Abstract
Purpose of Review
While guidelines exist for the evaluation and management of esophageal dysphagia in the general population, dysphagia disproportionately affects the elderly. In this article, we reviewed the literature on evaluating esophageal dysphagia in elderly patients and proposed a diagnostic algorithm based on this evidence.
Recent Findings
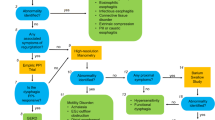
In older patients, dysphagia is often well compensated for by altered eating habits and physiologic changes, underreported by patients, and missed by healthcare providers. Once identified, dysphagia should be differentiated into oropharyngeal and esophageal dysphagia to guide diagnostic workup. For esophageal dysphagia, this review proposes starting with endoscopy with biopsies, given its relative safety even in older patients and potential for interventional therapy. If endoscopy shows a structural or mechanical cause, then further cross-sectional imaging should be considered to assess for extrinsic compression, and same session endoscopic dilation should be considered for strictures. If biopsies and endoscopy are normal, then esophageal dysmotility is more likely, and high-resolution manometry and additional workup should be performed following the updated Chicago Classification. Even after diagnosis of the root cause, complications including malnutrition and aspiration pneumonia should also be assessed and monitored, as they both result from and can further contribute to dysphagia.
Summary
The successful evaluation of esophageal dysphagia in elderly patients requires a thorough, standardized approach to collecting a history, selection of appropriate diagnostic workup, and assessment of risk of potential complications, including malnutrition and aspiration.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EoE:
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis
- BEDQ:
-
Brief Esophageal Dysphagia Questionnaire
- MDQ:
-
Mayo Dysphagia Questionnaire
- EAT-10:
-
Eating Assessment Tool
- EesAI:
-
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Activity Index
- PRO:
-
Patient-reported outcome
- I-SEE:
-
Index of Severity for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- SDQ:
-
Swallowing disturbance questionnaire
- MDT-PD:
-
Munich Dysphagia Test—Parkinson’s Disease
- z-POEM:
-
Zenker’s peroral endoscopic myotomy
- c-POEM:
-
Cricopharyngeal peroral endoscopic myotomy
- EAC:
-
Esophageal adenocarcinoma
- BE:
-
Barrett’s esophagus
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- AEN:
-
Acute esophageal necrosis
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- PD:
-
Pneumatic dilation
- LHM:
-
Laparoscopic Heller myotomy
- POEM:
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy
- OIED:
-
Opioid-induced esophageal dysmotility
- LES:
-
Lower esophageal sphincter
- EGJOO:
-
Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction
- EGD:
-
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- HRM:
-
High-resolution manometry
- TBE:
-
Timed barium esophagram
- FLIP:
-
Functional lumen imaging probe
- ACR:
-
American College of Radiology
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- EGD:
-
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Adkins C, Takakura W, Spiegel BMR, et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Dysphagia Based on a Population-Based Survey. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2020;18(9):1970-1979.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.029.
Thiyagalingam S, Kulinski AE, Thorsteinsdottir B, Shindelar KL, Takahashi PY. Dysphagia in Older Adults. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(2):488–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.08.001.
Gyawali CP, Carlson DA, Chen JW, Patel A, Wong RJ, Yadlapati RH. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Clinical Use of Esophageal Physiologic Testing. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG. 2020;115(9):1412. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000734.
Vaezi MF, Pandolfino JE, Yadlapati RH, Greer KB, Kavitt RT. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG. 2020;115(9):1393–411. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000731.
Expert Panel on Gastrointestinal Imaging:, Levy AD, Carucci LR, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Dysphagia. J Am Coll Radiol JACR. 2019;16(5S):S104-S115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2019.02.007.
•• Yadlapati R, Kahrilas PJ, Fox MR, et al. Esophageal Motility Disorders on High Resolution Manometry: Chicago Classification Version 4.0©. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2021;33(1):e14058. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14058 . Although the practice-changing implications of the updated Chicago Classification were not directly discussed in this article, the entire esophageal motility side of our proposed diagnostic algorithm relies on the recommendations from this guideline.
