Abstract
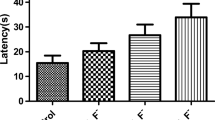
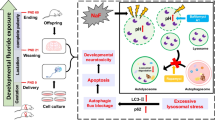
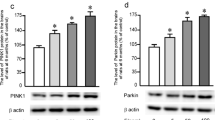
The cerebral cortex is closely associated with learning and memory, and fluoride is capable of inducing cortical toxicity, but its mechanism is unclear. This study aimed to investigate the role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in fluoride-induced cortical toxicity. Rats exposed to sodium fluoride (NaF) were used as an in vivo model. The results showed that NaF exposure impaired the learning and memory capacities and increased urinary fluoride levels in rats. In addition, NaF exposure induced excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated apoptosis, as evidenced by elevated IRE1α, GRP78, cleaved caspase-12, and cleaved caspase-3, as well as defective autophagy, as evidenced by increased expression of Beclin1, LC3-II, and p62 in cortical areas. Importantly, the endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) alleviated endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as defective autophagy, thus confirming the critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in fluoride-induced cortical toxicity. Taken together, these results suggest that excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress and its mediated defective autophagy lead to fluoride-induced cortical toxicity. This provides new insights into the mechanisms of fluoride-induced neurotoxicity and a new theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of fluoride-induced neurotoxicity.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khairnar MR, Dodamani AS, Jadhav HC, Naik RG, Deshmukh MA (2015) Mitigation of fluorosis - a review. J Clin Diagn Res 9(6):E5–E9. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/13261.6085
Dec K, Lukomska A, Maciejewska D, Jakubczyk K, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Chlubek D, Wasik A, Gutowska I (2017) The influence of fluorine on the disturbances of homeostasis in the central nervous system. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(2):224–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0871-4
Qing-Feng S, Ying-Peng X, Tian-Tong X (2019) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and p53 involved in chronic fluorosis induced blood-brain barrier damage and neurocyte changes. Arch Med Sci 15(2):457–466. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2019.83294
Prabhakar A, Abdulkhayarkutty K, Cheruvallil SV, Sudhakaran P (2021) Effect of endemic fluorosis on cognitive function of school children in Alappuzha District, Kerala: a cross sectional study. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 24(5):715–720. https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.AIAN_850_20
Wang M, Liu L, Li H, Li Y, Liu H, Hou C, Zeng Q, Li P, Zhao Q, Dong L, Zhou G, Yu X, Liu L, Guan Q, Zhang S, Wang A (2020) Thyroid function, intelligence, and low-moderate fluoride exposure among Chinese school-age children. Environ Int 134:105229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105229
Lukomska A, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Dec K, Pilutin A, Tarnowski M, Jakubczyk K, Zwierello W, Skorka-Majewicz M, Chlubek D, Gutowska I (2020) Changes in gene and protein expression of metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and their inhibitors TIMP2 and TIMP3 in different parts of fluoride-exposed rat brain. Int J Mol Sci 22(1):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010391
Rho HJ, Kim JH, Lee SH (2018) Function of selective neuromodulatory projections in the mammalian cerebral cortex: comparison between cholinergic and noradrenergic systems. Front Neural Circuits 12:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2018.00047
