Abstract
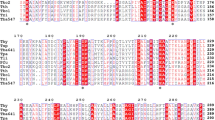
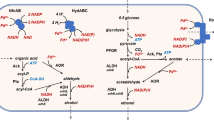
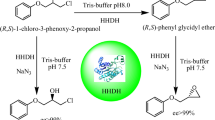
This study presents the first example of an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) from the halophilic archaeum Haloquadratum walsbyi (HwADH). A hexahistidine-tagged recombinant HwADH was heterologously overexpressed in Haloferax volcanii. HwADH was purified in one step and was found to be thermophilic with optimal activity at 65 °C. HwADH was active in the presence of 10% (v/v) organic solvent. The enzyme displayed dual cofactor specificity and a broad substrate scope, and maximum activity was detected with benzyl alcohol and 2-phenyl-1-propanol. HwADH accepted aromatic ketones, acetophenone and phenylacetone as substrates. The enzyme also accepted cyclohexanol and aromatic secondary alcohols, 1-phenylethanol and 4-phenyl-2-butanol. H. walsbyi may offer an excellent alternative to other archaeal sources to expand the toolbox of halophilic biocatalysts.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- ADH:
-
Alcohol dehydrogenase
- IMAC:
-
Immobilised metal-affinity chromatography
- iPrOH:
-
Isopropanol
- SDS–PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol
- BzOH:
-
Benzyl alcohol
- CycOH:
-
Cyclohexanol
- 1-PheOH:
-
1-Phenylethanol
- (S)-1-PheOH:
-
(S)-1-phenylethanol
- (R)-1-PheOH:
-
(R)-1-phenylethanol
- 2-Phe-1-Prop:
-
2-Phenyl-1-propanol
References
Allers, T., Barak, S., Liddell, S., Wardell, K., & Mevarech, M. (2010). Improved strains and plasmid vectors for conditional overexpression of His-tagged proteins in Haloferax volcanii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 76, 1759–1769.
Alsafadi, D., & Paradisi, F. (2013). Effect of organic solvents on the activity and stability of halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2) from Haloferax volcanii. Extremophiles, 17, 115–122.
Alsafadi, D., & Paradisi, F. (2014). Covalent immobilization of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2) from Haloferax volcanii: how to maximize activity and optimize performance of halophilic enzymes. Mol. Biotechnol., 56, 240–247.
Alsafadi, D., Alsalman, S., & Paradisi, F. (2017). Extreme halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase mediated highly efficient syntheses of enantiopure aromatic alcohols. Org. Biomol. Chem., 15, 9169–9175.
Becker, E. A., et al. (2014). Phylogenetically driven sequencing of extremely halophilic archaea reveals strategies for static and dynamic osmo-response. PLoS Genet., 10(11), e1004784.
Bolhuis, H., et al. (2006). The genome of the square archaeon Haloquadratum walsbyi: life at the limits of water activity. BMC Genom., 7, 169.
Borowitzka, M. A., & Siva, C. J. (2007). The taxonomy of the genus Dunaliella (Chlorophyta, Dunaliellales) with emphasis on the marine and halophilic species. J. Appl. Phycol., 19, 567–590.
Burns, D. G., Camakaris, H. M., Janssen, P. H., & Dyall-Smith, M. L. (2004). Cultivation of Walsby’s square haloarchaeon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 238, 469–473.
Cao, Y., Liao, L., Xu, X. W., Oren, A., Wang, C., Zhu, X. F., et al. (2008). Characterization of alcohol dehydrogenase from the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronomonas pharaonis. Extremophiles, 12, 471–476.
Cassidy, J., Bruen, L., Rosini, E., Molla, G., Pollegioni, L., & Paradisi, F. (2017). Engineering substrate promiscuity in halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase (HvADH2) by in silico design. PLoS ONE, 12(11), e0187482.
Chellapandi, P., & Balachandramohan, J. (2011). Molecular evolution-directed approach for designing archaeal formyltetrahydrofolate ligase. Turk. J. Biochem., 36, 122–135.
