Abstract
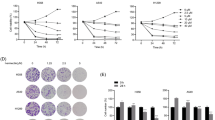
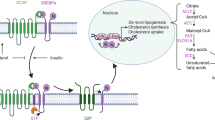
The effect of anti-programmed cell death 1 (anti-PD-1) immunotherapy is limited in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) expression increased in liver tumor cells in early HCC, and Akkermansia muciniphila abundance decreased in the colon. The response to anti-PD-1 treatment is associated with A. muciniphila abundance in many tumors. However, the interaction between A. muciniphila abundance and YAP1 expression remains unclear in HCC. Here, anti-PD-1 treatment decreased A. muciniphila abundance in the colon, but increased YAP1 expression in the tumor cells by mice with liver tumors in situ. Mechanistically, hepatocyte-specific Yap1 knockout (Yap1LKO) maintained bile acid homeostasis in the liver, resulting in an increased abundance of A. muciniphila in the colon. Yap1 knockout enhanced anti-PD-1 efficacy. Therefore, YAP1 inhibition is a potential target for increasing A. muciniphila abundance to promote anti-PD-1 efficacy in liver tumors. Dihydroartemisinin (DHA), acting as YAP1 inhibitor, increased A. muciniphila abundance to sensitize anti-PD-1 therapy. A. muciniphila by gavage increased the number and activation of CD8+ T cells in liver tumor niches during DHA treatment or combination with anti-PD-1. Our findings suggested that the combination anti-PD-1 with DHA is an effective strategy for liver tumor treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Konyn P, Ahmed A, Kim D. Current epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 15(11): 1295–1307
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Trojan J, Welling TH 3rd, Meyer T, Kang YK, Yeo W, Chopra A, Anderson J, Dela Cruz C, Lang L, Neely J, Tang H, Dastani HB, Melero I. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017; 389(10088): 2492–2502
Kim CG, Kim C, Yoon SE, Kim KH, Choi SJ, Kang B, Kim HR, Park SH, Shin EC, Kim YY, Kim DJ, Chung HC, Chon HJ, Choi HJ, Lim HY. Hyperprogressive disease during PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2021; 74(2): 350–359
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D, Verslype C, Zagonel V, Fartoux L, Vogel A, Sarker D, Verset G, Chan SL, Knox J, Daniele B, Webber AL, Ebbinghaus SW, Ma J, Siegel AB, Cheng AL, Kudo M; KEYNOTE-224 investigators. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2018; 19(7): 940–952
Ren Z, Li A, Jiang J, Zhou L, Yu Z, Lu H, Xie H, Chen X, Shao L, Zhang R, Xu S, Zhang H, Cui G, Chen X, Sun R, Wen H, Lerut JP, Kan Q, Li L, Zheng S. Gut microbiome analysis as a tool towards targeted non-invasive biomarkers for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2019; 68(6): 1014–1023
Routy B, Le Chatelier E, Derosa L, Duong CPM, Alou MT, Daillère R, Fluckiger A, Messaoudene M, Rauber C, Roberti MP, Fidelle M, Flament C, Poirier-Colame V, Opolon P, Klein C, Iribarren K, Mondragón L, Jacquelot N, Qu B, Ferrere G, Clémenson C, Mezquita L, Masip JR, Naltet C, Brosseau S, Kaderbhai C, Richard C, Rizvi H, Levenez F, Galleron N, Quinquis B, Pons N, Ryffel B, Minard-Colin V, Gonin P, Soria JC, Deutsch E, Loriot Y, Ghiringhelli F, Zalcman G, Goldwasser F, Escudier B, Hellmann MD, Eggermont A, Raoult D, Albiges L, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018; 359(6371): 91–97
Matson V, Fessler J, Bao R, Chongsuwat T, Zha Y, Alegre ML, Luke JJ, Gajewski TF. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018; 359(6371): 104–108
Salgia NJ, Bergerot PG, Maia MC, Dizman N, Hsu J, Gillece JD, Folkerts M, Reining L, Trent J, Highlander SK, Pal SK. Stool microbiome profiling of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur Urol 2020; 78(4): 498–502
Zheng Y, Wang T, Tu X, Huang Y, Zhang H, Tan D, Jiang W, Cai S, Zhao P, Song R, Li P, Qin N, Fang W. Gut microbiome affects the response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 2019; 7(1): 193
