Abstract
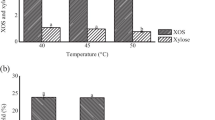
Xylooligosaccharides (XOS), as prebiotic oligomers, are increasingly receiving attention as high value-added products produced from lignocellulosic biomass. Although the XOS contains a series of different degrees of polymerization (DP) of xylose units, DP 2 and 3 (xylobiose (X2) and xylotriose (X3)) are regarded as the main active components in food and pharmaceutical fields. Therefore, in the study, in order to achieve the maximum production of XOS with the desired DP, a combination strategy of sequential auto-hydrolysis and xylanase hydrolysis was developed with corncob as raw material. The evidences showed that the hemicellulosic xylan could be effectively decomposed into various higher DP saccharides (> 4), which were dissolved into the auto-hydrolysate; sequentially, the soluble saccharides could be rapidly hydrolyzed into XOS with desired DP by xylanase hydrolysis. Finally, a maximum XOS yield of 56.3% was achieved and the ratio of (X2 + X3)/XOS was over 80%; meanwhile, the by-products could be controlled at lower levels. Overall, this study provides solid data that support the selective and precise preparation of XOS from corncob, vigorously promoting the application of XOS as functional sugar products.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Curran, L. M. C. L., Le Thanh, M. P., Sale, K. L., & Simmons, B. A. (2022). Review of advances in the development of laccases for the valorization of lignin to enable the production of lignocellulosic biofuels and bioproducts. Biotechnology Advances, 54, 107809.
Sun, D., Lv, Z., Rao, J., Tian, R., Sun, S., & Peng, F. (2022). Effects of hydrothermal pretreatment on the dissolution and structural evolution of hemicelluloses and lignin: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 281, 119050.
Zhang, J., Siika-aho, M., Tenkanen, M., & Viikari, L. (2011). The role of acetyl xylan esterase in the solubilization of xylan and enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw and giant reed. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 4, 60.
Martins, M., Sganzerla, W. G., Forster-Carneiro, T., & Goldbeck, R. (2023). Recent advances in xylo-oligosaccharides production and applications: A comprehensive review and bibliometric analysis. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 47, 102608.
Yan, B., Huang, C., Lai, C., Ling, Z., & Yong, Q. (2022). Production of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides from industrial-derived xylan residue by organic acid treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 292, 119641.
Gandam, P. K., Chinta, M. L., Pabbathi, N. P. P., Velidandi, A., Sharma, M., Kuhad, R. C., Tabatabaei, M., Aghbashlo, M., Baadhe, R. R., & Gupta, V. K. (2022). Corncob-based biorefinery: A comprehensive review of pretreatment methodologies, and biorefinery platforms. Journal of the Energy Institute, 101, 290–308.
Corim Marim, A. V., & Gabardo, S. (2021). Xylooligosaccharides: Prebiotic potential from agro-industrial residue, production strategies and prospects. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 37, 102190.
Hong, C., Corbett, D., Venditti, R., Jameel, H., & Park, S. (2019). Xylooligosaccharides as prebiotics from biomass autohydrolyzate. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 111, 703–710.
Yan, F., Tian, S., Chen, H., Gao, S., Dong, X., & Du, K. (2022). Advances in xylooligosaccharides from grain byproducts: Extraction and prebiotic effects. Grain & Oil Science and Technology, 5(2), 98–106.
Farias, D. D. P., de Araujo, F. F., Neri-Numa, I. A., & Pastore, G. M. (2019). Prebiotics: Trends in food, health and technological applications. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 93, 23–35.
Liu, X., Cao, R., & Xu, Y. (2023). Acidic hydrolyzed xylo-oligosaccharides bioactivity on the antioxidant and immune activities of macrophage. Food Research International, 163, 112152.
Su, Y., Fang, L., Wang, P., Lai, C., Huang, C., Ling, Z., Sun, S., & Yong, Q. (2021). Efficient production of xylooligosaccharides rich in xylobiose and xylotriose from poplar by hydrothermal pretreatment coupled with post-enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 342, 125955.
