaei HR, Rahimian N, Hamblin MR, Mirzaei H (2021) Gynecologic cancers and non-coding RNAs: epigenetic regulators with emerging roles. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 157:103192
Reichelt-Wurm S, Pregler M, Wirtz T, Kretz M, Holler K, Banas B, Banas MC (2022) The interplay of NEAT1 and miR-339-5p influences on mesangial gene expression and function in various diabetic-associated injury models. Non-Coding RNA 8:52
Ren J, Chen Y, Kong W, Li Y, Lu F (2021) Tumor protein D52 promotes breast cancer proliferation and migration via the long non-coding RNA NEAT1/microRNA-218-5p axis. Ann Transl Med 9:1008
Rochet E, Appukuttan B, Ma Y, Ashander LM, Smith JR (2019) Expression of long non-coding RNAs by human retinal Müller glial cells infected with clonal and exotic virulent Toxoplasma gondii. Non-Coding RNA 5:48
Ronchetti D, Favasuli V, Monti P, Cutrona G, Fabris S, Silvestris I, Agnelli L, Colombo M, Menichini P, Matis S (2020) NEAT1 long isoform is highly expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia irrespectively of cytogenetic groups or clinical outcome. Non-Coding RNA 6:11
Roslan N, Bièche I, Bright RK, Lidereau R, Chen Y, Byrne JA (2014) TPD52 represents a survival factor in ERBB2-amplified breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 53:807–819
Ruan Z, Ma H, Li J, Liu H, Jia H, Li F (2018) The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 contributes to extracellular matrix degradation in degenerative human nucleus pulposus cells. Exp Biol Med 243:595–600
Shao X, Zheng X, Ma D, Liu Y, Liu G (2021) Inhibition of lncRNA-NEAT1 sensitizes 5-Fu resistant cervical cancer cells through de-repressing the microRNA-34a/LDHA axis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20200533
Shen X, Zhao W, Zhang Y, Liang B (2020) Long non-coding RNA-NEAT1 promotes cell migration and invasion via regulating miR-124/NF-κB pathway in cervical cancer. Onco Targets Ther 13:3265
Shin VY, Chen J, Cheuk IW-Y, Siu M-T, Ho C-W, Wang X, Jin H, Kwong A (2019a) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 confers oncogenic role in triple-negative breast cancer through modulating chemoresistance and cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis 10:1–10
Shin VY, Chen J, Cheuk IW, Siu MT, Ho CW, Wang X, Jin H, Kwong A (2019b) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 confers oncogenic role in triple-negative breast cancer through modulating chemoresistance and cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis 10:270
Snyder M, Iraola-Guzmán S, Saus E, Gabaldón T (2022) Discovery and validation of clinically relevant long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer. Cancers 14:3866
Song W-S, Yang Y-P, Huang C-S, Lu K-H, Liu W-H, Wu W-W, Lee Y-Y, Lo W-L, Lee S-D, Chen Y-W (2016) Sox2, a stemness gene, regulates tumor-initiating and drug-resistant properties in CD133-positive glioblastoma stem cells. J Chin Med Assoc 79:538–545
Standaert L, Adriaens C, Radaelli E, Van Keymeulen A, Blanpain C, Hirose T, Nakagawa S, Marine JC (2014) The long noncoding RNA Neat1 is required for mammary gland development and lactation. RNA 20:1844–1849
Statello L, Guo C-J, Chen L-L, Huarte M (2021) Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22:96–118
Swellam M, El Magdoub HM, Shawki MA, Adel M, Hefny MM, El-Shazly SS (2021) Clinical impact of LncRNA XIST and LncRNA NEAT1 for diagnosis of high-risk group breast cancer patients. Curr Probl Cancer 45:100709
Taiana E, Ronchetti D, Todoerti K, Nobili L, Tassone P, Amodio N, Neri A (2020) LncRNA NEAT1 in paraspeckles: a structural scaffold for cellular DNA damage response systems? Non-Coding RNA 6:26
Thankachan S, Bhardwaj BK, Venkatesh T, Suresh PS (2021) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 as an emerging biomarker in breast and gynecologic cancers: a systematic overview. Reprod Sci 28:2436–2447
Venkatesh J, Wasson M-CD, Brown JM, Fernando W, Marcato P (2021) LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: novel points of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett 509:81–88
Wang J, Zhao X, Guo Z, Ma X, Song Y, Guo Y (2017) Regulation of NEAT1/miR-214-3p on the growth, migration and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells. Arch Gynecol Obstet 295:1469–1475
Wang X, Xu Y, Zhu YC, Wang YK, Li J, Li XY, Ji T, Bai SJ (2019a) LncRNA NEAT1 promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-27b-3p and ZEB1 in diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Physiol 234:12926–12933
Wang Z, Zhao Y, Xu N, Zhang S, Wang S, Mao Y, Zhu Y, Li B, Jiang Y, Tan Y (2019b) NEAT1 regulates neuroglial cell mediating Aβ clearance via the epigenetic regulation of endocytosis-related genes expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:3005–3018
Wang W, Ge L, Xu X-J, Yang T, Yuan Y, Ma X-L, Zhang X-H (2019c) LncRNA NEAT1 promotes endometrial cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating the miR-144-3p/EZH2 axis. Radiol Oncol 53:434
Wang Z, Li K, Huang W (2020) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1-centric gene regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:3769–3779
Wang M-Q, Zhu W-J, Gao P (2021) New insights into long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: biological functions and therapeutic prospects. Exp Mol Pathol 120:104640
Wang Y, Fang J, Gu F (2022) MiR-125b-5p/TPD52 axis affects proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Mol Biotechnol 64(9):1003-1012
Wu H-T, Zhong H-T, Li G-W, Shen J-X, Ye Q-Q, Zhang M-L, Liu J (2020) Oncogenic functions of the EMT-related transcription factor ZEB1 in breast cancer. J Transl Med 18:51
