Abstract
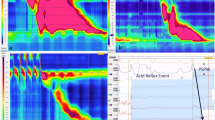
Dysphagia is a common symptom in children with Down syndrome and is conventionally evaluated with imaging and endoscopy; high-resolution manometry is not routinely utilized. The aim of this study was to describe and correlate pharyngeal and esophageal manometry findings with contrast studies and endoscopy in patients with Down syndrome and dysphagia. Electronic medical records of patients with Down syndrome with dysphagia seen at our center between January 2008 and January 2022 were reviewed. Data collected included demographics, co-morbidities, symptoms, imaging, endoscopy, and manometry. Twenty-four patients with Down syndrome [median age of 14.9 years (IQR 7.6, 20.5), 20.8% female] met inclusion criteria. Common presenting symptoms of dysphagia included vomiting or regurgitation in 15 (62.5%) patients, and choking, gagging, or retching in 10 (41.7%) patients. Esophageal manometry was abnormal in 18/22 (81.2%) patients. The most common findings were ineffective esophageal motility in 9 (40.9%) followed by esophageal aperistalsis in 8 (36.4%) patients. Rumination pattern was noted in 5 (22.8%) patients. All 6 (25%) patients who previously had fundoplication had esophageal dysmotility. Strong agreement was noted between upper gastrointestinal studies and high-resolution esophageal manometry (p = 1.0) but no agreement was found between pharyngeal manometry and video fluoroscopic swallow studies (p = 0.041). High-resolution pharyngeal and esophageal manometry provide complementary objective data that may be critical in tailoring therapeutic strategies for managing patients with Down syndrome with dysphagia.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGD:
-
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- RPM:
-
High-resolution pharyngeal manometry
- HREM:
-
High-resolution esophageal manometry
- IEM:
-
Ineffective esophageal motility
- UGI:
-
Upper gastrointestinal series
- VFSS:
-
Video-fluoroscopic swallow studies
References
Ostermaier KK 2022 Down syndrome: Clinical features and diagnosis - UpToDate. In: Drutz JE, Firth HV (eds): UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham, MA,.
Mai CT, Isenburg JL, Canfield MA, Meyer RE, Correa A, Alverson CJ, Lupo PJ, Riehle-Colarusso T, Cho SJ, Aggarwal D, Kirby RS. National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Res. 2019;111(18):1420–35.
Moore S. Down syndrome and the enteric nervous system. Pediatric Surg Int. 2008;24(8):873–83.
Buchin P, Levy J, Schullinger J. Down’s syndrome and the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986;8(2):111–4.
Stanley M, Shepherd N, Duvall N, Jenkinson S, Jalou H, Givan D, Steele G, Davis C, Bull M, Watkins D, Roper R. Clinical identification of feeding and swallowing disorders in 0–6 month old infants with down syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2019;179(2):177–82.
Cooper-Brown L, Copeland S, Dailey S, Downey D, Petersen M, Stimson C, Van Dyke D. Feeding and swallowing dysfunction in genetic syndromes. Develop Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(2):147–57.
Jackson A, Maybee J, Wolter-Warmerdam K, DeBoer E, Hickey F. Associations between age, respiratory comorbidities, and dysphagia in infants with down syndrome. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2019;54(11):1853–9.
Anil M, Shabnam S, Narayanan S. Feeding and swallowing difficulties in children with Down syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res: JIDR. 2019;63(8):992–1014.
Jackson A, Maybee J, Moran M, Wolter-Warmerdam K, Hickey F. Clinical Characteristics of Dysphagia in Children with Down Syndrome. Dysphagia. 2016;31(5):663–71.
Chenbhanich J, Wu A, Phupitakphol T, Atsawarungruangkit A, Treadwell T. Hospitalisation of adults with Down syndrome: lesson from a 10-year experience from a community hospital. J Intellect Disabil Res: JIDR. 2019;63(3):266–76.
Bermudez B, de Oliveira C, de Lima CM, Magdalena N, Celli A. Gastrointestinal disorders in down syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2019;179(8):1426–31.
Moroco A. Aaronson N: pediatric dysphagia. Pediatric Clin North Am. 2022;69(2):249–361.
