Abstract
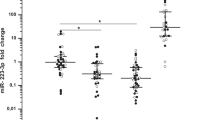
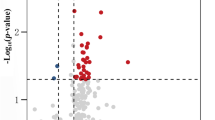
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the most common progressive neurodegenerative diseases. Some microRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in the development of many neurological diseases. This study aims to evaluate the clinical significance and biological function of miR-485-3p in the development and progression of PD. The expression of miR-485-3p in serum of PD patients was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). LPS-treated microglia BV2 cells were used to mimic neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of PD. The levels of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The diagnosis value of miR-485-3p was evaluated by plotting receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. A luciferase reporter assay was performed to demonstrate the interaction between miR-485-3p and FBXO45. The results showed that miR-485-3p was significantly up-regulated in serum of PD patients compared with that in both Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and healthy cases, and had diagnostic accuracy for PD screening. The activated microglia BV2 cells induced by LPS also had elevated miR-485-3p, and the knockdown of miR-485-3p inhibited the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. FBXO protein 45 (FBXO45) served as a potential target of miR-485-3p, which was speculated to mediate the function of miR-485-3p. Our results suggest that the up-regulated expression of miR-485-3p in PD may be a novel diagnostic biomarker for PD. Reducing the expression level of miR-485-3p can inhibit the inflammatory responses of BV2 cells, which indicated that miR-485-3p, as a regulator of neuroinflammation, may have the potential as a therapeutic target in PD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Lotankar, S., Prabhavalkar, K. S., & Bhatt, L. K. (2017). Biomarkers for parkinson’s disease: recent advancement. Neuroscience Bulletin., 33(5), 585–597.
Opara, J., Malecki, A., Malecka, E., & Socha, T. (2017). Motor assessment in Parkinson’s disease. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine : AAEM., 24(3), 411–415.
Schneider, R. B., Iourinets, J., & Richard, I. H. (2017). Parkinson’s disease psychosis: Presentation, diagnosis and management. Neurodegenerative Disease Management., 7(6), 365–376.
Samii, A., Nutt, J. G., & Ransom, B. R. (2004). Parkinson’s disease. Lancet, 363(9423), 1783–1793.
Tysnes, O. B., & Storstein, A. (2017). Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neural Transmission., 124(8), 901–905.
Ho, M. S. (2019). Microglia in Parkinson’s disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology., 1175, 335–353.
Backes, C., Meese, E., & Keller, A. (2016). Specific miRNA disease biomarkers in blood, serum and plasma: challenges and prospects. Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy., 20(6), 509–518.
Vishnoi, A., & Rani, S. (2017). MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases: an overview. Methods in Molecular Biology., 1509, 1–10.
Fyfe, I. (2020). MicroRNAs - diagnostic markers in Parkinson disease? Nature Reviews. Neurology, 16(2), 65.
Catanesi, M., d’Angelo, M., Tupone, M. G., Benedetti, E., Giordano, A., Castelli, V., et al. (2020). MicroRNAs Dysregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 5986.
Goh, S. Y., Chao, Y. X., Dheen, S. T., Tan, E. K., & Tay, S. S. (2019). Role of MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5649.
Sole, C., Domingo, S., Ferrer, B., Moline, T., Ordi-Ros, J., & Cortes-Hernandez, J. (2019). MicroRNA expression profiling identifies miR-31 and miR-485-3p as regulators in the pathogenesis of discoid cutaneous lupus. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology., 139(1), 51–61.
Li, B., Bai, L., Shen, P., Sun, Y., Chen, Z., & Wen, Y. (2017). Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in knee anterior cruciate ligament tissues surgically removed from patients with osteoarthritis. International Journal of Molecular Medicine., 40(4), 1105–1113.
Leggio, L., Vivarelli, S., L’Episcopo, F., Tirolo, C., Caniglia, S., Testa, N., et al. (2017). microRNAs in parkinson’s disease: from pathogenesis to novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences., 18(12), 2698.