•• Patel DA, Yadlapati R, Vaezi MF. Esophageal Motility Disorders: Current Approach to Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(6):1617–34. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.289 . This review by Patel et al. served as a strong framework in assessing the utility of each diagnostic test that was discussed in this manuscript and helped guide the development of our diagnostic algorithm.
Wilkins T, Gillies RA, Thomas AM, Wagner PJ. The prevalence of dysphagia in primary care patients: a HamesNet Research Network study. J Am Board Fam Med JABFM. 2007;20(2):144–50. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2007.02.060045.
Wolf U, Eckert S, Walter G, et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in geriatric patients and real-life associations with diseases and drugs. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21955. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99858-w.
Patel DA, Krishnaswami S, Steger E, et al. Economic and survival burden of dysphagia among inpatients in the United States. Dis Esophagus Off J Int Soc Dis Esophagus. 2018;31(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/dote/dox131.
Park YH, Han HR, Oh BM, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of dysphagia in nursing home residents. Geriatr Nurs N Y N. 2013;34(3):212–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2013.02.014.
Leder SB, Suiter DM. An epidemiologic study on aging and dysphagia in the acute care hospitalized population: 2000–2007. Gerontology. 2009;55(6):714–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000235824.
Roden DF, Altman KW. Causes of Dysphagia Among Different Age Groups: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013;46(6):965–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2013.08.008.
Sakai K, Nakayama E, Yoneoka D, et al. Association of Oral Function and Dysphagia with Frailty and Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cells. 2022;11(14):2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142199.
Wirth R, Pourhassan M, Streicher M, et al. The Impact of Dysphagia on Mortality of Nursing Home Residents: Results From the nutritionDay Project. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;19(9):775–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2018.03.016.
Gaber CE, Eluri S, Cotton CC, et al. Epidemiologic and Economic Burden of Achalasia in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(2):342-352.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.035.
Marik PE, Kaplan D. Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly. Chest. 2003;124(1):328–36. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.124.1.328.
Ahmed A, Stacey B. Dysphagia: Aspects of assessment and management for the Acute Physician. Acute Med. 2008;7(3):107–12.
Leder SB, Suiter DM, Agogo GO, Cooney LM. An Epidemiologic Study on Ageing and Dysphagia in the Acute Care Geriatric-Hospitalized Population: A Replication and Continuation Study. Dysphagia. 2016;31(5):619–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9714-x.
Miller N, Allcock L, Hildreth AJ, Jones D, Noble E, Burn DJ. Swallowing problems in Parkinson disease: frequency and clinical correlates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80(9):1047–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2008.157701.
Kayser-Jones J, Pengilly K. Dysphagia among nursing home residents. Geriatr Nurs N Y N. 1999;20(2):77–82; quiz 84. https://doi.org/10.1053/gn.1999.v20.97011.
Madhavan A, Lagorio LA, Crary MA, Dahl WJ, Carnaby GD. Prevalence of and risk factors for dysphagia in the community dwelling elderly: A systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging. 2016;20(8):806–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-016-0712-3.
Spronk PE, Spronk LEJ, Lut J, et al. Prevalence and characterization of dysphagia in hospitalized patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2020;32(3):e13763. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13763.
Olesen MD, Modlinski RM, Poulsen SH, Rosenvinge PM, Rasmussen HH, Holst M. Prevalence of signs of dysphagia and associated risk factors in geriatric patients admitted to an acute medical unit. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;41:208–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.12.020.
Brodsky MB, Nollet JL, Spronk PE, González-Fernández M. Prevalence, Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Modalities, and Treatment Options for Dysphagia in Critically Ill Patients. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99(12):1164–70. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000001440.
Ageing and health. n.d. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health. Accessed February 20, 2023.
Lehman HK, Lam W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019;66(5):955–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2019.06.003.
Durrani SR, Mukkada VA, Guilbert TW. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: An Important Co-Morbid Condition of Asthma? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;55(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-018-8670-7.