Deng, J., Yun, J., Gu, Y., Yan, B., Yin, B., & Huang, C. (2023). Evaluating the In Vitro and In Vivo Prebiotic Effects of Different Xylo-Oligosaccharides Obtained from Bamboo Shoots by Hydrothermal Pretreatment Combined with Endo-Xylanase Hydrolysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13422.
Capetti, C. C. D. M., Vacilotto, M. M., Dabul, A. N. G., Sepulchro, A. G. V., Pellegrini, V. O. A., & Polikarpov, I. (2021). Recent advances in the enzymatic production and applications of xylooligosaccharides. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 37(10), 169.
Ying, W., You, J., Xu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). An integrated process for the coproduction of xylooligosaccharides and Bacillus subtilis biomass from poplar. Industrial Crops and Products, 197, 116616.
Lu, J., Liu, H., Xia, F., Zhang, Z., Huang, X., Cheng, Y., & Wang, H. (2020). The hydrothermal-alkaline/oxygen two-step pretreatment combined with the addition of surfactants reduced the amount of cellulase for enzymatic hydrolysis of reed. Bioresource Technology, 308, 123324.
Xu, L., Ma, C., Zhang, C., Xu, Y., Wen, J., & Yuan, T. (2022). An integrated acetic acid-catalyzed hydrothermal-pretreatment (AAP) and rapid ball-milling for producing high-yield of xylo-oligosaccharides, fermentable glucose and lignin from poplar wood. Renewable Energy, 201, 691–699.
Liao, H., Xu, Y., Sun, F. F., & Zhang, J. (2023). Optimizing tri-acid mixture hydrolysis: An improved strategy for efficient xylooligosaccharides production from corncob. Bioresource Technology, 369, 128500.
Valladares-Diestra, K. K., De Souza, P., Vandenberghe, L., Zevallos Torres, L. A., Zandoná Filho, A., Lorenci Woiciechowski, A., & Ricardo Soccol, C. (2022). Citric acid assisted hydrothermal pretreatment for the extraction of pectin and xylooligosaccharides production from cocoa pod husks. Bioresource Technology, 343, 126074.
Xiao, X., Bian, J., Peng, X., Xu, H., Xiao, B., & Sun, R. (2013). Autohydrolysis of bamboo (Dendrocalamus giganteus Munro) culm for the production of xylo-oligosaccharides. Bioresource Technology, 138, 63–70.
Zhang, W., You, Y., Lei, F., Li, P., & Jiang, J. (2018). Acetyl-assisted autohydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse for the production of xylo-oligosaccharides without additional chemicals. Bioresource Technology, 265, 387–393.
Rahmati, S., Atanda, L., Deshan, A. D. K., Moghaddam, L., Dubal, D., Doherty, W., & Ostrikov, K. K. (2023). A green process for producing xylooligosaccharides via autohydrolysis of plasma-treated sugarcane bagasse. Industrial Crops and Products, 198, 116690.
Dias, L. M., Neto, F. S. P. P., Brienzo, M., de Oliveira, S. C., & Masarin, F. (2022). Experimental design, modeling, and optimization of production of xylooligosaccharides by hydrothermal pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse and straw. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 13, 12777–12794.
Monteiro, C. R. M., Rodrigues, L. G. G., Cesca, K., & Poletto, P. (2022). Evaluation of hydrothermal sugarcane bagasse treatment for the production of xylooligosaccharides in different pressures. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 45(2), 13965.
Zhang, H., Xu, Y., & Yu, S. (2017). Co-production of functional xylooligosaccharides and fermentable sugars from corncob with effective acetic acid prehydrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 234, 343–349.
Han, J., Cao, R., Zhou, X., & Xu, Y. (2020). An integrated biorefinery process for adding values to corncob in co-production of xylooligosaccharides and glucose starting from pretreatment with gluconic acid. Bioresource Technology, 307, 123200.
Martin, C., Dixit, P., Momayez, F., & Joensson, L. J. (2022). Hydrothermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks to facilitate biochemical conversion. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 846592.
Ruiz, H. A., Gustavo Sganzerla, W., Larnaudie, V., Veersma, R. J., van Erven, G., Shiva, Rios-Gonzalez., & L. J., Rodriguez-Jasso, R. M., Rosero-Chasoy, G., Daniel Ferrari, M., Kabel, M. A., Forster-Carneiro, T., & Lareo, C. (2023). Advances in process design, techno-economic assessment and environmental aspects for hydrothermal pretreatment in the fractionation of biomass under biorefinery concept. Bioresource Technology, 369, 128469.
