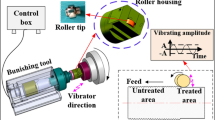
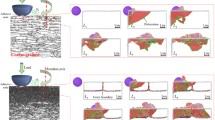
Abstract
Surface damage and corrosion are two major challenges in the long-time functional service life of industrial components. The surface modification approach was previously utilized to improve surface properties and increase corrosion resistance. This paper presents a comprehensive experimental investigation of ultrasonic-assisted burnishing to control surface integrity and corrosion performance of aerospace AA7075-T6 aluminum alloys. To this end, turned sample (control) was treated by conventional burnishing (without ultrasonic vibration), followed by 2D ultrasonic-assisted burnishing. The effect of radial and feed directional vibration on burnishing performance was evaluated. The surface roughness, microstructure, microhardness, and corrosion resistance of the treated samples were assessed. Results indicated that the mean surface roughness of the control sample (turned) was 0.247 µm which decreased to 0.121, 0.081, 0.023, and 0.067 µm after conventional burnishing (CB), ultrasonic-assisted burnishing on radial direction (R-UAB), ultrasonic-assisted burnishing on feed direction (F-UAB), and two-dimensional ultrasonic-assisted burnishing (2D-UAB), respectively. Grain refinement occurred after all burnishing processes and microhardness increased in the depth of 40 µm from 109 HV to 140, 186, 147, and 181 HV after CB, R-UAB, F-UAB, and 2D-UAB treatment, corresponding to 28, 70, 34, and 66% increase, respectively. In addition, the corrosion rate of control sample (turned) was 0.0858 mm/y which was decremented to 0.0541, 0.0498, 0.0249, and 0.0386 after CB, R-UAB, F-UAB, and 2D-UAB treatments, respectively. Interestingly, ultrasonic-assisted burnishing, in particular, along the feed direction outperformed the other treatments by reducing surface roughness and the corrosion rate by about 90 and 71%, respectively.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Victoria, S. Olukayode, B. Obadele, and P. Apata, Comparison Study on the Corrosion Behavior of Aluminum Alloys in Different Acidic Media, Mater. Today Proc., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.781
M.D. Vijayakumar, V. Dhinakaran, T. Sathish, G. Muthu, and P.M. Bupathi, Experimental Study of Chemical Composition of Aluminium Alloys, Mater. Today Proc., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.391
Z. Zhen-yu, Y. Guang-lei, Z. Qiu-yang, M. Guo-zheng, Y. Sen-bin, and D. Cong, Wear Behavior of 7075-Aluminum After Ultrasonic-Assisted Surface Burnishing, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 51, p 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.026
M. Jawahar, B.S. Kumarr, and P.V. Krishna, Experimental Design and Optimization of Ball Burnishing Process for Aluminum Alloy 5083, Int. Res. J. Automot. Tech., 2018, 5, p 33-40.
S. Hemanth, A. Harish, R.N. Bharadwaj, and A.B. Bhat, ScienceDirect Design of Roller Burnishing Tool and Its Effect on the Surface Integrity of Al 6061, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5(5), p 12848-12854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.02.269
V.J. Prasad, K.S. Joshi, V.S.N.V. Ramana, and R. Chiranjeevi, ScienceDirect Effect of Roller Burnishing on Surface Properties of Wrought AA6063 Aluminium Alloys, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5(2), p 8033-8040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.488
S.R. Thorat and A.G. Thakur, ScienceDirect Optimization of Burnishing Parameters by Taguchi Based GRA Method of AA 6061 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5(2), p 7394-7403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.410
A. Saldaña-robles, H. Plascencia-mora, A. Saldaña-robles, A. Marquez-, J. Angel, and D. Peña, Influence of Ball-Burnishing on Roughness, Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of AISI 1045 Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.02.013
A.J.S. Egea, A. Rodríguez, D. Celentano, A. Calleja, and L.N.L. De Lacalle, Joining Metrics Enhancement When Combining FSW and Ball-Burnishing in a 2050 Aluminium Alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2019, 367, p 327-335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.04.010
S. Hassanifard, M. Mousavi, and A. Varvani, The Influence of Low-Plasticity Burnishing Process on the Fatigue Life of Friction-Stir-Processed Al 7075-T6 Samples, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2018, 42, p 764-772. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12950
Y. Xie et al., Insight on Corrosion Behavior of Friction Stir Welded AA2219/AA2195 Joints in Astronautical Engineering, Corros. Sci., 2021, 192, p 109800.
X. Meng, Y. Huang, J. Cao, and J. Shen, J. Pre-proofs (2020)
Y. Huang, L. Wan, S. Lv, H. Liu, and J. Feng, Gradient Micro-Structured Surface Layer on Aluminum Alloy Fabricated by In situ Rolling Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Des., 2013, 52, p 821-827.
