Abstract
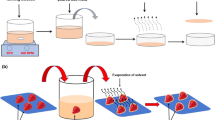
This work analyses the impact of lipid addition (beeswax) on the physicochemical, rheological, microstructural, mechanical, and moisture barrier properties of the chitosan/sodium caseinate composite solution. The addition of lipid affects the different parameters but improves the moisture barrier properties of the films in comparison to the films without lipid addition. The addition of lipid influences the rheological and microstructural properties as higher concentration results in more viscous solutions and films with a rough surface and larger droplets size. Film thickness and particle size increased as the concentration of beeswax increased from 0.5% to 1.5% in the film-forming solution. Transparency of the film is also influenced by the addition of lipids in the emulsion but the concentration of other film-forming constituents affects the transparency of the films. Mechanical properties of the films are inversely related to the increase in wax concentration as tensile strength and elongation at breakage decreased as the concentration of wax increased, however, young’s modulus has not been affected. Biodegradable edible films with improved moisture barrier and tensile properties are preferable in the food packaging industry as these can help in enhancing the package quality and shelf stability of foods especially mangoes, strawberries, bananas, and citrus fruits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Fratini, G. Cilia, B. Turchi, A. Felicioli, Beeswax: A minireview of its antimicrobial activity and its application in medicine. Asian Pac J Trop Med 9, 839–843 (2016)
Bogdanov, S. 2009. Beeswax: uses and trade. The Beeswax Book. pp. 1–16
P. Cazón, G. Velazquez, J.A. Ramírez, M. Vázquez, Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: a review. Food Hydrocoll. 68, 136–148 (2017)
S. Kaur, G.S. Dhillon, The versatile biopolymer chitosan: potential sources, evaluation of extraction methods and applications. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 40, 155–175 (2014)
A. Jiménez, M.J. Fabra, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Effect of sodium caseinate on properties and ageing behaviour of corn starch based films. Food Hydrocoll. 29, 265–271 (2012)
M.J. Fabra, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Influence of calcium on tensile, optical and water vapour permeability properties of sodium caseinate edible films. J. Food Eng. 96, 356–364 (2010)
A. Matsakidou, C.G. Biliaderis, V. Kiosseoglou, Preparation and characterization of composite sodium caseinate edible films incorporating naturally emulsified oil bodies. Food Hydrocoll. 30, 232–240 (2013)
L.J. Wang, Y.C. Yin, S.W. Yin, X.Q. Yang, W.J. Shi, C.H. Tang, J.M. Wang, Development of novel zein-sodium caseinate nanoparticle (ZP)-stabilized emulsion films for improved water barrier properties via emulsion/solvent evaporation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 11089–11097 (2013)
A.M. Sousa, M.P. Goncalves, Strategies to improve the mechanical strength and water resistance of agar films for food packaging applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 132, 196–204 (2015)
T.J. Madera-Santana, Y. Freile-Pelegrín, J.A. Azamar-Barrios, Physicochemical and morphological properties of plasticized poly(vinyl alcohol)–agar biodegradable films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 69, 176–184 (2014)
P.J.P. Espitia, W.X. Du, R. De Jesús Avena-Bustillos, N.D.F.F. Soares, T.H. Mchugh, Edible films from pectin: physical-mechanical and antimicrobial properties-a review. Food Hydrocoll. 35, 287–296 (2014)
Y. Song, Q. Zheng, Ecomaterials based on food proteins and polysaccharides. Polym. Rev. 54, 514–571 (2014)
M. Da Rocha, M.R. Loiko, G.V. Gautério, E.C. Tondo, C. Prentice, Influence of heating, protein and glycerol concentrations of film-forming solution on the film properties of Argentine anchovy (Engraulis anchoita) protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 116, 666–673 (2013)
