Abstract
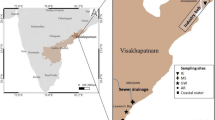
Deposition of atmospheric dust is reported to acidify surface waters in the northern Bay of Bengal (BoB). To examine the spatial variability in content and composition of total suspended matter (TSP), aerosol samples were collected at four locations (Damra, Chilika, Vizag and Chennai) along the east coast of India in the marine atmospheric boundary layer (MABL) to evaluate its impact on pH of surface waters due to deposition on surface waters using microcosm experiments. The concentration of total suspended matter (TSP) and [SO42– + NO3–] increased from southern (146 and 6.16 µg m–3, respectively) to northern coastal BoB (197 and 34.57 µg m–3, respectively) due to the influence of pollutants from Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP) in the north and dominant marine sources in the southern coastal BoB. The ionic balance in aerosols suggested that acidification potential (neutralization potential) increased (decreased) from southern to northern BoB. The dissolution of aerosols in surface seawater lowered pH by 0.018 ± 0.002 to 0.135 ± 0.005 in the coastal BoB with a higher decrease in the north than south. Our study suggests that aerosol dissolution in seawater results in ocean acidification in proportion to acidic anions (e.g., SO42–, NO3–). In addition, organic acids, such as carboxylic acids, aromatic (Benzoic acid) and hydroxy acids (Lactic and glycolic acids) also contribute significantly to ocean acidification and their contribution needs further evaluation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anttila P, Tuulia Hyötyläinen, Anu Heikkilä, Matti Jussila, Johan Finell, Markku Kulmala and Marja-Liisa Riekkola 2005 Determination of organic acids in aerosol particles from a coniferous forest by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; J. Sep. Sci. 28(4) 337–346, https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200401931.
Babu S S, Manoj M R, Moorthy K K, Gogoi M M, Nair V S, Kompalli S K, Satheesh S K, Niranjan K, Ramagopal K, Bhuyan P K and Darshan Singh 2013 Trends in aerosol optical depth over Indian region: Potential causes and impact indicators; J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 118(20) 11,711–11,806.
Bates N R, Astor Y M, Church M J, Currie K, Dore J E, Gonzalez-Davila M et al. 2014 A time-series view of changing ocean chemistry due to ocean uptake of anthropogenic CO2 and ocean acidification; Oceanography 27 126–141, https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2014.16.
Bhowmik H S, Naresh S, Bhattu D, Rastogi N, Prevot A S H and Tripathi S N 2021 Temporal and spatial variability of carbonaceous species (EC; OC; WSOC and SOA) in PM2.5 aerosol over five sites of Indo-Gangetic Plain; Atm. Poll. Res. 12 375–390, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.09.019.
Biswas H, Gadi S D, Ramana V V, Bharati M D, Priyan R K and Manjari D T 2012 Enhanced abundance of tintinnids under elevated CO2 level from coastal Bay of Bengal; Biodivers. Conserv. 21 1309–1326, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-011-0209-7.
Biswas H, Shaik A U R, Bandhyopadhyay D and Chowdhury N 2017 CO2 induced growth response in a diatom dominated phytoplankton community from SW Bay of Bengal coastal water; Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 198 29–42, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.07.022.
Boreddy K R, Tomoki Mochizuki, Kimitaka Kawamura, Srinivas Bikkina and Sarin M M 2017 Homologous series of low molecular weight (C1–C10) monocarboxylic acids, benzoic acid and hydroxyacids in fine-mode (PM2.5) aerosols over the Bay of Bengal: Influence of heterogeneity in air masses and formation pathways; Atmos. Environ. 167 170–180.
Cai W J, Hu X, Huang W J, Murrel M C, Lehrter J C, Lohrenz S E et al. 2011 Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication; Nat. Geosci. 4 766–770, https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO1297.
Deng X L, Shi C E, Wu B W, Yang Y J, Jin Q, Wang H L, Zhu S and Yu C 2016 Characteristics of the water-soluble components of aerosol particles in Hefei, China; J. Environ. Sci. 42 32–40.
Dey S and Di Girolamo L A 2010 Climatology of aerosol optical and microphysical properties over the Indian subcontinent from nine years (2000–2008) of multi angle imaging spectro radiometer (MISR) data; J. Geophys. Res. 115 D15204, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013395.
Dickson A G 1990 Standard potential of the reaction: AgCl(s) + 1/2 H2(g) = Ag(s) + HCl(aq), and the standard acidity constant of the ion HSO4− in synthetic seawater from 273.15 to 318.15 K; J. Chem. Thermodyn. 22 113–127.
