Abstract
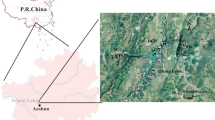
Metal pollution has become an major issue governing the wetland ecosystem health. The southern coastal wetland of the Qiangtang Estuary are facing unusual perturbation due to rapid development along the embayment in recent decades. This study evaluated the bioavailability of metals (Cu, Pb, Cd, Cr and Zn) in the sediment of the southern coastal wetland of the Qiangtang Estuary using diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) techniques and compared with several methods based on total metal content. The results showed that the contents of Cr, Pb, Cd and Cu in sediment, as detected using DGT, were considerably correlated with the exchangeable fraction and the content in Phragmites australis roots, while a weak correlation was observed for Zn. Therefore, DGT analysis could be used to evaluate the bioavailability and potential risk of Cr, Cd, Pb and Cu for P. australis. Quantitative indices, such as DGT concentration, bioaccumulation in P. australis, geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and potential ecological risk index (RI), revealed that Cd was a major potential ecological risk factor along the southern coast wetland of the Qiantang Estuary, especially in the upstream region, which is potentially more vulnerable to the anthropogenic pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, J. P. H., Passos, E. A., and Garcia, C. A. B., 2007. Metals and acid volatile sulfide in sediment cores from the Sergipe River Estuary, Northeast, Brazil. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 18: 748–758.
Amato, E. D., Simpson, S. L., Remaili, T. M., Spadaro, D. A., Jarolimek, C. V., and Jolley, D. F., 2016. Assessing the effects of bioturbation on metal bioavailability in contaminated sediments by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). Environmental Science & Technology, 50: 3055–3064.
Attrill, M. J., and Myles, T. R., 1995. Heavy metal concentrations in sediment from the Thames Estuary, UK. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 30 (11): 742–744.
Baptista, M. S., Vasconcelos, V. M., and Vasconcelos, M. T. S. D., 2014. Heavy metal concentration in a temperate freshwater reservoir seasonally subjected to blooms of toxin-producing cyanobacteria. Microbial Ecology, 68: 671–678.
Belzile, N., Chen, Y. W., Gunn, J. M., and Dixit, S. S., 2004. Sediment heavy metal profiles in lakes of Killarney Park, Canada: From regional to continental influence. Environmental Pollution, 130: 239–248.
Bermejo, J., Beltrán, R., and Gomez-Ariza, J. L., 2003. Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River (Southwest Spain). Environment International, 29 (1): 69–77.
Bi, C., Chen, Z. L., and Xia, S. Y., 2003. Chemical associations of heavy metals in the sediments near Bailonggang sewage discharge outlet of Shanghai. Marine Science Bulletin, 5: 52–58.
Chai, M., Shi, F., Li, R., and Shen, X., 2014. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Spartina alterniflora marsh in intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 84: 115–124.
Chen, M., Ding, S., Lin, J., Fu, Z., Tang, W., Fan, X., et al., 2019. Seasonal changes of lead mobility in sediments in algae- and macrophyte-dominated zones of the lake. Science of the Total Environment, 660: 484–492.
Chen, R. S., and Huang, Y. K., 1998. Study on River Sediment Pollution. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, 1–44.
Costello, D. M., Burton, G. A., Hammerschmidt, C. R., and Taulbee, W. K., 2012. Evaluating the performance of diffusive gradients in thin films for predicting Ni sediment toxicity. Environmental Science & Technology, 46: 10239–10246.
Cundy, A. B., Hopkinson, L., Lafite, R., Spencer, K., Taylor, J. A., Ouddane, B., et al., 2005. Heavy metal distribution and accumulation in two Spartina sp.-dominated macrotidal salt marshes from the Seine Estuary (France) and the Medway Estuary (UK). Applied Geochemistry, 20: 1195–1208.
De Jonge, M., Blust, R., and Bervoets, L., 2010. The relation between Acid Volatile Sulfides (AVS) and metal accumulation in aquatic invertebrates: Implications of feeding behavior and ecology. Environmental Pollution, 158: 1381–1391.
De Jonge, M., Teuchies, J., Meire, P., Blust, R., and Bervoets, L., 2012. The impact of increased oxygen conditions on metal-contaminated sediments part II: Effects on metal accumulation and toxicity in aquatic invertebrates. Water Research, 46: 3387–3397.
