Abstract
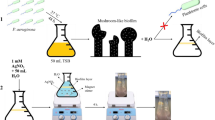
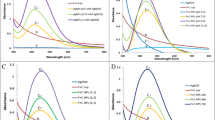
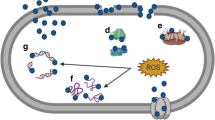
The silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were produced by employing a biogenic loom and tested for antipathogenic assets against multi-drug-resistant (MDR) ESKAPE bacteria. Biogenically synthesized AgNPs were characterized adopting various high-throughput techniques such as UHRTEM, SEM with EDX, DLS, TGA-DTA, and XRD and spectroscopic analysis showed polydispersion of nanoparticles. In this context, AgNPs with the attribute of spherical-shaped nanoparticles with an average size of 26 nm were successfully synthesized utilizing bacterial supernatant. The antipathogenic activities of AgNPs were assessed against 11 strains of MDR ESKAPE bacteria including Enterococcus faecium; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Klebsiella pneumonia; Acinetobacter baumannii; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Enterobacter aerogenes; and Enterobacter species. The exposure of biogenic AgNPs in a well diffusion assay showed all the growth inhibitions of ESKAPE bacteria at 200 μg/ml after 18 h of incubation. Growth kinetics demonstrated maximum killing at 60 μg/ml after 4 h of completion. The highest biofilm depletions were found at 100 μg/ml in adhesion assay. Live/dead assays showed effective killing of the ESKAPE bacteria at 10 μg/ml in pre-existing biofilms. The effective inhibitory concentrations of AgNPs were investigated ranging from 10 to 200 μg/ml. The selected pathogens found sensitive to AgNPs are statistically significant (P < 0.05) than that of cefotaxime/AgNO3. Consequently, a broad spectrum of antimicrobial potentials of AgNPs can be alternative to conventional antimicrobial agents for future medicine.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data sets generated during and/or analyzed for the current study are included in this manuscript.
References
Mehrad, B., Clark, N. M., Zhanel, G. G., & Lynch, J. P. (2015). Antimicrobial resistance in hospital-acquired gram-negative bacterial infections. Chest, 147, 1413–1421.
Kerr, K. G., & Snelling, A. M. (2009). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A formidable and ever-present adversary. Journal of Hospital Infection, 73(4), 338–344.
Radzig, M. A., Nadtochenko, V. A., Koksharova, O. A., Kiwi, J., Lipasova, V. A., & Khmel, I. A. (2013). Antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles on gram-negative bacteria: Influence on the growth and biofilms formation, mechanisms of action. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 102, 300–306.
Salomoni, R., Leo, P., Montemor, A. F., Rinaldi, B. G., & Rodrigues, M. F. A. (2017). Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 10, 115–121.
Rai, M. K., Deshmukh, S. D., Ingle, A. P., & Gade, A. K. (2012). Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 112(5), 841–852.
Oves, M., Aslam, M., Rauf, M. A., Qayyum, S., Qari, H. A., Khan, M. S., Alam, M. Z., Tabrez, S., Pugazhendhi, A., & Ismail, I. M. I. (2018). Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Materials Science and Engineering: C Materials Biology Applications, 1(89), 429–443.
Thakkar, K. N., Mhatre, S. S., & Parikh, R. Y. (2010). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed., 6, 257–262.
Oves, M., Ahmar, R. M., Aslam, M., Qari, H. A., Sonbol, H., Ahmad, I., Sarwar, Z. G., & Saeed, M. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Conocarpus Lancifolius plant extract and their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 29(1), 460–471.
Wang, L., Hu, C., & Shao, L. (2017). The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. International Journal of Nanomed., 12, 1227–1249.
Morones, J. R., Elechiguerra, J. L., Camacho, A., Holt, K., Kouri, J. B., Ramirez, J. T., & Yacaman, M. J. (2005). The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology, 16, 2346–2353.
