Abstract
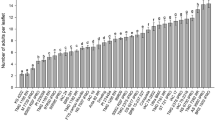
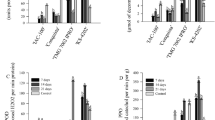
Piezodorus guildinii (Westwood) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) is a major soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) pest and reduces grain quality and yield worldwide. In the context of integrated pest management strategies, plant resistance stands out as an extremely valuable tool for the management of pest populations. Here, we evaluated the resistance of several soybean entries to P. guildinii using tests of attractiveness and feeding preference. We also evaluated trichome number and length as well as pod hardness to evaluate the relationships between these parameters and the resistance to stink bug. D 75-10169, PI 171451, PI 229358, PI 227687, “IAC 100,” IAC 78-2318, PI 274454, PI 274453 and “IAC 19” were less attractive and less consumed by stink bugs. D 75-10169, PI 227687 and PI 274454 received low probe numbers and a short consumption duration per probe; “IAC 100” and PI 274453 received low probe numbers; PI 171451 and PI 229358 received short probe durations; and “IAC 19” received the highest number of probes. There was no correlation between trichome density and length with the attractiveness and feeding preference of the adult insects; however, pod hardness results suggested that this morphological factor may influence the number of probes performed by the insect. PI’s entries, D 75-10169, “IAC 100” and “IAC 19” expressed antixenosis resistance and should be appropriate for use in soybean breeding programs aimed at developing entries with higher resistance to pest insects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baur ME, Baldwin J (2006) Red banded stink bug trouble in Louisiana. Lousiana Agric 49:9–10
Boesewinkel FD, Bouman F (1995) The seed: structure and function. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed development and germination. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–24
Borges M, Birkett M, Aldrich JR, Oliver JE, Chiba M, Murata Y, Laumann RA, Barrigossi JA, Pickett JA, Moraes MCB (2006) Sex attractant pheromone from the rice stalk stink bug, Tibraca limbativentris Stal. J Chem Ecol 32:2749–2761
Byrne FJ, Castle S, Prabhaker N, Toscano NC (2003) Biochemical study of resistence to imidacloprid in B biotype Bemisia tabaci from Guetemala. Pest Manag Sci 59:347–352
Campos M, Knutson A, Heitholt J, Campos C (2010) Resistance to seed feeding by southern green stink bug, Nezara viridula (Linnaeus), in soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Southwest Entomol 35:233–239
Capeleti I, Ferrarese MLL, Krzyzanowski FC, Ferrarese Filho O (2005) A new procedure for quantification of lignin in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merril) seed coat and their relationship with the resistance to mechanical damage. Seed Sci Technol 33:511–515
Castanheira EG, Freire F (2013) Greenhouse gas assessment of soybean production: implications of land use change and different cultivation systems. J Clean Prod 54:49–60
Chocorosqui VR, Panizzi AR (2004) Impact of cultivation systems on Dichelops melacanthus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) population and damage and its chemical control on wheat. Neotrop Entomol 33:487–492
Corrêa-Ferreira BS (1985) Criação massal do percevejo verde, Nezara viridula (L.). Embrapa-CNPSo, Londrina
Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Azevedo J (2002) Soybean seed damage by different species of stink bugs. Agric For Entomol 4:145–150
Fehr WR, Caviness CE (1977) Stages of soybean development. Iowa State University, Ames
Hoffmann-Campo CB, Mazzarin RM, Lustosa PR (1994) Mecanismos de resistência de genótipos de soja: teste de não -preferência para Anticarsia gemmatalis Hübner, 1818. (Lep.: Noctuidae). Pesqui Agropecu Brasileira 29:513–519
Hoffmann-Campo CB, Neto JAR, Oliveira MCN, Oliveira LJ (2006) Detrimental effect of rutin on Anticarsia gemmatalis. Pesqui Agropecu Brasileira 41:1453–1459
Hu Q, Zhao JW, Cui DW (1993) Relationship between content of secondary catabolite lignin in soybean and soybean resistance to the soybean aphid. Plant Prot 19:8–9
Kogan M (1989) Plant resistance in soybean insect control. In: Pascale AJ (ed) World research conference IV. Orientácion Gráfica Editora, Buenos Aires, pp 1519–1525
Leskey TC, Hogmire HW (2005) Monitoring stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in midatlantic apple and peach orchards. J Econ Entomol 98:143–153
Lin H, Kogan M, Fischer D (1990) Induced resistance in soybean to the mexican bean beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinelidae): comparisons of inducing factors. Environ Entomol 19:1852–1857
