Abstract
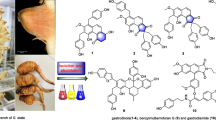
In this study, the chemical analysis of the marine sponge spieces, Haliclona cymaeformis, collected from the South China Sea was carried out, Two pairs of regioisomers of alkyl substitutional 6-oxy purine alkaloids (1a/1b and 2a/2b) were isolated. All of them possess two structural moieties, a 6-oxy purine nucleus and a pentan-2-one or hexan-2-one alkyl chain. Among them, 1a and 2a are the major N-9-substitutional regioisomers, and 1b and 2b are the minor N-7-substitutional regioisomers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calderón-Arancibia, J., Espinosa-Bustos, C., Cañete-Molina, Á., Tapia, R. A., Faúndez, M., Torres, M. J., Aguirre, A., Paulino, M., and Salas, C. O., 2015. Synthesis and pharmacophore modelling of 2,6,9-trisubstituted purine derivatives and their potential role as apoptosis-inducing agents in cancer cell lines. Molecules, 20: 6808–6826.
Chen, M., Shao, C. L., Fu, X. M., Xu, R. F., Zheng, J. J., Zhao, D. L., She, Z. G., and Wang, C. Y., 2013. Bioactive indole alkaloids and phenyl ether derivatives from a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus. Journal of Natural Products, 76: 547–553.
Chen, M., Shao, C. L., Meng, H., She, Z. G., and Wang, C. Y., 2014a. Anti-respiratory syncytial virus prenylated dihydroquinolone derivatives from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15. Journal of Natural Products, 77: 2720–2724.
Chen, M., Fu, X. M., Kong, C. J., and Wang, C. Y., 2014b. Nucleoside derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Natural Products Research, 28: 895–900.
Chen, M., Shao, C. L., Fu, X. M., Kong, C. J., She, Z. G., and Wang, C. Y., 2014c. Lumazine peptides penilumamides B-D and the cyclic pentapeptide asperpeptide A from a gorgonian-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus. Journal of Natural Products, 77: 1601–1606.
Fromtling, R. A., Galgiani, J. N., Pfaller, M. A., Espinel-Ingroff, A., Bartizal, K. F., Bartlett, M. S., Body, B. A., Frey, C., Hall, G., and Roberts, G. D., 1993. Multicenter evaluation of a broth macrodilution antifungal susceptibility test for yeasts. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 37: 39–45.
Gandelman, M., and Jacobsen, E. N., 2005. Highly enantioselective catalytic conjugate addition of N-heterocycles to alpha, beta-unsaturated ketones and imides. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 44: 2393–2397.
Mosmann, T., 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of Immunological Methods, 65: 55–63.
Jiang, M. Y., Feng T., and Liu, J. K., 2011. N-Containing compounds of macromycetes. Natural Products Reports, 28: 783–808.
Nakao, Y., and Fusetani, N., 2010. 2.10-Marine Invertebrates: Sponges. Elsevier, Oxford, 327–362.
Qi, S. H., Zhang, S., Gao, C. H., and Li, Q. X., 2008. Purine and pyrimidine derivatives from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 56: 993–994.
Sun, Z. H., Cai, Y. H., Fan, C. Q., Tang, G. H., Luo, H. B., and Yin, S., 2014. Six new tetraprenylated alkaloids from the South China Sea gorgonian Echinogorgia pseudossapo. Marine Drugs, 12: 672–681.
Wu, X. D., Mei, W. L., Shao, C. L., Nicole, J. V., Wang, H., Wang, C. Y., and Dai, H. F., 2011. Studies on the chemical constituents of sponge Haliclona cymaeformis from the South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 30: 12–17.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Changlun Shao, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, for collecting the sponge samples. This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 16KJB350005), the Yangzhou University Foundation for Fostering Talents in the Science and Technology Innovation (No. 2016CX J052), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81703411, U1606403), and the Taishan Scholars Program, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Wu, X., Shen, N. et al. Four new 6-oxy purine alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge, Haliclona cymaeformis. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 1183–1186 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3325-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3325-5