Abstract
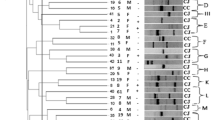
This study aimed to reveal antibiotic resistance patterns and molecular characterization of quinolone resistance Campylobacter isolates in patients with diarrhea. Campylobacter spp. isolated from 35.33% of the total samples, most of which were from male patients aged 3 months to 10 years. Identifying isolates at the species level made in MALDI-TOF MS, 82.4% were C. jejuni, and 17.6% were C. coli. Respectively 94% (47/50), 58% (29/50), and 2% (1/50) resistance rates were determined for ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. While C. jejuni isolates were more resistant to ciprofloxacin and tetracycline than C. coli, they showed no resistance to erythromycin. Quinolone resistance determining region (QRDR) were evaluated by mismatch amplification mutation test and all quinolone resistant strains gave positive results. One of the seven silent mutations identified was specific to this study, and two other novel mutations were also identified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elhadidy M, Ali MM, El-Shibiny A et al (2020) Antimicrobial resistance patterns and molecular resistance markers of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from human diarrheal cases. PLoS ONE 15:e0227833. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227833
Hizlisoy H, Sagiroglu P, Barel M et al (2023) Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in human stool samples: antibiotic resistance profiles, putative virulence determinants and molecular characterization of the isolates. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39:353
Kaakoush NO, Castaño-Rodríguez N, Mitchell HM, Man SM (2015) Global epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:687–720. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00006-15
Epps SV, Harvey RB, Hume ME et al (2013) Foodborne Campylobacter: infections, metabolism, pathogenesis and reservoirs. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:6292–6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10126292
Savaşan S, Çiftçi A, Diker KS (2004) Emergence of quinolone resistance among chicken isolates of Campylobacter in Türkiye. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci 28:391–397
Kapperud G, Lassen J, Ostroff SM, Aasen S (1992) Clinical features of sporadic Campylobacter infections in Norway. Scand J Infect Dis 24:741–749. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365549209062459
Igwaran A, Okoh AI (2019) Human campylobacteriosis: a public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 5:e02814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e0281
Butzler JP (2004) Campylobacter, from obscurity to celebrity. Clin Microbiol Infect 10:868–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.00983.x
Yoshida H, Bogaki M, Nakamura M, Nakamura S (1990) Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:1271–1272. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.34.6.1271
Lovin NM (2013) Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni. Virulence 4:230–240. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.23753
Kayman T, Abay S, Hızlısoy H (2013) Identification of Campylobacter spp. isolates with phenotypic methods and multiplex polymerase chain reaction and their antibiotic susceptibilities. Mikrobiyoloji Bülteni. 47:230–239
Aydin F, Kayman T, Abay S, Hizlisoy H et al (2023) MLST genotypes and quinolone resistance profiles of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from various sources in Türkiye. Int J Food Microbiol 391:110137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110137
EUCAST (2022) The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 12.0. https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_12.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf
Portes IAB, Panzenhagen P, dos Santos AMP et al (2023) Antibiotic resistance in campylobacter: a systematic review of South American. Antibiotics 12:548
Luangtongkum T, Jeon B, Han J, Plummer P, Logue CM, Zhang Q (2009) Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter: emergence, transmission and persistence. Fut Microbiol 4:189–200
Nachamkin I, Ung H, Li M (2002) Increasing Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni, Pennsylvania, USA, 1982–2001. Emerg Infect Dis 8:1501
Endtz HP, Ruijs GJ, van Klingeren B et al (1991) Quinolone resistance in Campylobacter isolated from man and poultry following the introduction of fluoroquinolones in veterinary medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother 27:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/27.2.199
Sam WI, Lyons MM, Waghorn DJ (1999) Increasing rates of ciprofloxacin resistant campylobacter. J Clin Pathol 52:708–712
Hart WS, Heuzenroeder MW, Barton MD (2004) Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter spp. Escherichia coli and Enterococci associated with pigs in Australia. J Vet Med Sci Ser B 51:216–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0450.2004.00760.x
Schönberg-Norio D, Hänninen ML, Katila ML et al (2006) Activities of telithromycin, erythromycin, fluoroquinolones, and doxycycline against Campylobacter strains isolated from Finnish subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:1086–1088. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.50.3.1086-1088.2006
Guerry P, Perez-Casal J, Yao R et al (1997) A genetic locus involved in iron utilization unique to some Campylobacter strains. J Bacteriol 179:3997–4002. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-47.3.750
Skjøt-Rasmussen L, Ethelberg S, Emborg HD et al (2009) Trends in occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolates from broiler chickens, broiler chicken meat, and human domestically acquired cases and travel associated cases in Denmark. Int J Food Microbiol 131:277–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.03.006
Han J, Sahin O, Barton YW (2008) Zhang Q () Key role of Mfd in the development of fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000083. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000083
Hizlisoy H, Kılıç H (2015) Broiler karkaslarından izole edilen Campylobacter jejuni izolatlarının makrolid, kinolon ve tetrasiklin grubu antibiyotiklere karşı direnç durumu. Erciyes Üniv Vet Fak Derg 12:81–92
Gusbi MM (2007) Aetiology of acute diarrhea in hospitalized children Tripoli-Libya. Jamahiriya Med J 1:23–29
Solomon EB, Hoover DG (1999) Campylobacter jejuni: a bacterial paradox. J Food Saf 19:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4565.1999.tb00239.x
Gibreel A, Taylor DE (2006) Macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:243–255. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkl210
Englen MD, Hill AE, Dargatz DA, Ladely SR, Fedorka-Cray PJ (2007) Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter in US dairy cattle. J Appl Microbiol 102:1570–1577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03189.x
Papavasileiou E, Voyatzi A, Papavasileiou K et al (2007) Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from hospitalized children in Athens, Greece, collected during 2004–2005. Eur J Epidemiol 22:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-006-9080-3
Hong J, Kim JM, Jung WK et al (2007) Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from chicken meat, pork, and beef in Korea from 2001 to 2006. J Food Prot 70:860–866. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-70.4.860
Premarathne J, Anuar AS, Thung TY et al (2017) Prevalence and antibiotic resistance against tetracycline in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli in Cattle and Beef Meat from Selangor, Malaysia. Front Microbiol 8:2254. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02254/full
Hong J, Berrang ME, Liu T et al (2007) Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from chicken meat, pork, and beef in Korea, from 2001 to 2006. J Food Prot 70:860–866
Komba EV, Mdegela RH, Msoffe PLM, Nielsen LN, Ingmer H (2015) Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and risk factors for thermophilic Campylobacter infections in symptomatic and asymptomatic humans in Tanzania. Zoo Public Health 62:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1111/zph.12185
Acknowledgements
We would also like to thank Prof. Dr. Semih Yılmaz, Abeer Babiker, Naima Sirad, and Sümeyye Temizgül for their contributions. The studies were conducted in the Bacteriology Laboratory of the Faculty of Medicine and the laboratories of the Faculty of Science and Faculty of Agriculture, Erciyes University. We specially thank Erciyes University Editing office for language improvement.
Funding
This work was supported by the Erciyes University Research Projects Unit (Grand Number: FYL-2022-12124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HAKA conceived and performed the experiment and contributed to the analysis, AA was involved in processing the experimental data, performed the analysis, drafted the manuscript. PS and MAA aided in interpreting the results, all authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis, and manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alobaidy, H.A.K., Ayvaz, A., Sağiroğlu, P. et al. Diagnosis of Campylobacter spp. Isolates and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns. Indian J Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-024-01199-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-024-01199-5