Shibata M, Ham K, Hoque MO. A time for YAP1: tumorigenesis, immunosuppression and targeted therapy. Int J Cancer 2018; 143(9): 2133–2144
Perra A, Kowalik MA, Ghiso E, Ledda-Columbano GM, Di Tommaso L, Angioni MM, Raschioni C, Testore E, Roncalli M, Giordano S, Columbano A. YAP activation is an early event and a potential therapeutic target in liver cancer development. J Hepatol 2014; 61(5): 1088–1096
Cao J, Zhang C, Jiang GQ, Jin SJ, Wang Q, Wang AQ, Bai DS. Identification of hepatocellular carcinoma-related genes associated with macrophage differentiation based on bioinformatics analyses. Bioengineered 2021; 12(1): 296–309
Yu M, Peng Z, Qin M, Liu Y, Wang J, Zhang C, Lin J, Dong T, Wang L, Li S, Yang Y, Xu S, Guo W, Zhang X, Shi M, Peng H, Luo X, Zhang H, Zhang L, Li Y, Yang XP, Sun S. Interferon-γ induces tumor resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by promoting YAP phase separation. Mol Cell 2021; 81(6): 1216–1230.e9
Hagi T, Geerlings SY, Nijsse B, Belzer C. The effect of bile acids on the growth and global gene expression profiles in Akkermansia muciniphila. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2020; 104(24): 10641–10653
Van den Bossche L, Hindryckx P, Devisscher L, Devriese S, Van Welden S, Holvoet T, Vilchez-Vargas R, Vital M, Pieper DH, Vanden Bussche J, Vanhaecke L, Van de Wiele T, De Vos M, Laukens D. Ursodeoxycholic acid and its taurine- or glycine-conjugated species reduce colitogenic dysbiosis and equally suppress experimental colitis in mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 2017; 83(7): e02766–16
Zheng X, Huang F, Zhao A, Lei S, Zhang Y, Xie G, Chen T, Qu C, Rajani C, Dong B, Li D, Jia W. Bile acid is a significant host factor shaping the gut microbiome of diet-induced obese mice. BMC Biol 2017; 15(1): 120
Anakk S, Bhosale M, Schmidt VA, Johnson RL, Finegold MJ, Moore DD. Bile acids activate YAP to promote liver carcinogenesis. Cell Rep 2013; 5(4): 1060–1069
Wang T, Luo R, Li W, Yan H, Xie S, Xiao W, Wang Y, Chen B, Bai P, Xing J. Dihydroartemisinin suppresses bladder cancer cell invasion and migration by regulating KDM3A and p21. J Cancer 2020; 11(5): 1115–1124
Li Q, Ma Q, Cheng J, Zhou X, Pu W, Zhong X, Guo X. Dihydroartemisinin as a sensitizing agent in cancer therapies. OncoTargets Ther 2021; 14: 2563–2573
Li Z, Tuteja G, Schug J, Kaestner KH. Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver cancer. Cell 2012; 148(1–2): 72–83
Zhang J, Bu X, Wang H, Zhu Y, Geng Y, Nihira NT, Tan Y, Ci Y, Wu F, Dai X, Guo J, Huang YH, Fan C, Ren S, Sun Y, Freeman GJ, Sicinski P, Wei W. Cyclin D-CDK4 kinase destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3-SPOP to control cancer immune surveillance. Nature 2018; 553(7686): 91–95
Jiang Z, Lim SO, Yan M, Hsu JL, Yao J, Wei Y, Chang SS, Yamaguchi H, Lee HH, Ke B, Hsu JM, Chan LC, Hortobagyi GN, Yang L, Lin C, Yu D, Hung MC. TYRO3 induces anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy resistance by limiting innate immunity and tumoral ferroptosis. J Clin Invest 2021; 131(8): e139434
Hao L, Guo Y, Peng Q, Zhang Z, Ji J, Liu Y, Xue Y, Li C, Zheng K, Shi X. Dihydroartemisinin reduced lipid droplet deposition by YAP1 to promote the anti-PD-1 effect in hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytomedicine 2022; 96: 153913
Guo Y, Peng Q, Hao L, Ji J, Zhang Z, Xue Y, Liu Y, Gao Y, Li C, Shi X. Dihydroartemisinin promoted FXR expression independent of YAP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. FASEB J 2022; 36(6): e22361
Li J, Lin S, Vanhoutte PM, Woo CW, Xu A. Akkermansia muciniphila protects against atherosclerosis by preventing metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in Apoe−/− mice. Circulation 2016; 133(24): 2434–2446
