Abstract
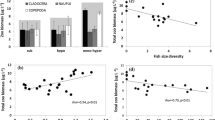
Understanding the relationship between the zooplankton distribution and salinity may provide key information to understand ecosystem function under the condition of a global mean sea level rise caused by global climate change. However, little is known about how increasing salinity level will affect the entire zooplankton community on a large scale. Here we completed 1 year of field investigations on the Pearl River Estuary and analyzed the distribution and structure of the zooplankton community. A total of 68 zooplankton species were identified during the survey. The number and diversity (richness, evenness, Shannon index, and Simpson’s index) of the zooplankton species decreased as salinity increased from 0.10 to 21.26. Salinity negatively affected the abundances of rotifers, cladocerans, and total zooplankton, while it had little effect on copepod abundance. Some salt-tolerant species, such as Keratella tropica, Polyarthra vulgaris, and Paracalanus crassirostris, survived at high-salinity sites. A pattern was observed at all sites: the peak in copepod abundance always occurred when rotifers were abundant (sites S1 and S2) or after rotifer abundance reached a maximum level (sites S3, S4, and S5). In general, salinity was the most important environmental factor shaping zooplankton biodiversity and abundance. This study provides insight into potential biodiversity and structure of the zooplankton community in response to salinity change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azémar, F., Damme, S. V, Meire, P., and Tackx, M., 2007. New occurrence of Lecane decipiens (Murray, 1913) and some other alien rotifers in the Schelde estuary (Belgium). Belgian Journal of Zoology, 137: 75–83.
Bailey, S. A., Duggan, I. C., Van-Overdijk, C. D. A., Johengen, T. H., Reid, D. F., and Macisaac, H. J., 2010. Salinity tolerance of diapausing eggs of freshwater zooplankton. Freshwater Biology, 49: 286–295.
Bänaru, D., and Harmelinvivien, M., 2018. Trophic links and riverine effects on food webs of pelagic fish of the northwestern Black Sea. Marine and Freshwater Research, 60: 529–540.
Boronat, L., Miracle, M. R., and Armengol, X., 2001. Cladoceran as semblages in a mineralization gradient. Hydrobiologia, 442: 75–88.
Bos, D. G., Cumming, B. F., and Smol, J. P., 1999. Cladocera and Anostraca from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia, Canada, as paleolimnological indicators of salinity and lake level. Hydrobiologia, 392: 129–141.
Chai, Z. Y., He, Z. L., Deng, Y. Y., Yang, Y. F., and Tang, Y. Z., 2018. Cultivation of seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis enhanced biodiversity in a eukaryotic plankton community as revealed via metagenomic analyses. Molecular Ecology, 27: 1081–1093.
Chengalath, R., 1982. A faunistic and ecological survey of the littoral Cladocera of Canada. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 60: 2668–2682.
Conde-porcuna, J. M., Pérez-martínez, C., and Moreno, E., 2018. Variations in the hatching response of rotifers to salinity and waterbird ingestion. Journal of Plankton Research, 40: 326–341.
Dumont, H. J., Sarma, S. S. S., and Ali, A. J., 2006. Laboratory studies on the population dynamics of Anuraeopsis fissa (Rotifera) in relation to food density. Freshwater Biology, 33: 39–46.
Fermani, P., Diovisalvi, N., Torremorell, A., Lagomarsino, L., and Zagarese, H. E., 2013. The microbial food web structure of a hypertrophic warm-temperate shallow lake, as affected by contrasting zooplankton assemblages. Hydrobiologia, 714: 115–130.
Fielder, D. S., Purser, G. J., and Battaglene, S. C., 2000. Effect of rapid changes in temperature and salinity on availability of the rotifers Brachionus rotundiformis and Brachionus plicatilis. Aquaculture, 189: 85–99.
Fontaneto, D., Smet, W. H., and Ricci, C., 2006. Rotifers in saltwater environments, re-evaluation of an inconspicuous taxon. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 86: 623–656.