Larrea J, Vega S, Martínez T, Torrent JM, Vega V, Núñez V. The nutritional status and immunological situation of cancer patients. Nutr Hosp. 1992;7(3):178–84.
Eckardt VF, Aignherr C, Bernhard G. Predictors of outcome in patients with achalasia treated by pneumatic dilation. Gastroenterology. 1992;103(6):1732–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(92)91428-7.
Belafsky PC, Mouadeb DA, Rees CJ, et al. Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10). Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008;117(12):919–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940811701210.
Taft TH, Riehl M, Sodikoff JB, et al. Development and validation of the brief esophageal dysphagia questionnaire. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2016;28(12):1854–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12889.
Cisternas D, Taft T, Carlson DA, et al. The Brief Esophageal Dysphagia Questionnaire shows better discriminative capacity for clinical and manometric findings than the Eckardt score: Results from a multicenter study. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2022;34(4):e14228. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14228.
Umay E, Sakin YS, Ates MP, et al. Esophageal dysphagia in neuromuscular disorder patients with validity and reliability study of the brief esophageal dysphagia questionnaire. Acta Neurol Belg. 2022;122(2):315–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01563-4.
McElhiney J, Lohse MR, Arora AS, et al. The Mayo Dysphagia Questionnaire-30: documentation of reliability and validity of a tool for interventional trials in adults with esophageal disease. Dysphagia. 2010;25(3):221–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-009-9246-8.
Schoepfer AM, Straumann A, Panczak R, et al. Development and validation of a symptom-based activity index for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147(6):1255-1266.e21. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.08.028.
Schoepfer A, Safroneeva E, Straumann A. How to measure disease activity in eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29(8):959–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/dote.12391.
Safroneeva E, Straumann A, Coslovsky M, et al. Symptoms Have Modest Accuracy in Detecting Endoscopic and Histologic Remission in Adults With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(3):581-590.e4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.004.
Dellon ES, Khoury P, Muir AB, et al. A Clinical Severity Index for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Development, Consensus, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):59–76. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.025.
Kalf JG, de Swart BJM, Bloem BR, Munneke M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(4):311–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006.
Manor Y, Giladi N, Cohen A, Fliss DM, Cohen JT. Validation of a swallowing disturbance questionnaire for detecting dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc. 2007;22(13):1917–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21625.
Simons JA, Fietzek UM, Waldmann A, Warnecke T, Schuster T, Ceballos-Baumann AO. Development and validation of a new screening questionnaire for dysphagia in early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014;20(9):992–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.008.
Dagna C, Avenali M, De Icco R, et al. From DYMUS to DYPARK: Validation of a Screening Questionnaire for Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia. 2022;37(4):824–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10332-1.
Garand KL, Beall J, Hill EG, et al. Effects of Presbyphagia on Oropharyngeal Swallowing Observed during Modified Barium Swallow Studies. J Nutr Health Aging. 2022;26(11):973–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-022-1854-0.
Azzolino D, Damanti S, Bertagnoli L, Lucchi T, Cesari M. Sarcopenia and swallowing disorders in older people. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019;31(6):799–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-019-01128-3.
de Lima Alvarenga EH, Dall’Oglio GP, Murano EZ, Abrahão M. Continuum theory: presbyphagia to dysphagia? Functional assessment of swallowing in the elderly. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;275(2):443–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4801-7.
Labeit B, Muhle P, von Itter J, et al. Clinical determinants and neural correlates of presbyphagia in community-dwelling older adults. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:912691. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.912691.
Mehraban-Far S, Alrassi J, Patel R, et al. Dysphagia in the elderly population: A Videofluoroscopic study. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021;42(2):102854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102854.
Tracy JF, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Jacob P, Kobara M, Krugler C. Preliminary observations on the effects of age on oropharyngeal deglutition. Dysphagia. 1989;4(2):90–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407151.
Park JS, Oh DH, Chang M. Comparison of maximal tongue strength and tongue strength used during swallowing in relation to age in healthy adults. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(2):442–5. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.442.
