Abstract
Background
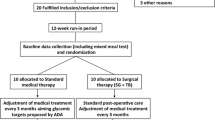
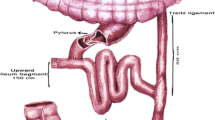
Metabolic surgery is an effective treatment method for glycemic control and weight loss in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to present the mid-term metabolic effects and weight loss results of the patients with T2DM who underwent transit bipartition with sleeve gastrectomy (TB-SG).
Methods
A total of 32 obese patients with T2DM who underwent TB-SG were included in the study. The T2DM remission status after surgery was evaluated. The postoperative glycemic variables, weight loss, lipid profile, and nutritional profile were also compared with the baseline values.
Results
At 36 months after surgery, T2DM remission occurred in 27 patients (84.3%) and the mean BMI decreased from 44.70 ± 9.34 to 29.75 ± 2.19 kg/m2. The percentage of total weight loss (TWL) and excess weight loss (EWL) was 33.84% and 77.19%, respectively. The mean LDL values significantly decreased compared to baseline; however, the mean HDL did not significantly differ. No significant difference was observed regarding the mean albumin, vitamin B12, and folic acid levels.
Conclusion
TB-SG procedure seems promising in terms of T2DM remission and weight loss with less malnutrition and vitamin deficiency in treating obese patients with T2DM.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahier J, Guiot Y, Goebbels R, et al. Pancreatic β-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:32–42.
Hossain P. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world-a growing challenge (vol 356, pg 213, 2007). N Engl J Med. 2007;356(9):973.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17):1567–76.
Yormaz S, Yılmaz H, Ece I, et al. Laparoscopic ileal interposition with diverted sleeve gastrectomy versus laparoscopic transit bipartition with sleeve gastrectomy for better glycemic outcomes in T2DM patients. Obes Surg. 2018;28(1):77–86.
Brown E, Wilding JP, Barber TM, et al. Weight loss variability with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: mechanistic possibilities. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):816–28.
Kapeluto JE, Tchernof A, Masckauchan D, et al. Ten-year remission rates in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes after biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020;16:1701–12.
Bianchi A, Pagan-Pomar A, Jimenez-Segovia M, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion in the surgical treatment of morbid obesity: long-term results and ,etabolic consequences. Obes Surg. 2020:1–9.
Turcotte A-F, Grenier-Larouche T, Lacombe J, et al. Association between changes in bioactive osteocalcin and glucose homeostasis after biliopancreatic diversion. Endocrine. 2020:1–10.
Rubino F, Kaplan LM, Schauer PR, et al. The Diabetes Surgery Summit consensus conference: recommendations for the evaluation and use of gastrointestinal surgery to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 2010;251(3):399–405.
Cohen RV, Shikora S, Petry T, et al. The diabetes surgery summit II guidelines: a disease-based clinical recommendation. Obes Surg. 2016;26(8):1989–91.
Rubino F, Nathan DM, Eckel RH, et al. Metabolic surgery in the treatment algorithm for type 2 diabetes: a joint statement by international diabetes organizations. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(6):1144–62.
Ghio B, Jiménez A, Corcelles R, et al. Midterm effects of bariatric surgery in patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(12):2004–9.
Santoro S, Castro LC, Velhote MC, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy with transit bipartition: a potent intervention for metabolic syndrome and obesity. Ann Surg. 2012;256(1):104–10.
Karaca FC. Effects of sleeve gastrectomy with transit bipartition on glycemic variables, lipid profile, liver enzymes, and nutritional status in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Obes Surg. 2020:1–9.
Brethauer SA, Kim J, El Chaar M, et al. Standardized outcomes reporting in metabolic and bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2015;25(4):587–606.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122(3):248–56. e5.
Welbourn R, Hollyman M, Kinsman R, et al. Bariatric surgery worldwide: baseline demographic description and one-year outcomes from the fourth IFSO global registry report 2018. Obes Surg. 2019;29(3):782–95.
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17):1577–85.
Misra S, Nandhini BD, Christinajoice S, et al. Is laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass still the gold standard procedure for Indians? Mid- to long-term outcomes from a tertiary care center. Obes Surg. 2020;30(11):4482–93.
Lebel S, Dion G, Marceau S, et al. Clinical outcomes of duodenal switch with a 200-cm common channel: a matched, controlled trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(5):1014–20.
Mason EE, Ito C. Gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 1969;170(3):329–39.
Topart P, Becouarn G, Ritz P. Weight loss is more sustained after biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch than Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in superobese patients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(4):526–30.
Livhits M, Mercado C, Yermilov I, et al. Preoperative predictors of weight loss following bariatric surgery: systematic review. Obes Surg. 2012;22(1):70–89.
Scopinaro N, Gianetta E, Civalleri D, et al. The bilio-pancreatic bypass for functional surgical treatment of obesity. Minerva Med. 1979;70(52):3537–47.
Nelson DW, Blair KS, Martin MJ. Analysis of obesity-related outcomes and bariatric failure rates with the duodenal switch vs gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Arch Surg. 2012;147(9):847–54.
von Drygalski A, Andris DA, Nuttleman PR, et al. Anemia after bariatric surgery cannot be explained by iron deficiency alone: results of a large cohort study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(2):151–6.
Shankar P, Boylan M, Sriram K. Micronutrient deficiencies after bariatric surgery. Nutrition. 2010;26(11-12):1031–7.
Blume CA, Boni CC, Casagrande DS, et al. Nutritional profile of patients before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 3-year follow-up. Obes Surg. 2012;22(11):1676–85.
Sala P, Belarmino G, Torrinhas RS, et al. Gastrointestinal transcriptomic response of metabolic vitamin B12 pathways in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2017;8(1):e212.