DOE 1998 Determination of total alkalinity in sea water; In: Hand book of methods for the analysis of the various parameters of the carbon dioxide system in seawater Version 2 (eds) Dickson A G and Goyet C, pp. 56–85, Oak Ridge, TN: Carbon Dioxide Information and Analysis Center ORNL/CDIAC-74.
Doney S C, Mahowald N, Lima I, Feely R A, Mackenzie F T, Lamarque J F and Rasch P J 2007 Impact of anthropogenic atmospheric nitrogen and sulfur deposition on ocean acidification and the inorganic carbon system; Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 104 14,580–14,585, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702218104.
Draxler R and Rolph G 2009 HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website, NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD, 2003.
Hagens M, Hunter K A, Liss P S and Middelburg J J 2014 Biogeochemical context impacts seawater pH changes resulting from atmospheric sulfur and nitrogen deposition; Geophys. Res. Lett. 41 935–941.
Hassellov I M, David R, Turner Axel, Lauer James J and Corbett 2013 Shipping contributes to ocean acidification; Geophys. Res. Lett. 40 2731–2736, https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50521.
Hegde P, Suresh Boreddy K R, Aswini A R and Aryasree S 2022 Influence of South Asian outflow on secondary organic aerosol formation over the Indian Ocean: Inferences from water-soluble low molecular weight dicarboxylic acids and related organic compounds during ICARB 2018 experiment; Mar. Chem. 239 104071, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2021.104071.
Henriksson S V, Laaksonen A, Kerminen V M, Raisanen P, Jarvinen H, Sundstrom A M and de Leeuw G 2011 Spatial distributions and seasonal cycles of aerosols in India and China seen in global climate-aerosol model; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 11(15) 7975–7990.
Huang T, Chen J, Zhao W, Cheng J and Cheng S 2016 Seasonal variations and correlation analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013; Atmosphere 7 49.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) 2001 The observed changes in the climate system; In: Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis (eds) Houghton J T, Ding Y, Griggs D J, Noguer M, van der Linden P J and co-authors, Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 25–30.
Javid M, Bahramifar N, Younesi H, Taghavi S M and Givehchi R 2015 Dry deposition, seasonal variation and source interpretation of ionic species at Abali, Firouzkouh and Varamin, Tehran province, Iran; Atmos. Res. 157 74–90.
Kaskaoutis D G, Kharol S K, Sinha P R, Singh R P, Badarinath K V S, Mehdi W and Sharma M 2011 Contrasting aerosol trends over South Asia during the last decade based on MODIS observations; Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 4 5275–5323, https://doi.org/10.5194/amtd-4-5275-2011.
Keene W C, Pszenny A A, Galloway J N and Hawley M E 1986 Sea-salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation; J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 91 6647–6658, https://doi.org/10.1029/JD091iD06p06647.
Khemani L T 1993 Air pollution and acid rain problems in the Indian region; Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 22 207–214.
Kumar A, Sudheer A K and Sarin M M 2008a Chemical characteristics of aerosols in MABL of Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea during spring inter-monsoon: A comparative study; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 117 325–332.
Kumar A, Sarin M M and Sudheer A K 2008b Mineral and anthropogenic aerosols in Arabian Sea–atmospheric boundary layer: Sources and spatial variability; Atmos. Environ. 42 5169–5181.
Kumar A et al. 2010 Aerosol iron solubility over Bay of Bengal: Role of anthropogenic sources and chemical processing; Mar. Chem. 121(1–4) 167–175.
Kumari V R, Yadav K, Sarma V V S S and Kumar M D 2021 Acidification of coastal Bay of Bengal by aerosol deposition; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 130(4) 1–13.
Kurokawa J and Ohara T 2020 Long-term historical trends in air pollutant emissions in Asia: Regional Emission inventory in Asia (REAS) version 3; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 20 12,761–12,793, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-12761-2020.
Lelieveld J, Crutzen P J, Ramanathan V, Andreae M O, Brenninkmeijer C A M, Campos T, Cass G R, Dickerson R R, Fischer H, de Gouw J A, Hansel A, Jefferson A, Kley D, deLaat A T J, Lal S, Lawrence M G, Lobert J M, Mayol-Bracero O L, Mitra A P, Novakov T, Oltmans S J, Prather K A, Reiner T, Rodhe H, Scheeren H A, Sikka D and Williams J 2001 The Indian Ocean experiment: Widespread air pollution from South and Southeast Asia; Science 291 1031–1036.