Lin WY, Chen YM, Wu KM, Chen PK, Hwu YJ. Age and Sex-Related Differences in the Tongue Pressure Generated during Maximum Isometric and Swallowing Tasks by Healthy Chinese Adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105452.
Nienstedt JC, Müller F, Rösler A, Pflug C. Presbyphagia Diagnostics Using M-Mode Ultrasound: Changes in the Tongue Movement Pattern. Dysphagia. 2020;35(4):696–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10076-z.
Be R, Ja M, Ra D. Patient localization of esophageal dysphagia. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49(4). https://doi.org/10.1023/b:ddas.0000026321.02927.39.
Ashraf HH, Palmer J, Dalton HR, et al. Can patients determine the level of their dysphagia? World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(6):1038–43. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.1038.
Smith DF, Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Chen MY. Lower esophageal mucosal ring: correlation of referred symptoms with radiographic findings using a marshmallow bolus. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171(5):1361–5. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.171.5.9798879.
Aslam M, Vaezi MF. Dysphagia in the Elderly. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;9(12):784–95.
Ney D, Weiss J, Kind A, Robbins J. Senescent Swallowing: Impact, Strategies and Interventions. Nutr Clin Pract Off Publ Am Soc Parenter Enter Nutr. 2009;24(3):395–413. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533609332005.
Malagelada JR, Bazzoli F, Boeckxstaens G, et al. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines: Dysphagia—Global Guidelines and Cascades Update September 2014. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49(5):370. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000307.
Upchurch B. Cricopharyngeal Bar Dysphagia Treated Successfully with Endoscopic Dilation: 432. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG. 2011;106:S169.
Elkholy S, El-Sherbiny M, Delano-Alonso R, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy as treatment for Zenker’s diverticulum (Z-POEM): a multi-center international study. Esophagus Off J Jpn Esophageal Soc. 2021;18(3):693–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-020-00809-7.
Elmunzer BJ, Moran RA. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for cricopharyngeal bar. VideoGIE Off Video J Am Soc Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;5(8):378–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vgie.2020.04.020.
Marston AP, Maldonado FJ, Ravi K, Kasperbauer JL, Ekbom DC. Treatment of oropharyngeal dysphagia secondary to idiopathic cricopharyngeal bar: Surgical cricopharyngeal muscle myotomy versus dilation. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016;37(6):507–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.07.006.
Drossman DA, Hasler WL. Rome IV—Functional GI Disorders: Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1257–61. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.035.
Schmulson M. How to use Rome IV criteria in the evaluation of esophageal disorders. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018;34(4):258. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000443.
Krishnamurthy C, Hilden K, Peterson KA, Mattek N, Adler DG, Fang JC. Endoscopic findings in patients presenting with dysphagia: analysis of a national endoscopy database. Dysphagia. 2012;27(1):101–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-011-9346-0.
Sonnenberg A, Massey BT, Jacobsen SJ. Hospital discharges resulting from esophagitis among medicare beneficiaries. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39(1):183–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090080.
Ruiz Manzanera JJ, Ruiz de Angulo Martín D, Fernández Pérez J, Munitiz Ruiz V. Esophageal stricture as an initial manifestation of Crohn’s disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2022;114(8):501–502. https://doi.org/10.17235/reed.2022.8766/2022.
Wang SY, Wang Z, Yang JL. Esophageal mucosal pemphigoid and esophageal stricture. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92(4):962–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.056.
Ravich WJ. Endoscopic Management of Benign Esophageal Strictures. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017;19(10):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-017-0591-8.
ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Evans JA, Early DS, et al. The role of endoscopy in the assessment and treatment of esophageal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77(3):328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2012.10.001.
Pazan F, Wehling M. Polypharmacy in older adults: a narrative review of definitions, epidemiology and consequences. Eur Geriatr Med. 2021;12(3):443–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-021-00479-3.
Hey H, Jørgensen F, Sørensen K, Hasselbalch H, Wamberg T. Oesophageal transit of six commonly used tablets and capsules. Br Med J Clin Res Ed. 1982;285(6356):1717–9.