Grasby KL, Jahanshad N, Painter JN, Colodro-Conde L, Bralten J, Hibar DP, Lind PA, Pizzagalli F, Ching C, Mcmahon M, Shatokhina N, Zsembik L, Thomopoulos SI, Zhu AH, Strike LT, Agartz I, Alhusaini S, Almeida M, Alnaes D, Amlien IK, Andersson M, Ard T, Armstrong NJ, Ashley-Koch A, Atkins JR, Bernard M, Brouwer RM, Buimer E, Bulow R, Burger C, Cannon DM, Chakravarty M, Chen Q, Cheung JW, Couvy-Duchesne B, Dale AM, Dalvie S, de Araujo TK, de Zubicaray GI, de Zwarte S, den Braber A, Doan NT, Dohm K, Ehrlich S, Engelbrecht HR, Erk S, Fan CC, Fedko IO, Foley SF, Ford JM, Fukunaga M, Garrett ME, Ge T, Giddaluru S, Goldman AL, Green MJ, Groenewold NA, Grotegerd D, Gurholt TP, Gutman BA, Hansell NK, Harris MA, Harrison MB, Haswell CC, Hauser M, Herms S, Heslenfeld DJ, Ho NF, Hoehn D, Hoffmann P, Holleran L, Hoogman M, Hottenga JJ, Ikeda M, Janowitz D, Jansen IE, Jia T, Jockwitz C, Kanai R, Karama S, Kasperaviciute D, Kaufmann T, Kelly S, Kikuchi M, Klein M, Knapp M, Knodt AR, Kramer B, Lam M, Lancaster TM, Lee PH, Lett TA, Lewis LB, Lopes-Cendes I, Luciano M, Macciardi F, Marquand AF, Mathias SR, Melzer TR, Milaneschi Y, Mirza-Schreiber N, Moreira J, Muhleisen TW, Muller-Myhsok B, Najt P, Nakahara S, Nho K, Olde LL, Orfanos DP, Pearson JF, Pitcher TL, Putz B, Quide Y, Ragothaman A, Rashid FM, Reay WR, Redlich R, Reinbold CS, Repple J, Richard G, Riedel BC, Risacher SL, Rocha CS, Mota NR, Salminen L, Saremi A, Saykin AJ, Schlag F, Schmaal L, Schofield PR, Secolin R, Shapland CY, Shen L, Shin J, Shumskaya E, Sonderby IE, Sprooten E, Tansey KE, Teumer A, Thalamuthu A, Tordesillas-Gutierrez D, Turner JA, Uhlmann A, Vallerga CL, van der Meer D, van Donkelaar M, van Eijk L, van Erp T, van Haren N, van Rooij D, van Tol MJ, Veldink JH, Verhoef E, Walton E, Wang M, Wang Y, Wardlaw JM, Wen W, Westlye LT, Whelan CD, Witt SH, Wittfeld K, Wolf C, Wolfers T, Wu JQ, Yasuda CL, Zaremba D, Zhang Z, Zwiers MP, Artiges E, Assareh AA, Ayesa-Arriola R, Belger A, Brandt CL, Brown GG, Cichon S, Curran JE, Davies GE, Degenhardt F, Dennis MF, Dietsche B, Djurovic S, Doherty CP, Espiritu R, Garijo D, Gil Y, Gowland PA, Green RC, Hausler AN, Heindel W, Ho BC, Hoffmann WU, Holsboer F, Homuth G, Hosten N, Jack CJ, Jang M, Jansen A, Kimbrel NA, Kolskar K, Koops S, Krug A, Lim KO, Luykx JJ, Mathalon DH, Mather KA, Mattay VS, Matthews S, Mayoral VSJ, Mcewen SC, Melle I, Morris DW, Mueller BA, Nauck M, Nordvik JE, Nothen MM, O'Leary DS, Opel N, Martinot MP, Pike GB, Preda A, Quinlan EB, Rasser PE, Ratnakar V, Reppermund S, Steen VM, Tooney PA, Torres FR, Veltman DJ, Voyvodic JT, Whelan R, White T, Yamamori H, Adams H, Bis JC, Debette S, Decarli C, Fornage M, Gudnason V, Hofer E, Ikram MA, Launer L, Longstreth WT, Lopez OL, Mazoyer B, Mosley TH, Roshchupkin GV, Satizabal CL, Schmidt R, Seshadri S, Yang Q, Alvim M, Ames D, Anderson TJ, Andreassen OA, Arias-Vasquez A, Bastin ME, Baune BT, Beckham JC, Blangero J, Boomsma DI, Brodaty H, Brunner HG, Buckner RL, Buitelaar JK, Bustillo JR, Cahn W, Cairns MJ, Calhoun V, Carr VJ, Caseras X, Caspers S, Cavalleri GL, Cendes F, Corvin A, Crespo-Facorro B, Dalrymple-Alford JC, Dannlowski U, de Geus E, Deary IJ, Delanty N, Depondt C, Desrivieres S, Donohoe G, Espeseth T, Fernandez G, Fisher SE, Flor H, Forstner AJ, Francks C, Franke B, Glahn DC, Gollub RL, Grabe HJ, Gruber O, Haberg AK, Hariri AR, Hartman CA, Hashimoto R, Heinz A, Henskens FA, Hillegers M, Hoekstra PJ, Holmes AJ, Hong LE, Hopkins WD, Hulshoff PH, Jernigan TL, Jonsson EG, Kahn RS, Kennedy MA, Kircher T, Kochunov P, Kwok J, Le Hellard S, Loughland CM, Martin NG, Martinot JL, Mcdonald C, Mcmahon KL, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Michie PT, Morey RA, Mowry B, Nyberg L, Oosterlaan J, Ophoff RA, Pantelis C, Paus T, Pausova Z, Penninx B, Polderman T, Posthuma D, Rietschel M, Roffman JL, Rowland LM, Sachdev PS, Samann PG, Schall U, Schumann G, Scott RJ, Sim K, Sisodiya SM, Smoller JW, Sommer IE, St PB, Stein DJ, Toga AW, Trollor JN, Van der Wee N, van T Ed, Volzke H, Walter H, Weber B, Weinberger DR, Wright MJ, Zhou J, Stein JL, Thompson PM, Medland SE (2020) The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Science 367(6484):eaay6690. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay6690
Fronczak KM, Li Y, Henchir J, Dixon CE, Carlson SW (2021) Reductions in synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 isoforms in the cortex and hippocampus in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 58(11):6006–6019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02534-3
