Abstract
A new chitosan derivative, N-guanidinium chitosan acetate, has been synthesized by direct guanylation of chitosan by cyanamide in presence of scandium(III) triflate under mild acidic condition. Starting from this material, N-guanidinium chitosan/silica microhybrids were prepared via a sol gel method using 3-glycidoxypropyl trimethoxysilane as silica precursor. Both N-guanidinium chitosan and the N-guanidinium chitosan/silica hybrid were characterized by a range of analytical techniques such as 29Si/13C solid state NMR, FT-IR, scanning electron microscopy, thermogravimetry and elemental analysis. The characterization of the chitosan/silica hybrid indicated that this material is a highly hydrophilic nanocomposite material containing an organic core and a highly condensed silica shell. The N-guanidinium chitosan/silica microhybrids display excellent adsorption properties for anionic dyes such as methyl orange (MO) with very high capacities up to 917 mg/g. The fixation of MO as anionic dye was investigated in detail as a function of contact time, pH and the MO concentration. The adsorption kinetics of MO on N-guanidinium chitosan/silica microhybrids was more accurately described by pseudo second-order model. Langmuir isotherm model exhibited a better fit with adsorption data than Freundlich isotherm model. This work opens new possibilities for using N-guanidinium chitosan as a reusable adsorbent for water purification.
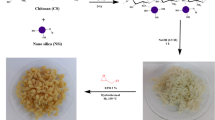
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Zhou Q, Ou L (2012) Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution by chitosan/alumina composite. J Chem Eng Data 57:412–419. doi:10.1021/je2009945
Niu P, Hao J (2011) Fabrication of titanium dioxide and tungstophosphate nanocomposite films and their photocatalytic degradation for methyl orange. Langmuir 27:13590–13597. doi:10.1021/la203178s
Ma J, Yu F, Zhou L et al (2012) Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5749–5760. doi:10.1021/am301053m
Salama A, Shukry N, El-Sakhawy M (2015) Carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) hydrogel as adsorbent for dye removal. Int J Biol Macromol 73:72–75. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.11.002
Budnyak TM, Pylypchuk IV, Tertykh V a et al (2015) Synthesis and adsorption properties of chitosan-silica nanocomposite prepared by sol–gel method. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:87. doi:10.1186/s11671-014-0722-1
Ghorai S, Sarkar A, Raoufi M et al (2014) Enhanced removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution using a nanocomposite of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide grafted xanthan gum and incorporated nanosilica. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:4766–4777. doi:10.1021/am4055657
Salama A (2017) New sustainable hybrid material as adsorbent for dye removal from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 487:348–353. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.034
Kołodyńska D, Gęca M, Pylypchuk IV, Hubicki Z (2016) Development of new effective sorbents based on nanomagnetite. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:152. doi:10.1186/s11671-016-1371-3
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J et al (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. doi:10.1039/c0cs00108b
Varghese JG, Karuppannan RS, Kariduraganavar MY (2010) Development of hybrid membranes using chitosan and silica precursors for pervaporation separation of water + isopropanol mixtures. J Chem Eng Data 55:2084–2092. doi:10.1021/je9003993
Kadib A, El Molvinger K, Guimon C et al (2008) Design of stable nanoporous hybrid chitosan/titania as cooperative bifunctional catalysts. Chem Mater 75:2198–2204
Salama A (2016) Polysaccharides/silica hybrid materials: new perspectives for sustainable raw materials. J Carbohydr Chem 35:131–149. doi:10.1080/07328303.2016.1154152
Budnyak TM, Yanovska ES, Kołodyńska D et al (2016) Preparation and properties of organomineral adsorbent obtained by sol–gel technology. J Therm Anal Calorim 125:1335–1351. doi:10.1007/s10973-016-5581-9
Han Y-H, Taylor A, Mantle MD, Knowles KM (2007) Sol–gel-derived organic–inorganic hybrid materials. J Non-Cryst Solids 353:313–320. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2006.05.042
Salama A, El-Sakhawy M (2014) Preparation of polyelectrolyte/calcium phosphate hybrids for drug delivery application. Carbohydr Polym 113:500–506. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.022
Roosen J, Spooren J, Binnemans K (2014) Adsorption performance of functionalized chitosan–silica hybrid materials toward rare. J Mater Chem A 2:19415–19426. doi:10.1039/C4TA04518A
Molvinger K, Quignard F, Brunel D et al (2004) Porous chitosan-silica hybrid microspheres as a potential catalyst. Chem Mater 16:3367–3372. doi:10.1021/cm0353299
Calnan BJ, Tidor B, Biancalana S et al (1991) Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science 252:1167–1171. doi:10.1126/science.252.5009.1167
Sasaki DY, Kurihara K, Kunitake T (1991) Specific, multiple-point binding of ATP and AMP to a guanidinium-functionalized monolayer. J Am Chem Soc 113:9685–9686. doi:10.1021/ja00025a051
Bouchal R, Prelot B, Hesemann P (2016) Alkylguanidinium based ionic liquids in a screening study for the removal of anionic pollutants from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6:39125–39130. doi:10.1039/C6RA03607D
Bouchal R, Hamel A, Hesemann P et al (2016) Micellization behavior of long-chain substituted alkylguanidinium surfactants. Int J Mol Sci 17:223–239. doi:10.3390/ijms17020223
Zhang X, Duan Y, Wang D, Bian F (2015) Preparation of arginine modified PEI-conjugated chitosan copolymer for DNA delivery. Carbohydr Polym 122:53–59. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.12.054