J. Rhim, L. Wang, S. Hong, Preparation and characterization of agar/silver nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 33, 327–335 (2013)
A. González, C.I.A. Igarzabal, Soy protein–Poly (lactic acid) bilayer films as biodegradable material for active food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 33, 289–296 (2013)
M.E. Embuscado, K.C. Huber, Edible films and coatings for food applications (Springer, New York, 2009)
H.D. Belitz, W. Grosch, P. Schieberle, Edible fats and oils: Food Chemistry (Springer, New York, 2009)
S.A. Mohamed, M. El-Sakhawy, M.A.M. El-Sakhawy, Polysaccharides, protein and lipid-based natural edible films in food packaging: a review. Carbohyd. Polym. 238, e116178 (2020)
Z.Z. Sikorski, A. Kolakowska, Chemical, biological, and functional aspects of food lipids, 2nd edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2010), pp. 1–485
T. Varzakas, C. Tzia, Edible coatings and films to preserve quality of fresh fruits and vegetables Handbook of Food Processing. Two set volume (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2015)
F. Debeaufort, A. Voilley, Lipid-based edible films and coatings, in edible films and coatings for food applications. ed. by M.E. Embuscado, K.C. Huber (Springer, London, 2009), pp. 135–168
D. Muscat, R. Adhikari, S. Mcknight, Q. Guo, B. Adhikari, The physicochemical characteristics and hydrophobicity of high amylose starch-glycerol films in the presence of three natural waxes. J. Food Eng. 119, 205–219 (2013)
S.L.M.E. Halal, E.D.R. Zavareze, M.D. Rocha, V.Z. Pinto, M.R. Nunes, M.D.M. Luvielmo, C. Prentice, Films based on protein isolated from croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) and palm oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 96, 2478–2485 (2016)
B. Hassan, S.A.S. Chatha, A.I. Hussain, K.M. Zia, N. Akhtar, Recent advances on polysaccharides, lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 109, 1095–1107 (2018)
M. Kaya, P. Ravikumar, S. Ilk, M. Mujtaba, L. Akyuz, J. Labidi, A.M. Salaberria, Y.S. Cakmak, S.K. Erkul, Production and characterization of chitosan based edible films from Berberis crataegina’s fruit extract and seed oil. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 45, 287–297 (2018)
N. Purwanti, A.S. Zehn, E.D. Pusfitasari, N. Khalid, E.Y. Febrianto, S.S. Mardjan, Andreas and I. Kobayashi., Emulsion stability of clove oil in chitosan and sodium alginate matrix. Int. J. Food Prop. 21, 566–581 (2018)
T. Senturk Parreidt, M. Schott, M. Schmid, K. Müller, Effect of presence and concentration of plasticizers, vegetable oils, and surfactants on the properties of sodium-alginate-based edible coatings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 742 (2018)
S. Sharifimehr, N. Soltanizadeh, S.A. Hossein Goli, Effects of edible coating containing nano-emulsion of Aloe vera and eugenol on the physicochemical properties of shrimp during cold storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 99, 3604–3615 (2019)
T. Nisar, Z.C. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Tian, M. Iqbal, Y. Guo, Characterization of citrus pectin films integrated with clove bud essential oil: Physical, thermal, barrier, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 106, 670–680 (2018)
M. Chiumarelli, M.D. Hubinger, Evaluation of edible films and coatings formulated with cassava starch, glycerol, carnauba wax, and stearic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 38, 20–27 (2014)
N. Brzoska, M. Mueller, L. Nasui, M. Schmid, Effects of film constituents on packaging-relevant properties of sodium caseinate-based emulsion films. Prog. Org. Coat. 114, 250–258 (2018)
ASTM. 2016. Standard test methods for water vapor transmission of materials (E96/E96M). Annual book of ASTM standards. Philadelphia: American Society for Testing and Materials.