Xie Q, Lin S, Zheng M, Cai Q, Tu Y (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the growth of cervical cancer cells via sponging miR-9-5p. Biochem Cell Biol 97:100–108
Xiong Y, Liu Z, Li Z, Wang S, Shen N, Xin Y, Huang T (2019) Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 interacts with microRNA-107 to modulate breast cancer growth and metastasis by targeting carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1. Int J Oncol 55:1125–1136
Xu D, Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Konno Y, Ihira K, Kobayashi N, Todo Y, Watari H (2020a) MicroRNA-361-mediated inhibition of HSP90 expression and EMT in cervical cancer is counteracted by oncogenic lncRNA NEAT1. Cells 9:632
Xu H, Sun X, Huang Y, Si Q, Li M (2020b) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 modifies cell proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via the miR-4500/BZW1 axis in ovarian cancer. Mol Med Rep 22:3347–3357
Xu C, Zhai J, Fu Y (2020c) Overexpression of nuclear enriched autosomal transcript 1 facilitates cell proliferation, migration invasion, and suppresses apoptosis in endometrial cancer by targeting MicroRNA-202–3p/T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 4 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 37(9):815–823
Yang X, Si Y, Tao T, Martin TA, Cheng S, Yu H, Li J, He J, Jiang WG (2016) The impact of TIMM17A on aggressiveness of human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res 36:1237–1241
Yang Y, Li M, Ma Y, Ye W, Si Y, Zheng X, Liu H, Cheng L, Zhang L, Zhang H (2022) LncRNA NEAT1 potentiates SREBP2 activity to promote inflammatory macrophage activation and limit hantaan virus propagation. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.849020
Yao L, Chen L, Zhou H, Duan F, Wang L, Zhang Y (2020) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the progression of breast cancer by regulating miR-138–5p/ZFX axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 37(8):636–649
Ye P, Feng L, Shi S, Dong C (2022) The mechanisms of lncRNA-mediated multidrug resistance and the clinical application prospects of lncRNAs in breast cancer. Cancers 14:2101
Yin L, Wang Y (2021) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 facilitates the growth, migration, and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via the let-7 g/MEST/ATGL axis. Cancer Cell Int 21:1–15
Yong W, Yu D, Jun Z, Yachen D, Weiwei W, Midie X, Xingzhu J, Xiaohua W (2018) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1, regulated by LIN28B, promotes cell proliferation and migration through sponging miR-506 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis 9:861
Yuan J, Yi K, Yang L (2021) LncRNA NEAT1 promotes proliferation of ovarian cancer cells and angiogenesis of co-incubated human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating FGF9 through sponging miR-365: an experimental study. Medicine 100:e23423
Yuan D, Zhu D, Yin B, Ge H, Zhao Y, Huang A, Wang X, Cao X, Xia N, Qian H (2022) Expression of lncRNA NEAT1 in endometriosis and its biological functions in ectopic endometrial cells as mediated via miR-124-3p. Genes Genom 44:527–537
Zhang M, Wu WB, Wang ZW, Wang XH (2017) lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer via promoting proliferation and EMT. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:1020–1026
Zhang M, Guo J, Liu L, Huang M, Li Y, Bennett S, Xu J, Zou J (2021) The role of long non-coding RNA, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) in cancer and other pathologies. Biochem Genet 60: 1–25
Zhao D, Zhang Y, Wang N, Yu N (2017) NEAT1 negatively regulates miR-218 expression and promotes breast cancer progression. Cancer Biomark 20:247–254
Zhong W, Yang J, Li M, Li L, Li A (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the growth of human retinoblastoma cells via regulation of miR-204/CXCR4 axis. J Cell Physiol 234:11567–11576
Zhou D, Gu J, Wang Y, Wu H, Cheng W, Wang Q, Zheng G, Wang X (2021) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 transported by extracellular vesicles contributes to breast cancer development by sponging microRNA-141-3p and regulating KLF12. Cell Biosci 11:68
Zhu S, Li W, Liu J, Chen C-H, Liao Q, Xu P, Xu H, Xiao T, Cao Z, Peng J (2016) Genome-scale deletion screening of human long non-coding RNAs using a paired-guide RNA CRISPR–Cas9 library. Nat Biotechnol 34:1279–1286
Zhu L, Wang F, Fan W, Jin Z, Teng C, Zhang J (2021) lncRNA NEAT1 promotes the Taxol resistance of breast cancer via sponging the miR-23a-3p-FOXA1 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53:1198–1206
Zhu Y, Zhu L, Wang X, Jin H (2022) RNA-based therapeutics: an overview and prospectus. Cell Death Dis 13:1–15
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Qatar National Library to support open access publication charges.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Qatar National Library.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MF, MAGD, AA, SN, MK, DD, AMS, MGH, SHA and SHU have made contributions to the writing of the manuscript. All authors have approved the submitted version of the article and have agreed to be personally accountable for the author’s own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Farzaneh, M., Abouali Gale Dari, M., Anbiyaiee, A. et al. Emerging roles of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in gynecologic cancers. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 531–547 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00746-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00746-x