Li X, Yang J, Liang C, Yang W, Zhu Q, Luo H, Liu X, Wang J, Zhang J (2022) Potential protective effect of riboflavin against pathological changes in the main organs of male mice induced by fluoride exposure. Biol Trace Elem Res 200(3):1262–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02746-7
Schwarz DS, Blower MD (2016) The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2052-6
Wang M, Kaufman RJ (2016) Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature 529(7586):326–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17041
Sprenkle NT, Sims SG, Sanchez CL, Meares GP (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in the central nervous system. Mol Neurodegener 12(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0183-y
Liu J, Yi S, Shi W, Zhang G, Wang S, Qi Q, Cong B, Li Y (2021) The pathology of morphine-inhibited nerve repair and morphine-induced nerve damage is mediated via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Front Neurosci 15:618190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.618190
Li F, Liu BB, Cai M, Li JJ, Lou SJ (2018) Excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress and decreased neuroplasticity-associated proteins in prefrontal cortex of obese rats and the regulatory effects of aerobic exercise. Brain Res Bull 140:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.04.003
Niu Q, Chen J, Xia T, Li P, Zhou G, Xu C, Zhao Q, Dong L, Zhang S, Wang A (2018) Excessive ER stress and the resulting autophagic flux dysfunction contribute to fluoride-induced neurotoxicity. Environ Pollut 233:889–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.015
Liu L, Zhang Y, Gu H, Zhang K, Ma L (2015) Fluorosis induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo. Biol Trace Elem Res 164(1):64–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0192-4
Li M, Feng J, Cheng Y, Dong N, Tian X, Liu P, Zhao Y, Qiu Y, Tian F, Lyu Y, Zhao Q, Wei C, Wang M, Yuan J, Ying X, Ren X, Yan X (2022) Arsenic-fluoride co-exposure induced endoplasmic reticulum stress resulting in apoptosis in rat heart and H9c2 cells. Chemosphere 288(Pt 2):132518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132518
Lin L, Zhang MX, Zhang L, Zhang D, Li C, Li YL (2021) Autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis: new regulatory mechanisms for atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:809955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.809955
Bar-Yosef T, Damri O, Agam G (2019) Dual role of autophagy in diseases of the central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci 13:196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00196
Lumkwana D, du Toit A, Kinnear C, Loos B (2017) Autophagic flux control in neurodegeneration: Progress and precision targeting-Where do we stand? Prog Neurobiol 153:64–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.03.006
Liu M, Pi H, Xi Y, Wang L, Tian L, Chen M, Xie J, Deng P, Zhang T, Zhou C, Liang Y, Zhang L, He M, Lu Y, Chen C, Yu Z, Zhou Z (2021) KIF5A-dependent axonal transport deficiency disrupts autophagic flux in trimethyltin chloride-induced neurotoxicity. Autophagy 17(4):903–924. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1739444
Dec K, Lukomska A, Skonieczna-Zydecka K, Kolasa-Wolosiuk A, Tarnowski M, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Gutowska I (2019) Long-term exposure to fluoride as a factor promoting changes in the expression and activity of cyclooxygenases (COX1 and COX2) in various rat brain structures. Neurotoxicology 74:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.06.001
Oka S, Li X, Zhang F, Taguchi C, Tewari N, Kim IS, Zhong L, Arikawa K, Liu Y, Bhawal UK (2020) Oral toxicity to high level sodium fluoride causes impairment of autophagy. J Physiol Pharmacol 71(5):749–760. https://doi.org/10.26402/jpp.2020.5.14
Yildiz MO, Celik H, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Gur C, Bayav I, Genc A, Kandemir O (2022) Neuromodulatory effects of hesperidin against sodium fluoride-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Involvement of neuroinflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and autophagy. Neurotoxicology 90:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2022.04.002