Frey, D. G., 1993. The penetration of Cladocera into saline waters. Hydrobiologia, 267: 233–248.
Garreta-Lara, E., Campos, B., Barata, C., Lacorte, S., and Tauler, R., 2018. Combined effects of salinity, temperature and hypoxia on, Daphnia magna, metabolism. Science of the Total Environment, 610–611: 602–612.
Gutierrez, M. F., Ülkü, N. T., Vidal, N., Yu, J. L., Mello, F. T., Çakiroglu, A. I., He, H., Liu, Z. W., and Jeppesen, E., 2018. Salinity shapes zooplankton communities and functional diversity and has complex effects on size structure in lakes. Hydrobiologia, 813: 237–255.
Holste, L., and Peck, M. A., 2006. The effects of temperature and salinity on egg production and hatching success of Baltic Acartia tonsa (Copepoda: Calanoida): A laboratory investigation. Marine Biology (Berlin), 148: 1061–1070.
Hwang, J. S., Kumar, R., Hsieh, C. W., Kuo, A. Y., Souissi, S., Hsu, M. H., Wu, J. T., Liu, W. C., Wang, C. F., and Chen, Q. C., 2010. Patterns of zooplankton distribution along the marine, estuarine, and riverine portions of the Danshuei ecosystem in northern Taiwan. Zoological Studies, 49: 335–352.
IPCC, 2001. Third report of the working group of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, http://www.ipcc.ch.
Jeppesen, E., Sendergaard, M., Kanstrup, E., Petersen, B., Eriksen, R. B., Hammerstuzj, M., Mortensen, E., Jensen, J. P., and Have, A., 1994. Does the impact of nutrients on the biological structure and function of brackish and fresh-water lakes differ? Hydrobiologia, 275: 15–30.
Ji, H. H., and Ye, S. F., 2006. Ecological distribution characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Changjiang River estuary. Marine Sciences, 30: 23–30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang, S. C., and Du, N. S., 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Cladocera. Science Press, Academia Sinica, Beijing, 80–271 (in Chinese).
Koste, W., 1978. Rotatoria, Die Rä dertiere Mitteleuropas. Ein Bestimmungswerk, begründet von Max Voigt. Ü berordnung Monogononta 2. Gebrüder Borntraeger, Berlin, 463pp.
Li, K. Z., Yin, J. Q., Huang, L. M., and Tan, Y. H., 2006. Spatial and temporal variations of mesozooplankton in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 67: 543–552.
Li, Y. H., Hong, Y. X., and Wu, S. J., 2011. Comparison of the antioxidation ability in different age classes of Aegiceras corniculatum population in Quanzhou Bay. Journal of Quanzhou Normal University, 2: 1–15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, X. B., Pan, J., Liu, Y., Li, M., and Gu, J. D., 2018. Diversity and distribution of Archaea in global estuarine ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, s637–638: 349–358.
Moderan, J., Bouvais, P., Valérie, D., Noc, S. L., Simon-Bouhet, B., Niquil, N., Miramand, P., and Fichet, D., 2010. Zooplankton community structure in a highly turbid environment (Charente estuary, France): Spatio-temporal patterns and environmental control. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 88: 219–232.
Neschuk, N., Claps, M., and Gabellone, N., 2002. Planktonic rotifers of a saline-lowland river: The Salado River (Argentina). Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 14: 191–198.
Nielsen, D. L., Brock, M. A., Crosslé, K., Harris, K., Healey, M., and Jarosinski, I., 2010. The effects of salinity on aquatic plant germination and zooplankton hatching from two wetland sediments. Freshwater Biology, 48: 2214–2223.
Oliveira, M. V. V. D., Intorne, A. C., Vespoli, L. D. S., Madureira, H. C., Leandro, M. R., Pereira, T. N. S., Oliveira, F. L., Berbert-Molina, M. A., and Filho, G. A. D. S., 2016. Differential effects of salinity and osmotic stress on the plant growth-promoting bacterium Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus PAL5. Archives of Microbiology, 198: 287–294.
