Abstract
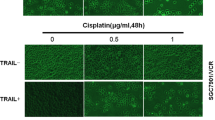
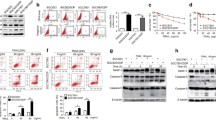
The purpose of present study was to investigate the roles of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor l (XAFl) in regulation apoptosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells after treatment with cisplatin (DDP). A total of ten paired cancerous and non-cancerous tissues were collected from patients with CRC after surgery. The levels of XAFl protein were detected by Western blot. Primary CRC cells were separated from cancer tissues, and its viability or apoptosis after treatment with DDP was determined with MTT or Annexin V/PI assays, respectively. Furthermore, we either up-regulated transfecting a XAF1 overexpression vector or down-regulated XAF1 by siRNA interference. And then, the XAF1 levels and its sensitivity to cisplatin were assessed. XAFl had a lower expression in the cancerous tissues from samples T1, T2 and T3 than their paired non-cancerous tissues N1, N2 and N3. However, the expression of XAF1 was not detected in samples T4 and N1. XAF1 levels in cancer tissues significantly decreased in comparison with normal tissues. Cell abilities of primary cells were significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner, after treatment with a series concentrations of cisplatin (2, 5, 10 μg/mL) for 48 h. Although, after down-expression of XAFl by siRNA, cisplatin caused a significant decreases in apoptosis rates in CRC cells. The up-regulation of XAF1 distinctly increased apoptosis in CRC cells administered by cisplatin (P < 0.001). The XAFl could promoted apoptosis and enhanced chemotherapy sensitivity to cisplatin in CRC cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30.
Li QG, Li P, Tang D, Chen J, Wang DR. Impact of postoperative complications on long-term survival after radical resection for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:4060–5.
Yang G, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Gao GF, Liang X, Zhou M, Wan X, Yu S, Jiang Y, Naghavi M, Vos T, Wang H, Lopez AD, Murray CJ. Rapid health transition in China, 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2013;381:1987–2015.
Schellerer VS, Merkel S, Schumann SC, Schlabrakowski A, Fortsch T, Schildberg C, Hohenberger W, Croner RS. Despite aggressive histopathology survival is not impaired in young patients with colorectal cancer: CRC in patients under 50 years of age. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012;27:71–9.
Nakamura K, Abu Lila AS, Matsunaga M, Doi Y, Ishida T, Kiwada H. A double-modulation strategy in cancer treatment with a chemotherapeutic agent and siRNA. Mol Ther. 2011;19:2040–7.
Troiani T, Zappavigna S, Martinelli E, Addeo SR, Stiuso P, Ciardiello F, Caraglia M. Optimizing treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer patients with anti-EGFR antibodies: overcoming the mechanisms of cancer cell resistance. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13:241–55.
Xia Y, Novak R, Lewis J, Duckett CS, Phillips AC. Xaf1 can cooperate with TNFalpha in the induction of apoptosis, independently of interaction with XIAP. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006;286:67–76.
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S, Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Korneluk RG. Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-caspase activity. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:128–33.
Kim SK, Park HJ, Seok H, Jeon HS, Kim JW, Chung JH, Kwon KH, Woo SH, Lee BW, Baik HH. Missense polymorphisms in XIAP-associated factor-1 (XAF1) and risk of papillary thyroid cancer: correlation with clinicopathological features. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:2205–10.
Huang J, Yao WY, Zhu Q, Tu SP, Yuan F, Wang HF, Zhang YP, Yuan YZ. XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:559–67.
Chen XY, He QY, Guo MZ. XAF1 is frequently methylated in human esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2844–9.
Lee MG, Huh JS, Chung SK, Lee JH, Byun DS, Ryu BK, Kang MJ, Chae KS, Lee SJ, Lee CH, Kim JI, Chang SG, Chi SG. Promoter CpG hypermethylation and downregulation of XAF1 expression in human urogenital malignancies: implication for attenuated p53 response to apoptotic stresses. Oncogene. 2006;25:5807–22.
Chen YB, Shu J, Yang WT, Shi L, Guo XF, Wang FG, Qian YY. XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in squamous cell lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124:3238–43.