Kim SH, Jeong JB, Kim JW, et al. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics of drug-induced esophagitis. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2014;20(31):10994–9. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10994.
Kikendall JW. Pill Esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999;28(4):298.
Hang TVP, Spiritos Z, Gamboa AM, et al. Epidemiology of early esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Endosc. 2022;55(3):372–80. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.152.
Cancer of the Esophagus - Cancer Stat Facts. NIH National Cancer Institute: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. n.d. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/esoph.html. Accessed February 21, 2023
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus: An Updated ACG Guideline. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG. 2022;117(4):559. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001680.
Richards J, Wei R, Anjum F. Esophageal Necrosis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572075/. Accessed 15 Mar 2023
Dias E, Santos-Antunes J, Macedo G. Diagnosis and management of acute esophageal necrosis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2019;32(6):529–40. https://doi.org/10.20524/aog.2019.0418.
Gurvits GE. Black esophagus: acute esophageal necrosis syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(26):3219–25. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3219.
Day A, Sayegh M. Acute oesophageal necrosis: A case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg. 2010;8(1):6–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.09.014.
Abdullah HM, Ullah W, Abdallah M, Khan U, Hurairah A, Atiq M. Clinical presentations, management, and outcomes of acute esophageal necrosis: a systemic review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13(5):507–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2019.1601555.
Yiğman ZA, Umay E, Cankurtaran D, Güzel Ş. Swallowing difficulty in the older adults: presbyphagia or dysphagia with sarcopenia? Int J Rehabil Res Int Z Rehabil Rev Int Rech Readaptation. 2021;44(4):336–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/MRR.0000000000000494.
Petermann-Rocha F, Balntzi V, Gray SR, et al. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12783.
Maeda K, Akagi J. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor of dysphagia in hospitalized older people. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016;16(4):515–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12486.
de Sire A, Ferrillo M, Lippi L, et al. Sarcopenic Dysphagia, Malnutrition, and Oral Frailty in Elderly: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(5):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050982.
Mori T, Fujishima I, Wakabayashi H, et al. Development, reliability, and validity of a diagnostic algorithm for sarcopenic dysphagia. JCSM Clin Rep. 2017;2(2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.17987/jcsm-cr.v2i2.17.
Pratap N, Kalapala R, Darisetty S, et al. Achalasia Cardia Subtyping by High-Resolution Manometry Predicts the Therapeutic Outcome of Pneumatic Balloon Dilatation. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;17(1):48–53. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2011.17.1.48.
Rohof WO, Salvador R, Annese V, et al. Outcomes of Treatment for Achalasia Depend on Manometric Subtype. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(4):718–25. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.027.
Salvador R, Costantini M, Zaninotto G, et al. The Preoperative Manometric Pattern Predicts the Outcome of Surgical Treatment for Esophageal Achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14(11):1635–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1318-4.
Khashab MA, Vela MF, Thosani N, et al. ASGE guideline on the management of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(2):213-227.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.04.231.
Schindler A, Pizzorni N, Cereda E, et al. Consensus on the treatment of dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci. 2021;430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2021.120008.
Suttrup I, Warnecke T. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia. 2016;31(1):24–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9671-9.
Sung HY, Kim JS, Lee KS, et al. The prevalence and patterns of pharyngoesophageal dysmotility in patients with early stage Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc. 2010;25(14):2361–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23290.
Mullins PM, Gilligan CJ, Bhattacharyya N. The prevalence of opioid medication use among adults in the United States. J Opioid Manag. 2022;18(6):503–9. https://doi.org/10.5055/jom.2022.0745.
• Penagini R, Bianchi PA. Effect of morphine on gastroesophageal reflux and transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Gastroenterology. 1997;113(2):409–14. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9247457 . Some studies have provided data supporting free water protocols for dysphagic patient, but this study highlights that physicians hesitate to implement them despite this evidence due to the lack of robust applicable data, a single standardized protocol, and guideline recommendations.
Kraichely RE, Arora AS, Murray JA. Opiate-induced oesophageal dysmotility. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31(5):601–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04212.x.