Lewis E and Wallace D W R 1998 Program developed for CO2 system calculations. Carbon dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, TN. ORNL/CDIAC-105.
Li J, Carlson B E and Lacis A A 2009 A study on the temporal and spatial variability of absorbing aerosols using total ozone mapping spectrometer and ozone monitoring instrument aerosol index data; J. Geophys. Res. 114 D09213, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD011278.
Liji Mary David, Ravishankara A R, John K Kodros, Chandra Venkataraman, Pankaj Sadavarte, Jeffrey R Pierce, Sreelekha Chaliyakunnel and Dylan B Millet 2018 Aerosol optical depth over India; J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 123(7) 3688–3703, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027719.
Mackenzie F T 1995 Will the warming feed the warning?; In: Biotic feedbacks in the global climatic system (eds) Woodwell G and Mackenzie F T, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 22–46.
Millero F J, Graham T B, Huang F, Bustos-Serrano H and Perrot D 2006 Dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater as a function of salinity and temperature; Mar. Chem. 100 80–94.
Moorthy K K et al. 2010 Optical and physical characteristics of Bay of Bengal aerosols during W-ICARB: Spatial and vertical heterogeneities in the marine atmospheric boundary layer and in the vertical column; J. Geophys. Res. 115 D24213, https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014094.
Mukhopadhyay S K, Biswas H, De T K, Sen S and Jana T K 2003 Seasonal effects on the air-water carbon dioxide exchange in the Hooghly estuary, NE coast of Bay of Bengal, India; J. Environ. Monit. 4 459–552.
Park S M, Seo B K, Lee G, Kahng S H and Jang Y W 2015 Chemical composition of water soluble inorganic species in precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea; Atmosphere 6 732–750.
Pavuluri C M, Kawamura K, Aggarwal S G and Swaminathan T 2011a Characteristics, seasonality and sources of carbonaceous and ionic components in the tropical aerosols from Indian region; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 11 8215–8230.
Pavuluri C M, Kawamura K, Swaminathan T and Tachibana E 2011b Stable carbon isotopic compositions of total carbon, dicarboxylic acids and glyoxylic acid in the tropical Indian aerosols: Implications for sources and photochemical processing of organic aerosols; J. Geophys. Res. 116 D18307.
Porch W, Chyleka P, Dubeya M and Massie S 2007 Trends in aerosol optical depth for cities in India; Atmos. Environ. 41 7524–7532.
Prasad A K, Singh R P and Singh A 2004 Variability of aerosol optical depth over Indian subcontinent using MODIS data; J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 32(4) 313–316.
Ram K and Sarin M 2015 Atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols from Indo-Gangetic Plain and Central Himalaya: Impact of anthropogenic sources; J. Environ. Manag. 158 153–163, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.08.015.
Ram K, Sarin M M and Tripathi S N 2010 A 1-year record of carbonaceous aerosols from an urban site in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Characterization, sources, and temporal variability; J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 115, https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014188.
Ramachandran S, Kedia S and Srivastava R 2012 Aerosol optical depth trends over different regions of India; Atmos. Environ. 49 338–347.
Rastogi N and Sarin M M 2006 Atmospheric abundances of nitrogen species in rain and aerosols over a semi-arid region sources and deposition fluxes; Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 6(4) 406–417.
Reddy M S and Venkataraman C 2002a Inventories of aerosol and sulphur dioxide emissions from India: I. Fossil fuel combustion; Atmos. Environ. 36 677–697.
Reddy M S and Venkataraman C 2002b Inventories of aerosols and sulphur dioxide emissions from India: II. Biomass combustion; Atmos. Environ. 36 699–712.
Rodhe H, Dentener F and Schulz M 2002 The global distribution of acidifying wet deposition; Environ. Sci. Tech. 36 4382–4388.
Sarkar S, Chokngamwong R, Cervone G, Singh R P and Kafatos M 2006 Variability of aerosol optical depth and aerosol forcing over India; Adv. Space Res. 37(12) 2153–2159.
Sarma V V S S 1998 Variability in forms and fluxes of carbon dioxide in the Arabian Sea; PhD Thesis, Goa University, Goa, India, pp. 1–256.
Sarma V V S S, Krishna M S, Rao V D, Viswanadham R, Kumar N A and Kumari V R et al. 2012a Sources and sinks of CO2 in the west coast of Bay of Bengal; Tellus B 64 10961, https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v64i0.10961.