A. Saldaña-robles et al., Influence of Ball-Burnishing on Roughness, Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of AISI 1045 Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 339, p 191-198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.02.013
S. Ramesh, S. Aditya Kudva, G. Anne, B. Manne, and S. Arya, Optimization of Ball-Burnishing Process Parameters on Surface Roughness, Micro Hardness of Mg-Zn-Ca Alloy and Investigation of Corrosion Behavior, Mater. Res. Expr., 2019, 6(10), p 1065. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab40f2
Z. Liu, Q. Dai, J. Deng, Y. Zhang, and V. Ji, “Analytical modeling and experimental verification of surface roughness in the ultrasonic-assisted ball burnishing of shaft targets,” 2020.
S. Tarvainen, Y. Watanabe, H. E. Hansen, and S. Sunde, Surface Roughness Variation in Ultrasonic Assisted Burnishing of High-Strength Steels. (2020), doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/896/1/012139
A. Estevez-urra, J. Llumà, and R. Jerez-mesa, Monitoring of Processing Conditions of an Ultrasonic Vibration-assisted Ball-burnishing Process, Sensors, 2020, 20, p 2562. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092562
R. Teimouri, S. Amini, and A.B. Bami, Evaluation of Optimized Surface Properties and Residual Stress in Ultrasonic Assisted Ball Burnishing of AA6061-T6, Measurement, 2018, 116, p 129-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.11.001
J.A. Travieso-rodriguez, Enhancing Surface Topology of Udimet R 720 Ball Burnishing, Metals, 2020 https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070915
Y.L. Shi, X.H. Shen, G.F. Xu, C.H. Xu, B.L. Wang, and G.S. Su, Surface Integrity Enhancement of Austenitic Stainless Steel Treated by Ultrasonic Burnishing with Two Burnishing Tips, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2020, 20(3), p 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00074-6
X. Shen, X. Gong, J. Zhang, and G. Su, An Investigation of Stress Condition in Vibration-Assisted Burnishing, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 105(1-4), p 1189-1207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04128-9
J. Zhao et al., Characterization of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties for Ti-6Al-4 V Processed by Rotary Ultrasonic Roller Burnishing, Mater. Charact., 2021, 178, p 111288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111288
Z. Zhou, Q. Zheng, C. Ding, G. Yu, G. Peng, and Z. Piao, Investigation of Two - Dimensional Ultrasonic Surface Burnishing Process on 7075-T6 Aluminum, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-021-00540-z
Z. Zhen-yu, Z. Qiu-yang, D. Cong, and Y. Ju-yu, Research on the Promotion Mechanism of Surface Burnishing Process by Two-dimensional Ultrasonic Vibration, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 13, p 1068-1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.05.038
J. Marteau, M. Bigerelle, P. Mazeran, and S. Bouvier, Relation Between Roughness and Processing Conditions of AISI 316L Stainless Steel Treated by Ultrasonic Shot Peening, Tribiol. Int., 2014, 82, p 319-329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.07.013
S. Attabi, A. Himour, L. Laouar, and A. Motallebzadeh, Effect of Ball Burnishing on Surface Roughness and Wear of AISI 316L, J. Bio- Tribo-Corrosion, 2021, 7, p 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00437-9
L.X. Lu, J. Sun, L. Li, and Q.C. Xiong, Study on Surface Characteristics of 7050-T7451 Aluminum Alloy by Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Process, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech., 2016, 87, p 2533-2539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8659-4
L. Jinlong and L. Hongyun, Investigation of Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Burnished Aluminum Alloy by TEM, EWF, XPS and EIS Techniques, Mater. Res. Bull., 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.05.013
P. Zhang and Z. Liu, Enhancing Surface Integrity and Corrosion Resistance of Laser Cladded Cr-Ni Alloys by Hard Turning and Low Plasticity Burnishing, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 409, p 169-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.028
H. Rachmat and E. A. Rahim, Effect of Number of Passes on Surface Properties Effect of Number of Passes on Surface Properties of Burnished Aluminium Alloy. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/1112/1/012011
H. Su, X. Shen, C. Xu, J. He, B. Wang, and G. Su, Surface Characteristics and Corrosion Behavior of TC11 Titanium Alloy Strengthened by Ultrasonic Roller Burnishing at Room and Medium Temperature, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(4), p 8172-8185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.059
Y. Zhang, F. Liu, J. Chen, and Y. Yuan, Effects of Surface Quality on Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Parts Manufactured via SLM, J. Laser Appl., 2017, 29(2), p 022306. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4983263
O. Takakuwa and H. Soyama, Effect of Residual Stress on the Corrosion Behavior of Austenitic Stainless Steel, Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci., 2015, 5, p 62-71.