Byun DS, Cho K, Ryu BK, Lee MG, Kang MJ, Kim HR, Chi SG. Hypermethylation of XIAP-associated factor 1, a putative tumor suppressor gene from the 17p13.2 locus, in human gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7068–75.
Yu LF, Wang J, Zou B, Lin MC, Wu YL, Xia HH, Sun YW, Gu Q, He H, Lam SK, Kung HF, Wong BC. XAF1 mediates apoptosis through an extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in colon cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:1996–2003.
Sun Y, Qiao L, Xia HH, Lin MC, Zou B, Yuan Y, Zhu S, Gu Q, Cheung TK, Kung HF, Yuen MF, Chan AO, Wong BC. Regulation of XAF1 expression in human colon cancer cell by interferon beta: activation by the transcription regulator STAT1. Cancer Lett. 2008;260:62–71.
Tu SP, Sun YW, Cui JT, Zou B, Lin MC, Gu Q, Jiang SH, Kung HF, Korneluk RG, Wong BC. Tumor suppressor XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) cooperates with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand to suppress colon cancer growth and trigger tumor regression. Cancer. 2010;116:1252–63.
Wang J, Gu Q, Li M, Zhang W, Yang M, Zou B, Chan S, Qiao L, Jiang B, Tu S, Ma J, Hung IF, Lan HY, Wong BC. Identification of XAF1 as a novel cell cycle regulator through modulating G(2)/M checkpoint and interaction with checkpoint kinase 1 in gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1507–16.
Zou Z, Yuan Z, Zhang Q, Long Z, Chen J, Tang Z, Zhu Y, Chen S, Xu J, Yan M, Wang J, Liu Q. Aurora kinase A inhibition-induced autophagy triggers drug resistance in breast cancer cells. Autophagy. 2012;8:1798–810.
Kim KY, Cha IH, Ahn JB, Kim NK, Rha SY, Chung HC, Roh JK, Shin SJ. Estimating the adjuvant chemotherapy effect in elderly stage II and III colon cancer patients in an observational study. J Surg Oncol. 2013;107:613–8.
Kurniali PC, Hrinczenko B, Al-Janadi A. Management of locally advanced and metastatic colon cancer in elderly patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:1910–22.
Jaganathan SK, Supriyanto E, Mandal M. Events associated with apoptotic effect of p-coumaric acid in HCT-15 colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:7726–34.
Weiswald LB, Richon S, Massonnet G, Guinebretiere JM, Vacher S, Laurendeau I, Cottu P, Marangoni E, Nemati F, Validire P, Bellet D, Bieche I, Dangles-Marie V. A short-term colorectal cancer sphere culture as a relevant tool for human cancer biology investigation. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:1720–31.
Lee J, Ballikaya S, Schonig K, Ball CR, Glimm H, Kopitz J, Gebert J. Transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2) changes sialylation in the microsatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer cell line HCT116. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57074.
Stevens JB, Horne SD, Abdallah BY, Ye CJ, Heng HH. Chromosomal instability and transcriptome dynamics in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32:391–402.
Long X, Li Y, Qi Y, Xu J, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang D, Zhang L, Huang J. XAF1 contributes to dengue virus-induced apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2013;27:1062–73.
Ding Y, Cheng X, Zhu L, Qiao M, Ye J, Jiang SR, Tu S. Tu1893 tumor suppressor XAF1 and TRAIL cooperate to inhibit migration and invasion of colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:S-874.
Wang J, He H, Yu L, Xia HH-x, Lin MC, Gu Q, Li M, Zou B, An X, Jiang B. HSF1 down-regulates XAF1 through transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:2451–9.
Zou B, Chim CS, Zeng H, Leung SY, Yang Y, Tu SP, Lin M, Wang J, He H, Jiang SH. Correlation between the single-site CpG methylation and expression silencing of the XAF1 gene in human gastric and colon cancers. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1835–43.
Fraser M, Leung BM, Yan X, Dan HC, Cheng JQ, Tsang BK. p53 is a determinant of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein/Akt-mediated chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7081–8.
Acknowledgments
Thanks for the support of the Bureau of Dongguan City Science and Technology 2010 Key Project Fund (201028).
Conflict of interest
This article has no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, WC., Huang, GB., Luo, XY. et al. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor l (XAFl) enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to cisplatin. Med Oncol 31, 273 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0273-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0273-4