Park, G. S., 2000. Estuarine relationships between zooplankton community structure and trophic gradients. Journal of Plankton Research, 22: 121–136.
Park, G. S., and Marshall, H. G., 2000. The trophic contributions of rotifers in tidal freshwater and estuarine habitats. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 51: 729–742.
Rougier, C., Pourriot, R., Lam-Hoai, T., and Guiral, D., 2005. Ecological patterns of the rotifer communities in the Kaw River Estuary (French Guiana). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 63: 83–91.
Sanoamuang, L., 1992. The ecology of mountain lake rotifers in Canterbury, with particular reference to Lake Grasmere and the genus Filinia Bory de St. Vincent. PhD thesis. University of Canterbury, New Zealand, 24–56.
Santangelo, J. M., Rocha, A. D. M., Bozelli, R. L., Carneiro, L. S., and Esteves, F. D. A., 2007. Zooplankton responses to sandbar opening in a tropical eutrophic coastal lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 71: 657–668.
Schallenberg, M., Hall, C. J., and Burns, C. W., 2003. Consequences of climate-induced salinity increases on zooplankton abundance and diversity in costal lakes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 251: 181–189.
Schriver, P., Begestrand, J., Jesppesen, E., and Sendergaard, M., 2010. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions: Large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshwater Biology, 33: 255–270.
Sheng, J. R., 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Copepoda. Science Press, Academia Sinica, Beijing, 53–418 (in Chinese).
Sholkovitz, E., 1976. Flacculation of dissolved organic and inorganic matter during mixing of river water and sea water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 40: 831–845.
Smilauer, P., and Leps, J., 2013. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom, 10–34.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC), 1996. Water and Exhausted Water Monitoring Analysis Method. Chinese Environmental Press, Beijing, 243–284 (in Chinese).
Tan, Y., Huang, L., Chen, Q., and Huang, X., 2004. Seasonal variation in zooplankton composition and grazing impact on phytoplankton standingstock in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Continental Shelf Research, 24: 1949–1968.
Viayeh, R. M., and Spoljar, M., 2012. Structure of rotifer assemblages in shallow waterbodies of semi-arid northwest Iran differing in salinity and vegetation cover. Hydrobiologia, 686: 73–89.
Vladimír, S., 1983. Rotifers as indicators of water quality. Hydrobiologia, 100: 169–201.
Wang, J. J., 1961. Rotifers of Freshwater in China. Science Press, Beijing, 288pp (in Chinese).
Wang, Q., Yang, Y. F., and Chen, J. F., 2009. Impact of environment on the spatio-temporal distribution of rotifers in the tidal Guangzhou segment of the Pearl River Estuary, China. International Review of Hydrobiology, 94: 688–705.
Xu, Y. G., Li, A. J., Qin, J. H., Li, Q., Ho, J. G., and Li, H. S., 2017. Seasonal patterns of water quality and phytoplankton dynamics in surface waters in Guangzhou and Foshan, China. Science of the Total Environment, s590–591: 361–369.
Yang, Y. F., Yang, J. X., and Huang, X. F., 1998. Feeding of Cyclops vicinus on zooplankton. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 22: 71–78.
Yang, Y. Z., Ni, P., Gao, Y. C., Xiong, W., Zhao, Y., and Zhan, A. B., 2018. Geographical distribution of zooplankton biodiversity in highly polluted running water ecosystems: Validation of fine-scale species sorting hypothesis. Evolutionary Ecology, 8: 4830–4840.
Yin, K. D., Qian, P. Y., Chen, J. C., Hsieh, D. P. H., and Harrison, P. J., 2000. Dynamics of nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent waters of Hong Kong during summer: Preliminary evidence for phosphorus and silicon limitation. Marine Ecology-Progress Series, 194: 295–305.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41673080) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M6 72449). We especially thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, D., Chen, L., Luan, L. et al. Effect of Salinity on the Zooplankton Community in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Ocean Univ. China 19, 1389–1398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-020-4449-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-020-4449-6