Lawlor C, Choi S. Diagnosis and management of pediatric dysphagia: a review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg. 2020;146(2):183.
O’Neill A, Richter G. Pharyngeal dysphagia in children with Down syndrome. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg: Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2013;149(1):146–50.
Hillemeier C, Buchin P, Gryboski J. Esophageal dysfunction in Down’s syndrome. J Pediatric Gastroenterol Nutr. 1982;1(1):101–40.
Zárate N, Mearin F, Hidalgo A, Malagelada J. Prospective evaluation of esophageal motor dysfunction in Down’s syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(6):1718–24.
Preiksaitis H, Miller L, Pearson F, Diamant N. Achalasia in Down’s syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994;19(2):105–7.
Zárate N, Mearin F, Gil-Vernet J, Camarasa F, Malagelada J. Achalasia and Down’s syndrome: coincidental association or something else? Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(6):1674–7.
Okawada M, Okazaki T, Yamataka A, Lane G, Miyano T. Down’s syndrome and esophageal achalasia: a rare but important clinical entity. Pediatric Surg Int. 2005;21(12):997–1000.
Fox M, Sweis R, Yadlapati R, Pandolfino J, Hani A, Defilippi C, Jan T, Rommel N. Chicago classification version 4.0 © technical review: Update on standard high-resolution manometry protocol for the assessment of esophageal motility. Neurogastroenterol Motil: Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2021;33(4):e14120.
Gyawali C, Penagini R. Clinical usefulness of esophageal high resolution manometry and adjunctive tests: An update. Digest Liver Dis: Off J Italian Soc Gastroenterol Italian Assoc Study Liver. 2021;53(11):1373–80.
Yadlapati R, Kahrilas PJ, Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ, Prakash Gyawali C, Roman S, Babaei A, Mittal RK, Rommel N, Savarino E, Sifrim D, Smout A, Vaezi MF, Zerbib F, Akiyama J, Bhatia S, Bor S, Carlson DA, Chen JW, Cisternas D, Cock C, Coss-Adame E, de Bortoli N, Defilippi C, Fass R, Ghoshal UC, Gonlachanvit S, Hani A, Hebbard GS, Jung KW, Katz P, Katzka DA, Khan A, Kohn GP, Lazarescu A, Lengliner J, Mittal SK, Omari T, Park MI, Penagini R, Pohl D, Richter JE, Serra J, Sweis R, Tack J, Tatum RP, Tutuian R, Vela MF, Wong RK, Wu JC, Xiao Y, Pandolfino JE. Esophageal motility disorders on high-resolution manometry: Chicago classification version 4.0©. Neurogastroenterol Motil : Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2021;33(1):e14058.
Rosen R, Garza J, Tipnis N, Nurko S. An ANMS-NASPGHAN consensus document on esophageal and antroduodenal manometry in children. Neurogastroenterol Motil: Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2018;30(3):e13239.
Alcala Gonzalez L, Oude Nijhuis R, Smout A, Bredenoord A. Normative reference values for esophageal high-resolution manometry in healthy adults: a systematic review. Neurogastroenterol Motil: Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2021;33:e13954.
Lundell L, Dent J, Bennett J, Blum A, Armstrong D, Galmiche J, Johnson F, Hongo M, Richter J, Spechler S, Tytgat G, Wallin L. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999;45(2):172–80.
Frazier J, Friedman B. Swallow function in children with Down syndrome: a retrospective study. Develop Med Child Neurol. 1996;38(8):695–703.
McDowell K, Craven D. Pulmonary complications of down syndrome during childhood. J Pediatrics. 2011;158(2):319–25.
Absah I, Rishi A, Talley N, Katzka D, Halland M. Rumination syndrome: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurogastroenterol Motil: Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2017;29(4):e12954.
Halland M, Pandolfino J, Barba E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Rumination Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol: The Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2018;16(10):1549–55.
Drossman D, Hasler W. Rome IV-functional GI disorders: disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1257–61.
Funding
No funding was secured for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dorfman, L., Jahagirdar, V., Kaul, S. et al. Comprehensive Manometric Evaluation of Dysphagia in Patients with Down Syndrome. Dysphagia 38, 1589–1597 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-023-10586-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-023-10586-x