Dong, D., 2000. Adsorption of Pb and Cd onto metal oxides and organic material in natural surface coatings as determined by selective extractions: New evidence for the importance of Mn and Fe oxides. Water Research, 34: 427–436.
Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, J., Vandecasteele, B., Meers, E., and Tack, F. M., 2009. Heavy metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 407: 3972–3985.
Ernstberger, H., Zhang, H., Tye, A., Young, S., and Davison, W., 2005. Desorption kinetics of Cd, Zn, and Ni measured in soils by DGT. Environmental Science and Technology, 39 (6): 1591–1597.
Feng, H., Cochran, J. K., and Hirschberg, D. J., 2002. Transport and sources of metal contaminants over the course of tidal cycle in the turbidity maximum zone of the Hudson. Water Research, 36: 733–743.
Feng, H., Kirk Cochran, J., Lwiza, H., Brownawell, B. J., and Hirschberg, D. J., 1998. Distribution of heavy metal and PCB contaminants in the sediments of an urban estuary: The Hudson River. Marine Environmental Research, 45: 69–88.
Galán, E., Gómez-Ariza, J. L., González, I., Fernández-Caliani, J. C., Morales, E., and Giráldez, I., 2003. Heavy metal partitioning in river sediments severely polluted by acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt. Applied Geochemistry, 18: 409–421.
Gambrell, R. P., Wiesepape, J. B., Patrick, W. H., and Duff, M. C., 1991. The effects of pH, redox, and salinity on metal release from a contaminated sediment. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 57-58: 359–367.
García-Hernández, J., García-Rico, L., Jara-Marini, M. E., Barraza-Guardado, R., and Hudson Weaver, A., 2005. Concentrations of heavy metals in sediment and organisms during a harmful algal bloom (HAB) at Kun Kaak Bay, Sonora, Mexico. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50: 733–739.
Gaw, S. K., Kim, N. D., Northcott, G. L., Wilkins, A. L., and Robinson, G., 2008. Uptake of ΣDDT, arsenic, cadmium, copper, and lead by lettuce and radish grown in contaminated horticultural soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56 (15): 6584–6593.
Guven, D. E., and Akinci, G., 2013. Effect of sediment size on bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated sediments of Izmir Inner Bay. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 25: 1784–1794.
Hakanson, L., 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14 (8): 975–1001.
Hamilton, R. S., Revitt, D. M., and Warren, R. S., 1984. Levels and physico-chemical associations of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in road sediments. Science of The Total Environment, 33: 59–74.
Harper, M. P., 2000. A modelling and simulation tool for DGT induced trace metal remobilisation in sediments and soils. Environmental Modelling and Technology, 35 (12): 2602–2607.
Hashimoto, Y., Takaoka, M., Oshita, K., and Tanida, H., 2009a. Incomplete transformations of Pb to pyromorphite by phosphate-induced immobilization investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy. Chemosphere, 76: 616–622.
Hashimoto, Y., Taki, T., and Sato, T., 2009b. Extractability and leachability of Pb in a shooting range soil amended with poultry litter ash: Investigations for immobilization potentials. Journal of Environmental Science & Health Part A Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 44: 583–590.
He, J. Y., Ren, Y. F., Wang, F. J., Pan, X. B., Zhu, C., and Jiang, D. A., 2009. Characterization of cadmium uptake and translocation in a cadmium-sensitive mutant of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 57: 299–306.
Hernandez-Crespo, C., and Martin, M., 2013. Mid-term variation of vertical distribution of acid volatile sulphide and simultaneously extracted metals in sediment cores from Lake Albufera (Valencia, Spain). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65: 654–664.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Raknuzzaman, M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., and Islam, M. K., 2015. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecological Indicators, 48: 282–291.
Jensen, H. S., Kristensen, P., Jeppesen, E., and Skytthe, A., 1992. Iron: Phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Sediment/Water Interactions, 235: 731–743.
Kelderman, P., and Osman, A. A., 2007. Effect of redox potential on heavy metal binding forms in polluted canal sediments in Delft (the Netherlands). Water Research, 41: 4251–4261.