Lin CY, Wu DC, Yu JZ, Chen BH, Wang CL, Ko WH (2009) Control of silverleaf whitefly, cotton aphid and kanzawa spider mite with oil and extracts from seeds of sugar apple. Neotrop Entomol 38:531–536
Liu SH, Norris DM (1989) Lyne P (1989) Volatiles from the foliage of soybean, Glycine max, and lima bean, Phaseolus lunatus: their behavioral effects on the insects Trichoplusia ni and Epilachna varivestis. J Agric Food Chem 37:496–501
Lourenção AL, Costa AS, Miranda MAC. Sources of resistance to insect pests and virus vectors in the soybean germplasm tested at Instituto Agronomico, SP, Brasil. In: World Soybean Research Conference, 4 (1989) Buenos Aires. Anais… Gráfica SRL, Buenos Aires, pp 1578–1581
Lourenção AL, Miranda MAC (1987) Resistência de soja a insetos: VIII. IAC 78-2318, linhagem com resistência múltipla. Bragantia 46:65–72
Lourenção AL, Miranda MAC, Nagai V (1987) Resistência de soja a insetos: VII. Avaliação de danos de percevejos em cultivares e linhagens. Bragantia 46:45–57
Lourenção AL, Miranda MAC, Pereira JCVNA, Ambrosano GMB (1997) Resistência de soja a insetos X. Comportamento de cultivares e linhagens em relação a percevejos e desfolhadores. An Soc Entomol Brasil 26:543–550
Lourenção AL, Pereira JCVNA, Miranda MAC, Ambrosano GM (2000) Avaliação de danos causados por percevejos e por lagartas em genótipos de soja de ciclos precoce e semiprecoce. Pesq Agropec Brasileira 35:879–886
Maia MCC, Vello NA, Rocha MDM, Fonseca Júnior NS, Lavorante OJ, Pinheiro JB, Dias CTS, Assis GML (2009) Seleção de linhagens experimentais de soja para características agronômicas e tolerância a insetos. Bragantia 68:85–97
Massoni F, Frana J (2005) Si no es en soja¿las chinches donde están? Información técnica de cultivos de verano, Publicación miscelánea 104, Campaña, pp 100–102
McPherson RM, Buss GR (2007) Evaluating lepidopteran defoliation resistance in soybean breeding lines containing the stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) resistance IAC-100 cultivar in their pedigrees. J Econ Entomol 100:962–968
McPherson JE, McPherson RM (2000) Stink bugs of economic importance in America North of Mexico. CRC Press, Boca Raton
McPherson RM, Buss GR, Roberts PM (2007) Assessing stink bug resistance in soybean breeding lines containing genes from germplasm IAC-100. J Econ Entomol 100:1456–1463
Miranda MAC, Rossetto CJ, Rossetto D, Braga NR, Mascarenhas HAA, Teixeira JPF, Massariol A (1979) Resistência de soja a Nezara viridula e Piezodorus guildinii em condições de campo. Bragantia 38:181–188
Miranda MAC, Braga NR, Lourenção AL, Miranda FTS, Uneda SH, Ito MF (2003) Descrição, produtividade e estabilidade da cultivar de soja IAC-24, resistente a insetos. Bragantia 62:29–37
Molina GAR, Trumper EV (2012) Selection of soybean pods by the stink bugs, Nezara viridula and Piezodorus guildinii. J Insect Sci 12:1–16
Oliveira EDM, Panizzi AR (2003) Performance of nymphs and adults of Piezodorus guildinii (Westwood) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on soybean pods at different development stages. Brazilian Arch Biol Technol 46:187–192
Panda N, Khush GS (1995) Host plant resistance to insects. CAB International, Wallingford
Panizzi AR (1991) Ecologia nutricional de insetos sugadores de sementes. In: Panizzi AR, Parra JRP (eds) Ecologia nutricional de insetos e suas implicações no manejo de pragas. Manole, Brasília, pp 253–287
Panizzi AR, Silva FAC (2009) Insetos sugadores de sementes (Heteroptera). In: Panizzi AR, Parra JRP (eds) Bioecologia e nutrição de insetos. Embrapa, Brasília, pp 465–522
Panizzi AR, Slansky F Jr (1985) Review of phytophagous pentatomids (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) associated with soybean in the Americas. Florida Entomol 68:184–203
Panizzi AR, McPherson JE, James DG, Javahery M, McPherson RM (2000) Stink bugs (Pentatomidae). In: Schaefer CW, Panizzi AR (eds) Heteroptera of economic importance. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton, pp 421–474
Paron MJFO, Lara FM (2005) Relação entre tricomas foliares de genótipos de feijoeiro comum, Phaseolus vulgaris L. e resistência a Diabrotica speciosa Germar, 1824 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Ciênc Agrotec 29:894–898
Pinheiro JB, Vello NA, Rossetti CJ, Zucchi MI (2005) Potential of soybean genotypes as insect resistance sources. Crop Breed Appl Biot 5:294–301
Piubelli GC, Hoffmann-Campo CB, Arruda IC, Lara FM (2003a) Nymphal development, lipid content, growth and weight gain of Nezara viridula (L.) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) fed on soybean genotypes. Neotrop Entomol 32:127–132
