Abstract
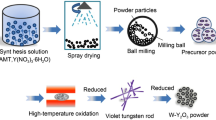
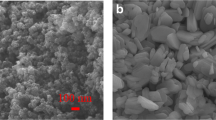
In this work, molybdenum powder was firstly prepared by using the hydrothermal method, and then mixed, dried, and calcined to obtain mixed powder. The processing route involves a molecular-level liquid-liquid doping technique, which causes the uniform distribution of cubic ZrO2 particles in the grains. Scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy were used to observe and analyze the reductive raw materials of molybdenum powder and products during various stages. The refinement mechanism of the doped molybdenum powder during the reduction process was analyzed by agglomeration theory. It is believed that nano-sized ZrO2 particles adsorbed on the surface of micro-sized MoO3 and MoO2 powders during the reduction process hinder the growth and fusion of the powder, and thus refine the reduction product, Mo powder. Finally, a mechanism by which zirconia particles inhibit powder growth during molybdenum powder reduction is proposed. This work provides a good research foundation and potential applications for alloy materials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. L. Xu, S. C. Tao, L. Z. Bao, J. M. Luo and Y. F. Zheng, Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 97 (2018).
C. Cui, Z. Xiangwei, L. Shulong, Li. Qiang, Z. Min, Z. Guangping, and W. Shizhong, C. Cui, Z. Xiangwei, L. Shulong, Li. Qiang, Z. Min, Z. Guangping, and W. Shizhong, J. Alloys Compd. 768, 81–87. (2018).
G. An, J. Sun, R.Z. Liu, J. Li, and Y.J. Sun, G. An, J. Sun, R.Z. Liu, J. Li, and Y.J. Sun, Rare Met. 34, 276–281. (2015).
M.F. Mada, M.F. Mada, J. Nucl. Mater. 233–237, 1397–1402. (1996).
Marie Franqoise Maday, Marie Franqoise Maday, Theodoros Dikonimos-Makris. J. Nucl. Mater. 246, 70–76. (1997).
G.R. Smolik, D.A. Petti, and S.T. Schuetz, G.R. Smolik, D.A. Petti, and S.T. Schuetz, J. Nucl. Mater. 283–287, 1458–1462. (2000).
I.G. Sharma, S.P. Chakraborty, and A.K. Suri, I.G. Sharma, S.P. Chakraborty, and A.K. Suri, J. Alloys Compd. 393, 122–128. (2005).
B.V. Cockeram, B.V. Cockeram, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 418, 120–136. (2006).
B.V. Cockeram, R.W. Smith, T.S. Byun, and L.L. Snead, B.V. Cockeram, R.W. Smith, T.S. Byun, and L.L. Snead, J. Nucl. Mater. 393, 12–21. (2009).
A. Ahmad, S. Mitra, S.K. Srivastava, and A.K. Das, A. Ahmad, S. Mitra, S.K. Srivastava, and A.K. Das, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 474, 599–604. (2019).
S. Yoon, T. Noh, W. Kim, J. Choi, and H. Lee, S. Yoon, T. Noh, W. Kim, J. Choi, and H. Lee, Ceram. Int. 39, 9247–9251. (2013).
S. Gu, M. Qin, H. Zhang, and J. Ma, S. Gu, M. Qin, H. Zhang, and J. Ma, Materials (Basel) 11, 12. (2018).
C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, Z. Guoshang, Z. Yucheng, P. Kunming, Z. Xiangwei, and G. Songliang, C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, Z. Guoshang, Z. Yucheng, P. Kunming, Z. Xiangwei, and G. Songliang, High Temp. Mater. Process. (Lond.) 36, 167–173. (2017).
C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, and Z. Guoshang, C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, and Z. Guoshang, High Temp. Mater. Process. (Lond.) 36, 163–166. (2017).
C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, and Z. Guoshang, C. Cui, G. Yimin, W. Shizhong, and Z. Guoshang, Appl. Phys. A 122, 214. (2016).