Lin, Y., Guo, M., and Zhuang, Y., 1997. Determination of acid volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals in sediment. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 17: 353–358.
Liu, B., Hu, K., Jiang, Z., Yang, J., Luo, X., and Liu, A., 2010. Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals in a sediment core from the Pearl River Estuary. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62: 265–275.
Luo, J., Zhang, H., Santner, J., and Davison, W., 2010. Performance characteristics of diffusive gradients in thin films equipped with a binding gel layer containing precipitated ferrihydrite for measuring arsenic(V), selenium(VI), vanadium (V), and antimony(V). Analytical Chemistry, 82: 8903–8909.
Luoma, S. N., 1983. Bioavailability of heavy metals to aquatic organisms—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 28: 1–22.
Maiz, I., Arambarri, I., Garcia, R., and Millán, E., 2000. Evaluation of heavy metal availability in polluted soils by two sequential extraction procedures using factor analysis. Environmental Pollution, 110: 3–9.
Martínez, C. E., and Motto, H. L., 2000. Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environmental Pollution, 107: 153–158.
Müller, G., 1979. Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veranderungenseitt 1971. Umschan, 79: 778–783
Munger, Z. W., Carey, C. C., Gerling, A. B., Hamre, K. D., Doubek, J. P., Klepatzki, S. D., et al., 2016. Effectiveness of hypolimnetic oxygenation for preventing accumulation of Fe and Mn in a drinking water reservoir. Water Research, 106: 1–14.
Nedell, D. B., and Taffaelli, D. G., 1999. Advances in Ecological Research: Estuaries. Academic Press, London, 22–42.
Nizoli, E. C., and Luiz-Silva, W., 2012. Seasonal AVS-SEM relationship in sediments and potential bioavailability of metals in industrialized estuary, southeastern Brazil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34: 263–272.
Nobi, E. P., Dilipan, E., Thangaradjou, T., Sivakumar, K., and Kannan, L., 2010. Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of different coastal ecosystems of Andaman Islands, India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 87: 253–264.
Olaniran, A. O., Balgobind, A., and Pillay, B., 2013. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: Impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. International Journal of Molecular Science, 14: 10197–10228.
Pardo, R., Barrado, E., Lourdes, P., and Vega, M., 1990. Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Pisuerga River. Water Research, 24: 373–379.
Peña-Icart, M., Pereira-Filho, E. R., Fialho, L. L., Joaquim A. Nóbrega, and Pomares-Alfonso M. S., 2016. Combining contamination indexes, sediment quality guidelines and multivariate data analysis for metal pollution assessment in marine sediments of Cienfuegos Bay, Cuba. Chemosphere, 168: 1267–1276.
Peng, J. F., Song, Y. H., Yuan, P., Cui, X. Y., and Qiu, G. L., 2009. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161: 633–640.
Persuad, D., Jaagumagi, R., and Hayton, A., 1993. Guidelines for the Protection and Management of Aquatic Sediment Quality in Ontario. Ontario Ministry of the Environment and Energy, Canada.
Rees, J. G., Ridgway, J., Knox, R. W. O. B., Wiggans, G., and Breward, N., 1999. Sediment-borne contaminants in rivers discharging into the Humber Estuary, UK. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 37: 316–329.
Ren, L., Li, X., Yang, S., Yan, Z., and Huang, X., 2014. The impact of salt marsh change on sediment accumulation and wave attenuation at the East Chongming Island. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 84: 3350–3358 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren L. Y., Wu, C. F., Yue, W. Z., Liu, Y., and Lu, Z. W., 2008. Impact of urban planning and industrial development on wetlands in Hangzhou Bay. Acta Geographica Sinica, 63: 1055–1063.
Richau, K. H., Kozhevnikova, A., Seregin, I. V., and Vooigs, R., 2009. Chelation by histidine inhibits the vacuolar sequestration of nickel in roots of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. New Phytologist, 183 (1): 106–116.
Riedel, G. F., Sanders, J. G., and Osman, R. W., 1999. Biogeochemical control on the flux of heavy elements from estuarine sediments: Effects of seasonal and short-term hypoxia. Marine Environmental Research, 47: 349–372.
Shaifullah, K., Mezbahuddin, M., Sujauddin, M., and Haque, S., 2008. Effects of coastal afforestation on some soil properties in Lakshmipur coast of Bangladesh. Journal of Forestry Research, 19: 32–36.
