Abstract
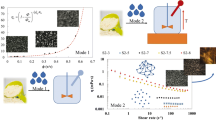
This paper analyses the structural stability of a premix powder that consists of a mixture of whey protein isolate, soy protein isolate, sodium caseinate, carrot juice, and honey bee, which are mixed together by spray-drying. The structural stability of the powder is determined by means of its critical water activity (RHc) at 25 °C, which is determined by three different procedures, namely, by the conventional graphical method, by calculating the inflection points in the adsorption isotherms, and by digital image analysis on the powders stored at different water activities (\(0.11\le a_{w}\le 0.53\)). These three methodological approaches can predict the value of RHc reliably.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.P.M.L. Fontes, J.L.A. Silva, N. Sampaio-Neta, J.C. da Costa Maria, S. Rodrigues, Dehydration of pre- biotic fruit drinks by spray drying: operating conditions and powder characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 7(10), 2942 (2014)
M.K. Movahhed, M. Mohebbi, Spray drying and process optimization of carrot-celery juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 40(2), 212 (2016)
P.A. Picouet, C. Sárraga, S. Cofán, N. Belletti, M.D. Guàrdia, Effects of thermal and high-pressure treatments on the carotene content, microbiological safety and sensory properties of acidified and of non-acidified carrot juice. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 62, 920 (2015)
D.M. Cano-Higuita, H.A. Villa-Vélez, J. Telis-Romero, H.A. Váquiro, V.R.N. Telis, Influence of alternative drying aids on water sorption of spray dried mango mix powders: a thermodynamic approach. Food Bioprod. Process. 93, 19 (2015)
K. Muzaffar, P. Kumar, Moisture sorption isotherms and storage study of spray dried tamarind pulp powder. Powder Technol. 291, 322 (2016)
S. Araujo, Evaluation of the physical properties and conservation of the antioxidants content, employing inulin and maltodextrin in the spray drying of blueberry juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 167, 317 (2017)
H.T.L. Nguyen, N. Panyoyai, V.D. Paramita, N. Mantri, S. Kasapis, Physicochemical and viscoelastic properties of honey from medicinal plants. Food Chem. 241, 143 (2018)
B. Nurhadi, Y.H. Roos, Dynamic water sorption for the study of amorphous content of vacuum-dried honey powder. Powder Technol. 301, 981 (2016)
W. Wang, W. Zhou, Water adsorption and glass transition of spray-dried soy sauce powders using maltodextrins as carrier. Food Bioprocess Technol. 6(10), 2791 (2013)
A. Nesterenko, I. Alric, F. Silvestre, V. Durrieu, Influence of soy proteins structural modifications on their microencapsulation properties: \(\alpha\)-tocopherol microparticle preparation. Food Res. Int. 48(2), 387 (2012)
Q. Shi, Z. Fang, B. Bhandari, Effect of addition of whey protein isolate on spray-drying behavior of honey with maltodextrin as a carrier material. Drying Technol. 31(13–14), 1681 (2013)
J. Charve, G.A. Reineccius, Encapsulation performance of proteins and traditional materials for spray dried flavors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(6), 2486 (2009)
A.M. Righetto, F.M. Netto, Effect of encapsulating materials on water sorption, glass transition and stability of juice from immature acerola. Int. J. Food Prop. 8(2), 337 (2005)
B.P. Carter, M.T. Galloway, G.S. Campbell, A.H. Carter, The critical water activity from dynamic dew-point isotherms as an indicator of crispness in low moisture cookies. J. Food Meas. Charact. 9(3), 463 (2015)
M.J. Kirkby, The fractal geometry of nature. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 8(4), 406 (1983)
F. Mendoza, P. Dejmek, J.M. Aguilera, Colour and image texture analysis in classification of commercial potato chips. Food Res. Int. 40(9), 1146 (2007)
American Association of Cereal Chemists (ed.), Approved methods of the AACC, revised October 1975, 8th edn. (Method 44-19, The Association: St. Paul, 1983)
M. Gordon, J.S. Taylor, Ideal copolymers and the second-order transitions of synthetic rubbers. i. non- crystalline copolymers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 26(2), 323 (1953)
R.V. Tonon, D. Alexandre, M.D. Hubinger, R.L. Cunha, Steady and dynamic shear rheological properties of açai pulp (Euterpe oleraceae mart.). J. Food Eng. 92(4), 425 (2009)
S.S. Sablani, R.M. Syamaladevi, B.G. Swanson, A review of methods, data and applications of state diagrams of food systems. Food Eng. Rev. 2(3), 168 (2010)
E.O. Timmermann, J. Chirife, H.A. Iglesias, Water sorption isotherms of foods and foodstuffs: bet or gab parameters? J. Food Eng. 48(1), 19 (2001)
M. Peleg, M.D. Normand, Estimation of the equilibrium water activity of multicomponent mixtures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 3, 157 (1992)
E. Bonilla, E. Azuara, C.I. Beristain, E.J. Vernon-Carter, Predicting suitable storage conditions for spray-dried microcapsules formed with different biopolymer matrices. Food Hydrocolloids 24(67), 633 (2010)
E. García-Armenta, D.I. Téllez-Medina, L. Alamilla-Beltrán, H. Hernández-Sánchez, G.F. Gutiérrez-López, Morphometric analysis of transverse surface of fractured maltodextrin agglomerates. Int. J. Food Prop. 19(11), 2451 (2016)
C.E. Shannon, A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(3), 379 (1948)
R.M. Haralick, K. Shanmugam, I. Dinstein, Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. SMC–3(6), 610 (1973)
Y. Suhag, V. Nanda, Evaluation of different carrier agents with respect to physico-chemical, functional and morphological characteristics of spray dried nutritionally rich honey powder. J. Food Process. Preserv. 40(6), 1429 (2016)
S. Jabbar, M. Abid, B. Hu, T. Wu, M.M. Hashim, S. Lei, X. Zhu, X. Zeng, Quality of carrot juice as influenced by blanching and sonication treatments. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 55(1), 16 (2014)
P.P. Lewicki, The applicability of the gab model to food water sorption isotherms. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 32(6), 553 (1997)
S. Radosta, Tp labuza, Moisture sorption: practical aspects of isotherm measurement and use. 150 seiten, 36 abb. american association of cereal chemists, st. paul, minnesota 1984. Food / Nahrung 29(1), 92 (1985)
C. McLaughlin, T. Magee, The determination of sorption isotherm and the isosteric heats of sorption for potatoes. J. Food Eng. 35(3), 267 (1998)
E. García-Armenta, D.I. Téllez-Medina, L. Alamilla-Beltrán, R. Arana-Errasquín, H. Hernández-Sánchez, G.F. Gutiérrez-López, Multifractal breakage patterns of thick maltodextrin agglomerates. Powder Technol. 266, 440 (2014)
J. Colín-Orozco, J. Chanona-Pérez, M.J. de Perea-Flores, R. Pedroza-Islas, Changes in large- deformation properties during dough fermentation by lactobacillus strains and their relationship with microstructure. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 13(2), 457 (2014)
Acknowledgements
YVGT acknowledges to CONACyT for the SNI program. VBF acknowledges to SIP project 20180438. The authors recognize the experimental support of the CNMN-IPN in the realization of the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Tejeda, Y.V., García-Armenta, E., Martínez-Audelo, J.M. et al. Determination of the structural stability of a premix powder through the critical water activity. Food Measure 13, 1323–1332 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00047-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00047-1