G. Liu, G.J. Zhang, F. Jiang, X.D. Ding, Y.J. Sun, J. Sun, and E. Ma, G. Liu, G.J. Zhang, F. Jiang, X.D. Ding, Y.J. Sun, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Nat. Mater. 12, 344–350. (2013).
M. Xiao, F. Li, H. Xie, and Y. Wang, M. Xiao, F. Li, H. Xie, and Y. Wang, Mater. Des. 34, 112–119. (2012).
W. Lin, S. Jun, L. Gang, S. Yuanjun, and Z. Guojun, W. Lin, S. Jun, L. Gang, S. Yuanjun, and Z. Guojun, Int. J. Refract. Metal Hard Mater. 29, 522–527. (2011).
B. Sun, P. Han, W. Zhao, Y. Liu, and P. Chen, B. Sun, P. Han, W. Zhao, Y. Liu, and P. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 18814–18819. (2014).
B. Sun, H. Li, L. Wei, and P. Chen, B. Sun, H. Li, L. Wei, and P. Chen, Cryst. Eng. Commun. 16, 9891–9895. (2014).
G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, B. Sun, S. Duan, and Q. Song, G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, B. Sun, S. Duan, and Q. Song, Mater. Horizons 6, 1877–1882. (2019).
G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, J. Wu, B. Sun, A. Zhou, G. Zhang, S. Zheng, S. Duan, and Q. Song, G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, J. Wu, B. Sun, A. Zhou, G. Zhang, S. Zheng, S. Duan, and Q. Song, Nano Energy 63, 103793. (2019).
G. Zhou, Z. Ren, B. Sun, J. Wu, Z. Zou, S. Zheng, L. Wang, S. Duan, and Q. Song, G. Zhou, Z. Ren, B. Sun, J. Wu, Z. Zou, S. Zheng, L. Wang, S. Duan, and Q. Song, Nano Energy 68, 104386. (2020).
L.E. Iorio, B.P. Bewlay, and M. Larsen, L.E. Iorio, B.P. Bewlay, and M. Larsen, Int. J. Refract. Metal Hard Mater. 24, 306–310. (2006).
T. Mrotzek, A. Hoffmann, and U. Martin, T. Mrotzek, A. Hoffmann, and U. Martin, Int. J. Refract. Metal Hard Mater. 24, 298–305. (2006).
J. Fan, M. Lu, H. Cheng, J. Tian, and B. Huang, J. Fan, M. Lu, H. Cheng, J. Tian, and B. Huang, Int. J. Refract. Metal Hard Mater. 27, 78–82. (2009).
A. Salama, and P. Hesemann, A. Salama, and P. Hesemann, J. Polym. Environ. 26, 1986–1997. (2018).
X. Yang, H. Tan, N. Lin, Z. Li, and Y. He, X. Yang, H. Tan, N. Lin, Z. Li, and Y. He, Int. J. Refract. Metal Hard Mater. 51, 301–308. (2015).
G. Zhang, G. Liu, Y. Sun, F. Jiang, L. Wang, R. Wang, and J. Sun, G. Zhang, G. Liu, Y. Sun, F. Jiang, L. Wang, R. Wang, and J. Sun, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 27, 173–176. (2009).
Y. Zhou, Y. Gao, S. Wei, and Y. Hu, Y. Zhou, Y. Gao, S. Wei, and Y. Hu, Microsc. Microanal. 22, 122–130. (2016).
G.D. Sun, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou, G.D. Sun, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 84, 105039. (2019).
S. Majumdar, S. Raveendra, I. Samajdar, P. Bhargava, and I.G. Sharma, S. Majumdar, S. Raveendra, I. Samajdar, P. Bhargava, and I.G. Sharma, Acta Mater. 57, 4158–4168. (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Anhui Natural Science Foundation (1908085QF293, 1908085QA36), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (KJ2019B14, KJ2018A0394), the Key Foundation of Educational Commission of Anhui Province (KJ2016SD53), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.1704152, No. U1804124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with this work. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interests that represent a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, C., Zhu, X. The Refining Mechanism of ZrO2-Doped Molybdenum Powder During the Reduction Process. JOM 73, 1646–1651 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04595-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04595-0