Abstract
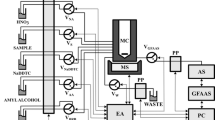
A novel procedure of dual direct immersion single-drop microextraction (DDI-SDME) was developed for the sequential separation and preconcentration of Fe(III) and Fe(II) followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry determination. At pH 1.5, Fe(III) can selectively react with N-benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylamine (BPHA) to form the hydrophobic complexes which can be extracted into one organic drop, while Fe(II) remained in the solution. Then, another organic drop containing BPHA was immersed in the sample solution after the extraction of Fe(III) for the preconcentration of Fe(II) at pH 4.5. This procedure eliminated the time-consuming and labor-intensive step of oxidation of Fe(II) or reduction of Fe(III), which may cause the incomplete conversion of the species and sample contamination. Main conditions influencing the separation and enrichment of Fe species were studied. Under the selected conditions, the detection limits of this procedure were 0.058 ng mL−1 and 0.074 ng mL−1 for Fe(III) and Fe(II) with relative standard deviations of 4.8% and 5.6%, respectively. Enrichment factors of 300-fold were obtained for Fe species. The proposed procedure was successfully utilized for detecting Fe(III) and Fe(II) in food samples. To evaluate accuracy of this procedure, a certified reference material of milk powder was analyzed, and the determined value was in good agreement with the certified value.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Feist, R. Sitko, Method for the determination of Pb, Cd, Zn, Mn and Fe in rice samples using carbon nanotubes and cationic complexes of batophenanthroline. Food Chem. 249, 38–44 (2018)
S.K. Grewal, K.P. Sharma, R.D. Bharadwaj, V. Hegde, S. Tripathi, S. Singh, P.K. Jain, P.K. Agrawal, B. Mondal, Understanding genotypic variation and identification of promising genotypes for iron and zinc content in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Food Compos. Aanl. 88, 103458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103458
B. Peng, Y. Shen, Z. Gao, M. Zhou, Y. Ma, S. Zhao, Determination of total iron in water and foods by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with microvolume UV–vis spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 176, 288–293 (2015)
M. Borzoei, M.A. Zanjanchi, H. Sadeghi-Aliabadi, L. Saghaie, Optimization of a methodology for determination of iron concentration in aqueous samples using a newly synthesized chelating agent in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Food Chem. 264, 9–15 (2018)
A. Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.M. Haji Shabani, S. Dadfarnia, M. Saeidi, M. Rohani Moghadam. Spectrophotometric determination of iron species using ionic liquid ultrasound assisted dispersive liquid liquid microextraction. Turk. J. Chem. 39(5), 1059–1068 (2015)
M.R. Moghadam, A.M.H. Shabani, S. Dadfarnia, Spectrophotometric determination of iron species using a combination of artificial neural networks and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop. J. Hazard. Mater. 197, 176–182 (2011)
E. Kazemi, N. Shokoufi, F. Shemirani, Speciation and preconcentration of iron by cloud point extraction combined with fibre optic linear array detection spectrophotometry. Chem. Spec. Bioavailab. 23(4), 249–255 (2011)
N.A. Kasa, E.G. Bakirdere, Determination of iron in licorice samples by slotted quartz tube flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) with matrix matching calibration strategy after complexation with Schiff base ligand-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Lett. 54(8), 1284–1294 (2021)
F. Xu, J. Hu, J. Zhang, X. Hou, X. Jiang, Nanomaterials in speciation analysis of mercury, arsenic, selenium, and chromium by analytical atomic/molecular spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 53(2–4), 333–348 (2018)
W. Zou, C. Li, J. Hu, X. Hou, Selective determination of Cr(VI) and non-chromatographic speciation analysis of inorganic chromium by chemical vapor generation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 218, 121128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121128
H. Yu, H. Du, L. Wu, R. Li, Q. Sun, X. Hou, Trace arsenic speciation analysis of bones by high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchem .J. 141, 176–180 (2018)
W.I. Mortada, M.M. El-Defrawy, E. Erfan, H.A. El-Asmy, Cloud point extraction coupled with back-extraction for speciation of inorganic vanadium in water and determination of total vanadium in food samples by ICP-OES. J. Food Compos. Anal. 108, 104445 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104445
M. Saraiva, P. Jitaru, J.J. Sloth, Speciation analysis of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in bread and breakfast cereals using species-specific isotope dilution and HPLC-ICP-MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 102, 103991 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103991
R. Clough, C.F. Harrington, S.J. Hill, Y. Madrid, J.F. Tyson, Atomic spectrometry update: review of advances in elemental speciation. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 37(7), 1387–1430 (2022)
L. Yao, Y. Zhu, W. Xu, H. Wang, X. Wang, J. Zhang, H. Liu, C. Lin, Combination of dispersive solid phase extraction with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the sequential speciation and preconcentration of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in water samples prior to graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry determination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 72, 189–195 (2019)
M. He, S. Su, B. Chen, B. Hu, Simultaneous speciation of inorganic selenium and tellurium in environmental water samples by polyaniline functionalized magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with ICP-MS detection. Talanta 207, 120314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120314
P. Liang, R. Liu, Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic in water samples by immobilized nanometer titanium dioxide separation and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 602(1), 32–36 (2007)