Collado MC, Derrien M, Isolauri E, de Vos WM, Salminen S. Intestinal integrity and Akkermansia muciniphila, a mucin-degrading member of the intestinal microbiota present in infants, adults, and the elderly. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007; 73(23): 7767–7770
Pieper R, Bindelle J, Rossnagel B, Van Kessel A, Leterme P. Effect of carbohydrate composition in barley and oat cultivars on microbial ecophysiology and proliferation of Salmonella enterica in an in vitro model of the porcine gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009; 75(22): 7006–7016
Wang L, Tang L, Feng Y, Zhao S, Han M, Zhang C, Yuan G, Zhu J, Cao S, Wu Q, Li L, Zhang Z. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurised bacterium blunts colitis associated tumourigenesis by modulation of CD8+ T cells in mice. Gut 2020; 69(11): 1988–1997
Jiu X, Liu Y, Wen J. Artesunate combined with verteporfin inhibits uveal melanoma by regulation of the MALAT1/yes-associated protein signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 2021; 22(2): 597
Liu R, Choi HS, Ko YC, Yun BS, Lee DS. 5-Desmethylsinensetin isolated from Artemisia princeps suppresses the stemness of breast cancer cells via Stat3/IL-6 and Stat3/YAP1 signaling. Life Sci 2021; 280: 119729
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L, Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, Prieto PA, Vicente D, Hoffman K, Wei SC, Cogdill AP, Zhao L, Hudgens CW, Hutchinson DS, Manzo T, Petaccia de Macedo M, Cotechini T, Kumar T, Chen WS, Reddy SM, Szczepaniak Sloane R, Galloway-Pena J, Jiang H, Chen PL, Shpall EJ, Rezvani K, Alousi AM, Chemaly RF, Shelburne S, Vence LM, Okhuysen PC, Jensen VB, Swennes AG, McAllister F, Marcelo Riquelme Sanchez E, Zhang Y, Le Chatelier E, Zitvogel L, Pons N, Austin-Breneman JL, Haydu LE, Burton EM, Gardner JM, Sirmans E, Hu J, Lazar AJ, Tsujikawa T, Diab A, Tawbi H, Glitza IC, Hwu WJ, Patel SP, Woodman SE, Amaria RN, Davies MA, Gershenwald JE, Hwu P, Lee JE, Zhang J, Coussens LM, Cooper ZA, Futreal PA, Daniel CR, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Tetzlaff MT, Sharma P, Allison JP, Jenq RR, Wargo JA. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018; 359(6371): 97–103
Gao ZY, Cui Z, Yan YQ, Ning LJ, Wang ZH, Hong J. Microbe-based management for colorectal cancer. Chin Med J (Engl) 2021; 134(24): 2922–2930
Sfanos KS, Markowski MC, Peiffer LB, Ernst SE, White JR, Pienta KJ, Antonarakis ES, Ross AE. Compositional differences in gastrointestinal microbiota in prostate cancer patients treated with androgen axis-targeted therapies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2018; 21(4): 539–548
Miller PL, Carson TL. Mechanisms and microbial influences on CTLA-4 and PD-1-based immunotherapy in the treatment of cancer: a narrative review. Gut Pathog 2020; 12(1): 43
Snider EJ, Compres G, Freedberg DE, Khiabanian H, Nobel YR, Stump S, Uhlemann AC, Lightdale CJ, Abrams JA. Alterations to the esophageal microbiome associated with progression from Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2019; 28(10): 1687–1693
Baxter NT, Zackular JP, Chen GY, Schloss PD. Structure of the gut microbiome following colonization with human feces determines colonic tumor burden. Microbiome 2014; 2(1): 20
Osman MA, Neoh HM, Ab Mutalib NS, Chin SF, Mazlan L, Raja Ali RA, Zakaria AD, Ngiu CS, Ang MY, Jamal R. Parvimonas micra, Peptostreptococcus stomatis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Akkermansia muciniphila as a four-bacteria biomarker panel of colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 2021; 11(1): 2925
Wang F, Cai K, Xiao Q, He L, Xie L, Liu Z. Akkermansia muciniphila administration exacerbated the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. J Cancer 2022; 13(1): 124–133
Santoni M, Piva F, Conti A, Santoni A, Cimadamore A, Scarpelli M, Battelli N, Montironi R. Re: gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Eur Urol 2018; 74(4): 521–522