F. Perrechil, R. Cunha, Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by sodium caseinate: Influence of pH, high-pressure homogenization and locust bean gum addition. J. Food Eng. 97, 441–448 (2010)
D. Rousseau, Trends in structuring edible emulsions with Pickering fat crystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 18, 283–291 (2013)
L. Cornacchia, Y.H. Roos, Lipid and water crystallization in protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1726–1736 (2011)
L. Alizadeh, K. Abdolmaleki, K. Nayebzadeh, M. Bahmaei, Characterization of sodium caseinate/Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose concentrated emulsions: effect of mixing ratio, concentration, and wax addition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 128, 796–803 (2019)
C. Huck-Iriart, R.J. Candal, M.L. Herrera, Effect of processing conditions and composition on sodium caseinate emulsions stability. Procedia Food Sci. 1, 116–122 (2011)
M. Mohammadi, S. Mirabzadeh, R. Shahvalizadeh, H. Hamishehkar, Development of novel active packaging films based on whey protein isolate incorporated with chitosan nanofiber and nano-formulated cinnamon oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 149, 11–20 (2020)
L. Atarés, J. Bonilla, A. Chiralt, Characterization of sodium caseinate-based edible films incorporated with cinnamon or ginger essential oils. J. Food Eng. 100, 678–687 (2010)
B. Xie, X. Zhang, X. Luo, Y. Wang, Y. Li, B. Li, S. Liu, Edible coating based on beeswax-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils and carboxymethyl chitosan. Food Chem. 331, e127108 (2020)
Syarifuddin, A., P. Hamsiohan and M. Bilang. 2019. Characterization of edible film from dangke whey/pectin, beeswax, and butter aroma. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019. AIP Publishing LLC
E. Rezvani, G. Schleining, G. Sümen, A.R. Taherian, Assessment of physical and mechanical properties of sodium caseinate and stearic acid based film-forming emulsions and edible films. J. Food Eng. 116, 598–605 (2013)
M.H. Haruna, Y. Wang, J. Pang, Konjac glucomannan-based composite films fabricated in the presence of carnauba wax emulsion: hydrophobicity, mechanical and microstructural properties evaluation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 56, 5138–5145 (2019)
M. Fabra, A. Jiménez, L. Atarés, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Effect of fatty acids and beeswax addition on properties of sodium caseinate dispersions and films. Biomacromol 10, 1500–1507 (2009)
A. Jiménez, M. Fabra, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Effect of lipid self-association on the microstructure and physical properties of hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose edible films containing fatty acids. Carbohyd. Polym. 82, 585–593 (2010)
Y. Zhang, B.K. Simpson, M.J. Dumont, Effect of beeswax and carnauba wax addition on properties of gelatin films: a comparative study. Food Biosci. 26, 88–95 (2018)
M. Fabra, R. Pérez-Masiá, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Influence of the homogenization conditions and lipid self-association on properties of sodium caseinate based films containing oleic and stearic acids. Food Hydrocolloids 25, 1112–1121 (2011)
D. Kowalczyk, W. Gustaw, E. Zięba, S. Lisiecki, J. Stadnik, B. Baraniak, Microstructure and functional properties of sorbitol-plasticized pea protein isolate emulsion films: effect of lipid type and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 60, 353–363 (2016)
T.M. Santos, A.M. Pinto, A.V. De Oliveira, H.L. Ribeiro, C.A. Caceres, E.N. Ito, H.M. Azeredo, Physical properties of cassava starch–carnauba wax emulsion films as affected by component proportions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49, 2045–2051 (2014)
S. Galus, E.A. Arik Kibar, M. Gniewosz, K. Kraśniewska, Novel materials in the preparation of edible films and coatings-a review. Coatings 10, 674 (2020)
S. Galus, J. Kadzińska, Food applications of emulsion-based edible films and coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 45, 273–283 (2015)
M.J. Fabra, P. Talens, A. Chiralt, Tensile properties and water vapor permeability of sodium caseinate films containing oleic acid–beeswax mixtures. J. Food Eng. 85, 393–400 (2008)
K. Khwaldia, Water vapor barrier and mechanical properties of paper-sodium caseinate and paper-sodium caseinate-paraffin wax films. J. Food Biochem. 34(5), 998–1013 (2010)
T. Janjarasskul, D.J. Rauch, K.L. Mccarthy, J.M. Krochta, Barrier and tensile properties of whey protein–candelilla wax film/sheet. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 56, 377–382 (2014)
D. Kowalczyk, B. Baraniak, Effect of candelilla wax on functional properties of biopolymer emulsion films–a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 41, 195–209 (2014)
M.J. Fabra, P. Talens, R. Gavara, A. Chiralt, Barrier properties of sodium caseinate films as affected by lipid composition and moisture content. J. Food Eng. 109, 372–379 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhtar, M., Butt, M.S., Maan, A.A. et al. Development and characterization of emulsion-based films incorporated with chitosan and sodium caseinate. Food Measure 16, 3278–3288 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01422-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01422-1