Abstract
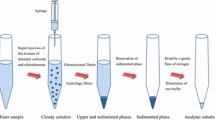
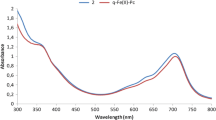
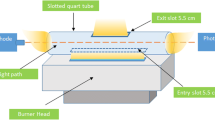
Paired-ion-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction as a simple, rapid and sensitive technique was used for speciation and determination of trace levels of iron (Fe2+, Fe3+) in different water samples. In this method, 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonic acid (tiron) was used as the complexing agent to form anionic complex with Fe3+ at pH 3 followed by addition of cetyl pyridinium chloride (CPC) as a positive counter ion to form a hydrophobic complex of Fe(ІІІ)–tiron–CPC. At this pH, Fe2+ complex (Fe2+–tiron–CPC) is not stable and therefore remains in the sample solution. The total Fe was determined after the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ with concentrated hydrogen peroxide and the concentration of Fe2+ was determined from the difference between the concentration of total Fe and the Fe3+. Different parameters such as pH, concentration of tiron, concentration of CPC, type and volume of disperser and extraction solvent were investigated and optimum conditions were selected. Under the optimum conditions, the calibration curve was linear in the range of 20–300 µg L−1 of Fe3+ with a correlation coefficient of 0.9988. The relative standard deviation (%) based on six replicate analysis of 50 µg L−1 of Fe3+ was 3.5%. In order to check the accuracy of the proposed method, the certified reference material (CRM-TMDW) was analyzed and the determined value was in good agreement with certified value. The proposed method was successfully applied for determination of iron species in local tap, spring, river water and food samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.B. Goldhaber, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 38, 232–242 (2003)
S. Pehkonen, Analyst 120, 2655–2663 (1995)
M. Chamsaz, M. Eftekhari, S. Tafreshi, A. Yekkebashi, A. Eftekhari, Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 94(4), 348–355 (2014)
S.O. Fakayode, A.G. King, M. Yakubu, A.K. Mohammed, D.A. Pollard, J. Chem. Educ. 89(1), 109–113 (2012)
T. Shamspur, I. Sheikhshoaie, M.H. Mashhadizadeh, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 20, 476–478 (2005)
K. Uysal, Y. Emre, E. Kose, Microchem. J 90(1), 67–70 (2008)
Z.O. Tesfaldet, J.F. van Staden, R.I. Stefan, Talanta 64(5), 1189–1195 (2004)
R. Segura, M.I. Toral, V. Arancibia, Talanta 75(4), 973–977 (2008)
A. Atanassova, R. Lam, D.B. Zamble, Anal. Biochem. 335(1), 103–111 (2004)
A.M. Ure, L.R.P. Butler, R.O. Scott, R. Jenkins, Spectrochim. Acta B 52, 409–420 (1997)
M. Rezaee, Y. Assadi, M.R. Milani Hosseini, E. Aghaee, F. Ahmadi, S. Berijani, J. Chromatogr. A 1116, 1–9 (2006)
M. Eftekhari, F. Javedani-Asleh, M. Chamsaz, Food Anal. Methods 9(7), 1985–1992 (2016)
K. Ozutsum, Y. Uchima, T. Kawashima, Anal. Sci. 6, 573–577 (1990)
B. Ebrahimpour, Y. Yamini, M. Moradi, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 66, 264–270 (2012)
S.M. Yousefi, F. Shemirani, J.Hazard. Mater. 254–255, 134–140 (2013)
S. Bahar, R. Zakerian, J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 23, 944–950 (2012)
M. Rohani Moghadam, A.M. Haji Shabani, S. Dadfarnia, J. Hazard. Mater. 197, 176–182 (2011)
G. Khayatian, S. Hassanpoor, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 59, 659–666 (2012)
A.B. Tabrizi, J. Hazard. Mater. 183, 688–693 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran for its financial support. Grant Number: 4/442.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alikhani, A., Eftekhari, M., Chamsaz, M. et al. Paired-ion-based liquid phase microextraction for speciation of iron (Fe2+, Fe3+) followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Measure 12, 573–580 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9669-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9669-0