Piubelli GC, Hoffmann-Campo CB, Arruda IC, Franchini JC, Lara FM (2003b) Flavonoid increase in soybean as a response to Nezara viridula injury and its effecton insect-feeding preference. J Chem Ecol 29:1221–1233
Piubelli GC, Hoffmann-Campo CB, Moscardi F, Miyakubo SH, de Oliveira MC (2005) Are chemical compounds important for soybean resistance to Anticarsia gemmatalis? J Chem Ecol 31:1509–1524
Raij B, Cantarella H, Quaggio J (1997) Recomendações de adubação e calagem para o Estado de São Paulo. Fundação IAC, Campinas
Rossetto CJ, Lourenção AL, Igue T, Miranda MAC (1981) Picadas de alimentação de Nezara viridula em cultivares e linhagens de soja de diferentes graus de suscetibilidade. Bragantia 40:109–114
Rossetto CJ, Gallo PB, Razera LF, Bortoletto N, Igue T, Medina PF, Tisseli Filho O, Aquilera V, Veiga RFA, Pinheiro JB (1995) Mechanisms of resistance to stink bug complex in the soybean cultivar IAC-100. An Soc Entomol Brasil 24:517–522
Saes Zobiole LH, de Oliveira Jr RS, Kremer RJ, Constantin J, Bonato CM, Saraiva Muniz A (2010) Water use efficiency and photosynthesis of glyphosate-resistant soybean as affected by glyphosate. Pestic Biochem Phys 97:182–193
Sas Software (2001) SAS/STAT: user’s guide, version 8.1. SAS Institute, Cary
Silva JPGF, Baldin ELL, Souza ES, Lourenção AL (2012) Assessing Bemisia tabaci (genn.) biotype B resistance in soybean genotypes: antixenosis and antibiosis. Chil J Agric Res 72:516–522
Sirisingh S, Kogan M (1982) Insects affecting soybeans in storage. In: Sinclair JB, Jackobs JA (ed) Soybean seed quality and stand establishment. Proceedings of a Conference for Scientists of Asia. Urbana-Champaign: University of Illinois, College of Agriculture, pp 77–82
Smith CM (1985) Expression mechanisms and chemistry of resistance in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) to soybean looper, Pseudoplusia includens (Walker). Insect Sci Appl 6:243–248
Smith CM (2005) Plant resistance to arthropods molecular and conventional approaches. Springer, Dordrecht
Smith JF, Luttrell RG, Greene JK (2009) Seasonal abundance, species composition and population dynamics of stink bug in production fields of early and late soybeans in South Arkansas. J Econ Entomol 102:229–236
Sosa-Goméz DR, Moscardi F (1995) Retenção foliar diferencial em soja provocada por percevejos (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). An Soc Entomol Brasil 24:401–404
Temple JH (2011) Redbanded stink bug, Piezodorus guildinii (Westwood): pest status, control strategies, and management in Louisiana soybean. Dissertation, Louisiana State University
Temple JH, Leonard BR, Davis JA, Fontenot K (2009) Insecticide efficacy against red banded stink bug, Piezodorus guildinii (Westwood), a new stink bug pest of Louisiana soybean. Midsouth Entomol 2:68–69
Tindall KV, Fothergill K (2011) First records of Piezodorus guildinii in Missouri. Southwest Entomol 36:203–205
Todd JW, Womack H (1973) Secondary infestations of cigarette beetle in soybean seed damaged by southern green stink bug. Environ Entomol 2:720
Valle GE, Lourenção AL (2002) Resistência de genótipos de soja a Bemisia tabaci (Genn.) biótipo B (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Neotrop Entomol 31:285–295
Valle GE, Lourenção AL, Pinheiro JB (2012) Adult attractiveness and oviposition preference of Bemisia tabaci biotype B in soybean genotypes with different trichome density. J Pest Sci 85:431–442
Vicentini R, Jimenez HA (1977) El vaneo de los frutos en soja. Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria, Paraná
Vieira SS, Bueno AF, Boff MIC, Bueno ECOF, Hoffman-Campo CB (2011) Resistance of soybean genotypes to Bemisia tabaci (Genn.) biotype B (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Neotrop Entomol 40:117–122
Webster JA (1975) Association of plant hairs and insect resistance. An annotated bibliography. USDA-ARS Misc. Publ, 1927:1–18
Winer BJ, Brown DR, Michels KM (1991) Statistical principles in experimental design, 3rd edn. MacGraw-Hill, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo for funding the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael Smith.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, J.P.G.F., Baldin, E.L.L., Canassa, V.F. et al. Assessing antixenosis of soybean entries against Piezodorus guildinii (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Arthropod-Plant Interactions 8, 349–359 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-014-9316-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-014-9316-1