Ni L, Wei Y, Pan J, Li X, Xu B, Deng Y, Yang T, Liu W (2021) The effects of mTOR or Vps34-mediated autophagy on methylmercury-induced neuronal apoptosis in rat cerebral cortex. Food Chem Toxicol 155:112386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112386
Manthari RK, Tikka C, Ommati MM, Niu R, Sun Z, Wang J, Zhang J, Wang J (2018) Arsenic induces autophagy in developmental mouse cerebral cortex and hippocampus by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: involvement of blood-brain barrier’s tight junction proteins. Arch Toxicol 92(11):3255–3275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2304-y
Kolb PS, Ayaub EA, Zhou W, Yum V, Dickhout JG, Ask K (2015) The therapeutic effects of 4-phenylbutyric acid in maintaining proteostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 61:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2015.01.015
Wang C, Zhang S, Ma R, Zhang X, Zhang C, Li B, Niu Q, Chen J, Xia T, Li P, Zhao Q, Dong L, Xu C, Wang A (2016) Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and autophagy in 2,2’,4,4’-tetrabromodiphenyl ether-induced rat ovarian injury. Reprod Toxicol 65:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.07.013
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11(1):47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
Mondal NK (2021) Diagnosis of fluorosis by analysis of fluoride content in body fluids using ion selective electrode method. Adv Exp Med Biol 1306:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63908-2_9
Reddy YP, Tiwari S, Tomar LK, Desai N, Sharma VK (2021) Fluoride-induced expression of neuroinflammatory markers and neurophysiological regulation in the brain of Wistar rat model. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(7):2621–2626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02362-x
Idowu OS, Duckworth RM, Valentine RA, Zohoori FV (2020) Biomarkers for the assessment of fluoride exposure in children. Caries Res 54(2):134–143. https://doi.org/10.1159/000504166
Sun Y, Ke L, Zheng X, Li T, Ouyang W, Zhang Z (2017) Effects of different levels of calcium intake on brain cell apoptosis in fluorosis rat offspring and its molecular mechanism. Biol Trace Elem Res 176(2):355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0850-9
Rango T, Vengosh A, Jeuland M, Tekle-Haimanot R, Weinthal E, Kravchenko J, Paul C, Mccornick P (2014) Fluoride exposure from groundwater as reflected by urinary fluoride and children’s dental fluorosis in the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley. Sci Total Environ 496:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.048
Nadei OV, Khvorova IA, Agalakova NI (2020) Cognitive decline of rats with chronic fluorosis is associated with alterations in hippocampal calpain signaling. Biol Trace Elem Res 197(2):495–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01993-z
Han X, Tang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Hu Z, Xu W, Xu S, Niu Q (2022) Impaired V-ATPase leads to increased lysosomal pH, results in disrupted lysosomal degradation and autophagic flux blockage, contributes to fluoride-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 236:113500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113500
Zheng H, Dong Y, Xu Z, Crosby G, Culley DJ, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2013) Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant mice induces neurotoxicity in fetal and offspring mice. Anesthesiology 118(3):516–526. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182834d5d
Schroder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem 74:739–789. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074134
Wu Z, Niu J, Xue H, Wang S, Zhao P (2021) Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate protects hypoxic-ischemic brain injury via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress in neonatal rats. Front Behav Neurosci 15:632143. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2021.632143
Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, Elfiky AA (2019) GRP78: a cell’s response to stress. Life Sci 226:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022
Hossain MM, Richardson JR (2020) Nerve growth factor protects against pyrethroid-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in primary hippocampal neurons. Toxicol Sci 174(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz239
Xu F, Ma R, Zhang G, Wang S, Yin J, Wang E, Xiong E, Zhang Q, Li Y (2018) Estrogen and propofol combination therapy inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and remarkably attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and OGD injury in hippocampus. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1596–1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.167
Rao RV, Bredesen DE (2004) Misfolded proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(6):653–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2004.09.012
Hu Z, Yang B, Mo X, Xiao H (2015) Mechanism and regulation of autophagy and its role in neuronal diseases. Mol Neurobiol 52(3):1190–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8921-4
Zhang L, Wang Y, Pan RL, Li Y, Hu YQ, Xv H, Zhu C, Wang X, Yin JW, Ma KT, Zhao D (2021) Neuritin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R)-induced neuronal injury by promoting autophagic flux. Exp Cell Res 407(2):112832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112832
Tran S, Fairlie WD, Lee EF (2021) BECLIN1: protein structure, function and regulation. Cells-Basel 10(6):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061522
Xu L, Deng C, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Linghu Y, Yu Y (2021) Expression of autophagy-related factors LC3A and Beclin 1 and apoptosis-related factors Bcl-2 and BAX in osteoblasts treated with sodium fluoride. Front Physiol 12:603848. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.603848
Wu Y, Ye L, Yuan Y, Jiang T, Guo X, Wang Z, Xu K, Xu Z, Liu Y, Zhong X, Ye J, Zhang H, Li X, Xiao J (2019) Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection in diabetes-associated cognitive decline. Aging Dis 10(6):1233. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.1024
Cai Y, Arikkath J, Yang L, Guo M, Periyasamy P, Buch S (2016) Interplay of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in neurodegenerative disorders. Autophagy 12(2):225–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1121360
Niu J, Wu Z, Xue H, Zhang Y, Gao Q, Li C, Zhao P (2021) Sevoflurane post-conditioning alleviated hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy via IRE1 signalings. Neurochem Int 150:105198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105198
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81860559 and Grant No. 82060580), the Program of Science and Technology Innovation in Bingtuan (Grant No. 2021CB046), and the High-Level Talent Research Project of Shihezi University (Grant No. RCZK2018C02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jingjing Zhang: methodology, formal analysis, writing — original draft. Yanling Tang: methodology, writing — review and editing. Wanjing Xu: writing — review and editing. Zeyu Hu: visualization, investigation. Shangzhi Xu: writing — review and editing. Qiang Niu: conceptualization, resources, writing — review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. NaF causes cortical toxicity in rats, leading to learning and memory impairment.
2. NaF induces excessive ERS and ERS-mediated apoptosis in the rat cortex.
3. NaF induces defective autophagy in the rat cortex.
4. 4-PBA alleviates NaF-induced cortical excessive ERS and its mediated defective autophagy.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Tang, Y., Xu, W. et al. Fluoride-Induced Cortical Toxicity in Rats: the Role of Excessive Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Its Mediated Defective Autophagy. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 3850–3860 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03463-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03463-5