Dastjerdi, R., & Montazer, M. (2010). A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on antimicrobial properties. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 79(1), 5–18.
Yaqoob, A. A., Ahmad, H., Parveen, T., Ahmad, A., Oves, M., Ismail, I. M. I., Qari, H. A., Umar, K., & Mohamad, I. M. N. (2020). Recent advances in metal decorated nanomaterials and their various biological applications: A review. Frontiers in Chemistry, 8, 341.
Pendleton, J. N., Gorman, S. P., & Gilmore, B. F. (2013). Clinical relevance of the ESKAPE pathogens. Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy, 11, 297–308.
Ramalingam, K., & Khan, M. H. (2022). Antimicrobial mechanisms and mode of actions of nanoemulsion against drug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens. In Handbook of Research on Nanoemulsion Applications in Agriculture, Food, Health, and Biomedical Sciences (pp. 142–168). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-8378-4.ch007
Zhang, X. F., Liu, Z. G., Shen, W., & Gurunathan, S. (2016). Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17, 1534.
Khan, M. H., Unnikrishnan, S., & Ramalingam, K. (2019). Bactericidal potential of silver-tolerant bacteria derived silver nanoparticles against multi drug resistant ESKAPE pathogens. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 18, 100939.
Oves, M., Khan, M. S., Zaidi, A., Ahmed, A. S., Ahmed, F., Ahmad, E., Sherwani, A., Owais, M., & Azam, A. (2013). Antibacterial and cytotoxic efficacy of extracellular silver nanoparticles biofabricated from chromium reducing novel OS4 strain of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. PLoS ONE, 8(3), e59140.
Ali, K., Ahmed, B., Dwivedi, S., & Saquib, Q. (2015). Microwave accelerated green synthesis of stable silver nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract and their antibacterial and antibiofilm activity on clinical isolates. PLoS ONE, 2015(10), e0131178.
Prakash, P., Gnanaprakasam, P., Emmanuel, R., Arokiyaraj, S., & Saravanan, M. (2013). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mimusops elengi, Linn for enhanced antibacterial activity against multi drug resistant clinical isolates. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 108, 255–259.
Mehta, B. K., Chhajlani, M., & Shrivastava, B. D. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their characterization by XRD. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 836, No. 1, p. 012050). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/836/1/012050
Saravanakumar, K., Chelliah, R., Ali, D. M., Oh, D. H., Kathiresan, K., & Wang, M. H. (2019). Unveiling the potentials of biocompatible silver nanoparticles on human lung carcinoma A549 cells and Helicobacter pylori’. Scientific Reports., 9, 5787.
Alahmad, A., Eleoui, M., Falah, A., & Alghoraibi, I. (2013). Preparation of colloidal silver nanoparticles and structural characterization. Physics Science Research International, 4, 89–96.
Mohamed, N. H., Ismail, M. A., Mageed, W. M. A., & Shoreit, A. A. M. (2014). Antimicrobial activity of latex silver nanoparticles using Calotropis procera. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 4(11), 876–883.
Schacht, V. J., Neumann, L. V., Sandhi, S. K., Chen, L., Henning, T., Klar, P. J., Theophel, K., Schnell, S., & Bunge, M. (2012). Effects of silver nanoparticles on microbial growth dynamics. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114, 25–35.
Ali, D. M., Lee, S. Y., Kim, S. C., & Kim, J. W. (2015). One-step synthesis of cellulose/silver nanobiocomposites using a solution plasma process and characterization of their broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy. RSC Advances, 5(44), 35052–35060.
Ramalingam, K., & Lee, V.A. (2018) Antibiofilm activity of an EDTA-containing nanoemulsion on multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1468771.
Khan, M. H., & Ramalingam, K. (2019). Synthesis of antimicrobial nanoemulsions and its effectuality for the treatment of multi-drug resistant ESKAPE pathogens. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019(18), 101025.