Sarma V V S S, Viswanadham R, Rao G D, Prasad V R, Kumar B S K, Naidu S A, Anil N et al. 2012b Carbon dioxide emissions from Indian monsoonal estuaries; Geophys. Res. Lett. 38 L03602, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL050709.
Sarma V V S S, Krishna M S, Paul Y S and Murthy V S N 2015 Observed changes in ocean acidity and carbon dioxide exchange in the coastal Bay of Bengal – a link to air pollution; Tellus B 67 24638.
Sarma V V S S, Kumari V R, Srinivas T N R, Krishna M S, Ganapathi P and Murty V S N 2018 East India coastal current controls the dissolved inorganic carbon in the coastal Bay of Bengal; Mar. Chem. 205 37–47, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2018.07.010.
Sarma V V S S, Yadav K and Behera S 2019 Role of eddies on organic matter production and f-ratios in the Bay of Bengal; Mar. Chem. 210 13–23.
Sarma V V S S, Krishna M S, Srinivas T N R, Kumari V R, Yadav K and Kumar M D 2021 Elevated acidification rates due to deposition of atmospheric pollutants in the coastal Bay of Bengal; Geophys. Res. Lett. 48(16), https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL095159.
Satheesh S K, Srinivasan J and Moorthy K K 2006a Spatial and temporal heterogeneity in aerosol properties and radiative forcing over Bay of Bengal: Sources and role of aerosol transport; J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 111 D08202.
Satsangi A, Pachauri T, Singla V, Lakhani A and Kumari K M 2010 Carbonaceous aerosols at a suburban site in Indo-Gangetic Plain; Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 39 218–222.
Satsangi A, Pachauri T, Singla V, Lakhani A and Kumari K M 2013 Water soluble ionic species in atmospheric aerosols: Concentrations and sources at Agra in the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP); Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13 1877–1889.
Saud T, Mandal T K, Gadi R, Singh D P, Sharma S K, Saxena M and Mukherjee A 2011 Emission estimates of particulate matter (PM) and trace gases (SO2, NO and NO2) from biomass fuels used in rural sector of Indo-Gangetic Plain, India; Atmos. Environ. 45 5913–5923.
Saud T, Gautam R, Mandal T K, Gadi R, Singh D P, Sharma S K, Dahiya M and Saxena M 2012 Emission estimates of organic and elemental carbon from household biomass fuel used over the Indo Gangetic Plain (IGP), India; Atmos. Environ. 61 212–220.
Saud T, Saxena M, Singh D P, Saraswati, Dahiya M, Sharma S K, Datta A, Gadi R and Mandal T K 2013 Spatial variation of chemical constituents from the burning of commonly used biomass fuels in rural areas of the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India; Atmos. Environ. 71 158–169.
Schlesinger W H 1997 Biogeochemistry: An analysis of global change; San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Singh R P, Dey S, Tripathi S N, Tare V and Holben B 2004 Variability of aerosol parameters over Kanpur, northern India; J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 109(D23) D23206, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004966.
Smith S J, Pitcher H and Wigley T M L 2001 Global and regional anthropogenic sulfur dioxide emissions; Global Planet. Change 29 99–119.
Sridevi B and Sarma V V S S 2021 Role of river discharge and warming on ocean acidification and pCO2 levels in the Bay of Bengal; Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 73(1) 1–20.
Srinivas B, Sarin M M and Sarma V V S S 2011 Atmospheric dry deposition of inorganic and organic nitrogen to the Bay of Bengal: Impact of continental outflow; Mar. Chem. 127 170–179.
Srinivas B and Sarin M 2012 Atmospheric pathways of phosphorous to the Bay of Bengal: Contribution from anthropogenic sources and mineral dust; Tellus B 64, https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v64i0.17174.
Srinivas B and Sarin M M 2013 Atmospheric dry-deposition of mineral dust and anthropogenic trace metals to the Bay of Bengal; J. Mar. Syst. 126 56–68, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.11.004.
Srinivas B, Sarin M M and Rengarajan R 2014 Atmospheric transport of mineral dust from the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Temporal variability, acid processing, and iron solubility; Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 15 3226–3243, https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GC005395.
Stein A, Draxler R, Rolph G, Stunder B, Cohen M and Ngan F 2015 NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system; Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 96 2059–2077, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00110.1.
Streets D G, Wu Y and Chin M 2006 Two decadal aerosol trends as a likely explanation of the global dimming/brightening transition; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 L15806, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026471.
Sudheer A K and Sarin M M 2008 Carbonaceous aerosols in MABL of Bay of Bengal: Influence of continental outflow; Atmos. Environ. 42 4089–4100.