Cuebas-Irizzarry, M. F., Irizarry-Caro, R. A., López-Morales, C., Badillo-Rivera, K. M., Rodríguez-Minguela, C. M., & Montalvo-Rodríguez, R. (2017). Cloning and molecular characterization of an alpha-glucosidase (MalH) from the halophilic archaeon Haloquadratum walsbyi. Life, 7, 46.
Fu, H. Y., Chang, Y. N., Jheng, M. J., & Yang, C. S. (2012). Ser(262) determines the chloride-dependent colour tuning of a new halorhodopsin from Haloquadratum walsbyi. Biosci. Rep., 32, 501–509.
Galletti, P., Emer, E., Gucciardo, G., Quintavalla, A., Pori, M., & Giacomini, D. (2010). Chemoenzymatic synthesis of (2S)-2-arylpropanols through a dynamic kinetic resolution of 2-arylpropanals with alcohol dehydrogenases. Org. Biomol. Chem., 8, 4117–4123.
Hartman, A. L., et al. (2010). The complete genome sequence of Haloferax volcanii DS2, a model archaeon. PLoS ONE, 5, e9605.
Kuipers, R. K., et al. (2009). Correlated mutation analyses on super-family alignments reveal functionally important residues. Proteins, 76, 608–616.
Large, A., Stamme, C., Lange, C., Duan, Z., Allers, T., Soppa, J., et al. (2007). Characterization of a tightly controlled promoter of the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii and its use in the analysis of the essential cct1 gene. Mol. Microbiol., 66, 1092–1106.
Liliensiek, A. K., Cassidy, J., Gucciardo, G., Whitely, C., & Paradisi, F. (2013). Heterologous overexpression, purification and characterisation of an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2) from Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. Mol. Biotechnol., 55, 143–149.
Magonet, E., Hayen, P., Delforge, D., Delaive, E., & Remacle, J. (1992). Importance of the structural zinc atom for the stability of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem. J., 287, 361–365.
Oren, A. (2002). Halophilic Microorganisms and Their Environments (Vol. 5). New York: Springer.
Oren, A. (2002). Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 28, 56–63.
Quaglia, D., Pori, M., Galletti, P., Emer, E., Paradisi, F., & Giacomini, D. (2013). His-tagged Horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase: immobilization and application in the bio-based enantioselective synthesis of (S)-arylpropanols. Process Biochem., 48, 810–818.
Sellek, G. A., & Chaudhuri, J. B. (1999). Biocatalysis in organic media using enzymes from extremophiles. Enyzme Microbial. Technol., 25, 471–482.
Stoeckenius, W. (1981). Walsby’s square bacterium: fine structure of an orthogonal procaryote. J. Bacteriol., 148, 352–360.
Strillinger, E., Grötzinger, S. W., Allers, T., Eppinger, J., & Weuster-Botz, D. (2016). Production of halophilic proteins using Haloferax volcanii H1895 in a stirred-tank bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 100, 1183–1195.
Sudo, Y., et al. (2011). A microbial rhodopsin with a unique retinal composition shows both sensory rhodopsin II and bacteriorhodopsin-like properties. J. Biol. Chem., 286, 5967–5976.
Timpson, L. M., Alsafadi, D., Mac Donnchadha, C., Liddell, S., Sharkey, M. A., & Paradisi, F. (2012). Characterization of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH12) from Haloarcula marismortui, an extreme halophile from the Dead Sea. Extremophiles, 16, 57–66.
Timpson, L. M., et al. (2013). A comparison of two novel alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes (ADH1 and ADH2) from the extreme halophile Haloferax volcanii. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 97, 195–203.
Walsby, A. E. (1980). A square bacterium. Nature, 283, 69–71.
Yu, H. Y., & Li, X. (2014). Characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant thermostable glucoamylase from a halophilic isolate, Halolactibacillus sp. SK71 and its application in raw starch hydrolysis for bioethanol production. Biotechnol. Prog., 30, 1262–1268.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the support from the Synthesis and Solid State Pharmaceutical Centre and Science Foundation Ireland, Grant Number 12/RC/2275, and Dr. Thorsten Allers for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassidy, J., Paradisi, F. Haloquadratum walsbyi Yields a Versatile, NAD+/NADP+ Dual Affinity, Thermostable, Alcohol Dehydrogenase (HwADH). Mol Biotechnol 60, 420–426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0083-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0083-6