Ramalingam, K., Amaechi, B. T., Rawls, H. R., & Lee, V. A. (2011). Antimicrobial activity of nanoemulsion on cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Archives of Oral Biology, 56, 437–445.
Ramalingam, K., & Lee, V. (2019). Synergistic effects of nanoemulsion and deferiprone (1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one) on multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nano Biomedicine and Engineering, 11(3), 226–237.
Krishnaraj, C., Ramachandran, R., Mohan, K., & Kalaichelvan, P. T. (2012). Optimization for rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Spectrochima Acta A., 93, 95–99.
Oladipo, I. C., Lateef, A., Azeez, M. A., Asafa, T. B., Yekeen, T. A., Akinboro, A., Akinwale, A. S., Gueguim-Kana, E. B., & Beukes, L. S. (2017). Green synthesis and antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles using cell free-extracts of Enterococcus species. Notulae Scientia Biologicae, 9(2), 196–203.
Anbu, P., Gopinath, S. C. B., Yun, H. S., & Lee, C. G. (2019). Temperature-dependent green biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using balloon flower plants and their antibacterial potential. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1177, 302–309.
Balashanmugam, P., & Kalaichelvan, P. T. (2015). Biosynthesis characterization of silver nanoparticles using Cassia roxburghii DC aqueous extract, and coated on cotton cloth for effective antibacterial activity. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 10, 87–97.
Singh, R., Wagh, P., Wadhwani, S., Gaidhani, S., Kumbhar, A., Bellare, J., & Chopade, B. A. (2013). Synthesis, optimization, and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and their enhanced antibacterial activity when combined with antibiotics. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 8, 4277–4290.
Meng, Y. (2015). Sustainable approach to fabricating Ag nanoparticles/PVA hybrid nanofiber and its catalytic activity. Nanomaterials, 5, 1124–1135.
Vanaja, M., & Annadurai, G. (2013). Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity. Applied Nanoscience, 3, 217–223.
Jyoti, K., Baunthiyal, M., & Singh, A. (2015). Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 9, 217–227.
Kasture, M. B., Patel, P., Prabhune, A. A., Ramana, C. V., Kulkarni, A. A., & Prasad, B. L. V. (2008). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by sophorolipids: Effect of temperature and sophorolipid structure on the size of particles. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 120(6), 515–520.
Khan, M. Z. H., Tarek, F. K., Nuzat, M., Momin, M. A., & Hasan, M. R. (2017). Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Ocimum sanctum and their characterization. Journal of Nanosci., 6, 1693416.
Kareem, T. A., & Kaliani, A. A. (2010). Synthesis and thermal study of octahedral silver nano-plates in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 4, 325–331.
Patil, U. S., Qu, H., Caruntu, D., O’Connor, Sharma, C. J., Cai, A. Y., & Tarr, M. A. (2013). Labeling primary amine groups in peptides and proteins with N–hydroxysuccinimidyl ester modified Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles containing cleavable disulfide–bond linkers. BioC-CheM, 24, 1562–1569.
Patel, K., Bharatiya, B., Mukherjee, T., Soni, T., Shukla, A., & Suhagia, B. N. (2017). Role of stabilizing agents in the formation of stable silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Characterization and stability study. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 38(5), 626–631.
Balaji, D. S., Basavaraja, S., Deshpande, R., Mahesh, D. B., Prabhakar, B. K., & Venkataraman, A. (2009). Extracellular biosynthesis of functionalized silver nanoparticles by strains of Cladosporium cladosporioides fungus. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 68, 88–92.
Hong, S., Chen, T., Zhu, Y., Li, A., Huang, Y., & Chen, X. (2014). Live-cell stimulated raman scattering imaging of alkyne-tagged biomolecules. Angewandte Chemie International, 53, 5827–5831.
Lindquist, B. A., Furse, K. E., & Corcelli, S. A. (2009). Nitrile groups as vibrational probes of biomolecular structure and dynamics: An overview. Physical Chemistry, 11, 8119–8132.