Hu Y, Du Y, Yang J et al (2007) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of guanidinylated chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 67:66–72. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.04.015
Wan Ngah WS, Teong LC, Hanafiah M, a KM (2011) Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: a review. Carbohydr Polym 83:1446–1456. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.004
Pylypchuk IV, Kołodyńska D, Kozioł M, Gorbyk PP (2016) Gd-DTPA adsorption on chitosan/magnetite nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:168–177. doi:10.1186/s11671-016-1363-3
Gandhi MR, Meenakshi S (2012) Preparation and characterization of silica gel/chitosan composite for the removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Int J Biol Macromol 50:650–657. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.01.012
Budnyak T, Tertykh V, Yanoska E (2014) Chitosan immobilized on silica surface for wastewater treatment. Mater Sci 20:177–182. doi:10.5755/j01.ms.20.2.4975
Shirosaki Y, Tsuru K, Hayakawa S et al (2009) Physical, chemical and in vitro biological profile of chitosan hybrid membrane as a function of organosiloxane concentration. Acta Biomater 5:346–355. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2008.07.022
Shirosaki Y, Tsuru K, Hayakawa S et al (2005) In vitro cytocompatibility of MG63 cells on chitosan-organosiloxane. Biomaterials 26:485–493. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.02.056
Innocenzi P, Kidchob T, Yoko T (2005) Hybrid organic-inorganic sol–gel materials based on epoxy-amine systems. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 35:225–235. doi:10.1007/s10971-005-2290-4
Dukat M, Abdel-Rahman A a, Ismaiel AM et al (1996) Structure–activity relationships for the binding of arylpiperazines and arylbiguanides at 5-HT 3 serotonin receptors. J Med Chem 39:4017–4026
Sasaki DY, Alam TM (2000) Solid-state 31P NMR study of phosphonate binding sites in guanidine-functionalized, molecular imprinted silica xerogels. Chem Mater 12:1400–1407. doi:10.1021/cm990737r
Bernatowicz MS, Wu Y, Matsueda GR (1992) 1 H-Pyrazole-1-carboxamidine hydrochloride: an attractive reagent for guanylation of amines and its application to peptide synthesis. J Org Chem 57:2497–2504. doi:10.1021/jo00034a059
Short JH, Darby TD (1967) Sympathetic nervous system blocking agents. 3. Derivatives of benzylguanidine. J Med Chem 10:833–840
Tsubokura K, Iwata T, Taichi M et al (2014) Direct guanylation of amino groups by cyanamide in water: catalytic generation and activation of unsubstituted carbodiimide by scandium(III) triflate. Synlett 25:1302–1306. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1341080
Kurita K, Ikeda H, Yoshida Y et al (2002) Chemoselective protection of the amino groups of chitosan by controlled phthaloylation: facile preparation of a precursor useful for chemical modifications. Biomacromolecules 3:1–4. doi:10.1021/bm0101163
Connell LS, Romer F, Suárez M et al (2014) Chemical characterisation and fabrication of chitosan–silica hybrid scaffolds with 3-glycidoxypropyl trimethoxysilane. J Mater Chem B 2:668. doi:10.1039/c3tb21507e
Toskas G, Cherif C, Hund R et al (2013) Chitosan (PEO)/ silica hybrid nanofibers as a potential biomaterial for bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym 94:713–722. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.068
Gong R, Ye J, Dai W et al (2013) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with finger-citron-residue-based activated carbon. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:14297–14303. doi:10.1021/ie402138w
Zhang S, Xu F, Wang Y et al (2013) Silica modified calcium alginate–xanthan gum hybrid bead composites for the removal and recovery of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 234:33–42. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.08.102
Lorencgrabowska E, Gryglewicz G (2007) Adsorption characteristics of Congo Red on coal-based mesoporous activated carbon. Dye Pigment 74:34–40. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.01.027
Periasamy K, Namasivayam C (1995) Removal of nickel(II) from aqueous solution and nickel plating industry wastewater using an agricultural waste: peanut hulls. Waste Manag 15:63–68. doi:10.1016/0956-053X(94)00071-S
Greluk M, Hubicki Z (2010) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of Reactive Black 5 removal by acid acrylic resins. Chem Eng J 162:919–926. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2010.06.043
Zhao B, Zhang X, Dou C, Han R (2015) Adsorption property of methyl orange by chitosan coated on quartz sand in batch mode. Desalin Water Treat 55:1598–1608. doi:10.1080/19443994.2014.925834
Obeid L, Bée A, Talbot D et al (2013) Chitosan/maghemite composite: a magsorbent for the adsorption of methyl orange. J Colloid Interface Sci 410:52–58. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.07.057
Tanhaei B, Ayati A, Lahtinen M, Sillanpää M (2015) Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of methyl orange adsorption. Chem Eng J 259:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.109
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore- and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5:212–223. doi:10.1021/i160018a011
Hammed AK, Dewayanto N, Du D et al (2016) Novel modified ZSM-5 as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue removal. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2607–2616. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.008
Acknowledgements
We thank the Université de Montpellier and the Egyptian Government for financial support. The authors are indebted to Christine Biolley for solid-state NMR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salama, A., Hesemann, P. Synthesis of N-Guanidinium-Chitosan/Silica Hybrid Composites: Efficient Adsorbents for Anionic Pollutants. J Polym Environ 26, 1986–1997 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1093-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1093-3