Snyder DL, Crowell MD, Horsley-Silva J, Ravi K, Lacy BE, Vela MF. Opioid-Induced Esophageal Dysfunction: Differential Effects of Type and Dose. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114(9):1464–9. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000369.
Abu-Shakra M, Guillemin F, Lee P. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994;24(1):29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0049-0172(94)90097-3.
Lepri G, Guiducci S, Bellando-Randone S, et al. Evidence for oesophageal and anorectal involvement in very early systemic sclerosis (VEDOSS): report from a single VEDOSS/EUSTAR centre. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):124–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203889.
Markus J, Pinto R de MC, Matoso AGB, Ranza R. Esophageal manometry in systemic sclerosis: findings and association with clinical manifestations. Rev Assoc Medica Bras 1992. 2020;66(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.66.1.48.
Ostojić P, Damjanov N. Different clinical features in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(4):453–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-005-0041-0.
Aggarwal N, Lopez R, Gabbard S, Wadhwa N, Devaki P, Thota PN. Spectrum of esophageal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis on high-resolution esophageal manometry as defined by Chicago classification. Dis Esophagus Off J Int Soc Dis Esophagus. 2017;30(12):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/dote/dox067.
Pasha SF, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, et al. The role of endoscopy in the evaluation and management of dysphagia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79(2):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.042.
Esfandyari T, Potter JW, Vaezi MF. Dysphagia: a cost analysis of the diagnostic approach. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(11):2733–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9270(02)05478-3.
Ergenç M, Uprak TK. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy in Patients Aged 75 Years and Older: A Single-Center Study. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e21846. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.21846.
Buri L, Zullo A, Hassan C, et al. Upper GI endoscopy in elderly patients: predictive factors of relevant endoscopic findings. Intern Emerg Med. 2013;8(2):141–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0598-3.
Lockhart SP, Schofield PM, Gribble RJ, Baron JH. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in the elderly. Br Med J Clin Res Ed. 1985;290(6464):283.
Jafri SM, Monkemuller K, Lukens FJ. Endoscopy in the Elderly: A Review of the Efficacy and Safety of Colonoscopy, Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44(3):161. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181c64d64.
Miyanaga R, Hosoe N, Naganuma M, et al. Complications and outcomes of routine endoscopy in the very elderly. Endosc Int Open. 2018;6(2):E224–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-120569.
• Jang JM, Park SB, Yoon JY, Kwak MS, Cha JM. Gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal complication rates associated with diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy under sedation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(19):e29266. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000029266 . This new observational study with a very large cohort, including 39,910 patients, provides robust data supporting the safety of EGD, even in older patients.
Blonski W, Kumar A, Feldman J, Richter JE. Timed Barium Swallow: Diagnostic Role and Predictive Value in Untreated Achalasia, Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction, and Non-Achalasia Dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(2):196–203. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2017.370.
O’Rourke AK, Lazar A, Murphy B, Castell DO, Martin-Harris B. Utility of Esophagram versus High-Resolution Manometry in the Detection of Esophageal Dysmotility. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2016;154(5):888–91. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816629379.
Carlson DA, Lin Z, Kahrilas PJ, et al. The Functional Lumen Imaging Probe Detects Esophageal Contractility not Observed with Manometry in Patients with Achalasia. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(7):1742–51. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2015.08.005.
Iyer R, DuBrow R. Imaging of esophageal cancer. Cancer Imaging. 2004;4(2):125–32. https://doi.org/10.1102/1470-7330.2004.0022.
Sui H, Ma R, Liu L, Gao Y, Zhang W, Mo Z. Detection of Incidental Esophageal Cancers on Chest CT by Deep Learning. Front Oncol. 2021;11:700210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.700210.
Wright L, Cotter D, Hickson M, Frost G. Comparison of energy and protein intakes of older people consuming a texture modified diet with a normal hospital diet. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2005;18(3):213–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2005.00605.x.