SOA, 2007. The specification for marine monitoring (GB 17378-2007). Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC), Beijing.
Song, Z., Shan, B., and Tang, W., 2018. Evaluating the diffusive gradients in thin films technique for the prediction of metal bioaccumulation in plants grown in river sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 344: 360–368.
Sun, Z., Mou, X., Tong, C., Wang, C., Xie, Z., Song, H., et al., 2015. Spatial variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in intertidal zone of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Catena, 126: 43–52.
Suresh, G., Ramasamy, V., Meenakshisundaram, V., Venkatachalapathy, R., and Ponnusamy, V., 2011. Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Applied Radiation & Isotopes Including Data Instrumentation & Methods for Use in Agriculture Industry & Medicine, 69 (10): 1466–1474.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., and Bisson, M., 1979. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate heavy metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51: 844–851.
USEPA, 1999. Screening level ecological risk assessment protocol for hazardous waste combustion facilities. Appendix E: Toxicity Reference Values. EPA 530-D99-001C, Vol. 3.
Wang, F. L., Song, N. N., Zhao, Y. J., Zhang, C. B., Shen, Y., and Liu, Z. Q., 2012. Predicting the cadmium bioavailability in the soil of sugarcane field based on the diffusive gradients in thin films with binding phase of sodium polyacrylate. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 33 (10): 3562–3568 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, J. Y., Ma, D. Y., Bao, Y. E., Liu, G. Y., and Liu, J., 2003. Evaluation on sediment quality in Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Marine Environmental Science, 22: 21–24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Warnken, K. W., Davison, W., and Zhang, H., 2008. Interpretation of in situ speciation measurements of inorganic and organically complexed trace metals in freshwater by DGT. Environmental Science and Technology, 42: 6903–6909.
Williams, P. N., Islam, S., Islam, R., Jahiruddin, M., Adomako, E., Soliaman, A. R. M., et al., 2009. Arsenic limits trace mineral nutrition (selenium, zinc, and nickel) in Bangladesh Rice Grain. Environmental Science and Technology, 43: 8430–8436.
Xu, D., Chen, Y., Ding, S., Sun, Q., Wang, Y., and Zhang, C., 2013. Diffusive gradients in thin films technique equipped with a mixed binding gel for simultaneous measurements of dissolved reactive phosphorus and dissolved iron. Environmental Science and Technology, 47 (18): 10477–10484.
Yang, Y., Chen, F., Zhang, L., Liu, J., Wu, S., and Kang, M., 2012. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent shelf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64 (9): 1947–1955.
Yao, F., Zhang, Y., Hu, X., and Liu, X., 2010. Occurrence states and potential mobility of heavy metals in sediments of Western Xiamen Bay. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 29: 532–538 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin, H., Cai, Y., Duan, H., Gao, J., and Fan, C., 2014. Use of DGT and conventional methods to predict sediment metal bioavailability to a field inhabitant freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from Chinese eutrophic lakes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 264: 184–194.
Zhang, H., and Davison, W., 1998. In situ measurements of solution concentrations and fluxes of trace metals in soils using DGT. Environmental Science and Technology, 32 (5): 704–710.
Zhang, H., Zhao, F. J., Sun, B., Davison, W., and Mcgrath, S. P., 2001. A new method to measure effective soil solution concentration predicts copper availability to plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 35 (12): 2602–2607.
Zhang, T., Liu, S., Song, Y. M., Pan, J. C., and Guo, P. R., 2019. Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of marine aquaculture in Zhelin Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39: 706–715 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, W., Feng, H., Chang, J., Qu, J., Xie, H., and Yu, L., 2009. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: An assessment from different indexes. Environmental Pollution, 157: 1533–1543.
Zhuang, W., and Gao, X., 2014. Assessment of heavy metal impact on sediment quality of the Xiaoqinghe Estuary in the coastal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Inconsistency between two commonly used criteria. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 83: 352–357.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41776119) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY15D060004) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, W., Wang, Z., Zhu, W. et al. Evaluation of the Bioavailability of Metals in Sediment from the Southern Coastal Wetland of the Qiantang Estuary by Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films Technique. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 375–387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4951-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4951-0