Qin, L., Liu, X., Wu, Q., Tian, H., Ma, Y., Cheng, S., Fan, G., & Teng, C. (2022). Combining autohydrolysis with xylanase hydrolysis for producing xylooligosaccharides from Jiuzao. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 187, 108678.
Tseng, Y., Lee, W., Krisomdee, K., Natesuntorn, W., Chatsurachai, S., & Sriroth, K. (2022). Xylooligosaccharide production from sugarcane bagasse using recombinant endoxylanase of Bacillus halodurans. Sugar Tech, 24(4), 1029–1036.
Nascimento, C. E. D. O., Simões, L. C. D. O., Pereira, J. D. C., Da Silva, R. R., de Lima, E. A., de Almeida, G. C., Penna, A. L. B., Boscolo, M., Gomes, E., & Da Silva, R. (2022). Application of a recombinant GH10 endoxylanase from Thermoascus aurantiacus for xylooligosaccharide production from sugarcane bagasse and probiotic bacterial growth. Journal of Biotechnology, 347, 1–8.
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D., & Crocker, D. (2008). Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Laboratory Analytical Procedure, 1617(1), 1–16.
Wyman, C. E., Dale, B. E., Elander, R. T., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M. R., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technology, 96(18), 1959–1966.
Huang, C., Yu, Y., Li, Z., Yan, B., Pei, W., & Wu, H. (2022). The preparation technology and application of xylo-oligosaccharide as prebiotics in different fields: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 996811.
Gullón, P., Moura, P., Esteves, M. P., Girio, F. M., Domínguez, H., & Parajó, J. C. (2008). Assessment on the fermentability of xylooligosaccharides from rice husks by probiotic bacteria. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(16), 7482–7487.
Huang, C., Lai, C., Wu, X., Huang, Y., He, J., Huang, C., Li, X., & Yong, Q. (2017). An integrated process to produce bio-ethanol and xylooligosaccharides rich in xylobiose and xylotriose from high ash content waste wheat straw. Bioresource Technology, 241, 228–235.
Zheng, Y., Zhao, X., Lin, W., Yong, Q., & Huang, C. (2023). Revealing the performance of phenoxyethanol-acid pretreatment on the intercellular structure of bamboo and its enzymatic hydrolysis. Industrial Crops and Products, 199, 116663.
Gu, Y., Guo, J., Nawaz, A., Ul Haq, I., Zhou, X., & Xu, Y. (2021). Comprehensive investigation of multiples factors in sulfuric acid pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of waste straw cellulose. Bioresource Technology, 340, 125740.
Khaleghipour, L., Linares-Pastén, J. A., Rashedi, H., Ranaei Siadat, S. O., Jasilionis, A., Al-Hamimi, S., Sardari, R. R. R., & Karlsson, E. N. (2021). Extraction of sugarcane bagasse arabinoxylan, integrated with enzymatic production of xylo-oligosaccharides and separation of cellulose. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 14, 153.
Iram, A., Cekmecelioglu, D., & Demirci, A. (2019). Optimization of dilute sulfuric acid, aqueous ammonia, and steam explosion as the pretreatments steps for distillers' dried grains with solubles as a potential fermentation feedstock. Bioresource Technology, 282, 475–481.
Kim, S. B., Lee, S. J., Jang, E. J., Han, S. O., Park, C., & Kim, S. W. (2012). Sugar recovery from rice straw by dilute acid pretreatment. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18(1), 183–187.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Advanced Analysis and Testing Center of Nanjing Forestry University.
Funding
This work was supported by the financial support from the Supported by the Opening Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control, Nanning 530004, PR China (2021KF25) and Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, China (SJCX22_0324).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and LZ performed the experiments, analyzed the data. XZ prepared the draft manuscript. SY and KJ reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
The authors declare that they consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
The authors declare that they consent for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Y., Zhang, L., Yao, S. et al. Green Process for Producing Xylooligosaccharides by Using Sequential Auto-hydrolysis and Xylanase Hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04800-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04800-7