Lupoli R, Lembo E, Saldalamacchia G, et al. Bariatric surgery and long-term nutritional issues. World J Diabetes. 2017;8(11):464–74.
Santoro S, Malzoni CE, Velhote MC, et al. Digestive adaptation with intestinal reserve: a neuroendocrine-based operation for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2006;16(10):1371–9.
Santoro S. From bariatric to pure metabolic surgery: new concepts on the rise. Ann Surg. 2015;262(2):e79–80.
Reis CE, Alvarez-Leite JI, Bressan J, et al. Role of bariatric-metabolic surgery in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetes with body mass index< 35 kg/m2: a literature review. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012;14(4):365–72.
Liu S, Zhang G, Wang L, et al. The entire small intestine mediates the changes in glucose homeostasis after intestinal surgery in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Ann Surg. 2012;256(6):1049–58.
Vella A. Enteroendocrine secretion after roux-en-Y gastric bypass: is it important? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(1):1–3.
Mingrone G, Nolfe G, Gissey GC, et al. Circadian rhythms of GIP and GLP1 in glucose-tolerant and in type 2 diabetic patients after biliopancreatic diversion. Diabetologia. 2009;52(5):873–81.
Azevedo FR, Santoro S, Correa-Giannella ML, et al. A prospective randomized controlled trial of the metabolic effects of sleeve gastrectomy with transit bipartition. Obes Surg. 2018;28(10):3012–9.
Asmar M, Holst JJ. Glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: new advances. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2010;17(1):57–62.
Bilecik T. Metabolic effects of sleeve gastrectomy with transit bipartition in obese females with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results after 1-year follow-up. Obes Surg. 2019;29(3):805–10.
Sjöström L, Lindroos A-K, Peltonen M, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(26):2683–93.
Vest AR, Heneghan HM, Agarwal S, et al. Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review. Heart. 2012;98(24):1763–77.
Leonetti F, Capoccia D, Coccia F, et al. Obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and other comorbidities: a prospective cohort study of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy vs medical treatment. Arch Surg. 2012;147(8):694–700.
Hirth M, Weiss C, Hardt P, et al. Analysis of the course of chronic pancreatitis: pancreatic burnout rates are only increased in a subgroup of patients with alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2019;48(5):726–33.
Iwase H, Kobayashi M, Nakajima M, et al. The ratio of insulin to C-peptide can be used to make a forensic diagnosis of exogenous insulin overdosage. Forensic Sci Int. 2001;115(1-2):123–7.
Abdemur A, Han S-M, Menzo EL, et al. Reasons and outcomes of conversion of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for nonresponders. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(1):113–8.
Iannelli A, Debs T, Martini F, et al. Laparoscopic conversion of sleeve gastrectomy to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: indications and preliminary results. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(8):1533–8.
Boru CE, Greco F, Giustacchini P, et al. Short-term outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy conversion to RY gastric bypass: multi-center retrospective study. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 2018;403(4):473–9.
Braghetto I, Korn O, Burgos A, et al. When should be converted laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy to laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric bypass due to gastroesophageal reflux? ABCD Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva (São Paulo). 2020;33(4)
Ukleja A. Dumping syndrome: pathophysiology and treatment. Nutr Clin Pract. 2005;20(5):517–25.
Hedberg J, Hedenström H, Karlsson FA, et al. Gastric emptying and postprandial PYY response after biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Obes Surg. 2011;21(5):609–15.
Kim TY, Kim S, Schafer AL. Medical Management of the Postoperative Bariatric Surgery Patient. [Updated 2020 Aug 24]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK481901/
Coupaye M, Calabrese D, Sami O, et al. Effectiveness of ursodeoxycholic acid in the prevention of cholelithiasis after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2019;29(8):2464–9.
Huang C-K, Liu C-C, Hsin M-C, et al. Sleeve and sleeve plus. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg. 2017;2(1):24.
Huang C-K, Katakwar A. Sleeve plus procedures: need of time. Surg Today. 2019:1–4.
Rutledge R. The mini-gastric bypass: experience with the first 1,274 cases. Obes Surg. 2001;11(3):276–80.
Huang C-K, Goel R, Tai C-M, et al. Novel metabolic surgery for type II diabetes mellitus: loop duodenojejunal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc PercutanTechn. 2013;23(6):481–5.
Kumar KH, Ugale S, Gupta N, et al. Ileal interposition with sleeve gastrectomy for control of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009;11(12):785–9.
Langer F, Hoda MR, Bohdjalian A, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding: effects on plasma ghrelin levels. Obes Surg. 2005;15(7):1024–9.
Vidal J, Ibarzabal A, Nicolau J, et al. Short-term effects of sleeve gastrectomy on type 2 diabetes mellitus in severely obese subjects. Obes Surg. 2007;17(8):1069–74.
Saarinen T, Räsänen J, Salo J, et al. Bile reflux scintigraphy after mini-gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2017;27(8):2083–9.
Gagner M. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy with ileal interposition (SGIT): a modified duodenal switch for resolution of type 2 diabetes mellitus in lesser obese patients (BMI< 35). World J Surg. 2011;35(1):109–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The need for patient informed consent for this retrospective study was waived by the institutional review board.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
• TB-SG leads significant weight loss and diabetes remission in obese T2DM patients
• TB-SG can be considered a safe and effective metabolic surgical method
• TB-SG may be a remarkable alternative to other metabolic surgeries
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calisir, A., Ece, I., Yilmaz, H. et al. The Mid-Term Effects of Transit Bipartition with Sleeve Gastrectomy on Glycemic Control, Weight Loss, and Nutritional Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Retrospective Analysis of a 3-Year Follow-up. OBES SURG 31, 4724–4733 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-021-05536-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-021-05536-1