K.D. Ralston and N. Birbilis, Effect of Grain Size on Corrosion: A Review, Corrosion, 2010, 66(7), p 0750051-07500513. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3462912
H. Wang, C. Ning, Y. Huang, Z. Cao, X. Chen, and W. Zhang, Improvement of Abrasion Resistance in Artificial Seawater and Corrosion Resistance in NaCl Solution of 7075 Aluminum Alloy Processed by Laser Shock Peening, Opt. Lasers Eng., 2017, 90, p 179-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.10.016
N. Ali, M. Pulp, and P. M. Limited, Determination of Corrosion Rate of Mild Steel in Different Medium Measuring Current Density. pp. 1-5 (2017)
Y. Madhavi, N. Narasaiah, and A. Jyothirmayi, Influence of Surface-Roughness on the Corrosion-Fatigue Behavior of MAO Coated 6061-T6 Al Alloy Assessed in NaCl Medium, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 414, p 127102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127102
Z. Feng et al., EBSD Characterization of 7075 Aluminum Alloy and its Corrosion Behaviors in SRB Marine Environment (2022)
N. Birbilis and R.G. Buchheit, Electrochemical Characteristics of Intermetallic Phases in Aluminum Alloys An Experimental Survey and Discussion, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152, p 140-151. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1869984
U. Sajjad, A. Abbas, A. Sadeghianjahromi, N. Abbas, J.S. Liaw, and C.C. Wang, Enhancing Corrosion Resistance of Al 5050 Alloy Based on Surface Roughness and its Fabrication Methods; an Experimental Investigation, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 11, p 1859-1867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.096
U. Reddy et al., Effect of Surface Roughness Induced by Milling Operation on the Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(10), p 7354-7364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05933-8
R. Bertolini, S. Bruschi, A. Ghiotti, L. Pezzato, and M. Dabalà, The Effect of Cooling Strategies and Machining Feed Rate on the Corrosion Behavior and Wettability of AZ31 Alloy for Biomedical Applications, Proc. CIRP, 2017, 65, p 7-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.168
R.I. Yakin, P.T. Iswanto, and E.U.K. Maliwemu, Shot Peening Effect on Surface Properties and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Biomedical Structural Steel AISI 316L, Metalurgija, 2021, 60(3-4), p 249-252.
L. Guo, G. Li, and Z. Gan, Effects of Surface Roughness on CMAS Corrosion Behavior for Thermal Barrier Coating Applications, J. Adv. Ceram., 2021, 10(3), p 472-481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0449-7
A. Shahryari, W. Kamal, and S. Omanovic, The Effect of Surface Roughness on the Efficiency of the Cyclic Potentiodynamic Passivation (CPP) Method in the Improvement of General and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of 316LVM Stainless Steel, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62(23), p 3906-3909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.05.032
J. Rajaguru and N. Arunachalam, Effect of Machined Surface Integrity on the Stress Corrosion Cracking Behaviour of Super Duplex Stainless Steel, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2021, 125, p 105411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105411
I. Journal, S. Entakly, A. Almansour, and M. Azizi, Effect of Surface Roughness on Corrosion Behavior of Aluminum Alloy 6061 in Salt Solution (3.5% NaCl)
A. S. Toloei, V. Stoilov, and D. Northwood, The Relationship Between Surface Roughness and Corrosion IMECE2013-65498. (2013) doi: https://doi.org/10.1115/IMECE2013-65498
L. Wei, Y. Liu, Q. Li, and Y.F. Cheng, Effect of Roughness on General Corrosion and Pitting of (FeCoCrNi)0.89(WC)0.11 High-Entropy Alloy Composite in 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution, Corros. Sci., 2019, 146, p 44-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.10.025
K.D. Ralston, D. Fabijanic, and N. Birbilis, Effect of Grain Size on Corrosion of High Purity Aluminium, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, p 1729-1736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.09.023
X.Y. Wang and D.Y. Li, Mechanical and Electrochemical Behavior of Nanocrystalline Surface of 304 Stainless Steel, Electrochim. Acta, 2002, 47, p 3939-3947.
Y. Xie, X. Meng, Y. Chang, D. Mao, Z. Qin, and L. Wan, Heteroatom Modification Enhances Corrosion Durability in Aluminum Matrix Composites, Adv. Sci., 2022, 9, p 2104464. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202104464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sayadi, D., Bagheri, M., Khosrojerdi, M.R. et al. 2D Ultrasonic-Assisted Burnishing to Control Surface Integrity and Electrochemical Behavior of AA7075-T6 Aluminum Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08352-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08352-z