Sutton A J, Wanninkhof R, Sabine C L, Feely R A, Cronin M F and Weller R A 2017 Variability and trends in surface seawater pCO2 and CO2 flux in the Pacific Ocean; Geophys. Res. Lett. 44 5627–5636, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017gl073814.
Tsyro S and Berge E 1997 The contribution of ship emissions from the North Sea and the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean to acidification in Europe, Oslo.
UNESCO 1969 Discharge of Selected Rivers of the World. UNESCO, Paris.
Unger D, Ittekkot V, Schafer P, Tiemann J and Reschke S 2003 Seasonality and inter annual variability of particle fluxes to the deep Bay of Bengal: Influence of riverine input and oceanographic processes; Deep-Sea Res. II 50 897–923.
Varkey M J, Murthy V S N and Suryanarayana A 1996 Physical Oceanography of the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea; In: Oceanography and marine biology: An annual review (eds) Ansell A D, Gibson R N and Margaret Barnes, 34 1–70.
Venkataraman C, Habib G, Eiguren-Fernandez A, Miguel A H and Friedlander S K 2005 Residential biofuels in South Asia: Carbonaceous aerosol emissions and climate impacts; Science 307(5714) 1454–1456.
Venkataraman C, Habib G, Kadamba D, Shrivastava M, Leon J F, Crouzille B, Boucher O and Streets D G 2006 Emissions from open biomass burning in India: Integrating the inventory approach with high-resolution Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro radiometer (MODIS) active-fire and land cover data; Global Biogeochem. Cycles 20 GB2013.
Verma S, Venkataraman C and Boucher O 2011 Attribution of aerosol radiative forcing over India during the winter monsoon to emissions from source categories and geographical regions; Atmos. Environ. 45(26) 4398–4407.
Wang H and Shooter D 2001 Water soluble ions of atmospheric aerosols in three New Zealand cities: Seasonal changes and sources; Atmos. Environ. 35 6031–6040.
Yadav K, Sarma V V S S, Rao D B and Kumar M D 2016 Influence of atmospheric dry deposition of inorganic nutrients on phytoplankton biomass in the coastal Bay of Bengal; Mar. Chem. 187 25–34.
Yadav K, Sarma V V S S and Kumar M D 2019 Spatial and temporal variability in concentration and characteristics of aerosols at Visakhapatnam (east) and Goa (west) coasts of India; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 532–546, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06784-6.
Yadav K, Rao V D, Sridevi B and Sarma V V S S 2021 Decadal variations in natural and anthropogenic aerosols optical depth over the Bay of Bengal: Influence of pollutants from Indo-Gangetic Plain; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 55,202–55,219, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14703-x.
Yang J, Wanyu Zhao, Lianfang Wei, Qiang Zhang, Yue Zhao, Wei Hu, Libin Wu, Xiaodong Li, Chandra Mouli Pavuluri, Xiaole Pan, Yele Sun, Zifa Wang, Cong-Qiang Liu, Kimitaka Kawamura and Pingqing Fu 2020 Molecular and spatial distributions of dicarboxylic acids, oxocarboxylic acids, and α-dicarbonyls in marine aerosols from the South China Sea to the eastern Indian Ocean; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 20 6841–6860, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-6841-2020.
Zhang J and Reid J S 2010 A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level 2 MISR aerosol products; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10 10,949–10,963.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Director and Scientist-in-Charge for their support and encouragement. We like to express our gratitude to the Chief Scientist (Dr T N R Srinivas), other participants and the ship’s crew of SSK 101 for their help during sampling. We would like to thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for funding. VRK would like to thank University Grants Commission (UGC) for funding. We thank anonymous reviewers for their critical evaluation of the manuscript and comments to improve the presentation of the manuscript. This work was carried out as a part of the project entitled Comprehensive assessment of the rate of ocean acidification and their drivers along the east coast of India (CORRODE), sponsored by Central Marine Living Resources and Ecology, Ministry of Earth Sciences. This has NIO contribution number 6945.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V R Kumari: Collection of samples, analysis of elemental composition, graphical representation, finalization of draft. V V S S Sarma: Conceptualization, funding, graphical representation writing of the original draft and finalization. M Dileep Kumar: Editing the draft and finalization.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Suresh Babu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, V.R., Sarma, V.V.S.S. & Kumar, M.D. Spatial variability in aerosol composition and its seawater acidification potential in coastal waters of the western coastal Bay of Bengal. J Earth Syst Sci 131, 251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01996-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01996-w