Mandal, S., Phadtare, S., & Sastry, M. (2005). Interfacing biology with nanoparticles. Current Applied Physics, 5(2), 118–127.
Winter, J. M., & Moore, B. S. (2009). Exploring the chemistry and biology of vanadium-dependent haloperoxidases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(28), 18577–18581.
Makarov, V. V., Love, A. J., Sinitsyna, O. V., Makarova, S. S., Yaminsky, I. V., Taliansky, M. E., & Kalinina, N. O. (2014). “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Naturae., 6(1), 35–44.
Paredes, D., Ortiz, C., & Torres, R. (2014). Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antibacterial effect of Ag nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). International Journal of Nanomedicine, 9, 1717–1729.
Phanjom, P., & Ahmed, G. (2015). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Aspergillus oryzae (MTCC No. 1846) and its characterizations. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 5, 14–21.
Kumar, S. R., Malarkodi, C., Kumar, V. S., Kumar, K. P., & Vanaja, M. (2014). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by using marine bacteria Vibrio alginolyticus. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences, 1, 19–23.
Priyadarshini, S., Gopinath, V., Priyadharshini, N. M., Ali, D. M., & Velusamy, P. (2013). Synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles using novel strain, Bacillus flexus and its biomedical application. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 102, 232–237.
Anandalakshmi, K., Venugobal, J., & Ramasamy, V. (2016). Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Applied Nanoscience, 6, 399–408.
Erjaee, H., Rajaian, H., & Nazifi, S. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of novel silver nanoparticles using Chamaemelum nobile extract for antibacterial application. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 8, 025004.
Saravanan, M., Barik, S. K., Ali, D. M., Prakash, P., & Pugazhendhi, A. (2018). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bacillus brevis (NCIM 2533) and their antibacterial activity against pathogenic bacteria. Microbial Pathology, 116, 221–226.
Morones, J. R., Elechiguerra, J. L., Camacho, A., & Ramirez, J. T. (2005). The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnol, 16(10), 2346–2353.
Pandey, J. K., Swarnkar, R. K., Soumya, K. K., Dwivedi, P., Singh, M. K., Sundaram, S., & Gopal, R. (2014). Silver nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation: As a potent antibacterial agent for human enteropathogenic gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174, 1021–1031.
Markowska, K., Grudniak, A. M., & Wolska, K. I. (2013). Silver nanoparticles as an alternative strategy against bacterial biofilms. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 60(4), 523–530.
Gutierreza, F. M., Boeglib, L., Agostinhob, A., Sánchezc, E. M., Bachd, H., Ruize, F., & Jamesb, G. (2013). Anti-biofilm activity of silver nanoparticles against different microorganisms. Biofouling, 29(6), 651–660.
Ramalingam, K., Amaechi, B. T., Rawls, H. R., & Lee, V. A. (2012). Antimicrobial activity of nanoemulsion on cariogenic planktonic and biofilm organisms. Archives of Oral Biology, 57, 15–22.
Acknowledgements
The authors are pleased to express thanks to ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research) for awarding Senior Research Fellowship [File No: AMR/Fellowship/6/2019/ECD-II] and SAIF, IIT-Madras for providing the facility to complete the characterization studies.
Funding
The DST Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), India [SERB/LS-267/2014] and AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homoeopathy), India [28015/209/2015-HPC], provided grants and fellowships to carry out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohd Hashim Khan: material preparation, investigation, experimental design, formal analysis, validation, and writing original draft.
Sneha Unnikrishnan: formal analysis and validation.
Karthikeyan Ramalingam: supervision of the work, corrections, and review and editing of the manuscript.
All authors of the article read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
There is no issue of morality since this study does not at all use any animal, human, or cell lines in their basic state.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.H., Unnikrishnan, S. & Ramalingam, K. Antipathogenic Efficacy of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Antibiofilm Activities Against Multi-drug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 2031–2052 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04630-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04630-7