Luo ZW, Xia K, Liu YW, Liu JH, Rao SS, Hu XK, Chen CY, Xu R, Wang ZX, Xie H. Extracellular vesicles from Akkermansia muciniphila elicit antitumor immunity against prostate cancer via modulation of CD8+ T cells and macrophages. Int J Nanomedicine 2021; 16: 2949–2963
Septer S, Edwards G, Gunewardena S, Wolfe A, Li H, Daniel J, Apte U. Yes-associated protein is involved in proliferation and differentiation during postnatal liver development. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012; 302(5): G493–G503
Wu H, Wei L, Fan F, Ji S, Zhang S, Geng J, Hong L, Fan X, Chen Q, Tian J, Jiang M, Sun X, Jin C, Yin ZY, Liu Q, Zhang J, Qin F, Lin KH, Yu JS, Deng X, Wang HR, Zhao B, Johnson RL, Chen L, Zhou D. Integration of Hippo signalling and the unfolded protein response to restrain liver overgrowth and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun 2015; 6(1): 6239
Xie G, Wang X, Huang F, Zhao A, Chen W, Yan J, Zhang Y, Lei S, Ge K, Zheng X, Liu J, Su M, Liu P, Jia W. Dysregulated hepatic bile acids collaboratively promote liver carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 2016; 139(8): 1764–1775
Fang Y, Han SI, Mitchell C, Gupta S, Studer E, Grant S, Hylemon PB, Dent P. Bile acids induce mitochondrial ROS, which promote activation of receptor tyrosine kinases and signaling pathways in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 2004; 40(4): 961–971
Perez MJ, Briz O. Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(14): 1677–1689
Luo P, Yin P, Hua R, Tan Y, Li Z, Qiu G, Yin Z, Xie X, Wang X, Chen W, Zhou L, Wang X, Li Y, Chen H, Gao L, Lu X, Wu T, Wang H, Niu J, Xu G. A large-scale, multicenter serum metabolite biomarker identification study for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018; 67(2): 662–675
Chen T, Xie G, Wang X, Fan J, Qiu Y, Zheng X, Qi X, Cao Y, Su M, Wang X, Xu LX, Yen Y, Liu P, Jia W. Serum and urine metabolite profiling reveals potential biomarkers of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011; 10(7): M110.004945
Loftfield E, Rothwell JA, Sinha R, Keski-Rahkonen P, Robinot N, Albanes D, Weinstein SJ, Derkach A, Sampson J, Scalbert A, Freedman ND. Prospective investigation of serum metabolites, coffee drinking, liver cancer incidence, and liver disease mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst 2020; 112(3): 286–294
Geerlings SY, Kostopoulos I, de Vos WM, Belzer C. Akkermansia muciniphila in the human gastrointestinal tract: when, where, and how? Microorganisms 2018; 6(3): 75
Foley MH, O’Flaherty S, Barrangou R, Theriot CM. Bile salt hydrolases: gatekeepers of bile acid metabolism and host-microbiome crosstalk in the gastrointestinal tract. PLoS Pathog 2019; 15(3): e1007581
Grajeda-Iglesias C, Durand S, Daillère R, Iribarren K, Lemaitre F, Derosa L, Aprahamian F, Bossut N, Nirmalathasan N, Madeo F, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Oral administration of Akkermansia muciniphila elevates systemic antiaging and anticancer metabolites. Aging (Albany NY) 2021; 13(5): 6375–6405
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873112) and Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (No. ZD2022120) for the economic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Zhiqin Zhang, Xinli Shi, Jingmin Ji, Yinglin Guo, Qing Peng, Liyuan Hao, Yu Xue, Yiwei Liu, Caige Li, Junlan Lu, and Kun Yu declare that they have no conflict of interest. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Shi, X., Ji, J. et al. Dihydroartemisinin increased the abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila by YAP1 depression that sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Front. Med. 17, 729–746 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0978-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0978-2