Joutsa, J., Gardberg, M., Roytta, M., & Kaasinen, V. (2014). Diagnostic accuracy of parkinsonism syndromes by general neurologists. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders., 20(8), 840–844.
McKhann, G., Drachman, D., Folstein, M., Katzman, R., Price, D., & Stadlan, E. M. (1984). Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 34(7), 939–944.
Beitz, J. M. (2014). Parkinson’s disease: A review. Frontiers in Bioscience., 6, 65–74.
Raza, C., Anjum, R., & Shakeel, N. U. A. (2019). Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management strategies. Life Sciences., 226, 77–90.
Tolosa, E., Wenning, G., & Poewe, W. (2006). The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet Neurology., 5(1), 75–86.
Caggiu, E., Paulus, K., Mameli, G., Arru, G., Sechi, G. P., & Sechi, L. A. (2018). Differential expression of miRNA 155 and miRNA 146a in Parkinson’s disease patients. eNeurologicalSci., 13, 1–4.
Zhang, L. M., Wang, M. H., Yang, H. C., Tian, T., Sun, G. F., Ji, Y. F., et al. (2019). Dopaminergic neuron injury in Parkinson’s disease is mitigated by interfering lncRNA SNHG14 expression to regulate the miR-133b/ alpha-synuclein pathway. Aging, 11(21), 9264–9279.
Cho, H. J., Liu, G., Jin, S. M., Parisiadou, L., Xie, C., Yu, J., et al. (2013). MicroRNA-205 regulates the expression of Parkinson’s disease-related leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 protein. Human Molecular Genetics., 22(3), 608–620.
Minones-Moyano, E., Porta, S., Escaramis, G., Rabionet, R., Iraola, S., Kagerbauer, B., et al. (2011). MicroRNA profiling of Parkinson’s disease brains identifies early downregulation of miR-34b/c which modulate mitochondrial function. Human Molecular Genetics., 20(15), 3067–3078.
Yu, L., Li, H., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Tian, Q., Li, H., et al. (2020). MiR-485–3p serves as a biomarker and therapeutic target of Alzheimer’s disease via regulating neuronal cell viability and neuroinflammation by targeting AKT3. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine, 9(1), 1548.
Gu, J., Shao, R., Li, M., Yan, Q., & Hu, H. (2020). MiR-485-3p modulates neural stem cell differentiation and proliferation via regulating TRIP6 expression. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine., 24(1), 398–404.
Chung, F. Z., Sahasrabuddhe, A. A., Ma, K., Chen, X., Basrur, V., Lim, M. S., et al. (2014). Fbxo45 inhibits calcium-sensitive proteolysis of N-cadherin and promotes neuronal differentiation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry., 289(41), 28448–28459.
Xu, M., Zhu, C., Zhao, X., Chen, C., Zhang, H., Yuan, H., et al. (2015). Atypical ubiquitin E3 ligase complex Skp1-Pam-Fbxo45 controls the core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors. Oncotarget, 6(2), 979–994.
Lin, M., Wang, Z. W., & Zhu, X. (2020). FBXO45 is a potential therapeutic target for cancer therapy. Cell Death Discovery., 6, 55.
Saiga, T., Fukuda, T., Matsumoto, M., Tada, H., Okano, H. J., Okano, H., et al. (2009). Fbxo45 forms a novel ubiquitin ligase complex and is required for neuronal development. Molecular and Cellular Biology., 29(13), 3529–3543.
Tada, H., Okano, H. J., Takagi, H., Shibata, S., Yao, I., Matsumoto, M., et al. (2010). Fbxo45, a novel ubiquitin ligase, regulates synaptic activity. The Journal of Biological Chemistry., 285(6), 3840–3849.
Dauer, W., & Przedborski, S. (2003). Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron, 39(6), 889–909.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The experimental procedures were all in accordance with the guideline of the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Central Hospital (Taizhou University Hospital).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Wang, R., Li, R. et al. Diagnostic Performance of miR-485-3p in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and its Relationship with Neuroinflammation. Neuromol Med 24, 195–201 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08676-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08676-w