S.K. Pradhan, B. Ambade, P.K. Tarafder, Speciation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) in geological samples by solvent extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). At. Spectrosc. 40(4), 145–151 (2019)
E.J. Kim, Y.S. Kim, J.M. Choi, Studies on solvent extraction using salphen for separative determination of trace Fe(II) and Fe(III) in water samples. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 29(1), 99–103 (2008)
L. Xia, Y. Wu, Z. Jiang, S. Li, B. Hu, Speciation of Fe(III) and Fe(II) in water samples by liquid–liquid extraction combined with low-temperature electrothermal vaporization (ETV) ICP-AES. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 83(11), 953–962 (2003)
C. Xiong, Z. Jiang, B. Hu, Speciation of dissolved Fe(II) and Fe(III) in environmental water samples by micro-column packed with N-benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylamine loaded on microcrystalline naphthalene and determination by electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 559(1), 113–119 (2006)
Y. Chen, Y. Huang, S. Feng, D. Yuan, Solid phase extraction coupled with a liquid waveguide capillary cell for simultaneous redox speciation analysis of dissolved iron in estuarine and coastal waters. Anal. Methods 7(12), 4971–4978 (2015)
Y. Chen, S. Feng, Y. Huang, D. Yuan, Redox speciation analysis of dissolved iron in estuarine and coastal waters with on-line solid phase extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection. Talanta 137, 25–30 (2015)
M. Asik, U. Ay, Speciation of iron (Fe2+, Fe3+) in various drinking waters using FAAS and UV–visible spectroscopy. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 29(8), 6591–6596 (2020)
T. Khezeli, A. Daneshfar, Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. Trends Anal. Chem. 89, 99–118 (2017)
H. Shirkhanloo, A. Khaligh, H.Z. Mousavi, A. Rashidi, Ultrasound assisted-dispersive-micro-solid phase extraction based on bulky amino bimodal mesoporous silica nanoparticles for speciation of trace manganese(II)/(VII) ions in water samples. Microchem. J. 124, 637–645 (2016)
L. Khalafi, P. Doolittle, J. Wright, Speciation and determination of low concentration of iron in beer samples by cloud point extraction. J. Chem. Educ. 95(93), 463–467 (2018)
A. Alikhani, M. Eftekhari, M. Chamsaz, M. Gheibi, Paired-ion-based liquid phase microextraction for speciation of iron (Fe2+, Fe3+) followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Meas. Charact. 12(1), 573–580 (2018)
N.Y.D. Door, A. Bazmandegan-Shamili, M.R. Moghadam, Spectrophotometric determination of iron species using ultrasound-assisted temperature-controlled deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid-phase microextraction and multisimplex optimization. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 101(2), 251–262 (2021)
S. Bahar, R. Zakerian, Speciation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) by using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 23(5), 944–950 (2012)
M. Chamsaz, M. Eftekhari, S. Tafreshi, A. Yekkebashi, A. Eftekhari, Speciation and determination of iron using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of organic drop followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 94(4), 348–355 (2014)
M.R. Jamali, M. Tavakoli, R. Rahnama, Development of ionic liquid-based in situ solvent formation microextraction for iron speciation and determination in water and food samples. J. Mol. Liq. 216, 666–670 (2016)
E.N. Tafti, A.M.H. Shabani, S. Dadfarnia, Z.D. Firouzabadi. In syringe-supramolecular dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by atomic absorption spectrometric determination for iron species in water and total iron in food samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1965135
M.A. Jeannot, F.F. Cantwell, Solvent microextraction into a single drop. Anal. Chem. 68, 2236–2240 (1996)
I.D. Tegladza, T. Qi, T. Chen, K. Alorku, S. Tang, W. Shen, D. Kong, A. Yuan, J. Liu, H.K. Lee, Direct immersion single-drop microextraction of semi-volatile organic compounds in environmental samples: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 393, 122403 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122403
S. Chen, Y. Liu, C. Wang, J. Yan, D. Lu, Magnetic dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for quantification of Se(IV) and Se(VI) in food samples. Food Addit. Contam. A 38(9), 1539–1550 (2021)
J. Liu, Y. Chi, G. Jiang, C. Tai, J. Peng, J. Hu, Ionic liquid-based liquid-phase microextraction, a new sample enrichment procedure for liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1026(1–2), 143–147 (2004)
P. Liang, H. Sang, Z. Sun, Cloud point extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry determination of manganese(II) and iron(III) in water samples. J. Colloid Interface Sci 304(2), 486–490 (2006)
X. Yan, N.J. Hendry, R. Kerrich, Speciation of dissolved iron(III) and iron(II) in water by on-line coupling of flow injection separation and preconcentration with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 72(8), 1879–1884 (2000)
X. Chang, N. Jiang, H. Zheng, Q. He, Z. Hu, Y. Zhai, Y. Cui, Solid-phase extraction of iron(III) with an ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique. Talanta 71(1), 38–43 (2007)
X. Pu, B. Hu, Z. Jiang, C. Huang, Speciation of dissolved iron(II) and iron(III) in environmental water samples by gallic acid-modified nanometer-sized alumina micro-column separation and ICP-MS determination. Analyst 130(8), 1175–1181 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Hubei Province, China (No. 2020BBB068), Central Committee Guides Local Science and Technology Development Special Project of Hubei Province, China (No. 2019ZYYD059) and Nature Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China (No. 2020CFB400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Wang, Y., Yan, J. et al. Determination of iron species in food samples with dual direct immersion single-drop microextraction followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Measure 17, 3745–3752 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01907-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-01907-7