Leibovitz A, Baumoehl Y, Lubart E, Yaina A, Platinovitz N, Segal R. Dehydration among long-term care elderly patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gerontology. 2007;53(4):179–83. https://doi.org/10.1159/000099144.
Bernard S, Loeslie V, Rabatin J. Use of a Modified Frazier Water Protocol in Critical Illness Survivors With Pulmonary Compromise and Dysphagia: A Pilot Study. Am J Occup Ther Off Publ Am Occup Ther Assoc. 2016;70(1):7001350040p1–5. https://doi.org/10.5014/ajot.2016.016857.
Gillman A, Winkler R, Taylor NF. Implementing the Free Water Protocol does not Result in Aspiration Pneumonia in Carefully Selected Patients with Dysphagia: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia. 2017;32(3):345–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9761-3.
• Murray J, Maloney S, Underdown K, Doeltgen S. Patient suitability for free water protocols in acute stroke and general medicine: a qualitative study of clinician perceptions. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022;57(3):630–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/1460-6984.12713 . Some studies have provided data supporting free water protocols for dysphagic patient, but this study highlights that physicians hesitate to implement them despite this evidence due to the lack of robust applicable data, a single standardized protocol, and guideline recommendations.
Murphy SL. Mortality in the United States, 2020. 2021;(427):8.
Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(9):665–71. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200103013440908.
Sue EE. Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia in older adults. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2010;22(1):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2009.00470.x.
Feng MC, Lin YC, Chang YH, et al. The Mortality and the Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia Related with Dysphagia in Stroke Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;28(5):1381–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.02.011.
Hinchey JA, Shephard T, Furie K, et al. Formal dysphagia screening protocols prevent pneumonia. Stroke. 2005;36(9):1972–6. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000177529.86868.8d.
• Khadka S, Khan S, King A, Goldberg LR, Crocombe L, Bettiol S. Poor oral hygiene, oral microorganisms and aspiration pneumonia risk in older people in residential aged care: a systematic review. Age Ageing. 2021;50(1):81–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afaa102 . This systematic review collected the evidence supporting that pathogenic microorganisms in the mouth are associated with aspiration pneumonia and that oral hygiene can reduce both the oral load of these pathogens as well as risk of aspiration pneumonia. Given there are effective ways to prevent aspiration pneumonia, it is even more important to diagnose dysphagia and risk stratify patients at risk of aspiration during evaluation.
Ebihara S, Sekiya H, Miyagi M, Ebihara T, Okazaki T. Dysphagia, dystussia, and aspiration pneumonia in elderly people. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(3):632–9. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2016.02.60.
Arrowsmith JB, Gerstman BB, Fleischer DE, Benjamin SB. Results from the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy/U.S. Food and Drug Administration collaborative study on complication rates and drug use during gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37(4):421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70773-6.
Celik M. Efficacy of early endoscopy and colonoscopy in very elderly patients with gastrointestinal bleeding. Pak J Med Sci. 2017;33(1):187–90. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.331.11616.
Kim SY, Moon CM, Kim MH, et al. Impacts of age and sedation on cardiocerebrovascular adverse events after diagnostic GI endoscopy: a nationwide population-based study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92(3):591-602.e16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.03.3864.
Ellis R, Livovsky DM, Shapiro DS, et al. Safety of oesophagogastroduodenoscopy in a nonagenarian population. Age Ageing. 2021;50(5):1840–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afab129.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH K23 DK125266 (PI: Yadlapati).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
KHNL: None.
RY: Consultant for Medtronic, Phathom Pharmaceuticals, StatLinkMD, Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare Ltd, Medscape; Research Support: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals; Advisory Board with Stock Options: RJS Mediagnostix.
Statements and Declarations
KHNL: None.
RY: Consultant for Medtronic, Phathom Pharmaceuticals, StatLinkMD, Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare Ltd, Medscape; Research Support: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals; Advisory Board with Stock Options: RJS Mediagnostix.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Le, K.H.N., Low, E.E. & Yadlapati, R. Evaluation of Esophageal Dysphagia in Elderly Patients. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 25, 146–159 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-023-00876-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-023-00876-7